Didymella rabiei
| Didymella rabiei | |
|---|---|

| |
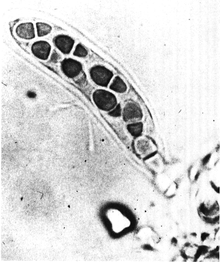
| Didymella rabiei growing on chickpea | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Fungi |
| Division: | Ascomycota |
| Class: | Dothideomycetes |
| Order: | Pleosporales |
| Family: | Didymellaceae |
| Genus: | Didymella |
| Species: | D. rabiei
|
| Binomial name | |
| Didymella rabiei | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
| chickpea ascochyta blight | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Common names | chickpea ascochyta, ascochyta blight, blight of chickpea |
| Causal agents | Didymella rabiei |
| Hosts | chickpea |
| EPPO Code | MYCORA |
| Distribution | worldwide in chickpea growing regions |
| NCBI genome ID | JYNV00000000 |
|---|---|
| Ploidy | aneuploid[1] |
| Genome size | 34.65[2] |
| Number of chromosomes | 12-16[1] |
| Year of completion | 2016[2] |
Didymella rabiei, commonly called chickpea ascochyta blight fungus is a fungal plant pathogen of chickpea. Didymella rabiei is the teleomorph of Ascochyta rabiei, which is the anamorph, but both names are the same species.[3]
Names
The specific epithet rabiei refers to rabbia del ceci or 'rabies of chickpea', a name for the disease.[4]
The disease is also referred to as ascochyta blight but there are other fungal species that cause diseases in other pulse species that also go by that term. It also goes by the name blight of chickpea.[5] In French it is called anthracnose du pois-chiche (lit. 'chickpea anthracnose') or ascochytose du pois-chiche ('chickpea ascochyta').[5] In German it is referred to as Anthraknose: Kichererbse (anthracnose: chickpea').[5] It is called ascoquita del garbanzo ('garbanzo ascochyta') or rabia del garbanzo ('rabies of garbanzo') in Spanish.[5]
Description
D. rabiei has a spherical punctiform and membranous pyrenium, at first lutescent then opening to a rounded black ostiole.[4] It has numerous elliptical and hyaline spores or varying size.[4]
Hosts
D. rabiei is known for infecting cultivated annual chickpea (Cicer arietinum),[6] but also commonly infects other wild perennial chickpea species such as Cicer monbretti, Cicer ervoides,[1] Cicer judaicum,[7] and Cicer pinnatifidum.[8]
Other host species include:
- dog fennel (Anthemis cotula)[1]
- alfalfa (Medicago sativa)[6]
- pea (Pisum sativum)[6][1]
- Berseem clover (Trifolium alexandrinum)[6]
- wheat (Triticum aestivum)[1]
- faba bean (Vicia faba)[1]
- hairy tare (Vicia hirsuta)[9]
- cowpea (Vigna unguiculata)[6]
Effects on aquafaba
A chemical analysis of aquafaba indicated that a number of proteins in a particularly well-performing batch were found to be versions from D. rabiei, specifically tRNA (cytosine-5-)-methyltransferase, o-acyltransferase, oxidoreductase, histone H3, and histone H2B.[10] It is unclear how much of an effect these proteins have on the properties of aquafaba.
External links
References
- ^ a b c d e f g Akamatsu, Hajime O.; Chilvers, Martin I.; Kaiser, Walter J.; Peever, Tobin L. (November 2012). "Karyotype polymorphism and chromosomal rearrangement in populations of the phytopathogenic fungus, Ascochyta rabiei". Fungal Biology. 116 (11): 1119–1133. doi:10.1016/j.funbio.2012.07.001. ISSN 1878-6146. OCLC 5902581684. PMID 23153803. Retrieved 24 February 2018.
- ^ a b Verma, Sandhya; Gazara, Rajesh Kumar; Nizam, Shadab; Parween, Sabiha; Chattopadhyay, Debasis; Verma, Praveen Kumar (19 April 2016). "Draft genome sequencing and secretome analysis of fungal phytopathogen Ascochyta rabiei provides insight into the necrotrophic effector repertoire". Scientific Reports. 6 (24638): 24638. Bibcode:2016NatSR...624638V. doi:10.1038/srep24638. OCLC 6029350225. PMC 4835772. PMID 27091329. Retrieved 24 February 2018.
- ^ Trapero-Casas, Antonio; Kaiser, Walter J. (November 1992). "Development of Didymella rabiei, the Teleomorph of Ascochyta rabiei, on Chickpea Straw" (pdf). Phytopathology. 82 (11): 1261–1266. doi:10.1094/Phyto-82-1261. ISSN 0031-949X. OCLC 193649327. Retrieved 27 February 2018.
- ^ a b c Passerini, Giovanni (December 1864). "Primo elenco di Funghi Parmensi" [First list of Mushrooms of Parma] (PDF). Commentario - Societa Crittogamologica Italiana, Milan (in Italiano). 2 (1): 497. Retrieved 21 February 2018.
Pyrenium globosum punctiforme membranaceum, primo lutescens dein nigrum osculo rotundato reclusum. Sporae numerosae ellipsoideae hyalinae magnitudine variae, plasmate granuloso repletae, madore erumpentes. Nella sommità de' ceci coltivati ne' campi e colpiti dalla così detta rabbia onde rapidamente periscono.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^ a b c d "Didymella rabiei (MYCORA)[Overview]". EPPO Global Database. Europe: European and Mediterranean Plant Protection Organization. 1 February 2002. Retrieved 21 February 2018.
- ^ a b c d e "chick pea blight (Didymella rabiei)". Plantwise Knowledge Bank. CABI. Retrieved 26 February 2018.
- ^ Frenkel, Omer; Peever, Tobin L.; Chilvers, Martin I.; Özkilinc, Hilal; Can, Canan; Abbo, Shahal; Shtienberg, Dani; Sherman, Amir (6 November 2009). "Ecological Genetic Divergence of the Fungal Pathogen Didymella rabiei on Sympatric Wild and Domesticated Cicer spp. (Chickpea)". Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 75 (1): 30–35. doi:10.1128/AEM.01181-09. ISSN 0099-2240. OCLC 505983590. PMC 2798644. PMID 19897759. Retrieved 26 February 2018.
- ^ Can, Canan; Özkilinc, Hilal; Kahraman, A.; Ozkan, H. (July 2007). Robertson, Alison E. (ed.). "First Report of Ascochyta rabiei Causing Ascochyta Blight of Cicer pinnatifidum". Plant Disease. 91 (7): 908. doi:10.1094/PDIS-91-7-0908C. ISSN 0191-2917. OCLC 4661716178.
- ^ Chilvers, Martin I.; Horton, T. L.; Peever, Tobin L.; Kaiser, W. J.; Muehlbauer, F. J. (December 2006). Robertson, Alison E. (ed.). "First Report of Ascochyta Blight of Vicia hirsuta (Hairy Tare) in the Republic of Georgia Caused by Ascochyta sp". Plant Disease. 90 (12): 1555. doi:10.1094/PD-90-1555A. ISSN 0191-2917. OCLC 202785383.
- ^ Shim, Youn Young; Mustafa, Rana; Shen, Jianheng; Ratanapariyanuch, Kornsulee; Reaney, Martin J. T. (10 February 2018). "Composition and Properties of Aquafaba: Water Recovered from Commercially Canned Chickpeas". Journal of Visualized Experiments (132): e56305. doi:10.3791/56305. OCLC 7317651690. PMID 29553544. Retrieved 24 February 2018.
