o-Coumaric acid
Appearance
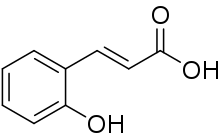
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(E)-3-(2-Hydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enoic acid
| |
| Other names
ortho-Coumaric acid
2-Hydroxycinnamic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.009.444 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H8O3 | |
| Molar mass | 164.16 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
o-Coumaric acid is a hydroxycinnamic acid, an organic compound that is a hydroxy derivative of cinnamic acid. There are three isomers of coumaric acids — o-coumaric acid, m-coumaric acid, and p-coumaric acid — that differ by the position of the hydroxy substitution of the phenyl group.
Natural occurrence
o-Coumaric acid can be found in vinegar.
2-Coumarate reductase is an enzyme that produces 2-coumarate from 3-(2-hydroxyphenyl)propanoate and NAD+. This enzyme participates in phenylalanine metabolism.[1]
References
- ^ Levy, Carl C.; Weinstein, Gerald D. (1964). "The Metabolism of Coumarin by a Microorganism. II. The Reduction of o-Coumaric Acid to Melilotic Acid". Biochemistry. 3 (12): 1944–7. doi:10.1021/bi00900a027. PMID 14269315.
External links
