Permafrost carbon cycle: Difference between revisions
m author wlink |
Many references in the article are over a decade old. Merged disparate information from here, permafrost, tundra, yedoma, climate change in the Arctic & Arctic methane emissions articles into a single reusable section. Removed passages which confused permafrost and clathrate processes. |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
The '''permafrost carbon cycle''' or '''Arctic carbon cycle''' is a sub-cycle of the larger global [[carbon cycle]]. [[Permafrost]] is defined as subsurface material that remains below 0<sup>o</sup> C (32<sup>o</sup> F) for at least two consecutive years. Because permafrost soils remain frozen for long periods of time, they store large amounts of carbon and other nutrients within their frozen framework during that time. Permafrost represents a large carbon reservoir that is seldom considered when determining global terrestrial carbon reservoirs. Recent and ongoing scientific research however, is changing this view.<ref name=zimov>{{Cite journal|vauthors=Zimov SA, Schuur EA, Chapin FS |title=Climate change. Permafrost and the global carbon budget |journal=Science |volume=312 |issue=5780 |pages=1612–3 |date=June 2006 |pmid=16778046 |doi=10.1126/science.1128908 |s2cid=129667039 }}</ref> |
The '''permafrost carbon cycle''' or '''Arctic carbon cycle''' is a sub-cycle of the larger global [[carbon cycle]]. [[Permafrost]] is defined as subsurface material that remains below 0<sup>o</sup> C (32<sup>o</sup> F) for at least two consecutive years. Because permafrost soils remain frozen for long periods of time, they store large amounts of carbon and other nutrients within their frozen framework during that time. Permafrost represents a large carbon reservoir that is seldom considered when determining global terrestrial carbon reservoirs. Recent and ongoing scientific research however, is changing this view.<ref name=zimov>{{Cite journal|vauthors=Zimov SA, Schuur EA, Chapin FS |title=Climate change. Permafrost and the global carbon budget |journal=Science |volume=312 |issue=5780 |pages=1612–3 |date=June 2006 |pmid=16778046 |doi=10.1126/science.1128908 |s2cid=129667039 }}</ref> |
||
The permafrost carbon cycle deals with the transfer of carbon from permafrost soils to terrestrial vegetation and microbes, to [[Atmosphere of Earth|the atmosphere]], back to vegetation, and finally back to permafrost soils through burial and sedimentation due to cryogenic processes. Some of this carbon is transferred to the ocean and other portions of the globe through the global carbon cycle. The cycle includes the exchange of [[carbon dioxide]] and [[methane]] between terrestrial components and the atmosphere, as well as the transfer of carbon between land and water as methane, [[dissolved organic carbon]], [[dissolved inorganic carbon]], [[particulate inorganic carbon]] and [[particulate organic carbon]].<ref |
The permafrost carbon cycle deals with the transfer of carbon from permafrost soils to terrestrial vegetation and microbes, to [[Atmosphere of Earth|the atmosphere]], back to vegetation, and finally back to permafrost soils through burial and sedimentation due to cryogenic processes. Some of this carbon is transferred to the ocean and other portions of the globe through the global carbon cycle. The cycle includes the exchange of [[carbon dioxide]] and [[methane]] between terrestrial components and the atmosphere, as well as the transfer of carbon between land and water as methane, [[dissolved organic carbon]], [[dissolved inorganic carbon]], [[particulate inorganic carbon]] and [[particulate organic carbon]].<ref>{{Cite journal|doi=10.1890/08-2025.1 |author=McGuire, A.D., Anderson, L.G., Christensen, T.R., Dallimore, S., Guo, L., Hayes, D.J., Heimann, M., Lorenson, T.D., Macdonald, R.W., and Roulet, N. |title=Sensitivity of the carbon cycle in the Arctic to climate change |journal=Ecological Monographs |volume=79 |issue=4 |pages=523–555 |year=2009 |hdl=11858/00-001M-0000-000E-D87B-C |hdl-access=free }}</ref> |
||
==Storage== |
==Storage== |
||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
===Current estimates=== |
===Current estimates=== |
||
It is estimated that the total soil organic carbon (SOC) stock in northern circumpolar permafrost region equals around 1,460-1,600 [[Kilogram#SI multiples|Pg]].<ref name=tarnocai>{{Cite journal |author=Tarnocai, C., Canadell, J.G., Schuur, E.A.G., Kuhry, P., Mazhitova, G., and Zimov, S. |title=Soil organic carbon pools in the northern circumpolar permafrost region |journal=Global Biogeochemical Cycles |volume=23 |issue=2 |year=2009 |pages=GB2023 |doi=10.1029/2008GB003327 |bibcode=2009GBioC..23.2023T |doi-access=free }}</ref> (1 Pg = 1 Gt = 10<sup>15</sup>g)<ref>{{Cite journal|last1=Hugelius|first1=G.|last2=Strauss|first2=J.|last3=Zubrzycki|first3=S.|last4=Harden|first4=J. W.|author-link4=Jennifer Harden|last5=Schuur|first5=E. A. G.|last6=Ping|first6=C.-L.|last7=Schirrmeister|first7=L.|last8=Grosse|first8=G.|last9=Michaelson|first9=G. J.|last10=Koven|first10=C. D.|last11=O'Donnell|first11=J. A.|date=2014-12-01|title=Estimated stocks of circumpolar permafrost carbon with quantified uncertainty ranges and identified data gaps|url=http://dx.doi.org/10.5194/bg-11-6573-2014|journal=Biogeosciences|volume=11|issue=23|pages=6573–6593|doi=10.5194/bg-11-6573-2014|bibcode=2014BGeo...11.6573H|s2cid=14158339 |issn=1726-4189}}</ref><ref name="ARC2019">{{Cite web|title=Permafrost and the Global Carbon Cycle|url=https://arctic.noaa.gov/Report-Card/Report-Card-2019/ArtMID/7916/ArticleID/844/Permafrost-and-the-Global-Carbon-Cycle|access-date=2021-05-18|website=Arctic Program|language=en-US}}</ref> With the [[Tibetan Plateau]] carbon content included, the total carbon pools in the permafrost of the Northern Hemisphere is likely to be around 1832 Gt.<ref>http://www.the-cryosphere.net/9/479/2015/tc-9-479-2015.pdf {{Bare URL PDF|date=March 2022}}</ref> This estimation of the amount of carbon stored in permafrost soils is more than double the amount currently in the atmosphere.<ref name=zimov/> |
