Prélude à l'après-midi d'un faune
| Prélude à l'après-midi d'un faune | |
|---|---|
| Symphonic poem by Claude Debussy | |
 Claude Debussy in 1905 | |
| English | Prelude to the Afternoon of a Faun |
| Catalogue | L. 86 |
| Based on | L'après-midi d'un faune by Stéphane Mallarmé |
| Scoring |
|
| Premiere | |
| Date | 22 December 1894 |
| Location | Paris, France |
| Conductor | Gustave Doret |
| Performers | Georges Barrère (flute) |
Prélude à l'après-midi d'un faune (L. 86), known in English as Prelude to the Afternoon of a Faun, is a symphonic poem for orchestra by Claude Debussy, approximately 10 minutes in duration. It was composed in 1894 and first performed in Paris on 22 December 1894, conducted by Gustave Doret.[1][2] The flute solo was played by Georges Barrère.
The composition was inspired by the poem L'après-midi d'un faune by Stéphane Mallarmé. It is one of Debussy's most famous works and is considered a turning point in the history of Western art music, as well as a masterpiece of Impressionist composition. Pierre Boulez considered the score to be the beginning of modern music, observing that "the flute of the faun brought new breath to the art of music."[3]
Debussy's work later provided the basis for the ballet Afternoon of a Faun choreographed by Vaslav Nijinsky and a later version by Jerome Robbins.
Background
About his composition Debussy wrote:
The music of this prelude is a very free illustration of Mallarmé's beautiful poem. By no means does it claim to be a synthesis of it. Rather there is a succession of scenes through which pass the desires and dreams of the faun in the heat of the afternoon. Then, tired of pursuing the timorous flight of nymphs and naiads, he succumbs to intoxicating sleep, in which he can finally realize his dreams of possession in universal Nature.[4]
Paul Valéry reported that Mallarmé himself was unhappy with his poem being used as the basis for music:
He believed that his own music was sufficient, and that even with the best intentions in the world, it was a veritable crime as far as poetry was concerned to juxtapose poetry and music, even if it were the finest music there is.[5]
However, after attending the premiere performance at Debussy's invitation, Mallarmé wrote to Debussy: "I have just come out of the concert, deeply moved. The marvel! Your illustration of the Afternoon of a Faun, which presents no dissonance with my text, but goes much further, really, into nostalgia and into light, with finesse, with sensuality, with richness. I shake your hand admiringly, Debussy. Yours, Mallarmé."[6][7]
Composition

The work is scored for three flutes, two oboes, cor anglais, two clarinets in A and B♭, two bassoons, four horns, two harps, two crotales and strings.
Although it is tempting to call this piece a tone poem, there is very little musical literalism in the piece; instead, the slow and mediated melody and layered orchestration as a whole evoke the eroticism of Mallarmé's poem.
[This prelude] was [Debussy's] musical response to the poem of Stephane Mallarmé (1842–1898), in which a faun playing his pan-pipes alone in the woods becomes aroused by passing nymphs and naiads, pursues them unsuccessfully, then wearily abandons himself to a sleep filled with visions. Though called a "prelude," the work is nevertheless complete – an evocation of the feelings of the poem as a whole.[8]
Debussy had intended to compose a second and third movement, an Interlude and Paraphrase finale, respectively, but he decided to concentrate all of his musical ideas into one movement.[9]
The Prélude at first listening seems improvisational and almost free-form; however, closer observation will demonstrate that the piece consists of a complex organization of musical cells, motifs carefully developed and traded between members of the orchestra. A close analysis of the piece reveals a high amount of consciousness of composition on Debussy's part.
The main musical themes are introduced by woodwinds, with delicate but harmonically advanced accompaniment of muted horns, strings and harp. Recurring tools in Debussy's compositional arsenal make appearances in this piece: extended whole-tone scale runs, harmonic fluidity without lengthy modulations between central keys, and tritones in both melody and harmony. The opening flute solo consists of a chromatic descent to a tritone below the original pitch and then subsequent ascent. The development of the slow main theme transitions smoothly between 9
8, 6
8, and 12
8. Debussy uses sophisticated voicings and orchestration, allowing the main melodic cell to move from solo flute to oboe, back to solo flute, then to two unison flutes (yielding a completely different atmosphere to the melody), then to clarinet, and so on. Even the accompaniment explores alternate voicings: the flute duo's crescendo during their melodic cells accompany legato strings with violas carrying the soprano part over alto violins (the tone of a viola in its upper register being especially pronounced).
