Irreducible complexity
| Part of a series on |
| Intelligent design |
|---|
 |
| Concepts |
| Movement |
| Campaigns |
| Authors |
| Organisations |
| Reactions |
|
|
| Creationism |
Irreducible complexity (IC) involves the idea that certain biological systems cannot have evolved by successive small modifications to pre-existing functional systems through natural selection, because no less complex system would function. Irreducible complexity has become central to the creationist concept of intelligent design, but the scientific community,[1] which regards intelligent design as pseudoscience, rejects the concept of irreducible complexity.[2] Irreducible complexity is one of two main arguments used by intelligent-design proponents, alongside specified complexity.[3]
Creation science presented the theological argument from design with assertions that evolution could not explain complex molecular mechanisms, and in 1993 Michael Behe, a professor of biochemistry at Lehigh University, presented these arguments in a revised version of the school textbook Of Pandas and People.[4] In his 1996 book Darwin's Black Box he called this concept irreducible complexity and said it made evolution through natural selection of random mutations impossible.[5][need quotation to verify] This was based on the mistaken assumption that evolution relies on improvement of existing functions, ignoring how complex adaptations originate from changes in function, and disregarding published research.[4] Evolutionary biologists have published rebuttals showing how systems discussed by Behe can evolve,[6][7] and examples documented through comparative genomics show that complex molecular systems are formed by the addition of components as revealed by different temporal origins of their proteins.[8][9]
In the 2005 Kitzmiller v. Dover Area School District trial, Behe gave testimony on the subject of irreducible complexity. The court found that "Professor Behe's claim for irreducible complexity has been refuted in peer-reviewed research papers and has been rejected by the scientific community at large."[1]
Definitions
Michael Behe defined irreducible complexity in natural selection in his book Darwin's Black Box:
... a single system which is composed of several well-matched, interacting parts that contribute to the basic function, and where the removal of any one of the parts causes the system to effectively cease functioning.[10]
A second definition given by Behe (his "evolutionary definition") is as follows:
An irreducibly complex evolutionary pathway is one that contains one or more unselected steps (that is, one or more necessary-but-unselected mutations). The degree of irreducible complexity is the number of unselected steps in the pathway.[11]
Intelligent design advocate William A. Dembski gives this definition:
A system performing a given basic function is irreducibly complex if it includes a set of well-matched, mutually interacting, nonarbitrarily individuated parts such that each part in the set is indispensable to maintaining the system's basic, and therefore original, function. The set of these indispensable parts is known as the irreducible core of the system.[12]
History
Forerunners
The argument from irreducible complexity is a descendant of the teleological argument for God (the argument from design or from complexity). This states that because certain things in nature appear very complicated, they must have been designed. William Paley famously argued, in his 1802 watchmaker analogy, that complexity in nature implies a God for the same reason that the existence of a watch implies the existence of a watchmaker.[13] This argument has a long history, and one can trace it back at least as far as Cicero's De Natura Deorum ii.34,[14][15] written in 45 BC.
Up to the 18th century
Galen (1st and 2nd centuries AD) wrote about the large number of parts of the body and their relationships, which observation was cited as evidence for creation.[16] The idea that the interdependence between parts would have implications for the origins of living things was raised by writers starting with Pierre Gassendi in the mid-17th century[17] and by John Wilkins (1614-1672), who wrote (citing Galen), "Now to imagine, that all these things, according to their several kinds, could be brought into this regular frame and order, to which such an infinite number of Intentions are required, without the contrivance of some wise Agent, must needs be irrational in the highest degree."[18] [19] In the late 17th-century, Thomas Burnet referred to "a multitude of pieces aptly joyn'd" to argue against the eternity of life.[20] In the early 18th century, Nicolas Malebranche[21] wrote "An organized body contains an infinity of parts that mutually depend upon one another in relation to particular ends, all of which must be actually formed in order to work as a whole", arguing in favor of preformation, rather than epigenesis, of the individual;[22] and a similar argument about the origins of the individual was made by other 18th-century students of natural history.[23] In his 1790 book, The Critique of Judgment, Kant is said by Guyer to argue that "we cannot conceive how a whole that comes into being only gradually from its parts can nevertheless be the cause of the properties of those parts".[24][25]
19th century
Chapter XV of Paley's Natural Theology discusses at length what he called "relations" of parts of living things as an indication of their design.[13]
Georges Cuvier applied his principle of the correlation of parts to describe an animal from fragmentary remains. For Cuvier, this related to another principle of his, the conditions of existence, which excluded the possibility of transmutation of species.[26]
While he did not originate the term, Charles Darwin identified the argument as a possible way to falsify a prediction of the theory of evolution at the outset. In The Origin of Species (1859), he wrote, "If it could be demonstrated that any complex organ existed, which could not possibly have been formed by numerous, successive, slight modifications, my theory would absolutely break down. But I can find out no such case."[27] Darwin's theory of evolution challenges the teleological argument by postulating an alternative explanation to that of an intelligent designer—namely, evolution by natural selection. By showing how simple unintelligent forces can ratchet up designs of extraordinary complexity without invoking outside design, Darwin showed that an intelligent designer was not the necessary conclusion to draw from complexity in nature. The argument from irreducible complexity attempts to demonstrate that certain biological features cannot be purely the product of Darwinian evolution.[28]
In the late 19th century, in a dispute between supporters of the adequacy of natural selection and those who held for inheritance of acquired characteristics, one of the arguments made repeatedly by Herbert Spencer, and followed by others, depended on what Spencer referred to as co-adaptation of co-operative parts, as in:
"We come now to Professor Weismann's endeavour to disprove my second thesis — that it is impossible to explain by natural selection alone the co-adaptation of co-operative parts. It is thirty years since this was set forth in "The Principles of Biology." In §166, I instanced the enormous horns of the extinct Irish elk, and contended that in this and in kindred cases, where for the efficient use of some one enlarged part many other parts have to be simultaneously enlarged, it is out of the question to suppose that they can have all spontaneously varied in the required proportions."[29][30]
Darwin responded to Spencer's objections in chapter XXV of The Variation of Animals and Plants under Domestication (1868).[31] The history of this concept in the dispute has been characterized: "An older and more religious tradition of idealist thinkers were committed to the explanation of complex adaptive contrivances by intelligent design. ... Another line of thinkers, unified by the recurrent publications of Herbert Spencer, also saw co-adaptation as a composed, irreducible whole, but sought to explain it by the inheritance of acquired characteristics."[32]
St. George Jackson Mivart raised the objection to natural selection that "Complex and simultaneous co-ordinations … until so far developed as to effect the requisite junctions, are useless"[33] which "amounts to the concept of "irreducible complexity" as defined by … Michael Behe".[34]
20th century
Hermann Muller, in the early 20th century, discussed a concept similar to irreducible complexity. However, far from seeing this as a problem for evolution, he described the "interlocking" of biological features as a consequence to be expected of evolution, which would lead to irreversibility of some evolutionary changes.[35] He wrote, "Being thus finally woven, as it were, into the most intimate fabric of the organism, the once novel character can no longer be withdrawn with impunity, and may have become vitally necessary."[36]
In 1974 the young Earth creationist Henry M. Morris introduced a similar concept in his book Scientific Creationism, in which he wrote; "This issue can actually be attacked quantitatively, using simple principles of mathematical probability. The problem is simply whether a complex system, in which many components function unitedly together, and in which each component is uniquely necessary to the efficient functioning of the whole, could ever arise by random processes."[37]
In 1975 Thomas H. Frazzetta published a book-length study of a concept similar to irreducible complexity, explained by gradual, step-wise, non-teleological evolution. Frazzetta wrote:
"A complex adaptation is one constructed of several components that must blend together operationally to make the adaptation "work". It is analogous to a machine whose performance depends upon careful cooperation among its parts. In the case of the machine, no single part can greatly be altered without changing the performance of the entire machine."
The machine that he chose as an analog is the Peaucellier–Lipkin linkage, and one biological system given extended description was the jaw apparatus of a python. The conclusion of this investigation, rather than that evolution of a complex adaptation was impossible, "awed by the adaptations of living things, to be stunned by their complexity and suitability", was "to accept the inescapable but not humiliating fact that much of mankind can be seen in a tree or a lizard."[38]
In 1981, Ariel Roth, in defense of the creation-science position in the trial McLean v. Arkansas, said of "complex integrated structures": "This system would not be functional until all the parts were there ... How did these parts survive during evolution ...?"[39]
In 1985 Cairns-Smith wrote of "interlocking": "How can a complex collaboration between components evolve in small steps?" and used the analogy of the scaffolding called centering - used to build an arch then removed afterwards: "Surely there was 'scaffolding'. Before the multitudinous components of present biochemistry could come to lean together they had to lean on something else."[40][41] However, neither Muller or Cairns-Smith claimed their ideas as evidence of something supernatural.[42]
An essay in support of creationism published in 1994 referred to bacterial flagella as showing "multiple, integrated components", where "nothing about them works unless every one of their complexly fashioned and integrated components are in place". The author asked the reader to "imagine the effects of natural selection on those organisms that fortuitously evolved the flagella ... without the concommitant [sic] control mechanisms".[43][4]
An early concept of irreducibly complex systems comes from Ludwig von Bertalanffy (1901-1972), an Austrian biologist.[44] He believed that complex systems must be examined as complete, irreducible systems in order to fully understand how they work. He extended his work on biological complexity into a general theory of systems in a book titled General Systems Theory.
