Mountainous Republic of the Northern Caucasus
Mountainous Republic of the Northern Caucasus | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1917–1920 | |||||||||
|
Flag | |||||||||
| Capital | Temir-Khan-Shura (now Buynaksk) | ||||||||
| Common languages | Russian · Chechen · Ingush Ossetic · Kabardian · Balkar Dagestani languages | ||||||||
| Government | Federal republic | ||||||||
| Historical era | World War I · Interwar period | ||||||||
• Independence declared | March 1917 | ||||||||
• Replaced by Mountain Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic | June 1920 | ||||||||
| Currency | Ruble | ||||||||
| |||||||||
The Mountainous Republic of the Northern Caucasus (MRNC; also known as the Mountain Republic or the Republic of the Mountaineers; 1917–1920) was a short-lived state situated in the Northern Caucasus. It broke away from the Russian Empire during the February Revolution, shortly before the start of the Russian Civil War.
MRNC included most of the territory of the former Terek Oblast and Dagestan Oblast of the Russian Empire, which now form the republics of Chechnya, Ingushetia, North Ossetia–Alania, Kabardino-Balkaria, Dagestan and part of Stavropol Krai of the Russian Federation. The total land area was about 70,000 square kilometers (27,000 sq mi), with a population of about 1 million. Its capital was initially at Vladikavkaz, then Nazran, and finally Temir-Khan-Shura.
The state was captured by Soviet Russian forces in 1920, who transformed it into the Mountain Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic.
History

The "Union of the Peoples of the Northern Caucasus" was created in March 1917, and an Executive Committee of the Union was elected. The Chairman of the Executive Committee was one of the leaders of the National‐Liberation movement of the Peoples of the Northern Caucasus, Tapa Tchermoeff. The "Nizam" of Imam Shamil (the Constitution of Shamil of 1847) was adopted on 5 August 1917 by the "Central Committee of the Northern Caucasus". The republic was officially established on 11 May 1918, after the collapse of the Russian Tsarist empire in the Russian revolution of 1917, when the Government of the MRNC was established.
The main founders of the MRNC included Said Shamil (grandson of Imam Shamil, who in 1924 would become a founder and leader of the "Committee of Independence of the Caucasus" in Germany), Prime Minister Tapa Tchermoeff, Sheikh Ali-Khaji Akusha and Haidar Bamat. The Republic's capital was Temir-Khan-Shura.
The Mountainous Republic was de jure recognized by the Ottoman Empire, Germany, the Azerbaijan Democratic Republic, the Democratic Republic of Georgia and the Kuban People's Republic.
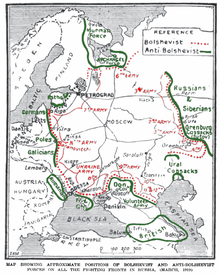
During the Russian Civil War, the Mountaineers were engaged in fierce clashes against the invading White troops of General Anton Denikin's Volunteer Army. The fighting ended in January 1920, when Denikin's army was completely defeated by the XI Red Army. The advancing Red Army was at first greeted with red flags in the villages of the Northern Caucasus, but the promises of autonomous rule made by the Bolsheviks went unrealized.
In June 1920, the MRNC was occupied by the Red Army of Bolshevik Russia and the Government of the republic was forced to leave the Caucasus. In January 1921, the Soviet Mountain Republic of the Russian SFSR was established.
See also
Further reading
- J. "Obedinennyi Kavkaz" ("Vereinigtes Kaukasien"), 1–3 (30–32), München, 1954. Template:Ru icon
- Levan Z. Urushadze, "About the history of the question of unity of the Caucasian Peoples". J. "Amirani", XIII, Montreal‐Tbilisi, 2005, pp. 72–87.
- Baddeley, J. F., 1908, The Russian Conquest of the Caucasus, Longmans, Green, and Co., London
- Madeleine Henrey, Madeleine Grown Up, J. M. Dent & Sons, London, 1954.
- "Caucasian Republic Mission to the Peace Conference Appeal for Help", The Morning Post, London, Friday 4 April 1919.
- Elti Temihan, Tapa Tchermoeff: Obituary, The Times.
- Storozhenko (ed.), Ingushetia and Chechen Republic Map, Northern Caucasian Aerogeodesic Company of Roskartografia, Russia, 1995.
- Kathleen R. Jackson, Marat Fidarov, Essays on the History of the North Caucasus, HHN Media, New York, 2009.

