Apodanthaceae
Appearance
| Apodanthaceae | |
|---|---|
| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Cucurbitales |
| Family: | Apodanthaceae Tiegh. ex Takht. |
| Genera | |
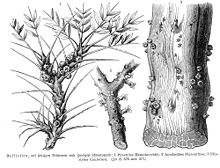
The family Apodanthaceae comprises about 10 species[1] of endoparasitic herbs. They live in the branches or stems of their hosts (as filaments similar to a fungal mycelium), emerging only to flower and fruit. The plants produce no green parts and do not carry out any photosynthesis (that is, they are holoparasitic).[2] There are two genera: Pilostyles and Apodanthes.[3] A third genus, Berlinianche, was never validly published.[4] Mitochondrial and nuclear DNA sequences confidently place the Apodanthaceae in the Cucurbitales, where they also fit well in terms of their flower morphology.[5]
References
- ^ Christenhusz, M. J. M.; Byng, J. W. (2016). "The number of known plants species in the world and its annual increase". Phytotaxa. 261 (3). Magnolia Press: 201–217. doi:10.11646/phytotaxa.261.3.1.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|lastauthoramp=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ Apodanthaceae: Family Description, Parasitic Plant Connection website, accessed 2009-12-31
- ^ Albert Blarer, Daniel L. Nickrent, and Peter K. Endress. 2004. "Comparative floral structure and systematics in Apodanthaceae (Rafflesiales)". Plant Systematics and Evolution 245(1-2):119-142.
- ^ Bellot, S., and S. S. Renner. 2013. "Pollination and mating systems of Apodanthaceae and the distribution of reproductive traits in parasitic angiosperms". "American Journal of Botany" 100(6): 1083–1094.
- ^ Filipowicz, N., and S. S. Renner. 2010. "The worldwide holoparasitic Apodanthaceae confidently placed in the Cucurbitales by nuclear and mitochondrial gene trees." BMC Evolutionary Biology 10:219.
