Deep fibular nerve
| Deep peroneal nerve | |
|---|---|
 Nerves of the right lower extremity Posterior view. | |
| Details | |
| From | common peroneal nerve |
| Innervates | anterior compartment of leg |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Nervus fibularis profundus, nervus peronaeus profundus |
| TA98 | A14.2.07.055 |
| TA2 | 6579 |
| FMA | 44771 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
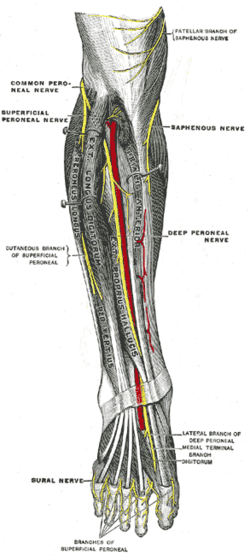
The deep peroneal nerve (deep fibular nerve) begins at the bifurcation of the common peroneal nerve between the fibula and upper part of the peroneus longus, passes infero-medially, deep to extensor digitorum longus, to the anterior surface of the interosseous membrane, and comes into relation with the anterior tibial artery above the middle of the leg; it then descends with the artery to the front of the ankle-joint, where it divides into a lateral and a medial terminal branch.
Structure
Lateral side of the leg
Deep peroneal nerve is the nerve of the anterior compartment of the leg and the dorsum of the foot. It is one of the terminal branches of the common peroneal nerve. It corresponds to the posterior interosseus nerve of the forearm. It begins at the lateral side of the fibula bone, and then enters the anterior compartment by piercing the anterior intermuscular septum. It then pierces the extensor digitorum longus and lies next to the anterior tibial artery, following the course of the artery until the ankle-joint where the nerve divides into medial and lateral terminal branches. In the leg, the deep peroneal nerve divides into several branches:[1]
- Muscular branches - supplies four muscles in the leg: tibialis anterior, extensor hallucis longus, extensor digitorum longus, and peroneous tertius[1]
Foot
Close to the ankle joint, deep peroneal nerve terminates by dividing into medial and lateral terminal branches.[1]
- Medial terminal branch - This nerve accompanies the dorsalis pedis artery along the dorsum of the foot, and, at the first interosseous space, divides into two dorsal digital nerves which supply the adjacent sides of the great and second toes,[1] communicating with the medial dorsal cutaneous branch of the superficial peroneal nerve. Before it divides it gives off to the first space an interosseous branch which supplies the metatarsophalangeal joint of the great toe and sends a filament to the first Interosseous dorsalis muscle.[2]
- Lateral terminal branch - This nerve passes across the tarsus, beneath the extensor digitorum brevis, and supplies the extensor digitorum brevis. This nerve ends in a pseudoganglion deep to the extensor digitorum brevis.[1] From the pseudoganglion, three minute branches are given off to supply the tarsal joints and the metatarsophalangeal joints of the second, third, and fourth toes.[2]
Function
In the leg, the deep peroneal nerve supplies muscular branches to the anterior compartment of extensor muscles in the leg which include the tibialis anterior, extensor digitorum longus, peroneus tertius, and extensor hallucis longus (propius), and an articular branch to the ankle-joint. After its bifurcation past the ankle joint, the lateral branch of the deep peroneal nerve innervates the extensor digitorum brevis and the extensor hallucis brevis, while the medial branch goes on to provide cutaneous innervation to the webbing between the first and second digits.
Clinical significance
Damage to the deep peroneal nerve, as is possible with traumatic injury to the lateral knee, results in foot drop. The deep peroneal nerve is also subject to injury resulting from lower motor neuron disease, diabetes, ischemia, and infectious or inflammatory conditions. Injury to the common peroneal nerve is the most common isolated mononeuropathy of the lower extremity and produces sensory problems on the lateral lower leg in addition to foot drop.[3]
Additional images
-
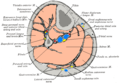
Cross-section through middle of leg.
-
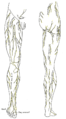
Cutaneous nerves of the right lower extremity. Anterior and posterior views.
-
Cutaneous nerves of the right lower extremity. Anterior and posterior views.
-
Deep nerves of the front of the leg.
-
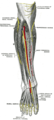
Nerves of the dorsum of the foot.
-
Deep fibular nerve
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 965 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 965 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ a b c d e Krishna, Garg (2010). "Front, lateral, and medial sides of leg and dorsum of foot (Chapter 8)". BD Chaurasia's Human Anatomy (Regional and Applied Dissection and Clinical) Volume 2 - Lower limb, abdomen, and pelvis (Fifth ed.). India: CBS Publishers and Distributors Pvt Ltd. p. 104,105,106. ISBN 978-81-239-1864-8.
- ^ a b Gray, Henry; Lewis, Warron Harmon (1918). Anatomy of the human body. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger. p. 965. Retrieved 22 February 2018.
- ^ [1]
External links
- Anatomy photo:16:st-0601 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "The Foot: Nerves"