Car float

A railroad car float or rail barge is an unpowered barge with rail tracks mounted on its deck. It is used to move railroad cars across water obstacles, or to locations they could not otherwise go, and is towed by a tugboat or pushed by a towboat. As such, the car float is a specialised form of the lighter,[1] as opposed to a train ferry, which is self-powered.
Historical operations
U.S. East Coast
Beginning in the 1870s, the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad (B&O) operated a carfloat across the Potomac River, just south of Washington, D.C., between Shepherds Landing on the east shore, and Alexandria, Virginia on the west. The ferry operation ended in 1906.[2] (See Capital Subdivision.)
The B&O operated a carfloat across the Baltimore Inner Harbor until the mid-1890s. It connected trains from Philadelphia to Washington, D.C. and points to the west. The operation was discontinued after the opening of the Baltimore Belt Line in 1895.[2]
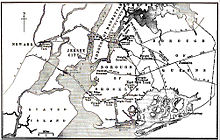
The Port of New York and New Jersey was especially rife with carfloat operations, which lost ground to the post-World War II expansion of trucking, but held out until and the rise of containerization in the 1970s.[3]
These carfloats operated between the Class 1 railroads termini on the west bank of Hudson River in Hudson County, New Jersey and the numerous online and offline terminals located in Brooklyn, Queens, Staten Island, Bronx & Manhattan. [4] [5] Class 1 railroads in the New York Harbor area providing carfloat services were:
- Baltimore and Ohio Railroad[6][7]
- Central Railroad of New Jersey[8][9]
- Delaware, Lackawanna and Western Railroad[10][11]
- Erie Railroad and Erie Lackawanna Railroad[12][13]
- Lehigh Valley Railroad[14][15]
- Long Island Rail Road[16][17]
- New York Central Railroad[18][19]
- New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad[20][21]
- Pennsylvania Railroad[22][23]
- Reading Railroad[24]
as well as the offline Terminal railroads
- Brooklyn Eastern District Terminal[25]
- Bush Terminal[26][27]
- Brooklyn Army Terminal
- Hoboken Manufacturers Railroad[28]
- Jay Street Connecting Railroad[29]
- New York Dock Railway[30][31]
- Pouch Terminal[32]
- East Jersey Railroad and Terminal Co.[32]
Carfloat service was also provided to many pier stations and waterfront warehouse facilities (that did not engage in carfloating service personally) by the above-mentioned railroads.
At their peak, the railroads had 3,400 employees operating small fleets totalling 323 car floats, plus 1,094 other barges, towed by 150 tugboats between New Jersey and New York City.
Abandoned float bridges are preserved as part of this history at:
- Gantry Plaza State Park in Long Island City, Queens; (former Long Island Railroad),
- West 26th Street float bridge (former Baltimore & Ohio) and the only surviving wood Howe Truss float bridge in New York Harbor
- North River Pier 66a, and 69th Street Transfer Bridge (former New York Central)
Also, several other abandoned but unrestored float bridges exist in various locations around New York Harbor. A complete list can be read here: Surviving Float Bridges of New York Harbor
The only remaining carfloat service currently in operation in New York Harbor is operated by New York New Jersey Rail. This company, operated by the bi-state government agency Port Authority of New York & New Jersey is the successor to the New York Cross Harbor Railroad. Carfloat service operates between Bush Terminal in Brooklyn, New York and Greenville Yard in Jersey City. It has been proposed that carfloat service be transferred from Bush Terminal 50th float bridge to 65th Street / Bay Ridge Yard float bridges.
Freight cars do not run in the East River Tunnels nor the North River Tunnels (under the Hudson River), in part due to inadequate tunnel clearances of the New York Tunnel Extension.
U.S. Midwest

Between 1912–1936 the Erie Railroad operated a car float service on the Chicago River in Chicago, Illinois.[33]
U.S. West Coast
- Santa Fe Railroad: San Francisco
- Southern Pacific Railroad (?)
- Union Pacific Railroad (?)
- Western Pacific Railroad: San Francisco
- Chicago, Milwaukee, St. Paul and Pacific Railroad: Seattle, Washington, Tacoma, Washington, Bellingham, Washington, Port Townsend, Washington
- Seattle and North Coast Railroad: Seattle, Washington, Port Townsend, Washington
Canada

- Various inland lakes of British Columbia (Okanagan, Arrow, Kootenay) (CN and CPR)
- Port Maitland, Ontario - Erie, Pennsylvania (TH&B Railway)
- Port Burwell, Ontario - Ashtabula, Ohio (CN)
- Cobourg, Ontario - Rochester, New York (Ontario Car Company)
- Sarnia, Ontario - Port Huron, Michigan - rail-barge - (CN, until the opening of the Paul Tellier Tunnel). The rail ferries Pere Marquette 12 and Pere Marquette 10 were converted to barges (PM 10 in 1974, PM 12 in the 1980s) and used until 1995 to carry dangerous cargoes and oversize cars.[34]
- Windsor, Ontario - Detroit, Michigan (Grand Trunk, CN, CPR, Michigan Central, Wabash, until the 1980s)[citation needed]
- BC Rail. until 1955 railcars were barged from North Vancouver to Squamish.
- A large number of isolated BC pulp mills had chemicals and freight moved by car floats.
Existing operations
Alaska
The Alaska Railroad provides the Alaska Rail Marine rail barge service from downtown Seattle, Washington to Whittier on the central Alaskan mainland.[35] Additionally, CN Rail provides the Aqua Train rail barge service from Prince Rupert, British Columbia to Whittier.[36]
New York / New Jersey

