S-IVB
This article needs additional citations for verification. (July 2009) |
 S-IVB-206 which was used for the Skylab 2 flight | |
| Manufacturer | Douglas |
|---|---|
| Country of origin | USA |
| Used on | Saturn IB (stage 2) Saturn V (stage 3) |
| General characteristics | |
| Height | 58 feet 5 inches (17.81 m) |
| Diameter | 21 feet 8 inches (6.60 m) |
| Gross mass | 253,000 pounds (115,000 kg) |
| Propellant mass | 229,000 lb (104,000 kg) |
| S-IVB | |
| Powered by | 1 J-2 engine |
| Maximum thrust | 232,250 pounds-force (1,033,100 N) |
| Specific impulse | 421 s (4.13 km/s) |
| Burn time | 475 seconds |
| Propellant | LOX/LH2 |
The S-IVB (sometimes S4b, always pronounced "ess four bee") was built by the Douglas Aircraft Company and served as the third stage on the Saturn V and second stage on the Saturn IB. It had one J-2 engine. For lunar missions it was fired twice: first for the orbit insertion after second stage cutoff, and then for translunar injection (TLI).
History
The S-IVB evolved from the upper stage of the Saturn I rocket, the S-IV, and was the first stage of the Saturn V to be designed. The S-IV used a cluster of six engines but used the same fuels as the S-IVB — liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen. It was also originally meant to be the fourth stage of a planned rocket called the C-4, hence the name S-IV.
Eleven companies submitted proposals for being the lead contractor on the stage by the deadline of 29 February 1960. NASA administrator T. Keith Glennan decided on 19 April that Douglas Aircraft Company would be awarded the contract. Convair had come a close second but Glennan did not want to monopolize the liquid hydrogen-fueled rocket market as Convair was already building the Centaur rocket stage.
In the end the Marshall Space Flight Center decided to use the C-5 rocket (later called the Saturn V), which had three stages and would be topped with an uprated S-IV called the S-IVB which instead of using a cluster of engines would have a single J-2 engine. Douglas was awarded the contract for the S-IVB because of the similarities between it and the S-IV. At the same time it was decided to create the C-IB rocket (Saturn IB) that would also use the S-IVB as its second stage and could be used for testing the Apollo spacecraft in Earth orbit.
Configuration
Douglas built two distinct versions of the S-IVB, the 200 series and the 500 series. The 200 series was used by the Saturn IB and differed from the 500 in the fact that it did not have a flared interstage and had less helium pressurization on board as it would not be restarted. On the 500 series, the interstage needed to flare out to match the larger diameter of the S-IC and S-II stages of the Saturn V. The 200 series also had three solid rockets for separating the S-IVB stage from the S-IB stage during launch. On the 500 series this was reduced to two, and additional linear APS thrusters were added for ullage operations prior to restarting the J-2 engine.
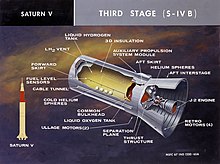
The S-IVB carried 73,280 liters (19,359 U.S. gallons) of LOX, massing 87,200 kg (192,243 lbs). It carried 252,750 liters (66,770 U.S. gallons) of LH2, massing 18,000 kg (39,683 lbs). Empty mass was 10,000 kg (23,000 lb)[1][2]
Attitude control was provided by 2 Auxiliary Propulsion System pods, and by engine gimballing. The APS modules provided 150 pounds of thrust each, and were fuelled by a hypergolic mixture of dinitrogen tetroxide and monomethyl hydrazine. They were used for three-axis control during coast phases, roll control during J-2 firings, and (on the 500 series) ullage for the second ignition of the J-2 engine and deorbit into the moon.[2]
A surplus S-IVB tank, serial number 212, was converted into the hull for Skylab, the United States' first space station. Skylab was launched on a Saturn V on May 14, 1973, and re-entered the atmosphere on July 11, 1979. A second S-IVB, serial number 515, was also converted into a backup Skylab, which never flew.
During Apollo 13, Apollo 14, Apollo 15, Apollo 16 and Apollo 17, the S-IVB stages were crashed into the Moon to perform seismic measurements used for characterizing the lunar interior.