After James Watson and Francis Crick published the structure of DNA in the early 1950s, General Systems Theory lost many of its adherents in the physical and biological sciences.[45] However, systems theory remained popular in the social sciences long after its demise in the physical and biological sciences.
Origins
Michael Behe developed his ideas on the concept around 1992, in the early days of the 'wedge movement', and first presented his ideas about "irreducible complexity" in June 1993 when the "Johnson-Behe cadre of scholars" met at Pajaro Dunes in California.[46] He set out his ideas in the second edition of Of Pandas and People published in 1993, extensively revising Chapter 6 Biochemical Similarities with new sections on the complex mechanism of blood clotting and on the origin of proteins.[47]
He first used the term "irreducible complexity" in his 1996 book Darwin's Black Box, to refer to certain complex biochemical cellular systems. He posits that evolutionary mechanisms cannot explain the development of such "irreducibly complex" systems. Notably, Behe credits philosopher William Paley for the original concept (alone among the predecessors) and suggests that his application of the concept to biological systems is entirely original.
Intelligent design advocates argue that irreducibly complex systems must have been deliberately engineered by some form of intelligence.
In 2001, Michael Behe wrote: "[T]here is an asymmetry between my current definition of irreducible complexity and the task facing natural selection. I hope to repair this defect in future work." Behe specifically explained that the "current definition puts the focus on removing a part from an already functioning system", but the "difficult task facing Darwinian evolution, however, would not be to remove parts from sophisticated pre-existing systems; it would be to bring together components to make a new system in the first place".[48] In the 2005 Kitzmiller v. Dover Area School District trial, Behe testified under oath that he "did not judge [the asymmetry] serious enough to [have revised the book] yet."[49]
Behe additionally testified that the presence of irreducible complexity in organisms would not rule out the involvement of evolutionary mechanisms in the development of organic life. He further testified that he knew of no earlier "peer reviewed articles in scientific journals discussing the intelligent design of the blood clotting cascade," but that there were "probably a large number of peer reviewed articles in science journals that demonstrate that the blood clotting system is indeed a purposeful arrangement of parts of great complexity and sophistication."[50] (The judge ruled that "intelligent design is not science and is essentially religious in nature".)[51]
According to the theory of evolution, genetic variations occur without specific design or intent. The environment "selects" the variants that have the highest fitness, which are then passed on to the next generation of organisms. Change occurs by the gradual operation of natural forces over time, perhaps slowly, perhaps more quickly (see punctuated equilibrium). This process is able to adapt complex structures from simpler beginnings, or convert complex structures from one function to another (see spandrel). Most intelligent design advocates accept that evolution occurs through mutation and natural selection at the "micro level", such as changing the relative frequency of various beak lengths in finches, but assert that it cannot account for irreducible complexity, because none of the parts of an irreducible system would be functional or advantageous until the entire system is in place.
The mousetrap example

Behe uses the mousetrap as an illustrative example of this concept. A mousetrap consists of five interacting pieces: the base, the catch, the spring, the hammer, and the hold-down bar. All of these must be in place for the mousetrap to work, as the removal of any one piece destroys the function of the mousetrap. Likewise, he asserts that biological systems require multiple parts working together in order to function. Intelligent design advocates claim that natural selection could not create from scratch those systems for which science is currently unable to find a viable evolutionary pathway of successive, slight modifications, because the selectable function is only present when all parts are assembled.
In his 2008 book Only A Theory, biologist Kenneth R. Miller challenges Behe's claim that the mousetrap is irreducibly complex.[53] Miller observes that various subsets of the five components can be devised to form cooperative units, ones that have different functions from the mousetrap and so, in biological terms, could form functional spandrels before being adapted to the new function of catching mice. In an example taken from his high school experience, Miller recalls that one of his classmates
...struck upon the brilliant idea of using an old, broken mousetrap as a spitball catapult, and it worked brilliantly.... It had worked perfectly as something other than a mousetrap.... my rowdy friend had pulled a couple of parts --probably the hold-down bar and catch-- off the trap to make it easier to conceal and more effective as a catapult... [leaving] the base, the spring, and the hammer. Not much of a mousetrap, but a helluva spitball launcher.... I realized why [Behe's] mousetrap analogy had bothered me. It was wrong. The mousetrap is not irreducibly complex after all.[53]
Other systems identified by Miller that include mousetrap components include the following:[53]
- use the spitball launcher as a tie clip (same three-part system with different function)
- remove the spring from the spitball launcher/tie clip to create a two-part key chain (base + hammer)
- glue the spitball launcher/tie clip to a sheet of wood to create a clipboard (launcher + glue + wood)
- remove the hold-down bar for use as a toothpick (single element system)
The point of the reduction is that - in biology - most or all of the components were already at hand, by the time it became necessary to build a mousetrap. As such, it required far fewer steps to develop a mousetrap than to design all the components from scratch.
Thus, the development of the mousetrap, said to consist of five different parts which had no function on their own, has been reduced to one step: the assembly from parts that are already present, performing other functions.
Consequences
Supporters of intelligent design argue that anything less than the complete form of such a system or organ would not work at all, or would in fact be a detriment to the organism, and would therefore never survive the process of natural selection. Although they accept that some complex systems and organs can be explained by evolution, they claim that organs and biological features which are irreducibly complex cannot be explained by current models, and that an intelligent designer must have created life or guided its evolution. Accordingly, the debate on irreducible complexity concerns two questions: whether irreducible complexity can be found in nature, and what significance it would have if it did exist in nature.[citation needed]
Behe's original examples of irreducibly complex mechanisms included the bacterial flagellum of E. coli, the blood clotting cascade, cilia, and the adaptive immune system.
Behe argues that organs and biological features which are irreducibly complex cannot be wholly explained by current models of evolution. In explicating his definition of "irreducible complexity" he notes that:
An irreducibly complex system cannot be produced directly (that is, by continuously improving the initial function, which continues to work by the same mechanism) by slight, successive modifications of a precursor system, because any precursor to an irreducibly complex system that is missing a part is by definition nonfunctional.
Irreducible complexity is not an argument that evolution does not occur, but rather an argument that it is "incomplete". In the last chapter of Darwin's Black Box, Behe goes on to explain his view that irreducible complexity is evidence for intelligent design. Mainstream critics, however, argue that irreducible complexity, as defined by Behe, can be generated by known evolutionary mechanisms. Behe's claim that no scientific literature adequately modeled the origins of biochemical systems through evolutionary mechanisms has been challenged by TalkOrigins.[54][55] The judge in the Dover trial wrote "By defining irreducible complexity in the way that he has, Professor Behe attempts to exclude the phenomenon of exaptation by definitional fiat, ignoring as he does so abundant evidence which refutes his argument. Notably, the NAS has rejected Professor Behe's claim for irreducible complexity..."[56]
Stated examples
Behe and others have suggested a number of biological features that they believed to be irreducibly complex.
