Infraorbital groove
| Infraorbital groove | |
|---|---|
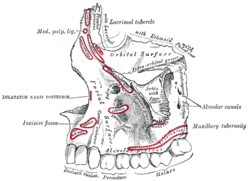 Left maxilla. Outer surface. (Infra-orbital groove labeled at upper right.) | |
 1 Foramen ethmoidale, 2 Canalis opticus, 3 Fissura orbitalis superior, 4 Fossa sacci lacrimalis, 5 Sulcus infraorbitalis, 6 Fissura orbitalis inferior, 7 Foramen infraorbitale | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Sulcus infraorbitalis maxillae |
| TA98 | A02.1.12.005 |
| TA2 | 760 |
| FMA | 57746 |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |
The infraorbital groove (or sulcus) is located in the middle of the posterior part of the orbital surface of the maxilla. Its function is to act as the passage of the infraorbital vessels and nerve.
The groove begins at the middle of the posterior border (with which it is continuous) near the upper edge of the infratemporal surface and, passing forward, ends in a canal which subdivides into two branches.
See also
Additional images
-
Horizontal section of nasal and orbital cavities. (Note distinction between infraorbital groove and inferior orbital fissure.)
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 159 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 159 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- Anatomy photo:29:os-0507 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center

