Renal cortex
This article needs additional citations for verification. (May 2015) |
| Renal cortex | |
|---|---|
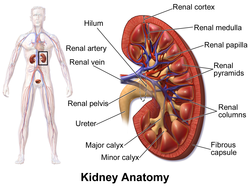 Kidney anatomy, with renal cortex labeled at top. | |

| |
| Details | |
| System | Urinary system |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Cortex renalis |
| MeSH | D007672 |
| TA98 | A08.1.01.015 |
| TA2 | 3368 |
| FMA | 15581 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The renal cortex is the outer portion of the kidney between the renal capsule and the renal medulla. In the adult, it forms a continuous smooth outer zone with a number of projections (cortical columns) that extend down between the pyramids. It contains the renal corpuscles and the renal tubules except for parts of the loop of Henle which descend into the renal medulla. It also contains blood vessels and cortical collecting ducts.
The renal cortex is the part of the kidney where ultrafiltration occurs. Erythropoietin is produced in the renal cortex.
Additional images
-
Kidney
-
Microscopic cross section of the renal cortex
-
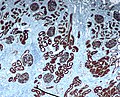
CD10 immunohistochemical staining of normal kidney. CD10 stains the proximal convoluted tubules and glomeruli.
-
Renal cortex
-
Renal cortex
Contains afferent arterioles
External links
- Anatomy photo:40:06-0103 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Posterior Abdominal Wall: Internal Structure of a Kidney"