Blood clotting cascade
The process of blood clotting or coagulation cascade in vertebrates is a complex biological pathway which is given as an example of apparent irreducible complexity.[57]
The irreducible complexity argument assumes that the necessary parts of a system have always been necessary, and therefore could not have been added sequentially. However, in evolution, something which is at first merely advantageous can later become necessary.[58] Natural selection can lead to complex biochemical systems being built up from simpler systems, or to existing functional systems being recombined as a new system with a different function.[56] For example, one of the clotting factors that Behe listed as a part of the clotting cascade (Factor XII, also called Hageman factor) was later found to be absent in whales, demonstrating that it is not essential for a clotting system.[59] Many purportedly irreducible structures can be found in other organisms as much simpler systems that utilize fewer parts. These systems, in turn, may have had even simpler precursors that are now extinct. Behe has responded to critics of his clotting cascade arguments by suggesting that homology is evidence for evolution, but not for natural selection.[60]
The "improbability argument" also misrepresents natural selection. It is correct to say that a set of simultaneous mutations that form a complex protein structure is so unlikely as to be unfeasible, but that is not what Darwin advocated. His explanation is based on small accumulated changes that take place without a final goal. Each step must be advantageous in its own right, although biologists may not yet understand the reason behind all of them—for example, jawless fish accomplish blood clotting with just six proteins instead of the full ten.[61]
Eye

(a) A pigment spot
(b) A simple pigment cup
(c) The simple optic cup found in abalone
(d) The complex lensed eye of the marine snail and the octopus
The eye is an example of a supposedly irreducibly complex structure, due to its many elaborate and interlocking parts, seemingly all dependent upon one another. It is frequently cited by intelligent design and creationism advocates as an example of irreducible complexity. Behe used the "development of the eye problem" as evidence for intelligent design in Darwin's Black Box. Although Behe acknowledged that the evolution of the larger anatomical features of the eye have been well-explained, he pointed out that the complexity of the minute biochemical reactions required at a molecular level for light sensitivity still defies explanation. Creationist Jonathan Sarfati has described the eye as evolutionary biologists' "greatest challenge as an example of superb 'irreducible complexity' in God's creation", specifically pointing to the supposed "vast complexity" required for transparency.[62][failed verification]
In an often misquoted[63] passage from On the Origin of Species, Charles Darwin appears to acknowledge the eye's development as a difficulty for his theory. However, the quote in context shows that Darwin actually had a very good understanding of the evolution of the eye (see fallacy of quoting out of context). He notes that "to suppose that the eye ... could have been formed by natural selection, seems, I freely confess, absurd in the highest possible degree". Yet this observation was merely a rhetorical device for Darwin. He goes on to explain that if gradual evolution of the eye could be shown to be possible, "the difficulty of believing that a perfect and complex eye could be formed by natural selection ... can hardly be considered real". He then proceeded to roughly map out a likely course for evolution using examples of gradually more complex eyes of various species.[64]
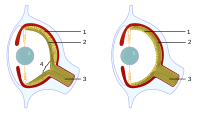
Since Darwin's day, the eye's ancestry has become much better understood. Although learning about the construction of ancient eyes through fossil evidence is problematic due to the soft tissues leaving no imprint or remains, genetic and comparative anatomical evidence has increasingly supported the idea of a common ancestry for all eyes.[65][66][67]
Current evidence does suggest possible evolutionary lineages for the origins of the anatomical features of the eye. One likely chain of development is that the eyes originated as simple patches of photoreceptor cells that could detect the presence or absence of light, but not its direction. When, via random mutation across the population, the photosensitive cells happened to have developed on a small depression, it endowed the organism with a better sense of the light's source. This small change gave the organism an advantage over those without the mutation. This genetic trait would then be "selected for" as those with the trait would have an increased chance of survival, and therefore progeny, over those without the trait. Individuals with deeper depressions would be able to discern changes in light over a wider field than those individuals with shallower depressions. As ever deeper depressions were advantageous to the organism, gradually, this depression would become a pit into which light would strike certain cells depending on its angle. The organism slowly gained increasingly precise visual information. And again, this gradual process continued as individuals having a slightly shrunken aperture of the eye had an advantage over those without the mutation as an aperture increases how collimated the light is at any one specific group of photoreceptors. As this trait developed, the eye became effectively a pinhole camera which allowed the organism to dimly make out shapes—the nautilus is a modern example of an animal with such an eye. Finally, via this same selection process, a protective layer of transparent cells over the aperture was differentiated into a crude lens, and the interior of the eye was filled with humours to assist in focusing images.[68][69][70] In this way, eyes are recognized by modern biologists as actually a relatively unambiguous and simple structure to evolve, and many of the major developments of the eye's evolution are believed to have taken place over only a few million years, during the Cambrian explosion.[71] Behe asserts that this is only an explanation of the gross anatomical steps, however, and not an explanation of the changes in discrete biochemical systems that would have needed to take place.[72]
Behe maintains that the complexity of light sensitivity at the molecular level and the minute biochemical reactions required for those first "simple patches of photoreceptor[s]" still defies explanation, and that the proposed series of infinitesimal steps to get from patches of photoreceptors to a fully functional eye would actually be considered great, complex leaps in evolution if viewed on the molecular scale. Other intelligent design proponents claim that the evolution of the entire visual system would be difficult rather than the eye alone.[73]
Flagella
The flagella of certain bacteria constitute a molecular motor requiring the interaction of about 40 different protein parts. Behe presents this as a prime example of an irreducibly complex structure defined as "a single system composed of several well-matched, interacting parts that contribute to the basic function, wherein the removal of any one of the parts causes the system to effectively cease functioning", and argues that since "an irreducibly complex system that is missing a part is by definition nonfunctional", it could not have evolved gradually through natural selection.[74]
Reducible complexity. In contrast to Behe's claims, many proteins can be deleted or mutated and the flagellum still works, even though sometimes at reduced efficiency.[75] In fact, the composition of flagella is surprisingly diverse across bacteria with many proteins only found in some species but not others.[76] Hence the flagellar apparatus is clearly very flexible in evolutionary terms and perfectly able to lose or gain protein components. Further studies have shown that, contrary to claims of "irreducible complexity", flagella and related protein transport mechanisms show evidence of evolution through Darwinian processes, providing case studies in how complex systems can evolve from simpler components.[77][78] Multiple processes were involved in the evolution of the flagellum, including horizontal gene transfer.[79]
Evolution from type three secretion systems. Scientists regard this argument as having been disproved in the light of research dating back to 1996 as well as more recent findings.[74][80] They point out that the basal body of the flagella has been found to be similar to the Type III secretion system (TTSS), a needle-like structure that pathogenic germs such as Salmonella and Yersinia pestis use to inject toxins into living eucaryote cells. The needle's base has ten elements in common with the flagellum, but it is missing forty of the proteins that make a flagellum work.[81] The TTSS system negates Behe's claim that taking away any one of the flagellum's parts would prevent the system from functioning. On this basis, Kenneth Miller notes that, "The parts of this supposedly irreducibly complex system actually have functions of their own."[82][83] Studies have also shown that similar parts of the flagellum in different bacterial species can have different functions despite showing evidence of common descent, and that certain parts of the flagellum can be removed without completely eliminating its functionality.[84]
Dembski has argued that phylogenetically, the TTSS is found in a narrow range of bacteria which makes it seem to him to be a late innovation, whereas flagella are widespread throughout many bacterial groups, and he argues that it was an early innovation.[85][86] Against Dembski's argument, different flagella use completely different mechanisms, and publications show a plausible path in which bacterial flagella could have evolved from a secretion system.[87]
Cilium motion
The cilium construction of axoneme microtubules movement by the sliding of dynein protein was cited by Behe as an example of irreducible complexity.[88] He further said that the advances in knowledge in the subsequent 10 years had shown that the complexity of intraflagellar transport for two hundred components cilium and many other cellular structures is substantially greater than was known earlier.[89]
Bombardier beetle's defense mechanism
The bombardier beetle is able to defend itself by directing a spray of hot fluid at an attacker. The mechanism involves a system for mixing hydroquinones and hydrogen peroxide, which react violently to attain a temperature near boiling point, and in some species a nozzle which allows the spray to be directed accurately in any direction.[90][91]
The unique combination of features of the bombardier beetle's defense mechanism—strongly exothermic reactions, boiling-hot fluids, and explosive release—have been claimed by creationists and proponents of intelligent design to be examples of irreducible complexity.[92] Biologists such as the taxonomist Mark Isaak note however that step-by-step evolution of the mechanism could readily have occurred. In particular, quinones are precursors to sclerotin, used to harden the skeleton of many insects, while peroxide is a common by-product of metabolism.[93][94][95]
Response of the scientific community
Like intelligent design, the concept it seeks to support, irreducible complexity has failed to gain any notable acceptance within the scientific community.
Reducibility of "irreducible" systems
Researchers have proposed potentially viable evolutionary pathways for allegedly irreducibly complex systems such as blood clotting, the immune system[96] and the flagellum[97][98] - the three examples Behe proposed. John H. McDonald even showed his example of a mousetrap to be reducible.[52] If irreducible complexity is an insurmountable obstacle to evolution, it should not be possible to conceive of such pathways.[99]
Niall Shanks and Karl H. Joplin, both of East Tennessee State University, have shown that systems satisfying Behe's characterization of irreducible biochemical complexity can arise naturally and spontaneously as the result of self-organizing chemical processes.[7] They also assert that what evolved biochemical and molecular systems actually exhibit is "redundant complexity"—a kind of complexity that is the product of an evolved biochemical process. They claim that Behe overestimated the significance of irreducible complexity because of his simple, linear view of biochemical reactions, resulting in his taking snapshots of selective features of biological systems, structures, and processes, while ignoring the redundant complexity of the context in which those features are naturally embedded. They also criticized his over-reliance of overly simplistic metaphors, such as his mousetrap.
A computer model of the co-evolution of proteins binding to DNA in the peer-reviewed journal Nucleic Acids Research consisted of several parts (DNA binders and DNA binding sites) which contribute to the basic function; removal of either one leads immediately to the death of the organism. This model fits the definition of irreducible complexity exactly, yet it evolves.[100] (The program can be run from Ev program.)
