Vatin culture
 | |
| Period | Bronze Age |
|---|---|
| Type site | Vatin |
| Characteristics |
|
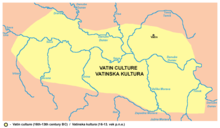
The Vatin culture (Serbian: Ватинска култура, romanized: Vatinska kultura / or Ватинска група, Vatinska grupa) is a name of an prehistoric Bronze Age culture, which was named after village Vatin in Serbia. The culture had Indo-European roots and was culturally connected with Mycenaean Greece.[1] The Vatin culture is dated to the middle Bronze Age and it is generally divided into three phases: Pančevo-Omoljica, Vatin-Vršac, and Belegiš-Ilandža.[2] It flourished from 16th to 13th century BC.[3]
The people of the Vatin culture inhabited the entire territory of Vojvodina (Banat, Bačka, Syrmia) and many surrounding areas (including Slavonia, Oltenia, Bosnia and Central Serbia). Its core area was in Serbian-Vojvodinian Podunavlje.[2] The remains of this culture were discovered at the beginning of the 20th century near the village of Vatin (Banat region, Vojvodina province, Serbia). However the real importance of this culture was only realised at the end of the 20th century, when the locality of Feudvar near the village of Mošorin was investigated.
Characteristics
The Vatin culture was highly influenced by Mycenaean Greece and had already developed social differentiation within its population. The culture also developed large central settlements, which were surrounded by smaller settlements and farms. Large settlements were economical and social centers, as well as the seats of tribal leaders. These fortified centers had a defensive character and a large number of them existed in the wider area. The thick network of large fortified settlements represents an example of the collective defense of a wide space.
The main occupations of inhabitants of the Vatin culture was agriculture and animal husbandry and it is assumed that they also produced beer. In many of the settlements, remains of children's toys were discovered. Tools, weapons and jewelry were mainly purchased by trade, but some larger settlements also had their own workshops that produced bronze objects. One foundry of bronze objects was discovered in Feudvar, and according to the researchers, it was probably used for several hundreds of years. There are indications that people of the Vatin culture also had basic mathematical knowledge.
Localities
Localities of the Vatin culture are:[2][4]
- Vatin
- Pančevo
- Omoljica
- Popov Salaš
- Belegiš
- Vinča
- Vinkovci
- Sotin
- Sarvaš
- Lovas
- Vukovar
- Feudvar near Mošorin
- Novigrad na Savi
- Ludoš
- Vršac - Židovar
- Gomolava
- Ljuljaci
- Dobrača
References
- ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-04-25. Retrieved 2011-11-03.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ a b c "brončano doba - skripta". Scribd.com. Retrieved 29 April 2019.
- ^ "[Projekat Rastko] Dragoslav Srejovic: Kad smo bili kulturno srediste svetaКад смо били културно средиште света". Rastko.rs. Retrieved 29 April 2019.
- ^ "Праисторија на тлу Србије". Scribd.com. Retrieved 29 April 2019.
Further reading
- Dr Predrag Medović, Praistorija na tlu Vojvodine, Novi Sad, 2001.
- Dr M. Grbić, Preistorisko doba Vojvodine, Zbornik "Vojvodina", knjiga I, PROMETEJ, Novi Sad, 2008.
External links
- Vatin čeka arheologe - Vatin waits for archaeologists (in Serbian)
- Bronzano doba - Bronze Age (in Croatian)
- Dragoslav Srejović, Kad smo bili kulturno središte sveta, Beograd, 2001. - When we were cultural center of the World (in Serbian)
- Praistorija na tlu Srbije - Prehistory on Serbian soil (in Serbian)
- Praistorija na tlu Srbije - Prehistory on Serbian soil (in Serbian)
- Kulture bronzanog doba u Vojvodini - Bronze Age cultures in Vojvodina (In Serbian)
- Archaeological cultures of Southeastern Europe
- Archaeological cultures in Serbia
- Archaeological cultures in Romania
- Archaeological cultures in Croatia
- Archaeological cultures in Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Bronze Age cultures of Europe
- Bronze Age Serbia
- Prehistory of Romania
- Prehistoric Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Prehistoric Bulgaria
- History of Banat
- Prehistory of Vojvodina
- Indo-European archaeological cultures