|||
Soil column in the permafrost soils is generally broken into three horizons, 0–30 cm, 0–100 cm, and 1–300 cm. The uppermost horizon (0–30 cm) contains approximately 200 Pg of organic carbon. The 0–100 cm horizon contains an estimated 500 Pg of organic carbon, and the 0–300 cm horizon contains an estimated 1024 Pg of organic carbon. These estimates more than doubled the previously known carbon pools in permafrost soils.<ref name=kimble/><ref name=bockheim/><ref name=tarnocai/> Additional carbon stocks exist in [[yedoma]] (400 Pg), carbon rich [[loess]] deposits found throughout Siberia and isolated regions of North America, and deltaic deposits (240 Pg) throughout the Arctic. These deposits are generally deeper than the 3 m investigated in traditional studies.<ref name=tarnocai/> Many concerns arise because of the large amount of carbon stored in permafrost soils. Until recently, the amount of carbon present in permafrost was not taken into account in climate models and global carbon budgets.<ref name=zimov/><ref name=schuur/> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
Carbon stored within arctic soils and permafrost is susceptible to release due to several different mechanisms. Carbon that is stored in permafrost is released back into the atmosphere as either carbon dioxide (CO<sub>2</sub>) or methane (CH<sub>4</sub>). [[Aerobic respiration]] releases carbon dioxide, while [[anaerobic respiration]] releases methane. |
|||
Carbon is continually cycling between soils, vegetation, and the atmosphere. As climate change increases mean annual air temperatures throughout the Arctic, it extends permafrost thaw and deepens the active layer, exposing old carbon that has been in storage for decades to millennia to biogenic processes which facilitate its entrance into the atmosphere. In general, the volume of permafrost in the upper 3 m of ground is expected to decrease by about 25% per 1 °C of global warming.<ref name=":2" /> According to the [[IPCC Sixth Assessment Report]], there is high confidence that global warming over the last few decades has led to widespread increases in permafrost temperature.<ref name="IPCC AR6 WG1">{{Cite journal |last1=Fox-Kemper |first1=B. |last2=Hewitt |first2=H.T.|author2-link=Helene Hewitt |last3=Xiao |first3=C. |last4=Aðalgeirsdóttir |first4=G. |last5=Drijfhout |first5=S.S. |last6=Edwards |first6=T.L. |last7=Golledge |first7=N.R. |last8=Hemer |first8=M. |last9=Kopp |first9=R.E. |last10=Krinner |first10=G. |last11=Mix |first11=A. |date=2021 |editor-last=Masson-Delmotte |editor-first=V. |editor2-last=Zhai |editor2-first=P. |editor3-last=Pirani |editor3-first=A. |editor4-last=Connors |editor4-first=S.L. |editor5-last=Péan |editor5-first=C. |editor6-last=Berger |editor6-first=S. |editor7-last=Caud |editor7-first=N. |editor8-last=Chen |editor8-first=Y. |editor9-last=Goldfarb |editor9-first=L. |title=Ocean, Cryosphere and Sea Level Change |journal=Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change |publisher=Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK and New York, NY, USA |pages=1237, 1238–1239, 1320 |doi=10.1017/9781009157896.011|doi-broken-date=9 July 2022 }}</ref> Observed warming was up to 3 °C in parts of Northern Alaska (early 1980s to mid-2000s) and up to 2 °C in parts of the Russian European North (1970-2020), and active layer thickness has increased in the European and Russian Arctic across the 21st century and at high elevation areas in Europe and Asia since the 1990s.<ref name="IPCC AR6 WG1" /><ref>{{cite web |date=10 November 2015 |title=Working Group I Contribution to the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report Climate Change 2013 - Summary for Policymakers - Template Lab |url=http://templatelab.com/climatechange-WGIAR5-SPM-Approved-27Sep2013/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170118050318/http://templatelab.com/climatechange-WGIAR5-SPM-Approved-27Sep2013/ |archive-date=2017-01-18 |access-date=2017-01-16}}</ref> In [[Yukon]], the zone of continuous permafrost might have moved {{convert|100|km}} poleward since 1899, but accurate records only go back 30 years. Based on high agreement across model projections, fundamental process understanding, and paleoclimate evidence, it is virtually certain that permafrost extent and volume will continue to shrink as global climate warms.<ref name=":2">IPCC AR6 WG1 Ch9 2021, p. 1283</ref> |
|||
Carbon emissions from permafrost thaw contribute to the same warming which facilitates the thaw, making it a [[Climate change feedback#Positive|positive climate change feedback]]. The amount of carbon that will be released from warming conditions depends on depth of thaw, carbon content within the thawed soil, physical changes to the environment<ref name=nowinski>{{Cite journal|vauthors=Nowinski NS, Taneva L, [[Susan Trumbore|Trumbore SE]], Welker JM |title=Decomposition of old organic matter as a result of deeper active layers in a snow depth manipulation experiment |journal=Oecologia |volume=163 |issue=3 |pages=785–92 |date=January 2010 |pmid=20084398 |pmc=2886135 |doi=10.1007/s00442-009-1556-x |bibcode=2010Oecol.163..785N }}</ref> and microbial and vegetation activity in the soil. Microbial respiration is the primary process through which old permafrost carbon is re-activated and enters the atmosphere. The rate of microbial decomposition within organic soils, including thawed permafrost, depends on environmental controls, such as soil temperature, moisture availability, nutrient availability, and oxygen availability.<ref name=schuur>{{Cite journal|author=Schuur, E.A.G., Bockheim, J., Canadell, J.G., Euskirchen, E., Field, C.B., Goryachkin, S.V., Hagemann, S., Kuhry, P., Lafleur, P.M., Lee, H., Mazhitova, G., Nelson, F.E., Rinke, A., Romanovsky, V.E., Skiklomanov, N., Tarnocai, C., Venevsky, S., Vogel, J.G., and Zimov, S.A. |title=Vulnerability of Permafrost Carbon to Climate Change: Implications for the Global Carbon Cycle |journal=BioScience |volume=58 |issue=8 |pages=701–714 |year=2008 |doi=10.1641/B580807 |doi-access=free }}</ref> |
