Vaccinium erythrocarpum
| Vaccinium erythrocarpum | |
|---|---|

| |
| In Situ at Blood Mountain, Georgia | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Asterids |
| Order: | Ericales |
| Family: | Ericaceae |
| Genus: | Vaccinium |
| Subgenus: | Vaccinium subg. Oxycoccus |
| Species: | V. erythrocarpum
|
| Binomial name | |
| Vaccinium erythrocarpum Michx. 1803
| |
| Synonyms | |
|
Hugeria erythrocarpa | |

Vaccinium erythrocarpum, commonly known as southern mountain cranberry or bearberry, more rarely as mountain blueberry or dingleberry,[2] is a deciduous flowering shrub native to the Southeastern United States.
Description
[edit]Vaccinium erythrocarpum flowers bloom in June, they are hermaphrodite, of a tubular shape with reflexed petals, and they have long tassel like stamens that drape below the corolla. They produce somewhat translucent scarlet berries that set in late summer or early autumn.[3] The fruits are edible, tasting quite similar to other Cranberries. Their rarity and the small quantity of fruits they set are major barriers for commercial production despite the quality of their berries.[4]
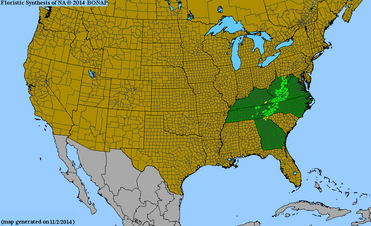
Range
[edit]This species is found in the Southern and Central Appalachians at high elevations, often at prominences within the landscape (especially at the southern end of their range).[3] They are state listed in Georgia (S1), Kentucky (S1), North Carolina (S4), Virginia (S4), and West Virginia (S4).[5]
Ecology
[edit]The flowers are pollinated by insects (primarily large bees). Their berries are edible, and are consumed readily by wildlife. The plant generally grows in woodlands and areas of dappled shade, primarily in mixed oak-heath forests.[6] This species is commonly found on Southern Appalachian heath balds, where it is often a prominent member of the shrub layer.[7]
Taxonomy
[edit]Vaccinium erythrocarpum was long considered synonymous with Vaccinium japonicum, found in East Asia, however two have since been split into separate species.[6] Both species are now considered members of the cranberry subgenus Oxycoccus, both also placed into the section Oxycoccoides. These species within sect. Oxycoccoides differ from the rest of the subgenus as they are deciduous shrubs while sect. Oxycoccus consists of trailing evergreen vines.
References
[edit]- ^ illustration from An illustrated flora of the northern United States, Canada and the British Possessions. Vol. 2: 705. Authors: Britton, N.L., & A. Brown.
- ^ "Vaccinium erythrocarpum". Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center.
- ^ a b "NameThatPlant.net: Vaccinium erythrocarpum". www.namethatplant.net. Retrieved 2023-06-23.
- ^ "Vaccinium erythrocarpum Southern Mountain Cranberry PFAF Plant Database". pfaf.org. Retrieved 2023-06-23.
- ^ "NatureServe Explorer 2.0". explorer.natureserve.org. Retrieved 2023-06-23.
- ^ a b Flora of north America, Vaccinium erythrocarpum Michaux, 1803
- ^ "Vaccinium erythrocarpum". georgiabiodiversity.org. Retrieved 2023-06-23.
"Vaccinium erythrocarpum". County-level distribution map from the North American Plant Atlas (NAPA). Biota of North America Program (BONAP). 2014. Retrieved 23 June 2023.

