Type XXI submarine
 U-3008 in U.S. Navy service during 1948.
| |
| Class overview | |
|---|---|
| Name | Type XXI U-boat |
| Operators | |
| Cost | 5,750,000 Reichsmark per boat[1] |
| Built | 1943–45[1] |
| Planned | 1170[2] |
| Building | 267[2] |
| Completed | 118 |
| Cancelled | 785[2] |
| Preserved | 1 |
| General characteristics | |
| Class and type | Submarine |
| Displacement | |
| Length | 76.70 m (251 ft 8 in)[1] |
| Beam | 8 m (26 ft 3 in)[1] |
| Draught | 6.32 m (20 ft 9 in)[1] |
| Propulsion |
|
| Range | |
| Test depth | 240 m (787 ft)[1] |
| Complement | 5 officers, 52 enlisted men[3] |
| Armament |
|
Type XXI U-boats, also known as "Elektroboote" (German: "electric boat"), were a class of German diesel-electric submarines designed during the Second World War. The submarines were produced prematurely, and all of those built had significant defects. As a result, only four of the submarines were completed during the war, and only two were sent for combat patrol and these were not used in combat.
They were the first submarines designed to operate primarily submerged, rather than spending most of their time as surface ships that could submerge for brief periods as a means to escape detection or to attack. They incorporated a very large number of batteries to improve the time they could spend underwater, as much as several days, and only needed to surface to periscope depth for recharging via a snorkel. The design included many general improvements as well; much greater underwater speed by an improved hull design, greatly improved diving times, power assisted torpedo reloading, and greatly improved crew accommodations.
After the war, several navies obtained XXIs and operated them for decades in various roles, and almost every navy introduced new submarine designs based on them. These include the Soviet Whiskey-class submarines, US Tang-class submarines, and the UK Porpoise-class submarines, all of which were based on the XXI design to some extent. The design remains the basis for diesel-electric submarines.
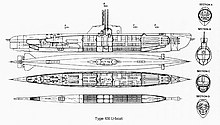
Description
The main features of the Type XXI were the hydrodynamically streamlined hull and conning tower, and the large number of battery cells, roughly triple that of the German Type VII submarine. This gave these boats great underwater range, and dramatically reduced the time spent on or near the surface. They could travel submerged at about 5 knots (9.3 km/h; 5.8 mph) for two or three days before recharging batteries, which took less than five hours using the snorkel. The Type XXI was also much quieter than the VIIC, making it more difficult to detect when submerged.
The Type XXI's streamlined hull design allowed great submerged speed. The ability to outrun many surface ships while submerged, combined with improved dive times (also a product of the new hull form), made it much more difficult to chase and destroy. It also gave the boat a 'sprint ability' when positioning itself for an attack. Older boats had to surface to sprint into position. This often revealed a boat's location, especially after aircraft became available for convoy escort.
They also featured an electric torpedo-reloading system that allowed all six bow torpedo tubes to be reloaded faster than a Type VIIC could reload one tube.[4] The Type XXI could fire 18 torpedoes in less than 20 minutes. The class also featured a very sensitive passive sonar for the time, housed in the "chin" of the hull.
The Type XXIs also had better facilities than previous U-boat classes, with roomier crew berths and a freezer for fresh foods.[5]
Construction
Between 1943 and 1945, 118 boats were assembled by Blohm & Voss of Hamburg, AG Weser of Bremen, and Schichau-Werke of Danzig. Each hull was constructed from eight prefabricated sections with final assembly at the shipyards. This new method could have resulted in construction time of less six months per vessel, but in practice all the assembled U-boats were plagued with severe quality problems that required extensive post-production work to rectify. One of the reasons for these shortcomings was that sections were made by companies having little experience with shipbuilding, after a decision by Albert Speer. As a result, of 118 Type XXIs constructed, only four were fit for combat before the Second World War ended in Europe. Of these, only two conducted combat patrols and neither sank any Allied ships.[6]
It was planned that final assembly of Type XXI boats would eventually be performed in the Valentin submarine pens, a massive, bomb–hardened concrete bunker built at the small port of Farge, near Bremen.[7] Construction of the pens was between 1943 and 1945, using about 10,000 concentration camp prisoners and prisoners of war as forced labour.[8] The facility was 90% completed when, during March 1945, it was damaged badly by Allied bombing with Grand Slam "earthquake" bombs and abandoned. A few weeks later, the area was captured by the British Army.[9]
Sensors
Radar detector
The FuMB Ant 3 Bali radar detector and antenna was located on top of the snorkel head.
