Goryōkaku
You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in Japanese. (January 2021) Click [show] for important translation instructions.
|
| Goryōkaku | |
|---|---|
五稜郭 | |
| Part of Boshin War | |
| Near Hakodate in Japan | |
 Goryōkaku viewed from Goryōkaku Tower | |
Governmental hall of the Republic of Ezo | |
| Coordinates | 41°47′49″N 140°45′25″E / 41.79694°N 140.75694°E |
| Type | Star fort |
| Site history | |
| Built | 1866 |
| Built by | Takeda Ayasaburō |
| Battles/wars | Boshin War |
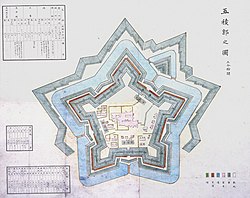 19th century map of Goryōkaku | |
Goryōkaku (五稜郭, lit. 'five-point fort') is a star fort in the Japanese city of Hakodate on the island of Hokkaido.[1] The fortress was completed in 1866. It was the main headquarters of the short-lived Republic of Ezo.
History
[edit]Goryōkaku was designed in 1855 by Takeda Ayasaburō, a scholar of Dutch. [2] He studied the fortified cities of Europe in the early modern period to design a fort that could protect against battles using guns and cannons. It took nearly seven years for the construction.[3] The fortress was completed in 1866, two years before the collapse of the Tokugawa shogunate. It is shaped like a five-pointed star. This allowed for greater numbers of gun emplacements on its walls than a traditional Japanese fortress, and reduced the number of blind spots where a cannon could not fire.
The fort was built by the Tokugawa shogunate, he ordered Takeda Ayasaburō to design the fort for the purpose of protecting Tsugaru Strait.[3] It became the capital of the Republic of Ezo, a state that existed only in 1869. It was the site of the last battle of the Boshin War between the Republic and the Empire of Japan. The fighting lasted for a week (June 20–27, 1869).
Park
[edit]Today, Goryōkaku is a park declared as a Special Historical Site, being a part of the Hakodate city museum and a citizens' favorite spot for cherry-blossom viewing in spring.
See also
[edit]- List of Special Places of Scenic Beauty, Special Historic Sites and Special Natural Monuments
- Benten Daiba, another key fortress of the Republic of Ezo
- Citadel Hill, a similar shaped fortress in Nova Scotia, Canada
- Fort Bourtange, a similarly shaped fortress in the Netherlands
- List of foreign-style castles in Japan
- Palmanova
References
[edit]- ^ Hinago, Motoo (1986). Japanese Castles. Kodansha International Ltd. and Shibundo. pp. 131–133. ISBN 0870117661.
- ^ Schmorleitz, Morton S. (1974). Castles in Japan. C. E. Tuttle Company. p. 144. ISBN 0-8048-1102-4.
- ^ a b url=https://www.goryokaku-tower.co.jp/en/history/
Further reading
[edit]- Benesch, Oleg and Ran Zwigenberg (2019). Japan's Castles: Citadels of Modernity in War and Peace. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 374. ISBN 9781108481946.
- De Lange, William (2021). An Encyclopedia of Japanese Castles. Groningen: Toyo Press. p. 600. ISBN 978-9492722300.
- Schmorleitz, Morton S. (1974). Castles in Japan. Tokyo: Charles E. Tuttle Co. p. 144. ISBN 0-8048-1102-4.