- Main theme

- Ambiguous chord progression
![\new PianoStaff <<
\new Staff \relative c' {
\clef treble \time 9/8 \key e \major
\set Score.tempoHideNote = ##t \tempo 4. = 36
\set Score.currentBarNumber = #4 \bar ""
\set Staff.midiInstrument = "french horn"
\once \override Staff.TimeSignature #'stencil = ##f
r4 r8 r8 e4~->(\p^"Horn" e8e4-- |
\time 6/8
<< { \dynamicUp f16(\< bes aes4\>)~ aes4.\! } \\ { r8 r16 c,([\p\< d8)~] d16(\> c d4\!) } >>
}
\new Staff \relative c' {
\clef treble \time 9/8 \key e \major
\set Staff.midiInstrument = "clarinet"
\once \override Staff.TimeSignature #'stencil = ##f
r4 r8 <ais' gis e cis>2.\p\>^"Winds" |
\set Staff.midiInstrument = "string ensemble 1"
\time 6/8 \clef bass
\once \override TextScript #'self-alignment-X = #-1.6
<bes, aes d, f, bes,>\pp_"Strings/Harp"
}
>>](//upload.wikimedia.org/score/f/1/f1s5c8lz13287n4lo5vbu0uub8z29zv/f1s5c8lz.png)
- Theme

- Theme – similar to the main theme in chromaticism and contour. Uses a whole-tone scale in m. 32.
![\relative c' \new Staff \with { \remove "Time_signature_engraver" } {
\clef treble \time 12/8 \key e \major
\set Score.tempoHideNote = ##t \tempo 4. = 36
\set Staff.midiInstrument = "clarinet"
\partial 8*3 eis4(\<^"Clarinet"\p fis8)\! |
\once \override Score.BarNumber #'break-visibility = ##(#f #t #t)
\set Score.currentBarNumber = #31 \bar "|"
g2.~\f\> g4\!~ g32 fis(\< f e)\! \override DynamicLineSpanner.staff-padding = #3.5 dis\p\<([ e f fis] g[ fis f e)\!] dis16(\> e)\! | \override DynamicLineSpanner.staff-padding = #2.5 \time 3/4 f32(\<[ g a b] cis[ dis eis dis)\!] \stemDown cis8(\>[ \acciaccatura { b16[ cis] } b8)\!] a([ \acciaccatura {g16[ a] } g8)] | \stemNeutral f }](//upload.wikimedia.org/score/6/t/6tnkl6iplvicbr2r8hx9kw0p7es01p6/6tnkl6ip.png)
- Theme – similar contour to the main theme.

- Secondary theme
![\relative c' \new Staff \with { \remove "Time_signature_engraver" } {
\clef treble \time 3/4 \key des \major
\set Score.tempoHideNote = ##t \tempo \markup \concat { "Même mouv" \raise #.5 t \translate #'(-0.8 . 0) "." "et très soutenu" } 4 = 56
\set Score.currentBarNumber = #55 \bar ""
\set Staff.midiInstrument = "clarinet"
aes''2(^"Woodwinds"\p_\markup \italic "expressif et très soutenu" f4 | ees4. des8~\< des[ f,)\!] | bes'4(~--\mf bes8 aes4 f8 | ees4~ ees8 des4 ces8)
}](//upload.wikimedia.org/score/t/1/t18hoiv1o8e4uo9hjx17jgqnpa73476/t18hoiv1.png)
- Theme – new melodic idea created by combining fragments of two previous melodies.
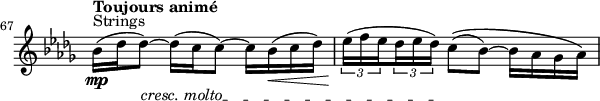
- Theme – related to main theme.
