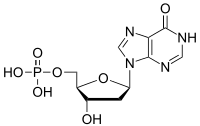
Deoxyinosine monophosphate
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2’-Deoxy-5’-inosinic acid
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.020.216 |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H13N4O7P | |
| Molar mass | 332.209 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Deoxyinosine monophosphate (dIMP) is a nucleoside monophosphate and a derivative of inosinic acid. It can be formed by the deamination of the purine base in deoxyadenosine monophosphate (dAMP). The enzyme deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate pyrophosphohydrolase, encoded by YJR069C in S. cerevisiae and containing (d)ITPase and (d)XTPase activities, hydrolyses dITP, resulting in the release of pyrophosphate and dIMP.[1]
References
- ^ Davies O, Mendes P, Smallbone K, Malys N (2012). "Characterisation of multiple substrate-specific (d)ITP/(d)XTPase and modelling of deaminated purine nucleotide metabolism". BMB Reports. 45 (4): 259–64. doi:10.5483/BMBRep.2012.45.4.259. PMID 22531138.
See also
