Giant house spider
This article may lack focus or may be about more than one topic. In particular, the species has now been split into three again, so separate articles are needed. (April 2020) |
| Giant house spider | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Subphylum: | Chelicerata |
| Class: | Arachnida |
| Order: | Araneae |
| Infraorder: | Araneomorphae |
| Family: | Agelenidae |
| Genus: | Eratigena |
| Species: | E. atrica
|
| Binomial name | |
| Eratigena atrica (C. L. Koch, 1843)[1]
| |
| |
| Synonyms[1] | |
| |
The giant house spider has been treated as either one species, under the name Eratigena atrica, or as three species, E. atrica, E. duellica and E. saeva. As of April 2020[update], the three species view was accepted by the World Spider Catalog. They are among the largest spiders of Central and Northern Europe. They were previously placed in the genus Tegenaria. In 2013, they were moved to the new genus Eratigena as the single species Eratigena atrica.[2] In 2018, the three separate species were restored.[3] The bite of these species does not pose a threat to humans or pets, and they are generally reluctant to bite, preferring instead to hide or escape.

Description
This section includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. (April 2016) |
The two sexes do not differ in coloration or markings. Its coloration is mainly dark brown. On its sternum is a lighter marking, with three light spots on each side. The opisthosoma features a lighter middle line with six "spots" on each side. The giant house spider has the same coloration as the domestic house spider, Tegenaria domestica; it has earthy tones of brown and muddy red or yellow. They also have conspicuously hairy legs, palps and abdomen. Despite its English name, this species is not the largest species in the genus (that being Tegenaria parietina). The female body size can reach 18.5 millimetres (0.73 in) in length, with males having a slightly smaller body at around 12 to 15 millimetres (0.47 to 0.59 in) in length. The female leg span is typically around 45 millimetres (1.8 in). The leg span of the male is highly variable, with spans between 25 to 75 millimetres (0.98 to 2.95 in) being common.
Its eight eyes are of equal size and are arranged in two rows. As the eyes contain fewer than 400 visual cells, E. atrica can probably only distinguish light and dark.
Taxonomy
The first description of a spider now assigned to this species was by Carl Ludwig Koch in 1843, under the name Tegenaria atrica. Other supposedly different species were described later, including Tegenaria saeva by John Blackwall in 1844, Tegenaria duellica by Eugène Simon in 1875 and Tegenaria gigantea by Ralph Vary Chamberlin and Wilton Ivie in 1935. T. gigantea was synonymized with T. duellica in 1978. The three remaining taxa have been regarded as distinct species, particularly in Britain.[2] Thus Roberts (1995) provides distinguishing characters for T. atrica, T. duellica and T. saeva,[4] as does Oxford (2008) for T. duellica (as T. gigantea) and T. saeva.[5] Others consider these three as part of a single morphologically variable species, for which the oldest name, and hence the senior synonym, is T. atrica.[2]
A phylogenetic study in 2013 concluded that Tegenaria, as then defined, was not monophyletic, and split off some species, including T. atrica, into the newly created segregate genus Eratigena. The study also consolidated the various giant house spider species into one species, E. atrica.[2] A subsequent genetic study of E. atrica specimens determined that there were three distinct morphological groups, leading to the restoration of three separate species: E. atrica, E. duellica, and E. saeva.[3]
Distribution and habitat
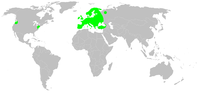
E. atrica is found in Europe, Central Asia and Northern Africa. It was unwittingly introduced to the Pacific Northwest of North America circa 1900 due to human activity and has strongly increased in numbers for the last century.[citation needed]
In the last few years the spider has been found in several European countries in which it was previously not recorded, like Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania. It is recorded in the checklist of Danish spider species,[6] and is also found in Iceland.[7]
The giant house spider's original habitat consists mostly of caves, or dry forests where it is found under rocks, but it is a common spider in people's homes.[citation needed]
Biology and behavior

The webs built by the giant house spider are flat and messy with a funnel at one end. They do not contain sticky threads. The spider lurks in the funnel until a small invertebrate happens to get trapped in the web, at which point the spider runs out and attacks it. They usually build their webs in corners (on both the floor and ceiling), between boxes in basements, behind cupboards, in attics, or any other area that is rarely disturbed by large animals or humans. Often found near window openings.[citation needed]
E. atrica normally lives for two or three years, but lifetimes of up to six years have been observed. While the female only leaves its nest to feed, males can often be seen wandering around houses during the late summer and early autumn looking for a mate. Males can be found from July to October, adult females occur all year.[citation needed]
At least 60 spiderlings emerge from an egg sac. Unusual for spiders, they are subsocial at this stage: they remain together for about a month, but do not cooperate in prey capture. The amount of cannibalism correlates with the amount of available food.[8] E. atrica molts seven or eight times before reaching the immature adult state, and after a final molt reaches maturity.[9]
Like most spiders, the spider possesses venom to subdue its prey. Since E. atrica bites can penetrate human skin on occasion, the effects of agatoxin might be felt by bite victims, though these spiders will not bite unless provoked.[citation needed]
With speeds clocked at 0.53 m/s (1.9 km/h; 1.2 mph; 1.7 ft/s), the giant house spider held the Guinness Book of World Records for top spider speed until 1987 when it was displaced by solifugids, although the latter are not true spiders.[10]
Relationship with Eratigena agrestis


