Eurocopter EC725
| EC725 Caracal/Super Cougar H225M | |
|---|---|

| |
| A French Air Force EC725R2 Caracal in 2009 | |
| Role | Tactical transport helicopter/armed helicopter |
| National origin | France |
| Manufacturer | Eurocopter Airbus Helicopters |
| First flight | 27 November 2000[citation needed] |
| Introduction | February 2005 |
| Status | In service |
| Primary users | French Armed Forces Brazilian Armed Forces Royal Malaysian Air Force Mexican Air Force Indonesian Air Force |
| Produced | 2000-present |
| Developed from | Eurocopter AS532 Cougar |
| Variants | Eurocopter EC225 Super Puma |
| Developed into | KAI KUH-1 Surion |
The Eurocopter EC725 Caracal, now called Airbus Helicopters H225M, is a long-range tactical transport military helicopter developed from the Eurocopter AS532 Cougar for military use. It is a twin-engined aircraft and can carry up to 29 seated troops along with two crew, depending on customer configuration. The helicopter is marketed for troop transport, casualty evacuation, and combat search and rescue duties, and is similar to the civilian EC225.
Development
The EC725 was developed to meet a French Air Force requirement for a specialist helicopter for Combat Search and Rescue operations. The AS 532 A2 Cougar model was examined and rejected for this purpose following extensive trials between 1996 and 1999. The primary improvements desired by the French Air Force were more powerful engines, greater flight endurance and improved combat durability.[1] Eurocopter opted to pursue development of a more ambitious derivative of the AS 532 to meet this need, which was later designated as the EC725. The EC725 was initially named Cougar Mk II+ due to treaty reasons. The new aircraft also featured new mission equipment and autonomous avionics, along with other changes to meet the French specification.[1]
On 27 November 2000, the first EC725 prototype performed its maiden flight at Marignane, and on 15 January 2001, the first public presentation of the new helicopter took place.[2] In concurrent development of the military-orientated EC725, Eurocopter also developed a civil-orientated counterpart, which was designated as the EC225. The French Air Force subsequently ordered an initial six EC725s to perform the Combat Search & Rescue mission, the first of these was delivered in February 2005. A follow-on order for eight more EC725s was placed for the French Armed Forces in November 2002; a total fleet of 20 EC725s in French service was envisioned in 2004.[1][3]
By 2015, the EC725, since re-designated as the H225M, was being manufactured on two separate production lines in France and Brazil. In July 2015, Airbus Helicopters announced that it was considering setting up a third assembly line in India if the firm was successful at winning an Indian tender for naval helicopters.[4]
Design

The EC725 is based on the Eurocopter AS 532 Cougar, improving upon the design with a five-blade composite main rotor incorporating a new airfoil shape to reduce vibration levels. The helicopter can be fitted with removable armour plating to protect the troops and is powered by two Turbomeca Makila 1A4 turboshaft engines mounted over the cabin, which feature a dual-channel Full Authority Digital Engine Control (FADEC) system. They can be fitted with an anti-icing system to enable the aircraft to operate in very cold climates. Other improvements include a reinforced main rotor gearbox and an all glass cockpit. The cockpit is equipped with an integrated display system featuring a digital map and Active Matrix Liquid Crystal Displays.[1]
The helicopter has day and night time search and rescue capabilities by way of a search radar and Forward Looking Infra Red (FLIR); these allow the EC725 to be flown under visual meteorological and instrument flight rules conditions.[5] The EC725 can be equipped with various military equipment and armaments, such as a pair of 7.62 mm FN MAG machine guns mounted within forward left and right windows, or a pair of 68 mm (2.75") Thales Brandt or Forges de Zeebrugge side-mounted rocket launchers, each with 19 rockets, or the MU90 Impact aerial-launched torpedo.[5]

Brazilian EC725s are equipped with a Helibras-built countermeasures suite, which includes chaff and flares to confuse radar and heat-guided missiles respectively;[6] Thales has also produced self-protection systems to equip French EC725s.[7] The Exocet anti-ship missile has also been integrated upon Brazilian Navy EC725s.[8]
