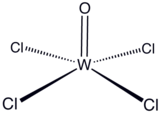
Tungsten(VI) oxytetrachloride
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Tungsten(IV) chloride oxide
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.033.497 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| WOCl4 | |
| Molar mass | 341.651 g/mol |
| Appearance | red crystals |
| Density | 11.92 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 211 °C (412 °F; 484 K) |
| Boiling point | 227.55 °C (441.59 °F; 500.70 K) |
| reacts | |
| Solubility | soluble in benzene and CS2 |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Tungsten(VI) oxytetrafluoride Tungsten(VI) oxytetrabromide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Tungsten(VI) oxytetrachloride is the inorganic compound with the formula WOCl4. This diamagnetic solid is used to prepare other complexes of tungsten. The yellow-green compound is soluble in nonpolar solvents but it reacts with alcohols and water and forms adducts with Lewis bases.
Structure
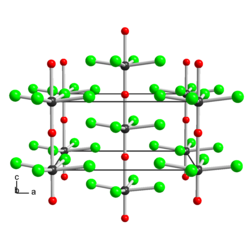
The solid consists of weakly associated square pyramidal monomers.[1] The compound is classified as an oxyhalide.
Synthesis and reactions
WOCl4 is prepared from tungsten trioxide:[2]
WOCl4 is Lewis acidic. It is a precursor to catalysts used for polymerization of alkynes.[3]
References
- ^ Hess, H.; Hartung, H. (1966). "Die Kristallstruktur von Wolframoxidchlorid WOCl4 und Wolframoxidbromid WOBr4". Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 34 (3–4): 157–166. doi:10.1002/zaac.19663440306.
- ^ Nielson, A. J. (1985). "Tungsten and Molybdenum Tetrachloride Oxides". Inorganic Syntheses. Inorganic Syntheses. Vol. 23. pp. 195–198. doi:10.1002/9780470132548.ch41. ISBN 9780470132548.
{{cite book}}:|journal=ignored (help) - ^ Hayano, S.; Masuda, T. (1999). "Living Polymerization of [o-(Trifluoromethyl)phenyl]acetylene by WOCl4-Based Catalysts such as WOCl4-n-Bu4Sn-t-BuOH (1:1:1)". Macromolecules. 32: 7344–7348. doi:10.1002/zaac.19663440306.