A population of giant house spiders is popularly thought to be a deterrent to the establishment of Eratigena agrestis, known in North America as the "hobo spider", and considered by some to be more likely to bite humans. Giant house spiders may compete with hobo spiders for the same resources. Hobo spiders grow no more than a body size of 15 millimetres (0.59 in) long whereas the larger female giant house spider can have a body size of 18 millimetres (0.71 in),[11] but has proportionately much longer legs.[12]
In popular culture
Humorist David Sedaris has written about his relationship with E. atrica. His essay "April In Paris" documents his growing affection towards and domestic association with giant house spiders, particularly one named April.[13] The essay can be found in the collection When You Are Engulfed in Flames.
References
- ^ a b "Taxon details Eratigena atrica (C. L. Koch, 1843)". World Spider Catalog. Natural History Museum Bern. Retrieved 2016-04-28.
- ^ a b c d Bolzern, Angelo; Burckhardt, Daniel; Hänggi, Ambros (2013). "Phylogeny and taxonomy of European funnel-web spiders of the Tegenaria−Malthonica complex (Araneae: Agelenidae) based upon morphological and molecular data". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. 168 (4): 723–848. doi:10.1111/zoj.12040.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|lastauthoramp=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help)
- ^ a b Oxford, Geoff S; Bolzern, Angelo (2018). "Molecules v. Morphology—is Eratigena atrica (Araneae: Agelenidae) One Species or Three?". Arachnology. 17 (7). doi:10.13156/arac.2017.17.7.337.
- ^ Roberts, Michael J. (1995). Spiders of Britain & Northern Europe. London: HarperCollins. pp. 243–245. ISBN 978-0-00-219981-0.
- ^ Oxford, G. (2008). "Identification of Tegenaria gigantea and T. saeva". Newsletter of the British Arachnological Society. 113: 21–23.
- ^ Checklist of Danish Spiders (Araneae). Version 26-10-2011 (list)
- ^ "Skemmukönguló (Eratigena atrica)". Náttúrufræðistofnun Íslands (in Icelandic). Icelandic Institute of Natural History. Retrieved 2017-10-11.
- ^ Pourié, Grégory; Trabalon, Marie (1999). "Relationships Among Food and Contact Signals in Experimental Group-Living Young of Tegenaria atrica". Archives of Insect Biochemistry and Physiology. 42 (3): 188–197. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1520-6327(199911)42:3<188::AID-ARCH3>3.0.CO;2-M.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|lastauthoramp=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ Collatz, K.G.; Mommsen, T. (1975). "Physiological conditions and variations of body constituents during the moulting of the spider Tegenaria atrica C.L. Koch (Agelenidae)". Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology. 52: 465–475. doi:10.1016/S0300-9629(75)80067-3.
{{cite journal}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|lastauthoramp=(help) - ^ "Giant House Spider (Tegenaria gigantea)". Woodland Park Zoo. Retrieved 20 August 2013.
- ^ "Species Tegenaria agrestis - Hobo Spider". BugGuide. Iowa State University. Retrieved 20 August 2013.
- ^ "Species Tegenaria gigantea - Giant House Spider". BugGuide. Iowa State University. Retrieved 20 August 2013.
- ^ "April & Paris". The New Yorker. Retrieved 14 September 2014.
Further reading
- Prouvost, Olivier; Trabalon, Marie; Papke, Mirjam; Schulz, Stefan (1999). "Contact sex signals on web and cuticle of Tegenaria atrica (Araneae, Agelenidae)". Archives of Insect Biochemistry and Physiology. 40 (4): 194–202. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1520-6327(1999)40:4<194::AID-ARCH4>3.0.CO;2-P.
- Pourié, Grégory; Ibarra, Fernando; Francke, Wittko; Trabalon, Marie (2005). "Fatty acids mediate aggressive behavior in the spider Tegenaria atrica". Chemoecology. 15 (3): 161–166. doi:10.1007/s00049-005-0308-6.