Radar transmitter
The Type XXI boats were fitted with the FuMO 65 Hohentwiel U1 with the Type F432 D2 radar transmitter.
-
Radar Transmitter Type F432 D2
Wartime and post-war service
Germany

U-2511 and U-3008 were the only Type XXIs to be used for war patrols, and neither sank any ships. The commander of U-2511 claimed the U-boat had a British cruiser in her sights on 4 May when news of the German cease-fire was received. He further claimed she made a practice attack before leaving the scene undetected.[10]
During 1957, U-2540, which had been scuttled at the end of the war, was raised and refitted as research vessel Wilhelm Bauer of the Bundesmarine. It was operated by both military and civilian crews for research purposes until 1982. During 1984, it was made available for display to the public by the Deutsches Schiffahrtsmuseum (German Maritime Museum) in Bremerhaven, Germany.
France
U-2518 became French submarine Roland Morillot. It was used for active service during the Suez Crisis in 1956, and remained in commission until 1967. It was scrapped in 1969.
Soviet Union
Four Type XXI boats were assigned to the USSR by the Potsdam Agreement; these were U-3515, U-2529, U-3035, and U-3041, which were commissioned into the Soviet Navy as B-27, B-28, B-29, and B-30 (later B-100) respectively. However, Western intelligence believed the Soviets had acquired several more Type XXI boats; a review by the U.S. Joint Intelligence Committee for the Joint Chiefs of Staff during January 1948 estimated the Soviet Navy then had 15 Type XXIs operational, could complete construction of 6 more within 2 months, and could build another 39 within a year and a half from prefabricated sections, since several factories producing Type XXI components and the assembly yard at Danzig had been captured by the Soviets at the end of World War II. U 3538 — U 3557 (respectively TS-5 – TS-19 and TS-32 – TS-38) remained incomplete at Danzig and were scrapped or sunk during 1947. The four boats assigned by Potsdam were used in trials and tests until 1955, then scuttled or used for weapon testing between 1958 and 1973. The Type XXI design formed the basis for several Soviet design projects, Projects 611, 613, 614, 633, and 644. These became the submarine classes known by their NATO codes as Zulu, Whiskey and Romeo submarine classes.[11]
United Kingdom

The U-3017 was commissioned into the Royal Navy as HMS N41. It was used for tests until being scrapped during November 1949.
United States
The United States Navy acquired the U-2513 and U-3008, operating them both in the Atlantic Ocean. During November 1946 President Harry S. Truman visited U-2513; the submarine dived to 440 feet (130 m) with the President aboard.[12] The U-2513 was sunk as a target during 1951; U-3008 was scrapped during 1956.
Survivor

The only boat to survive intact is Wilhelm Bauer (ex-U-2540). The wrecks of other Type XXI boats are known to exist. During 1985, it was discovered that the partially scrapped remains of U-2505, U-3004, and U-3506 were still in the partially demolished "Elbe II" U-boat bunker in Hamburg. The bunker has since been filled in with gravel, although even that did not initially deter many souvenir hunters who measured the position of open hatches and dug down to them to allow the removal of artifacts.[13] The wrecks now lie beneath a car park, making them inaccessible.[14]
U-2513 lies in 213 feet (65 m) of water 70 nautical miles (130 km) west of Key West, Florida. The boat has been visited by divers, but the depth makes this very difficult and the site is only considered suitable for advanced divers. Four other boats lie off the coast of Northern Ireland, where they were sunk during 1946 as part of Operation Deadlight. Both U-2511 and U-2506 were found by nautical archaeologist Innes McCartney during his Operation Deadlight expeditions between 2001 and 2003.[15][16] Both were found to be in remarkably good condition.
