Spine of sphenoid bone
| Spine of sphenoid bone | |
|---|---|
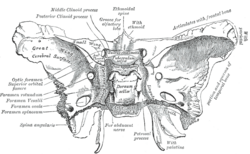 Sphenoid bone. Upper surface. (Spina angularis labeled at bottom left.) | |
 Articulation of the mandible. Medial aspect. (Spine of sphenoid labeled at center top.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Spina ossis sphenoidalis |
| TA98 | A02.1.05.040 |
| TA2 | 626 |
| FMA | 54777 |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |
The great wings, or alae-sphenoids, are two strong processes of bone, which arise from the sides of the body, and are curved upward, lateralward, and backward; the posterior part of each projects as a triangular process which fits into the angle between the squama and the petrous portion of the temporal bone and presents at its apex a downwardly directed process, the spina angularis (sphenoidal spine). It serves as the origin for the sphenomandibular ligament.
Additional images
-
Base of skull. Inferior surface. Spine of sphenoid bone marked with black circle
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 150 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 150 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- Anatomy figure: 27:02-04 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Schematic view of key landmarks of the infratemporal fossa."
- "Anatomy diagram: 34257.000-1". Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator. Elsevier. Archived from the original on 2014-01-01.

