Socket 3
Appearance
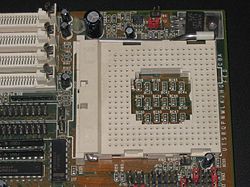 | |
| Type | ZIF |
|---|---|
| Chip form factors | PPGA |
| Contacts | 237 |
| FSB protocol | ? |
| FSB frequency | 25–83 MT/s |
| Voltage range | 3.3 V and 5 V |
| Processors | Intel 486 SX, 486 DX, 486 DX2, 486 DX4, 486 OverDrive, Pentium OverDrive AMD Am486 and Am5x86 |
This article is part of the CPU socket series | |
Socket 3 was one of the series of CPU Sockets into which various x86 microprocessors were inserted. It was sometimes found alongside a secondary socket designed for a math coprocessor chip, in this case the 487. Socket 3 resulted from Intel's creation of lower voltage microprocessors. An upgrade to Socket 2, it rearranged the pin layout and omitted one pin so that 3.3 V processors could not be plugged into older 5 V only sockets.
Socket 3 was a 237-pin low insertion force (LIF) or zero insertion force (ZIF) 19×19 pin grid array (PGA) socket suitable for the 3.3 V and 5 V, 25–50 MHz Intel 486 SX, 486 DX, 486 DX2, 486 DX4, 486 OverDrive and Pentium OverDrive processors as well as AMD Am486, Am5x86 and Cyrix Cx5x86 processors.[1]
See also
References
- ^ Intel Socket 3 Specification, pcguide.com, retrieved 2009-03-30