|||
*[[Methane clathrate]], or hydrates, occur within and below permafrost soils. Because of the low permeability of permafrost soils, methane gas is unable to migrate vertically through the soil column. As permafrost temperature increases, permeability also increases, allowing once trapped methane gas to move vertically and escape. [[Dissociation (chemistry)|Dissociation]] of gas hydrates is common along the Arctic coastline, yet estimates for dissociation of gas hydrates from terrestrial permafrost remains unclear.<ref name=mcguire>{{Cite journal|doi=10.1890/08-2025.1 |author=McGuire, A.D., Anderson, L.G., Christensen, T.R., Dallimore, S., Guo, L., Hayes, D.J., Heimann, M., Lorenson, T.D., Macdonald, R.W., and Roulet, N. |title=Sensitivity of the carbon cycle in the Arctic to climate change |journal=Ecological Monographs |volume=79 |issue=4 |pages=523–555 |year=2009 |hdl=11858/00-001M-0000-000E-D87B-C |hdl-access=free }}</ref> |
|||
*Thermokarst/permafrost degradation as a result of climate change and increased mean annual air temperatures throughout the Arctic threatens to release large quantities of carbon back into the atmosphere. The spatial extent of permafrost decreases in warming climate, releasing large amounts of stored carbon.<ref name=zimov/> |
|||
*As air and permafrost temperatures change, above ground vegetation also changes. Increasing temperatures facilitate the transfer of soil carbon to growing vegetation on the surface. This transfer removes carbon from the soil and relocates it to the terrestrial carbon pool where plants process, store, and respire it, moving it to the atmosphere.<ref name=kane>{{Cite journal |author1=Kane, E.S. |author2=Vogel, J.G. |name-list-style=amp |title=Patterns of Total Ecosystem Carbon Storage with Changes in Soil Temperature in Boreal Black Spruce Forests |journal=Ecosystems |volume=12 |issue=2 |pages=322–335 |date=February 2009 |doi=10.1007/s10021-008-9225-1 |s2cid=18318708 |url=http://www.lter.uaf.edu/pdf/1274_Kane_Vogel_2009.pdf |access-date=5 June 2010 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110716142810/http://www.lter.uaf.edu/pdf/1274_Kane_Vogel_2009.pdf |archive-date=16 July 2011 |url-status=dead }}</ref> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
*Hydrologic processes remove and mobilize carbon, carrying it downstream. Mobilization occurs due to leaching, litter fall, and erosion. Mobilization is believed to be primarily due to increased primary production in the Arctic resulting in increased leaf litter entering streams and increasing the dissolved organic carbon content of the stream. Leaching of soil organic carbon from permafrost soils is also accelerated by warming climate and by erosion along river and stream banks freeing the carbon from the previously frozen soil.<ref name=guo>{{Cite journal|author=Guo, L., Chien-Lu Ping, and Macdonald, R.W. |title=Mobilization pathways of organic carbon from permafrost to arctic rivers in a changing climate. '' |journal=Geophysical Research Letters |volume=34 |issue=13 |pages=L13603 |date=July 2007 |doi=10.1029/2007GL030689 |bibcode=2007GeoRL..3413603G}}</ref> |
|||
Altogether, the likelihood of the entire carbon pool mobilizing and entering the atmosphere is low despite the large volumes stored in the soil. Although temperatures will fit does not imply complete loss of permafrost and mobilization of the entire carbon pool. Much of the ground underlain by permafrost will remain frozen even if warming temperatures increase the thaw depth or increase thermokarsting and permafrost degradation.<ref name=bockheim/> However, once permafrost area thaws, it will not go back to being permafrost for centuries even if the temperature increase reversed, making it one of the best-known examples of [[tipping points in the climate system]]. |
|||
A 1993 study suggested that while the tundra was a [[carbon sink]] until the end of 1970s, it had already transitioned to a net carbon source by the time the study concluded.<ref name="Oechel1993">{{cite journal | first1=Walter C.|last1=Oechel|first2=Steven J. |last2=Hastings |first3=George |last3=Vourlrtis |first4=Mitchell |last4=Jenkins |first5=George |last5=Riechers |first6=Nancy|last6=Grulkelast|display-authors=4 | date = 1993 | title = Recent change of Arctic tundra ecosystems from a net carbon dioxide sink to a source | journal = [[Nature (journal)|Nature]] | volume = 361 | issue = 6412 | pages = 520–523 | doi = 10.1038/361520a0 |bibcode=1993Natur.361..520O |s2cid=4339256}}</ref> The 2019 Arctic Report Card estimated that Arctic permafrost releases between 0.3 and 0.6 Pg C per year.<ref name="ARC2019" /> That same year, a study settled on the 0.6 Pg C figure, as the net difference between the annual emissions of 1,66 Pg C during the winter season (October–April), and the model-estimated vegetation carbon uptake of 1 Pg C during the growing season. It estimated that [[Representative Concentration Pathway|RCP]] 8.5, a scenario of continually accelerating greenhouse gas emissions, winter {{CO2}} emissions from the norther permafrost domain would increase 41% by 2100. Under the "intermediate" scenario RCP 4.5, where greenhouse gas emissions peak and plateau within the next two decades, before gradually declining for the rest of the century (a rate of mitigation deeply insufficient to meet the [[Paris Agreement]] goals) permafrost carbon emissions would increase by 17%. <ref>{{Cite journal|last1=Natali|first1=Susan M.