Hereditary breast–ovarian cancer syndrome
| Hereditary breast–ovarian cancer syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Other names | HBOC |
 | |
| Ovarian and breast cancer patients in a pedigree chart of a family | |
| Specialty | Obstetrics and gynaecology, endocrinology, dermatology, oncology, medical genetics |
Hereditary breast–ovarian cancer syndromes (HBOC) are cancer syndromes that produce higher than normal levels of breast cancer, ovarian cancer and additional cancers in genetically related families (either one individual had both, or several individuals in the pedigree had one or the other disease). It accounts for 90% of the hereditary cancers.[1] The hereditary factors may be proven or suspected to cause the pattern of breast and ovarian cancer occurrences in the family.[2] The name HBOC may be misleading because it implies that this genetic susceptibility to cancer is mainly in women. In reality, both sexes have the same rates of gene mutations and HBOC can predispose to other cancers including prostate cancer and pancreatic cancer.[3] For this reason, the term "King syndrome" has recently come into use. The new name references Mary-Claire King who identified the genes BRCA1 and BRCA2.
Most hereditary breast-ovarian cancer syndromes are inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern. Biallelic and homozygous inheritance of defective alleles that confer this syndrome is usually an embryonically lethal condition; live cases usually experience a severe form of Fanconi anemia.
Causes
[edit]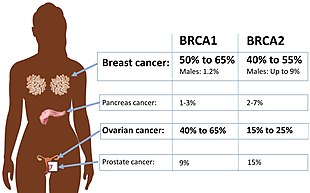
A number of genes are associated with HBOC.[5] The most common of the known causes of HBOC are:
- BRCA mutations:[5] Harmful mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes can produce very high rates of breast and ovarian cancer, as well as increased rates of other cancers. Mutations in BRCA1 are associated with a 39-46% risk of ovarian cancer and mutations in BRCA2 are associated with a 10-27% risk of ovarian cancer.[6]
Other identified genes include:
- MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, PMS2: mutations in genes that lead to Lynch Syndrome put individuals at risk for ovarian cancer.[7]
- TP53: Mutations cause Li-Fraumeni syndrome. It produces particularly high rates of breast cancer among younger women with mutated genes, and despite being rare, 4% of women with breast cancer under age 30 have a mutation in this gene.[5]
- PTEN: Mutations cause Cowden syndrome, which produces hamartomas (benign polyps) in the colon, skin growths, and other clinical signs, as well as an increased risk for many cancers.[5]
- CDH1: Mutations are associated with lobular breast cancer and gastric cancer.[5]
- STK11: Mutations produce Peutz–Jeghers syndrome. It is extremely rare, and creates a predisposition to breast cancer, intestinal cancer, and pancreatic cancer.[5]
- CHEK2: Approximately one out of 40 northern Europeans have a mutation in this gene, making it a common mutation. It is also one of the most frequently mutated genes after BRCA among Hispanics in the United States.[8] Considered a moderate-risk mutation, it may double or triple the carrier's lifetime risk of breast cancer, and also increase the risk of colon cancer and prostate cancer.[5]
- ATM: Mutations cause ataxia telangectasia; female carriers have approximately double the normal risk of developing breast cancer.[5]
- PALB2: Studies vary in their estimate of the risk from mutations in this gene and the frequency of mutations in this gene may be different among different populations.[8] It may be moderate risk, or as high as BRCA2.[5]
For many of these genes, inheriting both defective alleles usually result in an embryonically lethal phenotype. Live cases suffer from a severe form of Fanconi Anemia; biallelic mutations of BRCA1 lead to Fanconi anemia complementation group S, and biallelic mutations of BRCA2 lead to complementation group D1. [9]
Approximately 45% of HBOC cases involve unidentified genes, or multiple genes.[5]
Diagnosis
[edit]This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (September 2023) |
Prevention
[edit]People with BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations are recommended to have a transvaginal ultrasound 1-2 times per year. Screening with CA-125 is also recommended.