In addition, research published in the peer-reviewed journal Nature has shown that computer simulations of evolution demonstrate that it is possible for complex features to evolve naturally.[101]
One can compare a mousetrap with a cat in this context. Both normally function so as to control the mouse population. The cat has many parts that can be removed leaving it still functional; for example, its tail can be bobbed, or it can lose an ear in a fight. Comparing the cat and the mousetrap, then, one sees that the mousetrap (which is not alive) offers better evidence, in terms of irreducible complexity, for intelligent design than the cat. Even looking at the mousetrap analogy, several critics have described ways in which the parts of the mousetrap could have independent uses or could develop in stages, demonstrating that it is not irreducibly complex.[52][53]
Moreover, even cases where removing a certain component in an organic system will cause the system to fail do not demonstrate that the system could not have been formed in a step-by-step, evolutionary process. By analogy, stone arches are irreducibly complex—if you remove any stone the arch will collapse—yet humans build them easily enough, one stone at a time, by building over centering that is removed afterward. Similarly, naturally occurring arches of stone form by the weathering away of bits of stone from a large concretion that has formed previously.
Evolution can act to simplify as well as to complicate. This raises the possibility that seemingly irreducibly complex biological features may have been achieved with a period of increasing complexity, followed by a period of simplification.
A team led by Joseph Thornton, assistant professor of biology at the University of Oregon's Center for Ecology and Evolutionary Biology, using techniques for resurrecting ancient genes, reconstructed the evolution of an apparently irreducibly complex molecular system. The April 7, 2006 issue of Science published this research.[6][102]
Irreducible complexity may not actually exist in nature, and the examples given by Behe and others may not in fact represent irreducible complexity, but can be explained in terms of simpler precursors. The theory of facilitated variation challenges irreducible complexity. Marc W. Kirschner, a professor and chair of Department of Systems Biology at Harvard Medical School, and John C. Gerhart, a professor in Molecular and Cell Biology, University of California, Berkeley, presented this theory in 2005. They describe how certain mutation and changes can cause apparent irreducible complexity. Thus, seemingly irreducibly complex structures are merely "very complex", or they are simply misunderstood or misrepresented.
Gradual adaptation to new functions
The precursors of complex systems, when they are not useful in themselves, may be useful to perform other, unrelated functions. Evolutionary biologists argue that evolution often works in this kind of blind, haphazard manner in which the function of an early form is not necessarily the same as the function of the later form. The term used for this process is exaptation. The mammalian middle ear (derived from a jawbone) and the panda's thumb (derived from a wrist bone spur) provide classic examples. A 2006 article in Nature demonstrates intermediate states leading toward the development of the ear in a Devonian fish (about 360 million years ago).[103] Furthermore, recent research shows that viruses play a heretofore unexpected role in evolution by mixing and matching genes from various hosts.[104]
Arguments for irreducibility often assume that things started out the same way they ended up—as we see them now. However, that may not necessarily be the case. In the Dover trial an expert witness for the plaintiffs, Ken Miller, demonstrated this possibility using Behe's mousetrap analogy. By removing several parts, Miller made the object unusable as a mousetrap, but he pointed out that it was now a perfectly functional, if unstylish, tie clip.[53][105]
Methods by which irreducible complexity may evolve
Irreducible complexity can be seen as equivalent to an "uncrossable valley" in a fitness landscape.[106] A number of mathematical models of evolution have explored the circumstances under which such valleys can, nevertheless, be crossed.[107][108][106][109]
Falsifiability and experimental evidence
Some critics, such as Jerry Coyne (professor of evolutionary biology at the University of Chicago) and Eugenie Scott (a physical anthropologist and former executive director of the National Center for Science Education) have argued that the concept of irreducible complexity and, more generally, intelligent design is not falsifiable and, therefore, not scientific.
Behe argues that the theory that irreducibly complex systems could not have evolved can be falsified by an experiment where such systems are evolved. For example, he posits taking bacteria with no flagellum and imposing a selective pressure for mobility. If, after a few thousand generations, the bacteria evolved the bacterial flagellum, then Behe believes that this would refute his theory.[110][non-primary source needed]
Other critics take a different approach, pointing to experimental evidence that they consider falsification of the argument for intelligent design from irreducible complexity. For example, Kenneth Miller describes the lab work of Barry G. Hall on E. coli as showing that "Behe is wrong".[111]
Other evidence that irreducible complexity is not a problem for evolution comes from the field of computer science, which routinely uses computer analogues of the processes of evolution in order to automatically design complex solutions to problems. The results of such genetic algorithms are frequently irreducibly complex since the process, like evolution, both removes non-essential components over time as well as adding new components. The removal of unused components with no essential function, like the natural process where rock underneath a natural arch is removed, can produce irreducibly complex structures without requiring the intervention of a designer. Researchers applying these algorithms automatically produce human-competitive designs—but no human designer is required.[112]
Argument from ignorance
Intelligent design proponents attribute to an intelligent designer those biological structures they believe are irreducibly complex and therefore they say a natural explanation is insufficient to account for them.[113] However, critics view irreducible complexity as a special case of the "complexity indicates design" claim, and thus see it as an argument from ignorance and as a God-of-the-gaps argument.[114]
Eugenie Scott and Glenn Branch of the National Center for Science Education note that intelligent design arguments from irreducible complexity rest on the false assumption that a lack of knowledge of a natural explanation allows intelligent design proponents to assume an intelligent cause, when the proper response of scientists would be to say that we don't know, and further investigation is needed.[115] Other critics describe Behe as saying that evolutionary explanations are not detailed enough to meet his standards, while at the same time presenting intelligent design as exempt from having to provide any positive evidence at all.[116][117]
False dilemma
Irreducible complexity is at its core an argument against evolution. If truly irreducible systems are found, the argument goes, then intelligent design must be the correct explanation for their existence. However, this conclusion is based on the assumption that current evolutionary theory and intelligent design are the only two valid models to explain life, a false dilemma.[118][119]
In the Dover trial
While testifying during the 2005 Kitzmiller v. Dover Area School District trial, Behe conceded that there are no peer-reviewed papers supporting his claims that complex molecular systems, like the bacterial flagellum, the blood-clotting cascade, and the immune system, were intelligently designed nor are there any peer-reviewed articles supporting his argument that certain complex molecular structures are "irreducibly complex."[120]
In the final ruling of Kitzmiller v. Dover Area School District, Judge Jones specifically singled out Behe and irreducible complexity:[120]
- "Professor Behe admitted in "Reply to My Critics" that there was a defect in his view of irreducible complexity because, while it purports to be a challenge to natural selection, it does not actually address "the task facing natural selection." and that "Professor Behe wrote that he hoped to "repair this defect in future work..." (Page 73)
- "As expert testimony revealed, the qualification on what is meant by "irreducible complexity" renders it meaningless as a criticism of evolution. (3:40 (Miller)). In fact, the theory of evolution proffers exaptation as a well-recognized, well-documented explanation for how systems with multiple parts could have evolved through natural means." (Page 74)
- "By defining irreducible complexity in the way that he has, Professor Behe attempts to exclude the phenomenon of exaptation by definitional fiat, ignoring as he does so abundant evidence which refutes his argument. Notably, the NAS has rejected Professor Behe's claim for irreducible complexity..." (Page 75)
- "As irreducible complexity is only a negative argument against evolution, it is refutable and accordingly testable, unlike ID [Intelligent Design], by showing that there are intermediate structures with selectable functions that could have evolved into the allegedly irreducibly complex systems. (2:15–16 (Miller)). Importantly, however, the fact that the negative argument of irreducible complexity is testable does not make testable the argument for ID. (2:15 (Miller); 5:39 (Pennock)). Professor Behe has applied the concept of irreducible complexity to only a few select systems: (1) the bacterial flagellum; (2) the blood-clotting cascade; and (3) the immune system. Contrary to Professor Behe's assertions with respect to these few biochemical systems among the myriad existing in nature, however, Dr. Miller presented evidence, based upon peer-reviewed studies, that they are not in fact irreducibly complex." (Page 76)
- "...on cross-examination, Professor Behe was questioned concerning his 1996 claim that science would never find an evolutionary explanation for the immune system. He was presented with fifty-eight peer-reviewed publications, nine books, and several immunology textbook chapters about the evolution of the immune system; however, he simply insisted that this was still not sufficient evidence of evolution, and that it was not "good enough." (23:19 (Behe))." (Page 78)
- "We therefore find that Professor Behe's claim for irreducible complexity has been refuted in peer-reviewed research papers and has been rejected by the scientific community at large. (17:45–46 (Padian); 3:99 (Miller)). Additionally, even if irreducible complexity had not been rejected, it still does not support ID as it is merely a test for evolution, not design. (2:15, 2:35–40 (Miller); 28:63–66 (Fuller)). We will now consider the purportedly "positive argument" for design encompassed in the phrase used numerous times by Professors Behe and Minnich throughout their expert testimony, which is the "purposeful arrangement of parts." Professor Behe summarized the argument as follows: We infer design when we see parts that appear to be arranged for a purpose. The strength of the inference is quantitative; the more parts that are arranged, the more intricately they interact, the stronger is our confidence in design. The appearance of design in aspects of biology is overwhelming. Since nothing other than an intelligent cause has been demonstrated to be able to yield such a strong appearance of design, Darwinian claims notwithstanding, the conclusion that the design seen in life is real design is rationally justified. (18:90–91, 18:109–10 (Behe); 37:50 (Minnich)). As previously indicated, this argument is merely a restatement of the Reverend William Paley's argument applied at the cell level. Minnich, Behe, and Paley reach the same conclusion, that complex organisms must have been designed using the same reasoning, except that Professors Behe and Minnich refuse to identify the designer, whereas Paley inferred from the presence of design that it was God. (1:6–7 (Miller); 38:44, 57 (Minnich)). Expert testimony revealed that this inductive argument is not scientific and as admitted by Professor Behe, can never be ruled out. (2:40 (Miller); 22:101 (Behe); 3:99 (Miller))." (Pages 79–80)
Notes and references
- ^ a b "We therefore find that Professor Behe's claim for irreducible complexity has been refuted in peer-reviewed research papers and has been rejected by the scientific community at large." Ruling, Judge John E. Jones III, Kitzmiller v. Dover Area School District
- ^ "True in this latest creationist variant, advocates of so-called intelligent design ... use more slick, pseudoscientific language. They talk about things like "irreducible complexity" Shulman, Seth (2006). Undermining science: suppression and distortion in the Bush Administration. Berkeley: University of California Press. p. 13. ISBN 978-0-520-24702-4. "for most members of the mainstream scientific community, ID is not a scientific theory, but a creationist pseudoscience."