Eurocopter developed four primacy cabin configurations for the type. The Troop Transport version contains a seating arrangement for a maximum of 29 troops, in addition to the crew. A dedicated VIP transport version is designed to contain between 8 and 12 passengers. The Casualty Evacuation version can carry up to 12 stretchers along with a total of four seated medical staff. The Combat SAR configuration is fully equipped to perform search and rescue duties in a combat environment.[1] According to Airbus Helicopters, the H225M is capable of undertaking various mission roles including combat search and rescue, long-range tactical transport, aeromedical transport, logistic support and shipboard maritime operations.[9]
Armed version carries gun pods, rocket pods and Hellfire air-to-surface missiles (HForce Generic Weapon System (GWS) with Thales Scorpion helmet-mounted sight display (HMSD) and Wescam electro-optical sensor).[10][11][12][13]
Operational history
Less than six weeks after formally entering service, three French Air Force EC725s were dispatched to Cyprus to evacuate civilians from Lebanon during Opération Baliste in the summer of 2006.[14] In December 2006, the French Air Force began deploying EC725s to the war in Afghanistan to support the coalition forces operating in region. EC725s in the Afghan theatre were based at Kabul International Airport.[15][16] In 2013, French EC735s were receiving several upgrades, these include a new SAGEM Forward looking infrared sensor, new door-mounted Nexter-built machine guns, FADEC changes for low temperature operations, and reduced maintenance requirements.[17]

In 2008, the Brazilian Government announced that the Helibras factory in Itajubá, Minas Gerais, will produce an initial 50 EC725s under a $1 billion order.[18][19] These 50 helicopters are to be used by the Brazilian Navy, the Brazilian Air Force (FAB) and Brazilian Army Aviation Command.[20] By December 2010, three helicopters were undergoing flight tests prior to entering military service. In 2012, Helibras begin assembly of the rest of the order.[21] In April 2014, Helibras and MBDA were in the process of integrating the anti-ship Exocet missile, which are also 50%-built in Brazil.[22] On 19 June 2014, the Brazilian Navy formally accepted delivery of the first EC725.[23] By July 2015, the Brazilian armed forces had taken delivery of 16 H225Ms; deliveries were reported at the time to continue until 2019.[20] By 1 October 2015, Brazil's H225M fleet had attained 10,000 flight hours.[24] In December 2015, Helibras delivered the first pair of H225Ms to be delivered to a full operational capability (FOC) standard to the Brazilian military.[25]
In March 2009, Mexico became the second export customer for the type when the Secretariat of National Defense placed an order for six armed EC725s for civil security and transport missions; the second batch of six was ordered in September 2010.[26] On 30 April 2015, a Mexican Air Force EC725 made an emergency landing after the tail rotor was struck by a rocket-propelled grenade, killing six soldiers and wounding 12, while engaged in Operation Jalisco, a coordinated multi-force action to combat the Jalisco New Generation Cartel (CJNG) in both Jalisco and Colima.[27] In May 2015, Mexico was reportedly in the process of negotiating the purchase of an additional 50 H225Ms.[28]
In April 2009, Malaysia placed an order for 12 EC725s in a Search and Rescue configuration to replace the ageing Sikorsky SH-3 Sea King fleet.[29] In 2014, following Malaysia Airlines Flight 370 going missing, the Royal Malaysian Air Force deployed their EC725s was deployed to search the plane along C-130s around the South China Sea and Strait of Malacca.[30][31] Following the 2015 Sabah earthquake, several Royal Malaysia Air Force EC725s were despatched to Laban Rata in Mount Kinabalu to rescue stranded climbers and retrieve the deceased.[32][33]

In November 2014, the Indonesian Air Force took delivery of the first of six EC725s for Combat Search and Rescue (CSAR) operations.[34] Indonesian Aerospace (PT. Dirgantara Indonesia/PTDI) performs the maintenance, repair and overhaul activities upon Indonesia's EC725 fleet; the firm also supply the tail booms and airframe assemblies for EC225s and EC725s worldwide, the first locally assembled main fuselage assembly was delivered in November 2013.[35][36]