|last2=Watts|first2=Jennifer D.|last3=Rogers|first3=Brendan M.|last4=Potter|first4=Stefano|last5=Ludwig|first5=Sarah M.|last6=Selbmann|first6=Anne-Katrin|last7=Sullivan|first7=Patrick F.|last8=Abbott|first8=Benjamin W.|last9=Arndt|first9=Kyle A.|last10=Birch|first10=Leah|last11=Björkman|first11=Mats P.|date=2019-10-21|title=Large loss of CO2 in winter observed across the northern permafrost region|url=http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41558-019-0592-8|journal=Nature Climate Change|volume=9|issue=11|pages=852–857|doi=10.1038/s41558-019-0592-8|pmid=35069807|pmc=8781060|bibcode=2019NatCC...9..852N|hdl=10037/17795|s2cid=204812327|issn=1758-678X}}</ref> In 2022, this was challenged by a study which used a record of atmospheric observations between 1980 to 2017, and found that permafrost regions have been gaining carbon on net, as process-based models underestimated net CO2 uptake in the permafrost regions and overestimated it in the forested regions, where increased respiration in response to warming offsets more of the gains then was previously understood. <ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Liu |first1=Zhihua |last2=Kimball |first2=John S. |last3=Ballantyne |first3=Ashley P. |last4=Parazoo |first4=Nicholas C. |last5=Wang |first5=Wen J. |last6=Bastos |first6=Ana |last7=Madani |first7=Nima |last8=Natali |first8=Susan M. |last9=Watts |first9=Jennifer D. |last10=Rogers |first10=Brendan M. |last11=Ciais |first11=Philippe |last12=Yu |first12=Kailiang |last13=Virkkala |first13=Anna-Maria |last14=Chevallier |first14=Frederic |last15=Peters |first15=Wouter |last16=Patra |first16=Prabir K. |last7=Chandra |first7=Naveen |date=2019-10-21|title=Respiratory loss during late-growing season determines the net carbon dioxide sink in northern permafrost regions |url=https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-022-33293-x |journal=Nature Communications |volume=13 |doi=10.1038/s41467-022-33293-x}}</ref> |
|||
==Environmental impacts== |
|||
Warmer conditions are expected to cause spatial declines in permafrost extent and thickening of the [[active layer]]. This decline in the extent and volume of permafrost enables the mobilization of stored soil organic carbon to the biosphere and atmosphere as carbon dioxide and methane.<ref name=zimov/> Additionally, these changes are believed to impact ecosystems and alter the vegetation that is present on the surface.<ref name=kane/> Increased carbon uptake by plants is expected to be relatively small when compared to the amount of carbon released by permafrost degradation. Tundra vegetation contains 0.4 kg of carbon per m<sup>2</sup> while a shift to boreal forests could increase the above ground carbon pool to 5 kg of carbon per m<sup>2</sup>. Tundra soil however, contains ten times that amount.<ref name=schuur/> |
|||
Notably, estimates of carbon release alone do not fully represent the impact of permafrost thaw on climate change. This is because carbon can either be released as carbon dioxide (CO<sub>2</sub>) or methane (CH<sub>4</sub>). [[Aerobic respiration]] releases carbon dioxide, while [[anaerobic respiration]] releases methane. This is a substantial difference, as while biogenic methane lasts less than 12 years in the atmosphere, its [[global warming potential]] is around 80 times larger than that of CO<sub>2</sub> over a 20-year period and between 28 and 40 times larger over a 100-year period. |
|||
Additionally, a sudden and steady release of carbon dioxide and methane from permafrost soils may lead to a [[Climate change feedback#Positive|positive climate change feedback]] cycle where warming releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. This carbon dioxide, a [[greenhouse gas]], causes atmospheric concentrations to increase, causing subsequent warming.<ref name=tarnocai/> This scenario is thought to be a potential [[runaway climate change]] scenario. |
|||
===Carbon dioxide emissions=== |
|||
Most of the permafrost soil are oxic and provide a suitable environment for aerobic microbial respiration. As such, carbon dioxide emissions account for the overwhelming majority of permafrost emissions and of the Arctic emissions in general. <ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Miner |first1=Kimberley R. |last2=Turetsky |first2=Merritt R. |last3=Malina |first3=Edward |last4=Bartsch |first4=Annett |last5=Tamminen |first5=Johanna |last6=McGuire |first6=A. David |last7=Fix |first7=Andreas |last8=Sweeney |first8=Colm |last9=Elder |first9=Clayton D. |last10=Miller |first10=Charles E. |date=11 January 2022|title=Permafrost carbon emissions in a changing Arctic |url=https://www.nature.com/articles/s43017-021-00230-3 |journal=Nature Reviews Earth & Environment |volume=13 |pages=55–67 |doi=10.1038/s43017-021-00230-3}}</ref> There's some debate over whether the observed emissions from permafrost soils primarily constitute microbial respiration of ancient carbon, or simply greater respiration of modern-day carbon (i.e. leaf litter), due to warmer soils intensifying microbial metabolism. Studies published in the early 2020s indicate that while soil microbiota still primarily consumes and respires modern carbon when plants grow during the spring and summer, these microorganisms then sustain themselves on ancient carbon during the winter, releasing it into the atmosphere. <ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Estop-Aragonés |first1= Cristian |last2=Olefeldt |first2=David |display-authors=etal |date=2 September 2020 |title=Assessing the Potential for Mobilization of Old Soil Carbon After Permafrost Thaw: A Synthesis of 14C Measurements From the Northern Permafrost Region |url=https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1029/2020GB006672 |journal=Global Biogeochemical Cycles |volume=34 |issue=9 |doi=10.1029/2020GB006672}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Pedron |first1=Shawn A. |last2=Welker |first2=J. M. |last3=Euskirchen |first3=E. S. |last4=Klein |first4=E. S. |last5=Walker |first5=J. C. |last6=Xu |first6=X. |last7=Czimczik |first7=C. I. |date=14 March 2022 |title=Closing the Winter Gap—Year-Round Measurements of Soil CO2 Emission Sources in Arctic Tundra |url=https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1029/2021GL097347 |journal=Geophysical Research Letters |volume=49 |issue=6 |doi=10.1029/2021GL097347}}</ref> |