-
Distant view of Apollo 7 S-IVB stage
-
Apollo 8 S-IVB, shortly after separation
-
The three versions of the S-IV/S-IVB
Stages built
| 200 Series | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Serial number | Use | Launch date | Current location |
| S-IVB-S | "Battleship" static test stage | On display with the Saturn 1B SA-211 first stage stacked in a launch-ready condition at the Alabama Welcome Center on I-65 in Ardmore, Alabama. 34°57′16″N 86°53′31″W / 34.954548°N 86.89193°W | |
| S-IVB-F | Test stage for the facilities | ||
| S-IVB-D | "Dynamic" test stage delivered to Marshall Space Flight Center in 1965 | U.S. Space & Rocket Center, Huntsville, Alabama 34°42′38″N 86°39′27″W / 34.710456°N 86.657432°W | |
| S-IVB-T | Cancelled December 1964 | ||
| S-IVB-201 | AS-201 | February 26, 1966 | Suborbital test; impacted Atlantic Ocean at 9.6621S, 10.0783E[citation needed] |
| S-IVB-202 | AS-202 | August 25, 1966 | Suborbital test; impacted Atlantic Ocean[3] |
| S-IVB-203 | AS-203 | July 5, 1966 | Exploded in orbit during bulkhead test at end of mission; debris decayed |
| S-IVB-204 | Apollo 5 (originally intended for Apollo 1) | January 22, 1968 | Launched LM-1 into low earth orbit for unmanned test; decayed |
| S-IVB-205 | Apollo 7 | October 11, 1968 | Decayed from low earth orbit |
| S-IVB-206 | Skylab 2 | May 25, 1973 | Decayed from low earth orbit |
| S-IVB-207 | Skylab 3 | July 28, 1973 | Decayed from low earth orbit |
| S-IVB-208 | Skylab 4 | November 16, 1973 | Decayed from low earth orbit |
| S-IVB-209 | Skylab rescue vehicle | Kennedy Space Center | |
| S-IVB-210 | Apollo Soyuz Test Project | July 15, 1975 | Decayed from low earth orbit |
| S-IVB-211 | Unused | U.S. Space & Rocket Center, Huntsville, Alabama | |
| S-IVB-212 | Converted to Skylab | May 14, 1973 | |
| 500 Series | |||
| Serial number | Use | Launch date | Current location |
| S-IVB-501 | Apollo 4 | November 9, 1967 | J-2 restart during first unmanned Saturn V flight test placed S-IVB and spacecraft on earth-intersecting trajectory; impacted Pacific Ocean at 23.435N, 161.207E. |
| S-IVB-502 | Apollo 6 | April 4, 1968 | Second unmanned Saturn V flight test. J-2 restart failed due to damage from pogo oscillation of previous stages; decayed from low earth orbit |
| S-IVB-503 | Destroyed during testing | ||
| S-IVB-503N | Apollo 8 | December 21, 1968 | Heliocentric orbit |
| S-IVB-504 | Apollo 9 | March 3, 1969 | Heliocentric orbit |
| S-IVB-505 | Apollo 10 | May 18, 1969 | Heliocentric orbit |
| S-IVB-506 | Apollo 11 | July 16, 1969 | Heliocentric orbit |
| S-IVB-507 | Apollo 12 | November 14, 1969 | Heliocentric orbit; Believed to have been discovered as an asteroid in 2002 and given the designation J002E3 |
| S-IVB-508 | Apollo 13 | April 11, 1970 | Impacted lunar surface April 14, 1970*[4][5] |
| S-IVB-509 | Apollo 14 | January 31, 1971 | Lunar surface* |
| S-IVB-510 | Apollo 15 | July 26, 1971 | Lunar surface* |
| S-IVB-511 | Apollo 16 | April 16, 1972 | Lunar surface* |
| S-IVB-512 | Apollo 17 | December 7, 1972 | Lunar surface* |
| S-IVB-513 | Apollo 18 (cancelled) | N/A | Johnson Space Center |
| S-IVB-514 | Unused | Kennedy Space Center | |
| S-IVB-515 | Converted to Skylab B | N/A | National Air and Space Museum |
(* See List of artificial objects on the Moon for location.)
Future
The second stage of the Ares I rocket and the proposed Earth Departure Stage (EDS) would have had some of the characteristics of the S-IVB stage, as both would have had an uprated J-2 engine, called the J-2X, with the latter performing the same functions as that of the Series 500 version of the stage (placing the payload into orbit, and later firing the spacecraft into trans-lunar space).
See also
References
- Marshall Space Flight Center, Apollo Systems Description Volume II - Saturn Launch Vehicles, 1 February 1964
- ^ "SP-4206 Stages to Saturn".
- ^ a b "Saturn S=IVB". apollosaturn. Retrieved 2011-11-04.
- ^ AS-202 Press Kit
- ^ Satellite catalog
- ^ LROC page




