Morus rubra
| Morus rubra | |
|---|---|

| |
| 1809 illustration[1] | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| (unranked): | |
| (unranked): | |
| (unranked): | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | |
| Species: | M. rubra
|
| Binomial name | |
| Morus rubra L. 1753
| |
| |
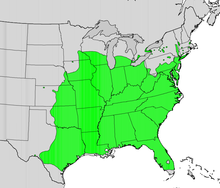
| Native range | |
Morus rubra, commonly known as the red mulberry, is a species of mulberry native to eastern and central North America. It is found from Ontario, Minnesota, and Vermont south to southern Florida, and west as far as southeastern South Dakota, Nebraska, Kansas, and central Texas. There have been reports of isolated populations (very likely naturalized) in New Mexico, Idaho, and British Columbia.[2]
Common in the United States, it is listed as an endangered species in Canada,[3][4] and is susceptible to hybridization with the invasive white mulberry (M. alba), introduced from Asia.[5]
Characteristics
Red mulberry is a deciduous tree, growing to 10–15 m (35–50 ft) tall, rarely 20 m (65 ft), with a trunk up to 50 cm (20 in)* in diameter. It is a small to medium-sized [6]tree that reaches a height of 70 feet and lives up to 125 years. The leaves are alternate, 7–14 cm (2+3⁄4–5+1⁄2 in) long and 6–12 cm (2+1⁄4–4+3⁄4 in) broad, simple, broadly cordate, with a shallow notch at the base, typically unlobed on mature trees although often with 2-3 lobes, particularly on young trees, and with a finely serrated margin.[3] The upper surface of the leaves is noticeably rough, similar in texture to fine sandpaper, and unlike the lustrous upper surface of the leaves of white mulberry (M. alba).[7] The underside of the leaves is covered with soft hairs. The leaf petiole exudes milky sap when severed.[8] Red mulberry is hardy to subzero temperatures, relatively hardy to drought, pollution, and poor soil, though the white mulberry is hardier.[9]
The flowers are relatively inconspicuous: small, yellowish green or reddish green, and opening as leaves emerge. Male and female flowers are usually on separate trees although they may occur on the same tree.
The fruit is a compound cluster of several small achenes surrounded by a fleshy calyx, similar in appearance to a blackberry, 2–3 cm (3⁄4–1+1⁄4 in) long, when it is ripening it is red or dark purple, edible and very sweet with a good flavor.[3]
Uses
The first English colonists to explore eastern Virginia in 1607 mentioned the abundance of both mulberry trees and their fruit, which was eaten, sometimes boiled, by the native Powhatan tribes.
Today, mulberries are eaten raw, used in fruit pastries, and fermented into wine.
The wood may be dried and used for smoking meats with a flavor that is mild and sweet.
References
- ^ Duhamel du Monceau, H.L., Traité des arbres et arbustes, Nouvelle édition [Nouveau Duhamel], vol. 4: t. 23 (1809) [P.J. Redouté] drawing: P.J. Redouté lithograph Tassaert family: Moraceae subfamily: Moroideae tribe: Moreae 202746 ruber, rubra, rubrum 202746 ruber, rubra, rubrum Illustration contributed by: Real Jardín Botánico, Madrid, Spain
- ^ "Morus rubra". County-level distribution map from the North American Plant Atlas (NAPA). Biota of North America Program (BONAP). 2014.
- ^ a b c Flora of North America Editorial Committee (ed.). "Morus rubra". Flora of North America North of Mexico (FNA). New York and Oxford: Oxford University Press – via eFloras.org, Missouri Botanical Garden, St. Louis, MO & Harvard University Herbaria, Cambridge, MA.
- ^ Ambrose, J. D., & Kirk, D. (2004). National Recovery Strategy for Red Mulberry (Morus rubra L.). Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources, Guelph, Ontario, Canada
- ^ Burgess, K. S.; Morgan, M.; Deverno, L.; Husband, B. C. (2005). "Asymmetrical introgression between two Morus species (M. alba, M. rubra) that differ in abundance" (PDF). Molecular Ecology. 14 (17). University of Toronto, Barrett Lab: 3471–3483. PMID 16156816.[dead link]
- ^ http://www.nrcs.usda.gov/Internet/FSE_PLANTMATERIALS/publications/lapmcbr7910.pdf
- ^ Farrar, J.L. (1995). Trees in Canada. Fitzhenry and Whiteside/Canadian Forest Service, Markham, Ontario.
- ^ Trees of Alabama and the Southeast: Red Mulberry, Morus rubra, Moraceae.
- ^ California Rare Fruit Growers
External links
![]() Media related to Morus rubra at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Morus rubra at Wikimedia Commons
![]() Data related to Morus rubra at Wikispecies
Data related to Morus rubra at Wikispecies