|||
| ⚫ | On the other hand, former permafrost areas consistently see increased vegetation growth, or primary production, as plants can set down deeper roots in the thawed soil and grow larger and uptake more carbon. This is generally the main counteracting feedback on permafrost carbon emissions. However, in areas with streams and other waterways, more of their leaf litter enters those waterways, increasing their dissolved organic carbon content. Leaching of soil organic carbon from permafrost soils is also accelerated by warming climate and by erosion along river and stream banks freeing the carbon from the previously frozen soil.<ref name=guo>{{Cite journal|author=Guo, L., Chien-Lu Ping, and Macdonald, R.W. |title=Mobilization pathways of organic carbon from permafrost to arctic rivers in a changing climate. '' |journal=Geophysical Research Letters |volume=34 |issue=13 |pages=L13603 |date=July 2007 |doi=10.1029/2007GL030689 |bibcode=2007GeoRL..3413603G}}</ref> Moreover, thawed areas become more vulnerable to wildfires, which alter landscape and release large quantities of stored organic carbon through combustion. As these fires burn, they remove organic matter from the surface. Removal of the protective organic mat that insulates the soil exposes the underlying soil and permafrost to increased [[solar radiation]], which in turn increases the soil temperature, active layer thickness, and changes soil moisture. Changes in the soil moisture and saturation alter the ratio of [[oxic]] to anoxic decomposition within the soil.<ref name=meyers>{{Cite journal|doi=10.1029/2007JG000423 |author=Meyers-Smith, I.H., McGuire, A.D., Harden, J.W., Chapin, F.S. |title=Influence of disturbance on carbon exchange in a permafrost collapse and adjacent burned forest |journal=Journal of Geophysical Research |volume=112 |issue=G4 |pages=G04017 |year=2007 |bibcode=2007JGRG..11204017M|url=https://www.pure.ed.ac.uk/ws/files/8365805/PDF_Myers_Smith.et.al2007.pdf |doi-access=free }}</ref> |
||
A hypothesis promoted by [[Sergey Zimov]] is that the reduction of herds of large herbivores has increased the ratio of energy emission and energy absorption tundra (energy balance) in a manner that increases the tendency for net thawing of permafrost.<ref>{{cite web|title=Mammoth steppe: a high-productivity phenomenon|author=S.A. Zimov, N.S. Zimov, A.N. Tikhonov, [[F. Stuart Chapin III|F.S. Chapin III]]|url=http://www.lter.uaf.edu/pdf/1754_Zimov_Zimov_2012.pdf|year=2012|publisher=In: [[Quaternary Science Reviews]], vol. 57, 4 December 2012, p. 42 fig.17|access-date=17 October 2014|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160304103247/http://www.lter.uaf.edu/pdf/1754_Zimov_Zimov_2012.pdf|archive-date=4 March 2016}}</ref> He is testing this hypothesis in an experiment at [[Pleistocene Park]], a nature reserve in northeastern Siberia.<ref>Sergey A. Zimov (6 May 2005): [https://www.science.org/doi/full/10.1126/science.1113442 "Pleistocene Park: Return of the Mammoth's Ecosystem."] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170220222928/http://science.sciencemag.org/content/308/5723/796.1.full |date=2017-02-20 }} In: ''[[Science (journal)|Science]]'', pages 796–798. Article also to be found in [http://www.pleistocenepark.ru/en/materials/ www.pleistocenepark.ru/en/ – Materials.] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161103172534/http://www.pleistocenepark.ru/en/materials/ |date=2016-11-03 }} Retrieved 5 May 2013.</ref> On the other hand, warming allows the [[beaver]]s to extend their habitat further north, where their [[Beaver dam#Effects|dams impair]] boat travel, impact access to food, affect water quality, and endanger downstream fish populations.<ref name=Guardian_20220104/> Pools formed by the dams store heat, thus changing local [[hydrology]] and causing localized permafrost thaw.<ref name=Guardian_20220104>{{cite news |last1=Milman |first1=Oliver |title=Dam it: beavers head north to the Arctic as tundra continues to heat up |url=https://www.theguardian.com/world/2022/jan/04/beavers-arctic-north-climate-crisis |newspaper=The Guardian |date=January 4, 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220104220623/https://www.theguardian.com/world/2022/jan/04/beavers-arctic-north-climate-crisis |archive-date=January 4, 2022 |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
===Methane emissions=== |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
