Labrador wolf
| Labrador wolf | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Family: | Canidae |
| Genus: | Canis |
| Species: | |
| Subspecies: | C. l. labradorius
|
| Trinomial name | |
| Canis lupus labradorius | |
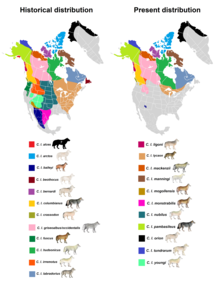
| |
| Historical and present range of gray wolf subspecies in North America | |
The Labrador wolf (Canis lupus labradorius) is a subspecies of gray wolf native to Labrador and northern Quebec. It has been described as ranging in color from dark grizzly-gray to almost white,[3] and of being closely related to the Newfoundland wolf (C. l. beothucus).[4] This wolf is recognized as a subspecies of Canis lupus in the taxonomic authority Mammal Species of the World (2005).[5]
History
Due to over-hunting in the early 1900s, Labrador wolf sightings were infrequent through the 1950s. Around that time period, the caribou population began to increase at a steady rate, which then correlated with an increase in the wolf population. However, the increase in number of the Labrador wolf was not enough to offset the continuing rise in caribou in the region, causing a reconsideration of the predation limitation hypothesis.[6]
In the late 2000s and early 2010s, there were several confirmed and unconfirmed sightings of the Labrador wolf on the island of Newfoundland.[7] In March 2012, a hunter shot and killed a large canine on the Bonavista Peninsula, thinking it to be a coyote; genetic testing found it to be a Labrador wolf.[7] In July 2012, a video posted on YouTube showed a canine which exhibited nearly all of the characteristics of a wolf. The video was taken in Clode Sound, Terra Nova National Park and was captured using a motion-sensitive trail camera set up as part of a joint research project on coastal river otters.[8] On 23 August 2012, the Newfoundland and Labrador Department of Environment and Conservation published the results of genetic testing of a large canine trapped on the Baie Verte Peninsula in 2009, confirming that this animal was also a Labrador wolf.[9]
References
- ^ "Canis lupus labradorius Goldman, 1937". Integrated Taxonomic Information System.
- ^ Joshua Ross Ginsberg, David Whyte Macdonald & IUCN/SSC Canid Specialist Group (1990). "Sorting out the Canidae". Foxes, wolves, jackals, and dogs: an action plan for the conservation of canids. International Union for Conservation of Nature. pp. 4–8. ISBN 978-2-88032-996-9.
- ^ Glover, A. (1942), Extinct and vanishing mammals of the western hemisphere, with the marine species of all the oceans, American Committee for International Wild Life Protection, p. 209.
- ^ R. South (31 March 1983). Biogeography and Ecology of the Island of Newfoundland. Springer. pp. 519–. ISBN 978-90-6193-101-0. Retrieved 29 December 2012.
- ^ Wozencraft, W. C. (2005). "Order Carnivora". In Wilson, D. E.; Reeder, D. M. (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. pp. 575–577. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494. url=https://books.google.com/books?id=JgAMbNSt8ikC&pg=PA576
- ^ "Characteristics of the Wolf (Canis lupus lubrudorius Goldman) in Northern Quebec and Labrador". Arctic. 39 (2). 1986. doi:10.14430/arctic2062. Archived from the original on 2013-11-26. Retrieved 2012-12-29.
- ^ a b "Wolf in Newfoundland probably made it to island on ice, experts say". The Telegram. 25 May 2012. Archived from the original on 5 January 2013. Retrieved 26 May 2012.
- ^ "Possible wolf captured on film in Terra Nova". The Telegram. 31 July 2012. Retrieved 26 August 2012.
- ^ "Genetic Retesting of DNA Confirms Second Wolf on Island of Newfoundland". Department of Environment and Conservation, Newfoundland and Labrador. 23 August 2012. Retrieved 26 August 2012.