![\relative c' {
\clef treble \time 4/4 \key a \minor
\set Score.tempoHideNote = ##t \tempo "Un peu plus animé" 4 = 56
\set Score.currentBarNumber = #83 \bar ""
\set Staff.midiInstrument = "oboe"
r8 g'--~\p^"Oboe" g[ g\startTrillSpan\sfz\>] \slashedGrace a8(\stopTrillSpan g16)\! fis-. f-. e-. e8--\< e32 f( fis g) | g16-.\p
}](//upload.wikimedia.org/score/6/g/6gq4ncva1jhcs90ly6vsdixyyhqnu1g/6gq4ncva.png)
- Final chromatic harmonization of the main theme

The composition totals 110 bars. If one counts the incomplete lines of verse as one, Mallarmé's text likewise adds up to 110 lines. The second section in D-flat starts at bar 55, exactly halfway through the work.
Ballet versions
In 1912, the piece was made into a short ballet, with costumes and sets by painter Léon Bakst, which was choreographed and performed by renowned dancer Vaslav Nijinsky. It proved to be highly controversial because of the dancers' non-traditional movements and because of a moment in which the faun appears to masturbate.[10]
In 1958, another ballet by Jerome Robbins was made, which has been frequently performed by many companies.
Literature
In Thomas Mann's The Magic Mountain it is implied that protagonist Hans Castorp listened to Debussy's piece on a gramophone. In the book, the Prélude is one of his favorite recordings, and leads him to daydream about a faun playing pipes in an oneiric landscape.
Transcription
Claude Debussy himself transcribed the piece for performance on two pianos in 1895.
Other transcriptions include: the arrangement of Maurice Ravel for piano four hands, the flute and piano version of Gustave Samazeuilh, the arrangement for Pierrot ensemble (flute, clarinet, violin, cello and piano) by Tim Mulleman,[11] a transcription for flute, clarinet and piano by Michael Webster, and an arrangement for the instruments of Ravel's Introduction and Allegro (flute, clarinet, harp and string quartet) with an additional double bass, by Graeme Steele Johnson. The Russian pianist Vyacheslav Gryaznov also transcribed it for solo piano.[12][13] Linos Piano Trio arranged the piece for piano trio and included it on their 2021 album "Stolen Music".[14]
Benno Sachs, a pupil of Arnold Schoenberg, reorchestrated the work for a chamber ensemble which included a piano and a harmonium, for Schoenberg's Society for Private Musical Performances, which took place on 27 October 1920.
In popular culture
Film
- The theme features prominently in the film Portrait of Jennie (1949), and is used as a musical motif for the ethereal heroine played by Jennifer Jones.
- Prelude to the Afternoon of a Faun is the first animated segment in Italian director and animator Bruno Bozzetto's film Allegro Non Troppo (1977). While retaining Debussy's music, the on-screen story instead depicts an aging faun's vain attempts to recapture his youth.
- A climactic scene from the film Passion (2013) finds the main character attending the ballet version, with a memorable, several-minute-long split screen, with the ballet on one side and the movie action on the other side.
- In the found-footage horror film “Leaving DC” (2012), the song was featured on a digital recorder the main character listened to after he placed it on his windowsill to document strange sounds he was hearing in the forest outside his isolated home. The song appeared to play at 3:11am every night for a few seconds, but different parts of the flute solo were heard every time.
Lectures
- The work is analyzed at the end of the 4th segment of Leonard Bernstein's Norton lecture The Unanswered Question (1973). Bernstein corroborates the earlier statement that the piece, with its extensive use of the tri-tone interval and whole-tone scale, stretches the limits of tonality, thus setting up the atonal works of the 20th century to come.[15]
Music
- It was rearranged and recorded by jazz musician Eumir Deodato for his album Prelude (1973).
- A synthesiser arrangement was performed by Isao Tomita on his album Firebird (1975).
- Electronic jazz group Koop features the Overture in its piece 'Glömd' (1997) on its album Sons of Koop.
