Lviv Railways
 | |
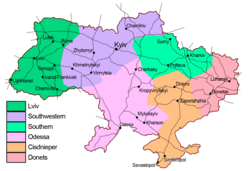 Subdivisions of Ukrainian Railways | |
| Overview | |
|---|---|
| Headquarters | Lviv |
| Locale | Ukraine |
| Dates of operation | 1861–present |
| Predecessor | Lvov Railways (Soviet Union) Kovel Railways (Soviet Union) |
| Technical | |
| Track gauge | 1,520 mm (4 ft 11+27⁄32 in) |
| Length | 4,521 km (2,810 mi) |
| Other | |
| Website | http://railway.lviv.ua/ |
Lviv Railways (abbreviated as LR) (Ukrainian: Львівська залізниця) is a territorial branch company of Ukrzaliznytsia headquartered in Lviv.
General description
Lviv Railways administers all railroads of Lviv Oblast, Zakarpattia Oblast, Ivano-Frankivsk Oblast, Chernivtsi Oblast, Ternopil Oblast, Volyn Oblast and most of Rivne Oblast. It has five directories of territorial administration: Lviv, Zakarpattia, Ivano-Frankivsk, Ternopil, Volyn. The jurisdiction of the directories does not necessarily correspond to the regional division of Ukraine. Its territorial administration coverage borders with the Belarusian Railway to the north, with its Ukrzaliznytsia partner Southwestern Railways to the east, with the Calea Ferată din Moldova to the southeast, with the Căile Ferate Române to the south, with the Hungarian State Railways and the Railways of Slovak Republic – ŽSR to the southwest, with the Polish State Railways to the west.
As of 2008 LR operates on 4521 km of track. 3207 km of track is electrificated majorly between Chop and Lviv. Partial electrification is available as well. There are 354 stations operated by Lviv Railways classified as passenger, freight, precinct, sorting, and intermediate. Eight out of the 354 stations are railroad terminals which are located in each regional center as well as the city of Chop. Lviv Railways has also 19 border-customs stations with Poland, Belarus, Slovakia, Hungary, Romania, and Moldova.
The double tracks lay between: Lviv – Zdolbuniv – Rivne; Lviv – Mostyska – (border checkpoint); Lviv – Stryi – Chop; Lviv – Ternopil – Pidvolochysk; Zdolbuniv – Kivertsi. Other branches consist of a single track.
Administrative divisions
- Lviv Administration
- Ternopil Administration
- Uzhhorod Administration
- Ivano-Frankivsk Administration
- Rivne Administration
Trains and rolling stock
International
Express
- 171/172 Lviv – Rivne
- 173/174 Lviv – Rivne
- 820/821 Lviv – Ternopil
Branded
- 25/26 "Karpaty" (Carpathians) Lviv – Odessa
- 43/44 "Prykarpattia" Ivano-Frankivsk – Kiev
- 83/84 "Holubi ozera" (Blue lakes) Kovel – Odessa
- 87/88 "Lisova pisnya" (Forest song) Kovel – Simferopol (It was rerouted to Novooleksiyivka after Russian occupiaton of Crimea in 2014)
- 91/92 "Lviv" Lviv – Kiev
- 97/98 "Halychyna" Lviv – Kiev
- 99/100 "Zakarpattia" Uzhhorod – Kiev
- 363/364 "Svityaz" Kovel – Kiev
- 627/628 "Bukovyna" Chernivtsi – Kiev
Suburban
Commuter lines are coded in regards to the railway administrative division. Lviv Railways commuter lines have four digits and start with 6. Second digit refers to one of the Lviv Railways administrations: 4 – Ivano-Frankivsk; 2 – Ternopil; 5 – Uzhhorod; 0 and 1 – Lviv; 3 – Lutsk.
Fast
Passenger
Electric/Diesel trains with elevated luxury
History
The first railway line built in the current territory of Ukraine was the Przemyśl – Lviv line, which was part of the connection from Kraków. The line was constructed by k.k. priv. Galizische Carl Ludwig-Bahn which later became nationalised by the Imperial Austrian State Railways. It was built in 1861 under the initiative of Leon Sapieha, and was 98 kilometres long. That was the first railway line on the Ukrainian territory.[1] The first steam locomotive which departed from Przemyśl to Lwow on 4 November 1861 at 10.00 in the morning was called "Jaroslaw". In 1866 another railway was built connecting Czernowitz with Lwow (by Lemberg-Czernowitz-Jassy Eisenbahn-Gesellschaft). At that time the Kovel railway station belonged to Vistula River Railroad. In 1869 Carl Ludwig Railways built a railroad from Lviv to Brody that was opened on 12 July. In 1870 another branch reached Tarnopil. On 4 November 1871 the railroad network was connected with railroads of Russian Empire near Volochysk over the Zbruch river, ultimately connecting Odessa with Hamburg. In 1884 was created the General Directory which included six state railways. Those railways later formed the local directory of state railway transport which effectively competed with the Carl Ludwig Railways. On 1 January 1892 the government of Austria-Hungary adopted a law nationalising all railways from private companies. In the Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria three railway directories were formed: Kraków, Lwow, and Stanislawow.
Before World War I the total length of railways in the region was 2676 kilometres.
Gallery
-
Railway tunnel in Carpathian Mountains