On 21 April 2015, Poland announced that the H225M was the sole winner of an order for 50 units to replace their tri-service fleet of Mil Mi-8 and Mil Mi-14. If signed, the contract would consist of 16 transport, 13 CSAR, eight ASW, eight SOS and five MEDEVAC helicopters to be assembled in Poland.[37] In May 2015, the H225M passed state trials held in 33rd Air Base over the course of two weeks.[38] In October 2015, Poland's armament inspectorate reported that the total procurement cost would be roughly PLN13.3 billion ($3.5 billion), 40 per cent of which being for training and logistical support.[39] However, in October 2016, Poland dropped out of offset negotiations prior to concluding the deal.[40] According to former President of Poland Aleksander Kwasniewski, the H225M purchase had been part of a gentlemen's agreement under which France had cancelled an arranged sale of two Mistral-class amphibious assault ships to Russia.[41]
In June 2015, it was revealed that Kuwait was negotiating to acquire up to 24 EC725s Caracals for the Kuwait Air Force.[42] In August 2016, the Kuwait Ministry of Defense and Airbus Helicopters signed a $1 billion contract for 30 H225M helicopters; 24 of these are for the Kuwait Air Force and six are for the Kuwait National Guard, these are to be armed with anti-ship missiles[43]
The EC725 has been submitted to the Indian Navy's Naval Multi-Role Helicopter (NMRH) competition, seeking 120 helicopters to replace its aging Westland Sea King fleet.[44][45] In October 2015, Indian authorities were holding discussions to finalize a deal for 14 H225s for the Indian Coast Guard. Media reports note that Airbus was in the lead to win the contract, having made a lower financial bid than rival Sikorsky for their S-92. The submitted bid complies with a 30% offset clause, requiring Airbus to invest Rs.600 crore of the Rs.2000 crore bid in India's defense and aerospace manufacturing sector.[46]
On 7 Nov 2016, Singapore announced that the H225M would replace its existing Super Pumas, which had been in service since 1983, after a rigorous evaluation process. This would enable the Republic of Singapore Air Force to meet its requirements for a wide spectrum of operations, including Search and Rescue (SAR), Aeromedical Evacuation (AME) and Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) operations, more efficiently with fewer helicopters and less manpower.[47]
Operators



- Hungarian Defence Forces (16 on order)[49]
- Kazakhstan Air Force (20 on order)[50]
- Republic of Singapore Air Force (16 on order)[48]
- Royal Thai Air Force (8 in service, 4 more on order)[48][51][52][53]
Specifications (EC725 Caracal)
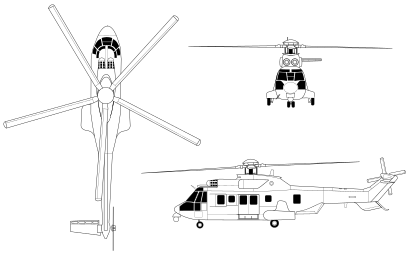


Data from {Eurocopter.com}[54]
General characteristics
- Crew: 1 or 2 (pilot + co-pilot)
- Capacity: 1 chief of stick + 28 troops or 5,670 kg (12,500 lb) payload
- Length: 19.5 m (64 ft 0 in)
- Height: 4.6 m (15 ft 1 in)
- Empty weight: 5,330 kg (11,751 lb)
- Gross weight: 11,000 kg (24,251 lb)
- Max takeoff weight: 11,200 kg (24,692 lb)
- Powerplant: 2 × Turboméca Makila 2A1 turboshaft engines, 1,776 kW (2,382 hp) each
- Main rotor diameter: 16.20 m (53 ft 2 in)
- Main rotor area: 206.1 m2 (2,218 sq ft)
Performance
- Maximum speed: 324 km/h (201 mph, 175 kn) in level flight
- Cruise speed: 285 km/h (177 mph, 154 kn)
- Never exceed speed: 324 km/h (201 mph, 175 kn)
- Range: 857 km (533 mi, 463 nmi)
- Ferry range: 1,325 km (823 mi, 715 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 6,095 m (19,997 ft)
- Rate of climb: 7.4 m/s (1,460 ft/min)
See also
Related development
- Atlas Oryx
- Aérospatiale SA 330 Puma
- Eurocopter AS332 Super Puma
- Eurocopter EC225 Super Puma
- Eurocopter AS532 Cougar
- KAI KUH-1 Surion
Aircraft of comparable role, configuration, and era
- Sikorsky S-92 (Sikorsky CH-148 Cyclone)
- AgustaWestland AW101 (Lockheed Martin VH-71 Kestrel and AgustaWestland CH-149 Cormorant)
- Mil Mi-38
- NHIndustries NH90
- Sikorsky MH-60R Seahawk
Related lists
References
- ^ a b c d e Cite error: The named reference
intellectwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "French Stimulus: 5 More EC725 Helicopters." Defense Industry Daily, 4 February 2010.