Television
- A production music version (arranged by Charlotte Georg) was featured in The Ren & Stimpy Show episode, "Powdered Toast Man".
References
- ^ "Pierre Meylan and Chris Walton. "Doret, Gustave."". Oxford. Retrieved 2009-05-25.
- ^ Fanning, Neil Cardew (2005). All music guide to classical music: the definitive guide to classical music. New York: Hal Leonard. p. 351.
- ^ Boulez, Pierre (1958), "Entries for a Musical Encyclopaedia: Claude Debussy", Stocktakings from an Apprenticeship, Oxford: Oxford University Press (published 1991), pp. 259–277, ISBN 0-19-311210-8
- ^ Original French: "La musique de ce prélude est une illustration très libre du beau poème de Mallarmé; elle ne prétend pas en être une synthèse. Il s'agit plutôt de fonds successifs sur lesquels se meuvent les désirs et les rêves du faune dans la chaleur de cet après-midi. Enfin, las de poursuivre les nymphes et les naïades apeurées dans leur fuite, il s'abandonne à un sommeil enivrant, riche de songes enfin réalisés, de pleine possession dans l'universelle nature." Quoted in "Les poètes symbolistes et la musique: de Verlaine à Blok" by Hélène Desgraupes.
- ^ Valéry, Paul (1933), "Stephane Mallarmé", Leonardo Poe Mallarmé, trans. James R. Lawler, London: Routledge & Kegan Paul (published 1972), p. 263, ISBN 0-7100-7148-5
- ^ Dumesnil, Maurice (1940), "Claude-Achille, Young Musician", Claude Debussy, Master of Dreams, Westport, Connecticut: Greenwood Press, Publishers (published 1979), p. 181, ISBN 0-313-20775-5
- ^ Lloyd, Rosemary (2005), Mallarmé: The Poet and His Circle, Cornell University Press, p. 154, ISBN 9780801489938
- ^ Burkhart, Charles. 2004. Anthology for Musical Analysis, Sixth Edition. p. 402.
- ^ "Debussy – Prélude à l'après-midi d'un faune". Classic FM. Retrieved 2019-03-19.
- ^ Järvinen, Hanna (2009). "Dancing without Space - On Nijinsky's "L'Après-midi d'un Faune" (1912)". Dance Research: The Journal of the Society for Dance Research. 27 (1): 28–64. doi:10.3366/E0264287509000243. ISSN 0264-2875. JSTOR 40264006.
- ^ >"Debussy's Faune – arrangement by Tim Mulleman (2016)". Tim Mulleman. 2019-12-24. Retrieved 2022-01-05.
- ^ C. Debussy – Prélude à l'aprés-midi d'un faune – V. Gryaznov's piano transcription on YouTube
- ^ "Vyacheslav Gryaznov Personal Page".
- ^ "Gestohlen, verarbeitet, aufgewertet". Pizzicato (in French). 2021-06-17. Retrieved 2021-07-05.
- ^ The Unanswered Question 1973: "4 The Delights & Dangers of Ambiguity", Bernstein Norton on YouTube
Further reading
- William W. Austin, ed. (1970). Debussy – Prelude to "The Afternoon of a Faun". An Authoritative Score – Mallarmé's Poem – Background and Sources – Criticism and Analysis. Norton Critical Scores. New York, London: W. W. Norton. ISBN 9780393021455 – via Internet Archive.
- Hendrik Lücke: "Mallarmé – Debussy. Eine vergleichende Studie zur Kunstanschauung am Beispiel von L'Après-midi d'un Faune". (Studien zur Musikwissenschaft, vol. 4). Dr. Kovac, Hamburg 2005, ISBN 3-8300-1685-9.
