Angioma
| Angioma | |
|---|---|
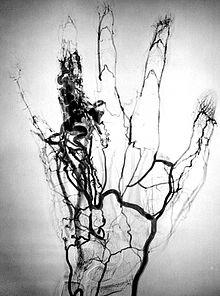 | |
| Arteriography showing the blood vessels involved in an angioma of the ring finger | |
| Specialty | Dermatology |
Angiomas are benign tumors derived from cells of the vascular or lymphatic vessel walls (endothelium) or derived from cells of the tissues surrounding these vessels.[1][2]
Angiomas are a frequent occurrence as patients age, but they might be an indicator of systemic problems such as liver disease. They are not commonly associated with malignancy.
Signs and symptoms

Angiomas usually appear at or near the surface of the skin anywhere on the body, and may be considered bothersome depending on their location. However, they may be present as symptoms of another more serious disorder, such as cirrhosis. When they are removed, it is generally for cosmetic reasons.
Types
- Naevus flammeus
- Telangiectasia - Spider, Hereditary hemorrhagic
- Reactive vascular proliferations
Diagnosis
This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (July 2018) |
See also
References
- ^ Robbins and Cotran, "Pathologic Basis of Disease", by Ninay Kumar, Abul K. Abbas, Nelson Fausto, 7th Edition, pages 545-547
- ^ "angioma" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
External links