Mu, David (Fall 2005). "Trojan Horse or Legitimate Science: Deconstructing the Debate over Intelligent Design" (PDF). Harvard Science Review. 19 (1). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2007-07-24.
Perakh, M (Summer 2005). "Why Intelligent Design Isn't Intelligent — Review of: Unintelligent Design". Cell Biol. Educ. 4 (2): 121–2. doi:10.1187/cbe.05-02-0071. PMC 1103713.
Mark D. Decker. College of Biological Sciences, General Biology Program, University of Minnesota Frequently Asked Questions About the Texas Science Textbook Adoption Controversy Archived 2010-09-30 at the Wayback Machine "The Discovery Institute and ID proponents have a number of goals that they hope to achieve using disingenuous and mendacious methods of marketing, publicity, and political persuasion. They do not practice real science because that takes too long, but mainly because this method requires that one have actual evidence and logical reasons for one's conclusions, and the ID proponents just don't have those. If they had such resources, they would use them, and not the disreputable methods they actually use."
See also list of scientific societies explicitly rejecting intelligent design - ^ Than, Ker (September 23, 2005). "Why scientists dismiss 'intelligent design' - LiveScience". NBC News. Retrieved 2010-05-17.
- ^ a b c Scott EC, Matzke NJ (May 2007). "Biological design in science classrooms". Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104 (suppl_1): 8669–76, See page 8672. Bibcode:2007PNAS..104.8669S. doi:10.1073/pnas.0701505104. PMC 1876445. PMID 17494747.
- ^ Behe, Michael J. (1996). Darwin's Black Box: The Biochemical Challenge to Evolution (10th Anniversary ed.). Simon and Schuster (published 2001). ISBN 9780743214858. Retrieved 24 Mar 2019.
- ^ a b Bridgham JT, Carroll SM, Thornton JW (April 2006). "Evolution of hormone-receptor complexity by molecular exploitation". Science. 312 (5770): 97–101. Bibcode:2006Sci...312...97B. doi:10.1126/science.1123348. PMID 16601189.
- ^ a b Shanks, Niall; Joplin, Karl H. (1999). "Redundant Complexity: A Critical Analysis of Intelligent Design in Biochemistry". Philosophy of Science. 66 (2, June): 268–282. doi:10.1086/392687. JSTOR 188646.
- ^ Finnigan, Gregory C.; Hanson-Smith, Victor; Stevens, Tom H.; Thornton, Joseph W. (2012). "Evolution of increased complexity in a molecular machine". Nature. 481 (7381): 360–364. Bibcode:2012Natur.481..360F. doi:10.1038/nature10724. PMC 3979732. PMID 22230956.
- ^
Del Bem, Luiz Eduardo V.; Vincentz, Michel GA (5 November 2010). "Evolution of xyloglucan-related genes in green plants". BMC Evolutionary Biology. 10: 341. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-10-341. PMC 3087550. PMID 21054875.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Darwin's Black Box page 39 in the 2006 edition
- ^ In Defense of the Irreducibility of the Blood Clotting Cascade: Response to Russell Doolittle, Ken Miller and Keith Robison, July 31, 2000, Discovery Institute article Archived 2015-09-06 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ No Free Lunch: Why Specified Complexity Cannot Be Purchased without Intelligence. by William Dembski pp. 285
- ^ a b William Paley:Natural Theology; or, Evidences of the Existence and Attributes of the Deity. Collected from the Appearances of Nature 12th edition, 1809 Archived 2008-04-30 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ On the Nature of the Gods, translated by Francis Brooks, London: Methuen, 1896.
- ^ See Henry Hallam Introduction to the Literature of Europe in the Fifteenth, Sixteenth, and Seventeenth Centuries Boston: Little, Brown and Company, 1854 volume 2 page 385 part iii chapter iii section i paragraph 26 footnote u
- ^ De Formatione Foetus=The Construction of the Embryo, chapter 11 in Galen: Selected Works, translated by P. N. Singer, The World's Classics, Oxford, Oxford University Press, 1997 ISBN 978-0-19-282450-9. One 18th-century reference to Galen is David Hume Dialogues Concerning Natural Religion, 1779, Part 12 Archived 2005-11-22 at the Wayback Machine, § 3, page 215. Also see Galen's De Usu Partium=On the Usefulness of the Parts of the Body, translated and edited by Margaret Tallmadge May, Ithaca, New York, Cornell University Press, 1968, especially book XVII. For a relevant discussion of Galen and other ancients see pages 121-122, Goodman, Lenn Evan (2010). Creation and evolution. Milton Park, Abingdon, Oxon and New York: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-91380-5.
- ^ De Generatione Animalium, chapter III. Partial translation in: Howard B. Adelmann, Marcello Malpighi and the Evolution of Embryology Ithaca, New York, Cornell University Press, 1966, volume 2, pages 811-812.
- ^ John Wilkins,Of the Principles and Duties of Natural Religion, London, 1675, book I, chapter 6, page 82 Early English Books Online
- ^ "The appeal to irreducible complexity goes back more than three centuries. To quote John Wilkins ...", Paul Braterman "Darwin Does Devolve. Sometimes. So What?" 3 Quarks Daily February 25, 2019
- ^ The Sacred Theory of the Earth Archived 2007-10-20 at the Wayback Machine, 2nd edition, London: Walter Kettilby, 1691. Book I Chapter IV page 43
- ^ Malebranche, Nicolas (1712). De la recherche de la verité: où l'on traite de la nature de l'esprit de l'homme, & de l'usage qu'il en doit faire pour éviter l'erreur dans les sciences (6ième ed.). Paris: Chez Michel David. Livre 6ième, 2ième partie, chapître 4; English translation: Malebranche, Nicholas (1997). Thomas M. Lennon; Paul J. Olscamp (eds.). The Search After Truth: With Elucidations of The Search After Truth. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 465. ISBN 978-0-521-58004-5. Second paragraph from the end of the chapter, on page 465.
- ^ Pages 202-204 of Pyle, Andrew (2006). "Malebranche on Animal Generation: Preexistence and the Microscope". In Smith JH (ed.). The problem of animal generation in early modern philosophy. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. pp. 194–214. ISBN 978-0-521-84077-4.
- ^ "The Chicken or the Egg". talkreason.org. Archived from the original on 29 April 2017. Retrieved 7 May 2018.
- ^ This is Guyer's exposition on page 22 of Guyer, Paul (1992). "Introduction". In Paul Guyer (ed.). The Cambridge Companion to Kant. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 1–25. ISBN 978-0-521-36768-4. Guyer adds this parenthetical comment: "(here is where the theory of natural selection removes the difficulty)". See Kant's discussion in section IX of the "First Introduction" to the Critique of Judgment and in §§61, 64 (where he uses the expression wechselsweise abhängt="reciprocally dependent"), and §66 of "Part Two, First Division". For example, Kant, Immanuel (2000). "§64". In Paul Guyer; Eric Matthews (eds.). Critique of the power of judgment. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 243–244. ISBN 978-0-521-34447-0. German original Kritik der Urtheilskraft. Kants gesammelte Schriften. Vol. 5 (Königlich Preußischen Akademie der Wissenschaften ed.). Berlin: Georg Reimer. 1913. p. 371. ISBN 978-3-11-001438-9.