The only remaining carfloat service currently in operation in the Port of New York and New Jersey is operated by New York New Jersey Rail. This company, operated by the bi-state government agency Port Authority of New York & New Jersey is the successor to the New York Cross Harbor Railroad. Car float service operates between Bush Terminal in Brooklyn, New York and Greenville Yard in Jersey City, New Jersey. It has been proposed that carfloat service be transferred from Bush Terminal 50th float bridge to 65th Street / Bay Ridge Yard float bridges.
Virginia
Bay Coast Railroad currently operates a 2-barge car float connecting Virginia's Eastern Shore with the city of Norfolk, Virginia across the Chesapeake Bay.
Canada
- Prince Rupert - Whittier (AquaTrain)
- Delta - Nanaimo, British Columbia (E and N Railway)
- Matane, Quebec - Baie-Comeau, Quebec (COGEMA) [37]
See also
- Alaska Rail Marine
- Aqua Train
- Bay Ridge Branch
- Cross-Harbor Rail Tunnel (proposed)
- Ferry slip (includes examples of rail ferry and barge slips)
- Linkspan
- New York tugboats
- Santa Fe Dock and Channel Company
- Train ferry
References
- ^ Lederer, Eugene H. (1945). Port Terminal Operation: Port Terminal Management, Stevedoring, Stowage, Lighterage and Harbor Boats. New York, NY: Cornell Maritime Press. pp. 291–292.
- ^ a b Harwood, Jr., Herbert H. (1979). Impossible Challenge: The Baltimore & Ohio Railroad in Maryland. Baltimore, MD: Barnard, Roberts. ISBN 0-934118-17-5.
- ^ Cudahy, Brian J. (2006). Box Boats: How Container Ships Changed the World. New York, NY: Fordham University Press. pp. 45–47. ISBN 0-8232-2568-2.
- ^ Flagg, Thomas R. (2000). New York Harbor Railroads in Color, Volume 1. Scotch Plains, NJ: Morning Sun Books. ISBN 1-58248-082-6.
- ^ Flagg, Thomas R. (2002). title= New York Harbor Railroads in Color, Volume 2. Scotch Plains, NJ: Morning Sun Books. ISBN 1-58248-048-6.
{{cite book}}: Missing pipe in:|title=(help) - ^ Flagg, 2000, pp. 16-23.
- ^ Flagg, 2002, pp. 26-29.
- ^ Flagg, 2000, pp. 24-33.
- ^ Flagg, 2002, pp. 38-39.
- ^ Flagg, 2000, pp. 34-45.
- ^ Flagg, 2002, pp. 40-51.
- ^ Flagg, 2000, pp. 46-55.
- ^ Flagg, 2002, pp. 52-57.
- ^ Flagg, 2000, pp. 56-61.
- ^ Flagg, 2002, pp. 58-63.
- ^ Flagg, 2000, pp. 62-65.
- ^ Flagg, 2002, pp. 64-67.
- ^ Flagg, 2000, pp. 66-83.
- ^ Flagg, 2002, pp. 68-93.
- ^ Flagg, 2000, pp. 84-91.
- ^ Flagg, 2002, pp. 94-97.
- ^ Flagg, 2000, pp. 92-101.
- ^ Flagg, 2002, pp. 98-109.
- ^ Flagg, 2002, pp. 30-37.
- ^ Flagg, 2002, pp. 110-116.
- ^ Flagg, 2000, pp. 118-125.
- ^ Flagg, 2002, pp. 120-127.
- ^ Flagg, 2000, pp. 126-127.
- ^ Flagg, 2002, p. 118.
- ^ Flagg, 2000, pp. 110-117.
- ^ Flagg, 2002, p. 119.
- ^ a b Flagg, 2002, p. 117.
- ^ Sennstrom, Bernard H. (1992). "Erie Railroad's Chicago River Service". The Diamond. 7 (1): 4–10.
- ^ The Pere Marquette Marine Fleet, Pere Marquette Historical Society, 10-MAY-2011, accessed July 16, 2012
- ^ Alaska Rail Marine
- ^ Aqua train
- ^ Trains (Magazine) February 2009 p9
External links
- Railroad ferry, Hudson River, New York, Andreas Feininger, 1940. Still Photograph Archive, George Eastman House, Rochester, NY.
- NYNJ Rail - official site
- Industrial & Offline Terminal Railroads of Brooklyn, Queens, Staten Island, Bronx & Manhattan
