Newark Basin
The Newark Basin is a sediment-filled rift basin located mainly in northern New Jersey but also stretching into south-eastern Pennsylvania and southern New York. It is part of the system of Eastern North America Rift Basins.
Geology
Approximately 220 million years ago, during the late Triassic Period, the supercontinent Pangaea began to break apart. The focus of the rifting began somewhere between where present-day eastern North America and north-western Africa were joined.
As in all rifting environments, grabens formed. Many of these grabens were created, but for some of them, extension stopped before full rifting occurred. Where only partial rifting occurred, basins formed, analogous to the present-day Basin and Range Province in western United States. By definition, a basin is any area that collects sediments. These "aborted rifts" (rifts that are tectonically inactive and no longer collecting sediments) extend from North Carolina to Newfoundland.
Along certain basins, rifting was not partial. Where full rifting occurred, the Atlantic Ocean was created. It is important to note that along these rifts, magmatic activity never stopped, as shown by the ongoing eruption of lava along the Mid-Atlantic Ridge.
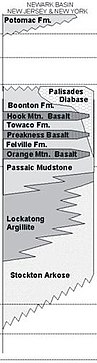
The Newark Basin is one in a series of these failed rifts. It is a half-graben filled over time by characteristic red bed sediments, sediments eroded from the uplifted footwalls of the border faults that were deposited within the basin; they are red due to their abundance in oxidized iron oxide minerals. The border fault is the Ramapo Fault on the western boundary of the basin; this is where the hanging wall of the graben slid down to its current position. Estimates to the depth of accumulated sediments on the western side of the basin, and therefore the depth of the hanging wall, are in the area of 11,000 feet. The beds dip roughly 15 degrees to the west throughout the basin. Though the north-eastern end of the basin is well-defined (it ends at the Hudson River), the south-western "end" is not an end at all, but merely a narrowing where the graben then re-opens into the Gettysburg Basin.
A significant geological feature within the Newark Basin is the Palisades Sill. During rifting events, magmatism is common due to decompression melting. The Palisades Sill is a result of this process.
-
A USGS cartoon showing the break-up of Pangaea and the origin of the Newark Basin
-
USGS cross-section of the Newark Basin
See also
References
Sources
- "The Newark Basin" on the USGS website
- "Mesozoic Basins" on the USGS website