- ^ See also Kant, Imanuel (1993). Eckart Förster (ed.). Opus Postumum. Translated by Eckart Förster; Michael Rosen. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 64. ISBN 0-521-31928-5.
The definition of an organic body is that it is a body, every part of which is there for the sake of the other (reciprocally as end and, at the same time, means).
German original Kritik der Urtheilskraft. Kants gesammelte Schriften. Vol. 21 (Königlich Preußischen Akademie der Wissenschaften ed.). Berlin: Georg Reimer. February 1971. p. 210. ISBN 978-3-11-090167-2. - ^ See especially chapters VI and VII of Coleman, William (1964). Georges Cuvier, Zoologist: A Study in the History of Evolution Theory. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press. See also the discussion of these principles in the Wikipedia article on Cuvier.
- ^ Darwin, Charles (1859). On the Origin of Species. London: John Murray. page 189, Chapter VI Archived 2007-09-30 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ See for example, Rogers, Alan R. (2011). The Evidence for Evolution. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. ISBN 978-0-226-72382-2. in pages 37–38, 48–49 citing Joseph John Murphy accepting natural selection within limits, excepting "the eye" with its multiple parts. Murphy, Joseph John (November 19, 1866). "Presidential Address to the Belfast Natural History and Philosophical Society". Northern Whig. Belfast. Archived from the original on July 18, 2012. and in page 48 citing Pritchard, C. "Appendix Note A On the Origin of Species by Natural Selection". The Continuity of the Schemes of Nature and Revelation: A Sermon Preached, by request, on the occasion of the meeting of the British Association at Nottingham. With remarks on some relations of modern knowledge to theology. London: Bell and Daldy. pp. 31–37., especially page 33
- ^ Page 594 in: Spencer, Herbert (October 1894). "Weismannism Once More". The Contemporary Review. 66: 592–608. Another essay of Spencer's treating this concept is: Spencer, Herbert (1893). "The Inadequacy of "Natural Selection"". The Contemporary Review. 63: 153–166. (Part I: February) and pages 439-456 (Part II: March). These essays were reprinted in Spencer, Herbert (1891). The Works of Herbert Spencer. Vol. 17. London: Williams and Norgate. (also Osnabrück: Otto Zeller, 1967). See also part III, Chapter XII, §166, pages 449-457 in: Spencer, Herbert (1864). Principles of Biology. Vol. I. London: Williams and Norgate. And: Spencer, Herbert (1886). "The Factors of Organic Evolution". The Nineteenth Century. 19: 570–589. (Part I: April) and pages 749-770 (Part II: May). "Factors" was reprinted in pages 389-466 of Spencer, Herbert (1891). The Works of Herbert Spencer. Vol. 13. London: Williams and Norgate. (also Osnabrück: Otto Zeller, 1967)= volume 1 of Essays: Scientific, Political, and Speculative.
- ^ One example of a response was in Section III(γ) pages 32-42 of Weismann, August (1909). "The Selection theory". In Albert Charles Seward (ed.). Darwin and Modern Science: Essays in Commemoration of the Centenary of the Birth of Charles Darwin and of the Fiftieth Anniversary of the Publication of The Origin of Species. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 19–65. See also Chapter VII, §12(1), pages 237-238 in: Thomson, J. Arthur (1908). Heredity. London: John Murray. Both of these referred to what has become known as the Baldwin effect. An analysis of both sides of the issue is: Romanes, George John (1895). "III: Characters as Hereditary and Acquired (continued)". Darwin and After Darwin: Post-Darwinian Questions, Heredity, Utility. Vol. II. London: Longman, Green. pp. 60–102.
- ^ Darwin, Charles (1868). "XXV. Laws of Variation continued - Correlated Variability". The Variation of Animals and Plants under Domestication. Vol. 2. London: John Murray. pp. 321–338. Archived from the original on 2015-09-25. especially page 333 and following.
- ^ Pages 67-68 in: Ridley, Mark (March 1982). "Coadapatation and the Inadequacy of Natural Selection". British Journal for the History of Science. 15 (1): 45–68. doi:10.1017/S0007087400018938.
- ^ Mivart, St. George Jackson (1871). On the Genesis of Species. London: Macmillan. p. 52.
- ^ Asher, Robert J. (2012). Evolution and belief: confessions of a religious paleontologist. Cambridge & New York: Cambridge University Press. p. 214. ISBN 9780521193832. See also Irreducible Complexity Archived 2011-10-18 at the Wayback Machine and the references cited there.
- ^ Muller, HJ (1918). "Genetic variability, twin hybrids and constant hybrids, in a case of balanced lethal factors". Genetics. 3 (5): 422–99. PMC 1200446. PMID 17245914. Archived from the original on 2007-05-18., especially pages 463–4.
- ^ Muller, HJ (1939). "Reversibility in evolution considered from the standpoint of genetics". Biological Reviews of the Cambridge Philosophical Society. 14 (3): 261–80, quotation from 272. doi:10.1111/j.1469-185x.1939.tb00934.x.
- ^ Morris, Henry (1974). Scientific creationism (2nd ed.). San Diego, Calif: Creation-Life Publishers. p. 59. ISBN 978-0-89051-003-2.
- ^ T. H. Frazzetta, Complex Adaptations in Evolving Populations, Sunderland, Massachusetts: Sinauer Associates, 1975. ISBN 0-87893-194-5. Referencing pages 3, 4-7, 7-20, and xi, respectively.
- ^ Keough, Mark J.; Geisler, Norman L. (1982). The Creator in the courtroom "Scopes II": the 1981 Arkansas creation-evolution trial. Milford, Mich: Mott Media. p. 146. ISBN 978-0-88062-020-8.
- ^ Cairns-Smith, A. G. (1985). Seven clues to the origin of life: a scientific detective story. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. pp. 39, 58–64. ISBN 978-0-521-27522-4.
- ^ McShea, Daniel W. and Wim Hordijk. "Complexity by Subtraction." Evolutionary Biology (April 2013). PDF Archived 2013-05-13 at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ Perakh, Mark (2008). "Bacteria Flagella Look Like Man-made Machines". 14 (3). Skeptic (U.S. magazine). Archived from the original on 2008-12-08. Retrieved 2008-12-06.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Lumsden, RD (June 1994). "Not So Blind A Watchmaker". Creation Research Society Quarterly. 31 (1): 13–22, quotations from 13, 20.
- ^ Ludwig von Bertalanffy (1952). Problems of Life: An Evaluation of Modern Biological and Scientific Thought, pg 148 ISBN 1-131-79242-4
- ^ Monod, Jacques (1972). Chance and necessity: an essay on the natural philosophy of modern biology. New York: Vintage Books. ISBN 978-0-394-71825-5.
- ^ Barbara Forrest, The Wedge at Work Archived 2014-09-05 at the Wayback Machine. Talk Reason.
Forrest, B (2001). "1: The Wedge at Work: How Intelligent Design Creationism is Wedging its way into the Cultural and Academic Mainstream". In Pennock, RT (ed.). Intelligent design creationism and its critics: philosophical, theological, and scientific perspectives. Cambridge, Mass: MIT Press. pp. 5–54. ISBN 978-0-262-66124-9. - ^ The New Pandas: Has Creationist Scholarship Improved? Comments on 1993 Revisions by Frank J. Sonleitner (1994)
Introduction: Of Pandas and People, the foundational work of the 'Intelligent Design' movement Archived 2008-12-29 at the Wayback Machine by Nick Matzke 2004,
Design on Trial in Dover, Pennsylvania Archived 2008-12-29 at the Wayback Machine by Nicholas J Matzke, NCSE Public Information Project Specialist - ^ Behe, MJ (November 2001). "Reply to My Critics: A Response to Reviews of Darwin's Black Box: The Biochemical Challenge to Evolution" (PDF). Biology and Philosophy. 16 (5): 685–709. doi:10.1023/A:1012268700496. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-07-11.
- ^ Behe's testimony in Kitzmiller v. Dover Archived 2006-06-29 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Behe, Michael 2005 Kitzmiller v. Dover Area School District 4: whether ID is science (p. 88)
- ^ Kitzmiller v. Dover Area School District 6: Conclusion, section H
- ^ a b c A reducibly complex mousetrap Archived 2014-02-22 at the Wayback Machine (graphics-intensive, requires JavaScript)
- ^ a b c d e Miller, Kenneth R. (2008). Only A Theory. New York: Viking Penguin. pp. 54–55. ISBN 978-0-670-01883-3.