Global warming in the Arctic accelerates methane release from both existing stores and [[methanogenesis]] in rotting [[Biomass (ecology)|biomass]].<ref>{{Cite journal| doi = 10.1029/2007JG000569| title = Methane production and bubble emissions from arctic lakes: Isotopic implications for source pathways and ages| year = 2008| last1 = Walter | first1 = K. M.| last2 = Chanton | first2 = J. P. |author-link2=Jeff Chanton| last3 = Chapin | first3 = F. S.| last4 = Schuur | first4 = E. A. G.| last5 = Zimov | first5 = S. A.| journal = Journal of Geophysical Research| volume = 113| pages = G00A08 | bibcode=2008JGRG..11300A08W}}</ref> Methanogenesis requires thoroughly anaerobic environments, which slows down the mobilization of old carbon. A 2015 ''[[Nature (magazine)|Nature]]'' review estimated that the cumulative emissions from thawed anaerobic permafrost sites were 75-85% lower than the cumulative emissions from aerobic sites, and that even there, methane emissions amounted to only 3% to 7% of CO2 emitted in situ. While they represented between 25% to 45% of the CO2's potential impact on climate over a 100-year timescale, the review concluded that aerobic permafrost thaw still had a greater warming impact overall.<ref>{{Cite journal|last1=Schuur |first1=E. A. G. |last2=McGuire |first2=A. D. |last3=Schädel |first3=C. |last4=Grosse |first4=G. |last5=Harden |first5=J. W. |display-authors=etal |date=9 April 2015|title=Climate change and the permafrost carbon feedback|url=https://www.nature.com/articles/nature14338 |journal=Nature |volume=520 |pages=171–179 |doi=10.1038/nature14338}}</ref> In 2018, however, another study in ''[[Nature Climate Change]]'' found that at many anaerobic sites, methane production was equivalent to CO2 production, substantially raising the overall warming impact they represented. <ref>{{Cite journal|last1=Pfeiffer|first1=Eva-Maria|last2=Grigoriev|first2=Mikhail N. |last3=Liebner |first3=Susanne |last4=Beer |first4=Christian |last5=Knoblauch|first5=Christian|date=April 2018|title=Methane production as key to the greenhouse gas budget of thawing permafrost|journal=Nature Climate Change|volume=8|issue=4|pages=309–312|doi=10.1038/s41558-018-0095-z|issn=1758-6798|bibcode=2018NatCC...8..309K|s2cid=90764924|url=http://gfzpublic.gfz-potsdam.de/pubman/item/escidoc:3094899}}</ref> |
|||
Since methanogenesis requires anaerobic environments, it is frequently associated with Arctic lake environments, where the emergence of bubbles of methane can be observed.<ref>{{cite journal|journal=Nature|volume=443|issue=7107|pages=71–75|date=7 September 2006| doi=10.1038/nature05040|pmid=16957728|title=Methane bubbling from Siberian thaw lakes as a positive feedback to climate warming |first1=KM |last1=Walter |first2=SA |last2=Zimov |first3=JP |last3=Chanton |first4=D |last4=Verbyla |first5=FS, III|last5=Chapin|display-authors=4|bibcode=2006Natur.443...71W|s2cid=4415304}}</ref><ref name="NYT Thaw">{{cite news|title=As Permafrost Thaws, Scientists Study the Risks|url=https://www.nytimes.com/2011/12/17/science/earth/warming-arctic-permafrost-fuels-climate-change-worries.html|access-date=December 17, 2011|newspaper=The New York Times|date=December 16, 2011|first=Justin|last=Gillis}}</ref> Lake produced by the thaw of particularly ice-rich permafrost are known as [[thermokarst]] lakes. Another process which frequently results in substantial methane emissions is the [[erosion]] of permafrost-stabilized hillsides and their ultimate collapse. <ref>{{Cite journal|last=Turetsky|first=Merritt R.|date=2019-04-30|title=Permafrost collapse is accelerating carbon release|journal=Nature|volume=569|issue=7754|pages=32–34|bibcode=2019Natur.569...32T|doi=10.1038/d41586-019-01313-4|pmid=31040419|doi-access=free}}</ref> Altogether, these two processes - hillside collapse and thermokarst lake formation - are known as abrupt thaw, as they can rapidly expose substantial volumes of soil to microbial respiration in a matter of days, as opposed to the gradual, cm by cm, thaw of formerly frozen soil which dominates across most permafrost environments. This rapidity was illustrated in 2019, when three permafrost sites which would have been safe from thawing under the "intermediate" [[Representative Concentration Pathway]] 4.5 for 70 more years had undergone abrupt thaw. <ref name="Reuters">{{Cite news|url=https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2019/jun/18/arctic-permafrost-canada-science-climate-crisis|title=Scientists shocked by Arctic permafrost thawing 70 years sooner than predicted|last=Reuters|date=2019-06-18|work=The Guardian|access-date=2019-07-02|language=en-GB|issn=0261-3077}}</ref> |
|||
Until recently, Permafrost carbon feedback (PCF) modeling had mainly focused on gradual permafrost thaw, due to the difficulty of modelling abrupt thaw, and because of the flawed assumptions about the rates of methane production.<ref name=":5" /> Nevertheless, a study from 2018, by using field observations, radiocarbon dating, and remote sensing to account for [[thermokarst]] lakes, determined that abrupt thaw will more than double permafrost carbon emissions by 2100.<ref name=":6" /> And a second study from 2020, showed that under a high RCP 8.5 scenario, abrupt thaw carbon emissions across 2.5 million km2 are projected to provide the same feedback as gradual thaw of near-surface permafrost across the whole 18 million km2 it occupies.<ref name=":5" /> Thus, compared to just gradual thaw, abrupt thaw increases carbon emissions by ~125–190%.<ref name=":5">{{Cite journal|last1=Turetsky|first1=Merritt R.|last2=Abbott|first2=Benjamin W.|last3=Jones|first3=Miriam C.|last4=Anthony|first4=Katey Walter|last5=Olefeldt|first5=David|last6=Schuur|first6=Edward A. G.|last7=Grosse|first7=Guido|last8=Kuhry|first8=Peter|last9=Hugelius|first9=Gustaf|last10=Koven|first10=Charles|last11=Lawrence|first11=David M.|date=February 2020|title=Carbon release through abrupt permafrost thaw|url=http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41561-019-0526-0|journal=Nature Geoscience|volume=13|issue=2|pages=138–143|doi=10.1038/s41561-019-0526-0|bibcode=2020NatGe..13..138T|s2cid=213348269|issn=1752-0894}}</ref><ref name=":6">{{Cite journal|last1=Walter Anthony|first1=Katey|last2=Schneider von Deimling|first2=Thomas|last3=Nitze|first3=Ingmar|last4=Frolking|first4=Steve|last5=Emond|first5=Abraham|last6=Daanen|first6=Ronald|last7=Anthony|first7=Peter|last8=Lindgren|first8=Prajna|last9=Jones|first9=Benjamin|last10=Grosse|first10=Guido|date=2018-08-15|title=21st-century modeled permafrost carbon emissions accelerated by abrupt thaw beneath lakes|url=http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-05738-9|journal=Nature Communications|volume=9|issue=1|page=3262|doi=10.1038/s41467-018-05738-9|pmid=30111815|pmc=6093858|bibcode=2018NatCo...9.3262W|issn=2041-1723}}</ref> |