External links
- Prélude à l'après-midi d'un faune: Scores at the International Music Score Library Project
- Prélude à l'après-midi d'un faune, score, patachonf.free.fr
- Program notes by Richard Freed, January 2004
- Audio recording, arr. Tim Mulleman (2016) on YouTube, Tmesis Ensemble, Etcetera Records 2019


![\new PianoStaff <<
\new Staff \relative c' {
\clef treble \time 9/8 \key e \major
\set Score.tempoHideNote = ##t \tempo 4. = 36
\set Score.currentBarNumber = #4 \bar ""
\set Staff.midiInstrument = "french horn"
\once \override Staff.TimeSignature #'stencil = ##f
r4 r8 r8 e4~->(\p^"Horn" e8e4-- |
\time 6/8
<< { \dynamicUp f16(\< bes aes4\>)~ aes4.\! } \\ { r8 r16 c,([\p\< d8)~] d16(\> c d4\!) } >>
}
\new Staff \relative c' {
\clef treble \time 9/8 \key e \major
\set Staff.midiInstrument = "clarinet"
\once \override Staff.TimeSignature #'stencil = ##f
r4 r8 <ais' gis e cis>2.\p\>^"Winds" |
\set Staff.midiInstrument = "string ensemble 1"
\time 6/8 \clef bass
\once \override TextScript #'self-alignment-X = #-1.6
<bes, aes d, f, bes,>\pp_"Strings/Harp"
}
>>](http://upload.wikimedia.org/score/f/1/f1s5c8lz13287n4lo5vbu0uub8z29zv/f1s5c8lz.png)

![\relative c' \new Staff \with { \remove "Time_signature_engraver" } {
\clef treble \time 12/8 \key e \major
\set Score.tempoHideNote = ##t \tempo 4. = 36
\set Staff.midiInstrument = "clarinet"
\partial 8*3 eis4(\<^"Clarinet"\p fis8)\! |
\once \override Score.BarNumber #'break-visibility = ##(#f #t #t)
\set Score.currentBarNumber = #31 \bar "|"
g2.~\f\> g4\!~ g32 fis(\< f e)\! \override DynamicLineSpanner.staff-padding = #3.5 dis\p\<([ e f fis] g[ fis f e)\!] dis16(\> e)\! | \override DynamicLineSpanner.staff-padding = #2.5 \time 3/4 f32(\<[ g a b] cis[ dis eis dis)\!] \stemDown cis8(\>[ \acciaccatura { b16[ cis] } b8)\!] a([ \acciaccatura {g16[ a] } g8)] | \stemNeutral f }](http://upload.wikimedia.org/score/6/t/6tnkl6iplvicbr2r8hx9kw0p7es01p6/6tnkl6ip.png)

![\relative c' \new Staff \with { \remove "Time_signature_engraver" } {
\clef treble \time 3/4 \key des \major
\set Score.tempoHideNote = ##t \tempo \markup \concat { "Même mouv" \raise #.5 t \translate #'(-0.8 . 0) "." "et très soutenu" } 4 = 56
\set Score.currentBarNumber = #55 \bar ""
\set Staff.midiInstrument = "clarinet"
aes''2(^"Woodwinds"\p_\markup \italic "expressif et très soutenu" f4 | ees4. des8~\< des[ f,)\!] | bes'4(~--\mf bes8 aes4 f8 | ees4~ ees8 des4 ces8)
}](http://upload.wikimedia.org/score/t/1/t18hoiv1o8e4uo9hjx17jgqnpa73476/t18hoiv1.png)
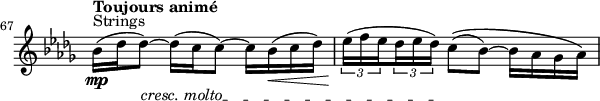
![\relative c' {
\clef treble \time 4/4 \key a \minor
\set Score.tempoHideNote = ##t \tempo "Un peu plus animé" 4 = 56
\set Score.currentBarNumber = #83 \bar ""
\set Staff.midiInstrument = "oboe"
r8 g'--~\p^"Oboe" g[ g\startTrillSpan\sfz\>] \slashedGrace a8(\stopTrillSpan g16)\! fis-. f-. e-. e8--\< e32 f( fis g) | g16-.\p
}](http://upload.wikimedia.org/score/6/g/6gq4ncva1jhcs90ly6vsdixyyhqnu1g/6gq4ncva.png)