- ^ "EC 725 Cougar Medium Multimission Helicopter". airforce-technology.com. Retrieved 26 September 2013.[unreliable source?]
- ^ Perry, Dominic. "Airbus Helicopters may build fourth H225M assembly line." Flight International, 10 July 2015.
- ^ a b Glowacki, Bartosz. "Poland begins evaluation tests of H225M Caracal." Flight International, 15 May 2015.
- ^ "Brazilian EC725 integrated with self-protection system." Shepard Media, 17 September 2013.
- ^ "Thales to provide self-protection systems for French forces' EC725 Caracal."[permanent dead link] Thales Group, 8 February 2010.
- ^ Perry, Dominic. "Helibras continues Exocet integration on H225M." Flight International, 4 December 2015.
- ^ Parameswaran, Prashanth. "Thailand’s Air Force Gets a Boost with New Helicopters." The Diplomat, 27 August 2015.
- ^ https://www.airbus.com/newsroom/press-releases/en/2018/12/hungary-orders-16-h225m-multi-role-helicopters.html
- ^ https://www.janes.com/article/85232/hungary-buys-h225m-helos-with-hforce-weapons-system
- ^ https://www.flightglobal.com/news/articles/analysis-airbus-helicopters-on-target-with-hforce-s-450758/
- ^ https://www.airbus.com/helicopters/military-helicopters/hforce.html
- ^ "‘Baliste’ Operation." ROTOR Online, January 2006.
- ^ Hoyle, Craig. "VIDEO: French air force EC725 helicopters complete Afghan deployment." Flight International, 19 September 2007.
- ^ "Afghanistan: mission accomplished." ROTOR Online, February 2008.
- ^ Pocock, Chris. "French Squadron Uses EC725 Helicopters to “Fight and Rescue." AIN Online, 18 June 2013.
- ^ Farias, Ivy (8 September 2008). "Brasil produzirá em Minas Gerais helicópteros para as Forças Armadas". Agência Brasil. Retrieved on 11 July 2009.
- ^ "Brazil’s $1B+ Order for EC725 Cougar Helicopters." Defense Industry Daily, 5 January 2012.
- ^ a b "Continued delivery of the H225M for the Brazilian armed forces despite announcement of 2 year delay." defesanet, 3 July 2015.
- ^ "Brazil's armed forces test-fly EC725". Retrieved 2 January 2011.
- ^ "Helibras Integrating Exocet Onto EC725 Helicopter." Aviation Week, 29 April 2014.
- ^ Perry, Dominic. "Airbus Helicopters hands over first EC725 fully assembled in Brazil." Flight International, 19 June 2014.
- ^ "Brazilian Armed Forces Exceed 10,000 Flight Hours with H225M." Airbus Helicopters, 1 October 2015.
- ^ Dominic, Perry. "Brazilian army and air force take first FOC-standard H225Ms." Flight International, 22 December 2015.