|||
However, there is still scientific debate about the rate and the trajectory of methane production in the thawed permafrost environments. For instance, a 2017 paper suggested that even in the thawing peatlands with frequent thermokarst lakes, less than 10% of methane emissions can be attributed to the old, thawed carbon, and the rest is anaerobic decomposition of modern carbon. <ref>{{Cite journal|last1=Cooper |first1=M. |last2=Estop-Aragonés |first2=C. |last3=Fisher |first3=J. |display-authors=etal|date=26 June 2017 |title=Limited contribution of permafrost carbon to methane release from thawing peatlands|url=https://www.nature.com/articles/nature14338 |journal=Nature Climate Change |volume=7 |pages=507–511 |doi=10.1038/nclimate3328}}</ref> A follow-up study in 2018 had even suggested that increased uptake of carbon due to rapid peat formation in the thermokarst wetlands would compensate for the increased methane release.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Estop-Aragonés |first1=Cristian |last2=Cooper |first2=Mark D.A. |last3=Fisher |first3=James P. |display-authors=etal |date=March 2018 |title=Limited release of previously-frozen C and increased new peat formation after thaw in permafrost peatlands |url=https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0038071717306892 |journal=Soil Biology and Biochemistry |volume=118 |pages=115-129 |doi=10.1016/j.soilbio.2017.12.010}}</ref> Another 2018 paper suggested that permafrost emissions are limited following thermokarst thaw, but are substantially greater in the aftermath of wildfires.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Estop-Aragonés |first1=Cristian |display-authors=etal|date=13 August 2018 |title=Respiration of aged soil carbon during fall in permafrost peatlands enhanced by active layer deepening following wildfire but limited following thermokarst |url=https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1748-9326/aad5f0 |journal=Environmental Research Letters |volume=13 |doi=10.1088/1748-9326/aad5f0}}</ref> In 2022, a paper demonstrated that peatland methane emissions from permafrost thaw are initially quite high (82 milligrams of methane per square meter per day), but decline by nearly three times as the permafrost bog matures, suggesting a reduction in methane emissions in several decades to a century following abrupt thaw.<ref>{{Cite journal|last1=Heffernan|first1=Liam |last2=Cavaco |first2= Maria A. |last3=Bhatia |first3=Maya P. |last4=Estop-Aragonés |first4= Cristian |last5=Knorr |first5=Klaus-Holger |last6=Olefeldt |first6=David |date=24 June 2022 |title=High peatland methane emissions following permafrost thaw: enhanced acetoclastic methanogenesis during early successional stages |url=https://bg.copernicus.org/articles/19/3051/2022/ |journal=Biogeosciences |volume=19 |issue=8 |pages=3051–3071 |doi=10.5194/bg-19-3051-2022}}</ref> |
|||
===Subsea permafrost=== |
|||
Subsea permafrost occurs beneath the seabed and exists in the continental shelves of the polar regions.<ref>{{cite web|author=IPCC AR4|title=Climate Change 2007: Working Group I: The Physical Science Basis|date=2007|url=http://www.ipcc.ch/publications_and_data/ar4/wg1/en/ch4s4-7-2-4.html|access-date=12 April 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140413125748/http://www.ipcc.ch/publications_and_data/ar4/wg1/en/ch4s4-7-2-4.html|archive-date=13 April 2014|url-status=dead}}</ref> Thus, it can be defined as "the unglaciated continental shelf areas exposed during the [[Last Glacial Maximum]] (LGM, ~26 500 BP) that are currently inundated". Large stocks of organic matter (OM) and methane ({{CH4}}) are accumulated below and within the subsea permafrost deposits.This source of methane is different from [[methane clathrate]]s, but contributes to the overall outcome and feedbacks in the Earth's climate system.<ref name=":4" /> |
|||
The size of today's subsea permafrost has been estimated at around 2 million km<sup>2</sup> (~1/5 of the terrestrial permafrost domain size), which constitutes a 30-50% reduction since the LGM. Containing around 560 GtC in OM and 45 GtC in CH<sub>4</sub>, with a current release of 18 and 38 MtC per year respectively, which is due to the warming and thawing that the subsea permafrost domain has been experiencing since after the LGM (~14000 years ago). In fact, because the subsea permafrost systems responds at millennial timescales to climate warming, the current carbon fluxes it is emitting to the water are in response to climatic changes occurring after the LGM. Therefore, human-driven climate change effects on subsea permafrost will only be seen hundreds or thousands of years from today. According to predictions under a business-as-usual emissions scenario [[RCP8.5|RCP 8.5]], by 2100, 43 GtC could be released from the subsea permafrost domain, and 190 GtC by the year 2300. Whereas for the low emissions scenario RCP 2.6, 30% less emissions are estimated. This constitutes a significant anthropogenic-driven acceleration of carbon release in the upcoming centuries.<ref name=":4" /> |
|||
===Cumulative=== |
|||