Influences
The Type XXI design directly influenced advanced post-war submarines, the Greater Underwater Propulsion Power Program (GUPPY) improvements to the United States Gato-, Balao-, and Tench-class submarines and the Soviet submarine projects designated by NATO as the Whiskey, Zulu[17] and Romeo classes. The Chinese built Romeo-class submarines were based on Soviet-supplied designs. The subsequent Ming class, some of which were still in operation during 2013, was based on the Romeo.
See also
Notes
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Gröner 1991, p. 84–85.
- ^ a b c Gröner 1991, pp. 84–89.
- ^ a b Gröner 1991, p. 85.
- ^ Breyer, pp. 18–19.
- ^ Gerken, Louis (1989). Torpedo Technology (Illustrated ed.). United States: Pennsylvania State University. p. 57. ISBN 0961716320. Retrieved 30 June 2017.
- ^ Tooze, Adam (2006). The Wages of Destruction. London: Penguin Books. pp. 616–618. ISBN 978-0-14-100348-1.
- ^ Flower, Stephen (2004). Barnes Wallis' Bombs. Tempus. p. 350. ISBN 0-7524-2987-6.
- ^ Marc Buggeln. "Neuengamme / Bremen-Farge". Holocaust Encyclopedia. United States Holocaust Memorial Museum. Retrieved 29 January 2011.
- ^ Flower, Stephen (2004). Barnes Wallis' Bombs. Tempus. p. 351. ISBN 0-7524-2987-6.
- ^ Van der Vat, Dan (1994). Stealth at Sea. London: Orion. p. 353. ISBN 1-85797-864-1.
- ^ Polmar, Norman; Kenneth J. Moore (2004). Cold War Submarines: The Design and Construction of U.S. and Soviet Submarines. Brassey's. pp. 23–24. ISBN 1-57488-594-4.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|nopp=(help) - ^ "Truman Dives 440 Feet In German Sub", The Pittsburgh Press, November 21, 1946, p9
- ^ Hitler's U-boat Bases (2002), Jak P Mallmann Showell, Sutton Publishing ISBN 0-7509-2606-6
- ^ "3 Type XXI boats in the Elbe II in Hamburg". uboat.net.
- ^ "Uboat.net Operation Deadlight dives 2001".
- ^ "Uboat.net Operation Deadlight dives 2002".
- ^ Fitzsimons, Bernard, general editor. The Encyclopedia of 20th Century Weapons and Warfare (London: Phoebus Publishing Company, 1978), Volume 24, p.2594, "'Whiskey'", and p.2620, "'Zulu'".
References
- Breyer, Siegfried (1999). German U-Boat Type XXI. Translated by Force, Ed. Atglen: Schiffer. ISBN 0-7643-0787-8.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Fitzsimons, Bernard, general editor. The Encyclopedia of 20th Century Weapons and Warfare (London: Phoebus Publishing Company, 1978), Volume 24, p. 2594, "'Whiskey'", and p. 2620, "'Zulu'".
- Gröner, Erich; Jung, Dieter; Maass, Martin (1991). U-boats and mine warfare vessels. Vol. 2. Translated by Thomas, Keith; Magowan, Rachel. London: Conway Maritime Press. ISBN 0-85177-593-4.
{{cite book}}:|work=ignored (help); Cite has empty unknown parameter:|last-author-amp=(help); Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Kohl, Fritz; Eberhard Rossler (1991). The Type XXI U-boat. Conway Maritime. ISBN 1-55750-829-1.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|nopp=(help)
External links
- U-Boot Type XXI in Detail with photos.
- Helgason, Guðmundur. "Type XXI". German U-boats of WWII - uboat.net. Retrieved 20 April 2015.
- Type XXI on www.uboataces.com