- ^ "Mexico Orders Eurocopter’s EC725 Helicopters." Defense Industry Daily, 20 September 2010.
- ^ "7 dead, 19 wounded, 19 arrested in Jalisco." Mexico News Daily, 2 May 2015.
- ^ "Mexico may buy 50 Airbus military helicopters -source." Reuters, 27 May 2015.
- ^ "Malaysia Ordering EC725 SAR Helicopters." Defense Industry Daily, 22 April 2009.
- ^ "M.O.T Malaysia on Twitter".
- ^ "Alert 5 " Aircraft searching for #MH370 using RMAF Gong Kedak as base". Military Aviation News.
- ^ "Sabah Quake: Army on standby to be deployed says Hishammuddin". Retrieved 6 June 2015.
- ^ Sario, Ruben; Lee, Stephanie. "Sabah quake: Missing mostly Malaysians and Singaporeans – Nation | The Star Online". Retrieved 6 June 2015.
- ^ "Indonesia receives first CSAR dedicated EC725 helicopter." helipress.it, 10 November 2014.
- ^ "Airbus Helicopters". Archived from the original on 26 February 2014. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Indonesia delivers first locally produced main fuselage assembly Eurocopter EC725 and EC225." Australian Aviation, 28 November 2013.
- ^ Warsaw details reasons behind H225M selection. flightglobal.com, 22 April 2015
- ^ Larrinaga, Nicholas de. "H225M Caracal passes Polish helicopter trials". IHS Jane's Defence Weekly, 28 May 2015.
- ^ Glowacki, Bartosz. "Poland to launch attack helicopter talks with bidders." Flight International, 7 October 2015.
- ^ "Poland drops Caracal Helicopter talks with Airbus" Defense News, 5 Oct 2016.
- ^ Fryer-Biggs, Zachary. "Former Polish president says failed helicopter deal supposed to 'make up' for Mistrals." IHS Jane's Defence Industry, 18 October 2016.
- ^ "France nears $1.1bn Kuwait deal to sell Airbus helicopters." Reuters, 11 June 2015.
- ^ Pocock, Chris. "Kuwait Signs Contract for 30 H225M Caracal Helicopters." AIN Online, 9 August 2016.
- ^ Sobie, Brendan. "EC725, NH90 S-70B and MH-60R in frame as Indian navy starts hunt for anti-submarine warfare helicopter replacement." Flight International, 30 May 2006.
- ^ "The EC725 has been proposed for the 120 Naval Multi-Role Helicopter (NMRH) campaign and the 14 shore-based helicopters requirement of the Indian Coast Guard." Archived 4 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine forceindia.net, February 2015.
- ^ "Coast Guard to finally get choppers it wanted post 26/11; Airbus emerges as lead". Economic Times. EconomicTimes.IndiaTimes.com. ET Bureau. 15 October 2015. Retrieved 15 October 2015.
- ^ Government of Singapore (7 November 2016). "MINDEF Signs Contracts to Acquire New Medium- and Heavy-Lift Helicopters". Retrieved 7 November 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k "World Air Forces 2018". Flightglobal Insight. 2018. Retrieved 4 August 2018.
- ^ "Hungary orders 16 H225M multi-role helicopters". Airbus. Retrieved 14 December 2018.
- ^ "Kazakhstan orders 20 Eurocopter EC725s". helihub.com. Retrieved 12 March 2013.
- ^ Jennings, Gareth (20 September 2018). "Thailand orders four more H225M helos". IHS Jane's 360. London. Archived from the original on 20 September 2018. Retrieved 20 September 2018.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Dominguez, Gabriel (24 October 2018). "RTAF receives two more H225M helos". IHS Jane's 360. London. Archived from the original on 24 October 2018. Retrieved 29 October 2018.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Steuer, Guillaume (24 October 2018). "The Royal Thai Air Force receives two new H225Ms". Airbus. Thailand. Archived from the original on 25 October 2018. Retrieved 29 October 2018.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Eurocopter Cougar EC725 Technical Data" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 29 September 2007. Retrieved 12 July 2007.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)

