Golgi cell
| Golgi cell | |
|---|---|
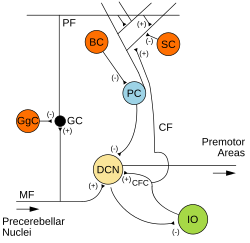 Microcircuitry of the cerebellum. Excitatory synapses are denoted by (+) and inhibitory synapses by (-). MF: Mossy fiber. DCN: Deep cerebellar nuclei. IO: Inferior olive. CF: Climbing fiber. GC: Granule cell. PF: Parallel fiber. PC: Purkinje cell. GgC: Golgi cell. SC: Stellate cell. BC: Basket cell. | |
| Details | |
| Location | Granular layer of the cerebellum |
| Identifiers | |
| NeuroLex ID | nifext_129 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
In neuroscience, Golgi cells are inhibitory interneurons found within the granular layer of the cerebellum. They were first identified as inhibitory by Eccles et al. in 1964.[1] It was also the first example of an inhibitory feed back network, where the inhibitory interneuron was identified anatomically. These cells synapse onto the dendrite of granule cells and unipolar brush cells. They receive excitatory input from mossy fibres, also synapsing on granule cells, and parallel fibers, which are long granule cell axons. Thereby this circuitry allows for feed-forward and feed-back inhibition of granule cells.
The main synapse made by these cells is a synapse onto the mossy fibre - granule cell excitatory synapse in a glomerulus. The glomerulus is made up of the mossy fibre terminal, granule cell dendrites, the Golgi terminal and is enclosed by a glial coat.[2] The Golgi cell acts by altering the mossy fibre - granule cell synapse.
The Golgi cells use GABA as their transmitter. The basal level of GABA produces a postsynaptic leak conductance by tonically activating alpha 6-containing GABA-A receptors on the granule cell.[3][4][5] These high-affinity receptors are located both synaptically and extrasynaptically on the granule cell. The synaptic receptors mediate phasic contraction, duration of around 20-30ms whereas the extrasynapatic receptors mediate tonic inhibition of around 200ms, and are activated by synapse spill over.[6]
Additionally the GABA acts on GABA-B receptors which are located presynaptically on the mossy fibre terminal. These inhibit the mossy fibre evoked EPSCs of the granule cell in a temperature and frequency dependent manner. At high mossy firing frequency (10 Hz) there is no effect of GABA acting on presynaptic GABA-B receptors on evoked EPSCs. However, at low (1 Hz) firing the GABA does have an effect on the EPSCs mediated via these presynaptic GABA-B receptors.
Type I
A Golgi I (or Golgi type I) neuron is a neuron which has a long axon that begins in the grey matter of the central nervous system and may extend from there. It is also known as a projection neuron. They include the neurons forming peripheral nerves and long tracts of brain and spinal cord. [7] Golgi II neurons, in contrast, are defined as having short axons or no axon at all. This distinction was introduced by the pioneering neuroanatomist Camillo Golgi, on the basis of the appearance under a microscope of neurons stained with the Golgi stain that he had invented. Santiago Ramón y Cajal postulated that higher developed animals had more Golgi type II in comparison to Golgi type I neurons. These Golgi type 2 neurons have star-like appearance.These Golgi Golgi type 2 neurons are found in cerebral and cerebellar cortices and retina. [8]
Type II
A Golgi II or Golgi type II neuron is a neuron having either no axon or else a short axon that does not send branches out of the gray matter of the central nervous system.[9]
References
- ^ Eccles, JC; Llinas, R; Sasaki, K (1964). "Golgi cell inhibition in the cerebellar cortex". Nature. 204 (4965): 1265–1266. doi:10.1038/2041265a0. PMID 14254404.
- ^ Jakab, RL; Hámori, J (1988). "Quantitative morphology and synaptology of cerebellar glomeruli in the rat". Anatomy and Embryology. 179 (100): 81–88. doi:10.1007/BF00305102. PMID 3213958.
- ^ Brickley SG, Cull-Candy SG, Farrant M (1996). "Development of a tonic form of synaptic inhibition in rat cerebellar granule cells resulting from persistent activation of GABAA receptors". J Physiol. 497 (Pt 3): 753–759. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.1996.sp021806. PMC 1160971. PMID 9003560.
- ^ Tia S, Wang JF, Kotchabhakdi N, Vicini S (June 1, 1996). "Developmental changes of inhibitory synaptic currents in cerebellar granule neurons: role of GABAA receptor alpha 6 subunit" (abstract). Journal of Neuroscience. 16 (11): 3630–3640. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-11-03630.1996. PMID 8642407.
- ^ Wall MJ, Usowicz MM (1997). "Development of action potential-dependent and independent spontaneous GABAA receptor-mediated currents in granule cells of postnatal rat cerebellum". European Journal of Neuroscience. 9 (3): 533–548. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.1997.tb01630.x. PMID 9104595.
- ^ Nusser Z, Sieghart W, Somogyi P (March 1, 1998). "Segregation of different GABAA receptors to synaptic and extrasynaptic membranes of cerebellar granule cells" (abstract). Journal of Neuroscience. 18 (5): 1693–1703. PMID 9464994.
- ^ "Golgi type I neuron definition". Dictionary.com. 2008. Retrieved 2008-12-25.
- ^ Dowling JE (2001). Neurons and Networks: An Introduction to Behavioral Neuroscience. Harvard University Press. p. 46. ISBN 978-0-674-00462-7.
- ^ "Golgi type II neuron definition". Dictionary.com. Retrieved 2019-08-15.
External links
- NIF Search - Golgi Cell via the Neuroscience Information Framework
- NIF Search - Golgi II Cell via the Neuroscience Information Framework
