Asterion (anatomy)
Appearance
| Asterion | |
|---|---|
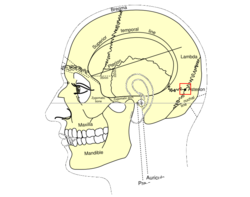 Side view of head, showing surface relations of bones. (Asterion visible at center right.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Asterion |
| TA98 | A02.1.00.020 |
| TA2 | 422 |
| FMA | 76625 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The asterion is the point on the skull corresponding to the posterior end of the parietomastoid suture.
Location
In human anatomy, the asterion is a visible, so-called craniometric, point on the exposed skull, just behind the ear, where three cranial sutures meet:
- the lambdoid,
- parieto-mastoid, and
- occipito-mastoid sutures,
or where three cranial bones meet:
- Parietal bone,
- Occipital bone,
- and Mastoid portion of the Temporal bone.
In the adult, it lies 4 cm behind and 12 mm above the center of the entrance to the ear canal.
Clinical significance
Neurosurgeons use this point to orient themselves, in order to plan safe entry into the skull for some operations.
Etymology
The asterion receives its name from the Greek ἀστέριον (astērion), meaning "star" or "starry".
The Mercedes point is an alternative term for the asterion, for its resemblance to the Mercedes-Benz logo.
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Asterion (anatomy).