Prophylactic salpingo-oophorectomy (removal of the ovaries and fallopian tubes to prevent cancer) is recommended at age 35-40 for people with BRCA1 mutations and at age 40-45 for people with BRCA2 mutations.[6] An increasing number women who test positive for faulty BRCA1 or BRCA2 genes choose to have risk-reducing surgery. At the same time the average waiting time for undergoing the procedure is two-years which is much longer than recommended.[10][11]
References
[edit]- ^ Bickerstaff, Helen (2017). Gynaecology by Ten Teachers. United Kingdom: CRC Press. p. 330. ISBN 978-1-4987-4428-7.
- ^ "Hereditary Breast Ovarian Cancer Syndrome (BRCA1 / BRCA2)". Stanford University. Retrieved 2008-09-02.
- ^ Pritchard, Colin C. (July 2019). "New name for breast-cancer syndrome could help to save lives". Nature. 571 (7763): 27–29. Bibcode:2019Natur.571...27P. doi:10.1038/d41586-019-02015-7. PMID 31270479.
- ^ Petrucelli N, Daly MB, Pal T (December 2016) [September 1998]. "BRCA1- and BRCA2-Associated Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer". In Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Bean LJ, Mirzaa G, Amemiya A (eds.). GeneReviews. University of Washington, Seattle. PMID 20301425.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Morris, Joi L.; Gordon, Ora K. (Ora Karp) (2010). Positive results : making the best decisions when you're at high risk for breast or ovarian cancer. Amherst, N.Y.: Prometheus Books. pp. 337–340. ISBN 978-1-59102-776-8.
- ^ a b Ring, Kari L.; Garcia, Christine; Thomas, Martha H.; Modesitt, Susan C. (November 2017). "Current and future role of genetic screening in gynecologic malignancies". American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. 217 (5): 512–521. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2017.04.011. ISSN 1097-6868. PMID 28411145. S2CID 29024566.
- ^ Woolderink, J. M.; De Bock, G. H.; de Hullu, J. A.; Hollema, H.; Zweemer, R. P.; Slangen, B. F. M.; Gaarenstroom, K. N.; van Beurden, M.; van Doorn, H. C. (August 2018). "Characteristics of Lynch syndrome associated ovarian cancer". Gynecologic Oncology. 150 (2): 324–330. doi:10.1016/j.ygyno.2018.03.060. hdl:1887/96199. ISSN 1095-6859. PMID 29880284. S2CID 46967266.
- ^ a b Weitzel, Jeffrey N.; Neuhausen, Susan L.; Adamson, Aaron; Tao, Shu; Ricker, Charité; Maoz, Asaf; Rosenblatt, Margalit; Nehoray, Bita; Sand, Sharon (2019-06-17). "Pathogenic and likely pathogenic variants in PALB2, CHEK2, and other known breast cancer susceptibility genes among 1054 BRCA-negative Hispanics with breast cancer". Cancer. 125 (16): 2829–2836. doi:10.1002/cncr.32083. ISSN 1097-0142. PMC 7376605. PMID 31206626.
- ^ Sawyer SL, Tian L, Kahkonen M, Schwartzentruber J, Kircher M, Majewski J, Dyment DA, Innes AM, Boycott KM, Moreau LA, Moilanen JS, Greenberg RA (2014). "Biallelic Mutations in BRCA1 Cause a New Fanconi Anemia Subtype". Cancer Discov. 5 (2): 135–42. doi:10.1158/2159-8290.CD-14-1156. PMC 4320660. PMID 25472942.
- ^ "Earlier decisions on breast and ovarian surgery reduce cancer in women at high risk". NIHR Evidence (Plain English summary). National Institute for Health and Care Research. 2021-12-07. doi:10.3310/alert_48318.
- ^ Marcinkute, Ruta; Woodward, Emma Roisin; Gandhi, Ashu; Howell, Sacha; Crosbie, Emma J; Wissely, Julie; Harvey, James; Highton, Lindsay; Murphy, John; Holland, Cathrine; Edmondson, Richard; Clayton, Richard; Barr, Lester; Harkness, Elaine F; Howell, Anthony (10 February 2021). "Uptake and efficacy of bilateral risk reducing surgery in unaffected female BRCA1 and BRCA2 carriers". Journal of Medical Genetics. 59 (2): 133–140. doi:10.1136/jmedgenet-2020-107356. ISSN 0022-2593. PMID 33568438. S2CID 231876899.
