Tosyl group
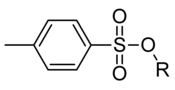

A tosyl group (abbreviated Ts or Tos) is CH3C6H4SO2. This group is usually derived from the compound 4-toluenesulfonyl chloride, CH3C6H4SO2Cl, which forms esters and amides of toluenesulfonic acid. The para orientation illustrated (p-toluenesulfonyl) is most common, and by convention tosyl refers to the p-toluenesulfonate ester.
A tosylate ester has a limited shelf life in air due to its ready hydrolysis in the presence of light. The tosyl group is electron-withdrawing and is an excellent leaving group. The tosyl group is also a protecting group for alcohols, prepared by combining the alcohol with 4-toluenesulfonyl chloride, usually in an aprotic solvent, often the pyridine of which basicity activates the reaction[1]. Toluenesulfonate esters undergo nucleophilic attack or elimination.
A similar group is brosyl, "Bs" or brosylate (p-bromobenzenesulfonyl) group wherein the methyl group of toluene is replaced by a bromide. Nosyl groups in nosylates, "Ns", are 4-nitrobenzenesulfonyl groups with a nitro group in the para position, "Nps" stands for 2-nitrobenzenesulfonyl.
Applications
The use of these functional groups is examplified in organic synthesis of the drug tolterodine, wherein one of the steps a phenol group is blocked as a tosyl group and the primary alcohol as a nosyl group. The latter is a leaving group for displacement by diisopropylamine [2][3]:
References
- ^ Nucleophilic Substitution
- ^ Kathlia A. De Castro, Jungnam Ko, Daejong Park, Sungdae Park, and Hakjune Rhee (2007). "Reduction of Ethyl Benzoylacetate and Selective Protection of 2-(3-Hydroxy-1-phenylpropyl)-4-methylphenol: A New and Facile Synthesis of Tolterodine". Organic Process Research & Development. 11: 918. doi:10.1021/op7001134.
{{cite journal}}:|format=requires|url=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Reaction sequence: organic reduction of ethyl benzoylacetate by sodium borohydride to a diol, followed by Friedel-Crafts alkylation with p-cresol and iron(III) chloride to a phenol. The tosyl and nosyl groups are introduced as their respective chlorides with either sodium hydroxide or triethylamine as a base. The next step is nucleophilic displacement of the nosyl group by diisopropylamine, the remaining tosyl group is removed by another round of NaOH. Not shown: optical resolution by L-tartaric acid to optically pure (R)-isomer