- ^ Claim CA350: Professional literature is silent on the subject of the evolution of biochemical systems Archived 2007-03-04 at the Wayback Machine TalkOrigins Archive.
- ^ Behe, Michael J. (1996) [1996]. Darwin's black box: the biochemical challenge to evolution. New York, NY: Free Press. p. 72. ISBN 978-0-684-82754-4.
Yet here again the evolutionary literature is totally missing. No scientist has ever published a model to account for the gradual evolution of this extraordinary molecular machine.
- ^ a b Ruling, Kitzmiller v. Dover Area School District, December 2005. Page 74.
- ^ Action, George "Behe and the Blood Clotting Cascade" Archived 2005-06-05 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Boudry, Maarten; Blancke, Stefaan; Braeckman, Johan (September 2010). "Irreducible Incoherence and Intelligent Design: A Look into the Conceptual Toolbox of a Pseudoscience". Quarterly Review of Biology. 85 (3): 473–82. doi:10.1086/656904. hdl:1854/LU-952482. PMID 21243965. Archived from the original on 2010-11-30.
- ^ Semba U, Shibuya Y, Okabe H, Yamamoto T (1998). "Whale Hageman factor (factor XII): prevented production due to pseudogene conversion". Thromb Res. 90 (1): 31–7. doi:10.1016/S0049-3848(97)00307-1. PMID 9678675.
- ^ Behe, Michael "In Defense of the Irreducibility of the Blood Clotting Cascade: Response to Russell Doolittle, Ken Miller and Keith Robison" Archived 2010-09-17 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Creationism special: A sceptic's guide to intelligent design Archived 2015-05-06 at the Wayback Machine, New Scientist, 9 July 2005
- ^ Sarfati, Jonathan (2000). Argument: 'Irreducible complexity' Archived 2005-11-23 at the Wayback Machine, from Refuting Evolution (Answers in Genesis).
- ^ Isaak, Mark. "CA113.1: Evolution of the eye". www.talkorigins.org. Archived from the original on 3 October 2017. Retrieved 7 May 2018.
- ^ Darwin, Charles (1859). On the Origin of Species. London: John Murray. pages 186ff, Chapter VI Archived 2007-09-27 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Halder G, Callaerts P, Gehring WJ (October 1995). "New perspectives on eye evolution". Current Opinion in Genetics & Development. 5 (5): 602–9. doi:10.1016/0959-437X(95)80029-8. PMID 8664548.
- ^ Halder G, Callaerts P, Gehring WJ (March 1995). "Induction of ectopic eyes by targeted expression of the eyeless gene in Drosophila". Science. 267 (5205): 1788–92. Bibcode:1995Sci...267.1788H. doi:10.1126/science.7892602. PMID 7892602.
- ^ Tomarev SI, Callaerts P, Kos L, et al. (March 1997). "Squid Pax-6 and eye development". Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 94 (6): 2421–6. Bibcode:1997PNAS...94.2421T. doi:10.1073/pnas.94.6.2421. PMC 20103. PMID 9122210.
- ^ Fernald, Russell D. (2001). The Evolution of Eyes: Why Do We See What We See? Archived 2006-03-19 at the Wayback Machine Karger Gazette 64: "The Eye in Focus".
- ^ Fernald, RD (1988). "Aquatic Adaptations in Fish Eyes". In Atema, J (ed.). Sensory biology of aquatic animals. Berlin: Springer-Verlag. ISBN 978-0-387-96373-0.
- ^ Fernald, RD (1997). "The evolution of eyes". Brain Behav. Evol. 50 (4): 253–9. doi:10.1159/000113339. PMID 9310200.
- ^ Conway-Morris, S (1999). The Crucible of Creation: The Burgess Shale and the Rise of Animals. Oxford [Oxfordshire]: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-286202-0.
- ^ Behe, Michael (2006). Darwin's Black Box. Free Press. p. 38. ISBN 978-0-7432-9031-9.
- ^ Wiker, Benjamin; Witt, Jonathan (2006). A Meaningful World. p. 44.
- ^ a b Miller, Kenneth R. The Flagellum Unspun: The Collapse of "Irreducible Complexity" Archived 2014-02-14 at the Wayback Machine with reply here "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2006-04-03. Retrieved 2006-04-26.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ Rajagopala SV, Titz B, Goll J, Parrish JR, Wohlbold K, McKevitt MT, Palzkill T, Mori H, Finley RL Jr, Uetz P (2007). "The protein network of bacterial motility". Mol Syst Biol. 3: 128. doi:10.1038/msb4100166. PMC 1943423. PMID 17667950.
- ^ Titz B, Rajagopala SV, Ester C, Häuser R, Uetz P (Nov 2006). "Novel conserved assembly factor of the bacterial flagellum". J Bacteriol. 188 (21): 7700–6. doi:10.1128/JB.00820-06. PMC 1636259. PMID 16936039.
- ^ Pallen, M. J.; Gophna, U. (2007). Bacterial Flagella and Type III Secretion: Case Studies in the Evolution of Complexity. Genome Dynamics. Vol. 3. pp. 30–47. doi:10.1159/000107602. ISBN 978-3-8055-8340-4. PMID 18753783.
{{cite book}}:|journal=ignored (help) - ^ Clements, A.; Bursac, D.; Gatsos, X.; Perry, A.; Civciristov, S.; Celik, N.; Likic, V.; Poggio, S.; Jacobs-Wagner, C.; Strugnell, R. A.; Lithgow, T. (2009). "The reducible complexity of a mitochondrial molecular machine". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 106 (37): 15791–15795. Bibcode:2009PNAS..10615791C. doi:10.1073/pnas.0908264106. PMC 2747197. PMID 19717453.
- ^ Zuckerkandl, Emile (December 2006). "Intelligent design and biological complexity". Gene. 385: 2–18. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2006.03.025. PMID 17011142.
- ^ Pallen, M.J.; Matzke, N.J. (2006). "From The Origin of Species to the origin of bacterial flagella". Nature Reviews Microbiology. 4 (10): 784–790. doi:10.1038/nrmicro1493. PMID 16953248.
- ^ Kenneth Miller's The Collapse of Intelligent Design: Section 5 Bacterial Flagellum Archived 2016-10-17 at the Wayback Machine (Case Western Reserve University, 2006 January 3)
- ^ Unlocking cell secrets bolsters evolutionists (Chicago Tribune, 2006 February 13)
- ^ Evolution in (Brownian) space: a model for the origin of the bacterial flagellum Archived 2016-09-19 at the Wayback Machine (Talk Design, 2006 September)
- ^ Egelman, E. H. (1 January 2013). Intelligent Design A2 - Maloy, Stanley. Academic Press. pp. 112–114. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-374984-0.00806-8. ISBN 9780080961569.
{{cite book}}:|journal=ignored (help) - ^ "Spinning Tales About the Bacterial Flagellum - Evolution News". evolutionnews.org. 21 January 2010. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 7 May 2018.
- ^ Dembski, Rebuttal to Reports by Opposing Expert Witnesses, p. 52
- ^ Isaak, Mark (2006). "CB200.1: Bacterial flagella and Irreducibly Complexity". TalkOrigins Archive. Archived from the original on 4 July 2013. Retrieved 25 June 2013.
- ^ page 90: "Just as a mousetrap does not work unless all of its constituent parts are present, ciliary motion simply does not exist in the absence of microtubules, connectors, and motors. Therefore we can conclude that the cilium is irreducibly complex - an enormous monkey wrench thrown into its presumed gradual, Darwinian evolution."Behe, Michael (1999). Signs of Intelligence, article Darwin's Breakdown: Irreducible Complexity and Design at the Foundation of Life. Brazos Press. ISBN 978-1587430046.
- ^ pg 95 Behe, Michael (2007). The Edge of Evolution. FreePress division of Simon & Schuster. ISBN 978-0743296229.
- ^ Aneshansley, D. J.; et al. (1969). "Biochemistry at 100 C: Explosive Secretory Discharge of Bombardier Beetles (Brachinus)". Science Magazine. 165 (3888): 61–3. doi:10.1126/science.165.3888.61. PMID 17840686.
- ^ Eisner, T.; Aneshansley, D. J. (August 1999). "Spray aiming in the bombardier beetle: Photographic Evidence". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 96 (17): 9705–9. Bibcode:1999PNAS...96.9705E. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.17.9705. PMC 22274. PMID 10449758.
- ^ Rice, Stanley A. (2007). Encyclopedia of Evolution. Infobase Publishing. p. 214. ISBN 978-0-8160-5515-9.
- ^ Isaak, Mark (30 May 2003) [1997]. "Bombardier Beetles and the Argument of Design". TalkOrigins. Retrieved 3 August 2018.
- ^ GrrlScientist (17 January 2011). "Irreducible complexity cut down to size". The Guardian.
This video specifically focuses on debunking the so-called "irreducible complexity" of the favourite examples used by creationists; the eye, the bombardier beetle, the venus flytrap and bacterial flagella.
- ^ Brunet, P. C. J.; Kent, P. W. (1955). "Mechanism of sclerotin formation: The participation of a beta-glucoside". Nature. 175 (4462): 819–820. Bibcode:1955Natur.175..819B. doi:10.1038/175819a0. PMID 14370229.
- ^ Matt Inlay, 2002. "Evolving Immunity Archived 2006-01-11 at the Wayback Machine." In TalkDesign.org.
- ^ Nicholas J. Matzke, 2003. "Evolution in (Brownian) space: a model for the origin of the bacterial flagellum Archived 2005-12-20 at the Wayback Machine."
- ^ Pallen MJ, Matzke NJ (October 2006). "From The Origin of Species to the origin of bacterial flagella". Nature Reviews Microbiology. 4 (10): 784–90. doi:10.1038/nrmicro1493. PMID 16953248. Archived from the original on 2006-09-27.
- ^ Pigliucci, Massimo "Secular Web Kiosk: Design Yes, Intelligent No: A Critique of Intelligent Design Theory and Neo-Creationism". Archived from the original on 2010-01-05. Retrieved 2009-12-26. Collaboration Sept. 2001
- ^ Schneider, TD (2000). "Evolution of Biological Information". Nucleic Acids Research. 28 (14): 2794–2799. doi:10.1093/nar/28.14.2794. PMC 102656. PMID 10908337.
- ^ Lenski RE, Ofria C, Pennock RT, Adami C (2003). "The evolutionary origin of complex features" (PDF). Nature. 423 (6936): 139–44. Bibcode:2003Natur.423..139L. doi:10.1038/nature01568. PMID 12736677.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Press release Archived 2007-09-30 at the Wayback Machine University of Oregon, April 4, 2006.
- ^ M. Brazeau; P. Ahlberg (January 19, 2006). "Tetrapod-like middle ear architecture in a Devonian fish". Nature. 439 (7074): 318–21. Bibcode:2006Natur.439..318B. doi:10.1038/nature04196. PMID 16421569.
- ^ Boto, Luis (October 28, 2009). "Horizontal gene transfer in evolution: facts and challenges". Proceedings of the Royal Society B. 277 (1683): 819–827. doi:10.1098/rspb.2009.1679. PMC 2842723. PMID 19864285.
- ^ "NOVA: Transcripts: Judgment Day: Intelligent Design on Trial Chapter 8". PBS. November 13, 2007. Archived from the original on November 23, 2008. Retrieved 2008-12-17.
- ^ a b Trotter, Meredith V.; Weissman, Daniel B.; Peterson, Grant I.; Peck, Kayla M.; Masel, Joanna (December 2014). "Cryptic genetic variation can make "irreducible complexity" a common mode of adaptation in sexual populations". Evolution. 68 (12): 3357–3367. doi:10.1111/evo.12517. PMC 4258170. PMID 25178652.
- ^ Weissman, Daniel B.; Desai, Michael M.; Fisher, Daniel S.; Feldman, Marcus W. (June 2009). "The rate at which asexual populations cross fitness valleys". Theoretical Population Biology. 75 (4): 286–300. doi:10.1016/j.tpb.2009.02.006. PMC 2992471. PMID 19285994.
- ^ Weissman, D. B.; Feldman, M. W.; Fisher, D. S. (5 October 2010). "The Rate of Fitness-Valley Crossing in Sexual Populations". Genetics. 186 (4): 1389–1410. doi:10.1534/genetics.110.123240. PMC 2998319. PMID 20923976.
- ^ Covert, Arthur; Lenski, Richard; Wilke, Claus; Ofria, Charles (2013). "Experiments on the role of deleterious mutations as stepping stones in adaptive evolution". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 110 (34): E3171 – E3178. Bibcode:2013PNAS..110E3171C. doi:10.1073/pnas.1313424110. PMC 3752215. PMID 23918358.
- ^ Behe, Michael (October 27, 2016). "Philosophical Objections to Intelligent Design: A Response to Critics". Evolution News & Science Today. Retrieved August 17, 2018.
- ^ Miller, K (1999). Finding Darwin's God: a scientist's search for common ground between God and evolution. New York: Cliff Street Books. ISBN 978-0-06-093049-3.
- ^ "Human Competitive". www.genetic-programming.com. Archived from the original on 8 July 2016. Retrieved 7 May 2018.
- ^ Michael Behe. Evidence for Intelligent Design from Biochemistry. Archived 2006-09-03 at the Wayback Machine 1996.
- ^ Index to Creationist Claims. Mark Isaak. The Talk.Origins Archive. "Irreducible complexity and complex specified information are special cases of the "complexity indicates design" claim; they are also arguments from incredulity." "CI101: Complexity and design". Archived from the original on 2013-10-04. Retrieved 2014-03-24. "The argument from incredulity creates a god of the gaps." "CA100: Argument from incredulity". Archived from the original on 2013-10-20. Retrieved 2014-03-24.
- ^ Eugenie C. Scott and Glenn Branch, "Intelligent Design" Not Accepted by Most Scientists Archived 2009-03-30 at the Wayback Machine, National Center for Science Education website, September 10, 2002.
- ^ "Darwin's Black Box by Michael Behe". Archived from the original on 2015-07-15. Retrieved 2015-07-15.
- ^ Amerikanbeat.net: A Critique of Behe, Dembski on "Irreducible Complexity"[1]
- ^ IC and Evolution Archived 2004-08-13 at the Wayback Machine makes the point that: if "irreducible complexity" is tautologically redefined to allow a valid argument that intelligent design is the correct explanation for life then there is no such thing as "irreducible complexity" in the mechanisms of life; while, if we use the unmodified original definition then "irreducible complexity" has nothing whatever to do with evolution.
- ^ The Court in Dover noted that this implicit assumption of the defendant school board created a "flawed and illogical contrived dualism" (Opinion p. 64).
- ^ a b Memorandum Opinion, Judge John E. Jones III, Kitzmiller v. Dover Area School District
Further reading
- Behe, Michael (1996). Darwin's Black Box. New York: The Free Press. ISBN 978-0-684-83493-1. OCLC 34150540.
- Denton, Michael (1986). Evolution: A Theory in Crisis. Bethesda: Adler & Adler. ISBN 978-0-917561-05-4.
- Jantzen, Benjamin C. (2014). "12: Intelligent design I: irreducible complexity". An Introduction to Design Arguments. Cambridge, New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-18303-1.
- Macnab, RM (2004). "Type III flagellar protein export and flagellar assembly". Biochim Biophys Acta. 1694 (1–3): 207–17. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2004.04.005. PMID 15546667.
- Ruben, J.A.; Jones, T.D.; Geist, N.R.; Hillenius, W.J. (November 14, 1997). "Lung Structure and Ventilation in Theropod Dinosaurs and Early Birds". Science. 278 (5341): 1267–70. Bibcode:1997Sci...278.1267R. doi:10.1126/science.278.5341.1267.
- Zimmer, Carl (February 2005). "Testing Darwin". Discover Magazine. 26 (2). Archived from the original on 18 May 2005.
- Sober, Elliott (29 November 2018). The Design Argument. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-1-108-64392-4.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help)
External links
- Supportive
- Michael J. Behe home page
- About Irreducible Complexity Discovery Institute
- Behe's Reply to his Critics (pdf)
- How to Explain Irreducible Complexity -- A Lab Manual Discovery Institute
- Institute for Creation Research (pdf)
- Irreducible Complexity: Definition & Evaluation by Craig Rusbult, Ph.D.
- Irreducible Complexity Revisited (pdf)
- Critical
- Behe, Biochemistry, and the Invisible Hand
- Darwin vs. Intelligent Design (again), by H. Allen Orr (review of Darwin's Black Box)
- Devolution: Why intelligent design isn't (The New Yorker)
- Does irreducible complexity imply Intelligent Design? by Mark Perakh
- Evolution of the Eye (Video) Zoologist Dan-Erik Nilsson demonstrates eye evolution through intermediate stages with working model. (PBS)
- Facilitated Variation
- Himma, Kenneth Einar. Design Arguments for the Existence of God. Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy: 2. Contemporary Versions of the Design Argument, a. The Argument from Irreducible Biochemical Complexity
- Kitzmiller vs. Dover transcripts
- Miller, Kenneth R. textbook website
- Miller's "The Flagellum Unspun: The Collapse of Irreducible Complexity"
- Talk.origins archive (see talk.origins)
- TalkDesign.org (sister site to talk.origins archive on intelligent design)
- The bacterial flagellar motor: brilliant evolution or intelligent design? Matt Baker, ABC Science, 7 July 2015
- Unlocking cell secrets bolsters evolutionists (Chicago Tribune)