In 2011, preliminary computer analyses suggested that permafrost emissions could be equivalent to around 15% of anthropogenic emissions.<ref>{{cite news |title=As Permafrost Thaws, Scientists Study the Risks |first=Justin |last=Gillis |newspaper=The New York Times |date=December 16, 2011 |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2011/12/17/science/earth/warming-arctic-permafrost-fuels-climate-change-worries.html?pagewanted=all |access-date=2017-02-11 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170519052405/http://www.nytimes.com/2011/12/17/science/earth/warming-arctic-permafrost-fuels-climate-change-worries.html?pagewanted=all |archive-date=2017-05-19 |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
A 2018 perspectives article discussing [[tipping points in the climate system]] at 2 degrees of warming suggested that at 2 degrees Celsius of global warming, permafrost thaw would add a further 0.09 °C to global temperatures by 2100, with a range between 0.04°C and 0.16°C <ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Schellnhuber |first1=Hans Joachim |last2=Winkelmann |first2=Ricarda |last3=Scheffer |first3=Marten |last4=Lade |first4=Steven J. |last5=Fetzer |first5=Ingo |last6=Donges |first6=Jonathan F. |last7=Crucifix |first7=Michel |last8=Cornell |first8=Sarah E. |last9=Barnosky |first9=Anthony D. |author-link9=Anthony David Barnosky |date=2018 |title=Trajectories of the Earth System in the Anthropocene |journal=[[Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences]] |volume=115 |issue=33 |pages=8252–8259 |bibcode=2018PNAS..115.8252S |doi=10.1073/pnas.1810141115 |issn=0027-8424 |pmc=6099852 |pmid=30082409 |doi-access=free}}</ref> In 2021, another study estimated that in a future where [[net zero|zero emissions]] were reached following a emission of a further 1000 Pg C into the atmosphere (a scenario where temperatures ordinarily stay stable after the last emission, or start to decline slowly) permafrost carbon would add 0.06°C (with a range between 0.02°C and 0.14°C) 50 years after the last anthropogenic emission, 0.09°C (with a range between 0.04°C to 0.21°C) 100 years later and 0.27°C (ranging between 0.12 to 0.49°C) 500 years later.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=MacDougall |first1=Andrew H. |date=10 September 2021 |title=Estimated effect of the permafrost carbon feedback on the zero emissions commitment to climate change |url=https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1748-9326/aad5f0 |journal=Biogeosciences |volume=18 |pages=4937–4952 | doi=10.5194/bg-18-4937-2021}}</ref> However, neither study was able to take abrupt thaw into account. |
|||
In 2020, a study of the northern permafrost peatlands (a smaller subset of the entire permafrost area, covering 3.7 million km<sup>2</sup> out of the estimated 18 million km<sup>2</sup><ref name=":4">{{Cite journal|last1=Sayedi|first1=Sayedeh Sara|last2=Abbott|first2=Benjamin W|last3=Thornton|first3=Brett F|last4=Frederick|first4=Jennifer M|last5=Vonk|first5=Jorien E|last6=Overduin|first6=Paul|last7=Schädel|first7=Christina|last8=Schuur|first8=Edward A G|last9=Bourbonnais|first9=Annie|last10=Demidov|first10=Nikita|last11=Gavrilov|first11=Anatoly|date=2020-12-01|title=Subsea permafrost carbon stocks and climate change sensitivity estimated by expert assessment|url=http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/abcc29|journal=Environmental Research Letters|volume=15|issue=12|pages=B027-08|doi=10.1088/1748-9326/abcc29|bibcode=2020AGUFMB027...08S|s2cid=234515282|issn=1748-9326}}</ref>) would amount to ∼1% of anthropogenic [[radiative forcing]] by 2100, and that this proportion remains the same in all warming scenarios considered, from 1.5°C to 6°C. It had further suggested that after 200 more years, those peatlands would have absorbed more carbon than what they had emitted into the atmosphere.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Hugelius |first1=Gustaf |last2=Loisel |first2=Julie |last3=Chadburn |first3=Sarah |display-authors=etal |date=10 August 2020 |title=Large stocks of peatland carbon and nitrogen are vulnerable to permafrost thaw |url=https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.1916387117 |journal=Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary Sciences |volume=117 |issue=34 |pages=20438-20446 |doi=10.1073/pnas.1916387117}}</ref> |
|||
In 2021, a group of prominent permafrost researchers like [[Merritt Turetsky]] had presented their collective estimate of permafrost emissions as part of an effort to advocate for a 50% reduction in anthropogenic emissions by 2030 as a necessary milestone to help reach net zero by 2050. Their figures included abrupt thaw, and compared the combined permafrost emissions by 2100 to the cumulative historical emissions of [[Canada]] if 1.5 degrees target was met, but to those of the [[European Union]] if the warming reached 2 degrees, as 2 million more square kilometers of permafrost would be lost. If the warming was allowed to exceed 4 degrees, then permafrost emissions would match the cumulative emissions of the [[United States]] or [[China]], and would be equivalent to the today's remaining budget for staying within a 1.5 degrees target. <ref>{{cite web |date=2021 |title=Carbon Emissions from Permafrost |url=https://www.50x30.net/carbon-emissions-from-permafrost |language=en |website=50x30 |access-date=8 October 2022}}</ref> |
|||
The [[IPCC Sixth Assessment Report]] estimates that carbon dioxide and methane released from permafrost could amount to the equivalent of 14-175 billion tonnes of carbon dioxide per 1<sup>o</sup>C of warming.<ref name="IPCC AR6 WG1" /> For comparison, by 2019 the anthropogenic emission of all carbon dioxide into the atmosphere stood around 40 billion tonnes.<ref name="IPCC AR6 WG1"/> |
|||
An updated 2022 assessment of climate tipping points concluded that abrupt permafrost thaw would add 50% to gradual thaw rates, and would add 14 billion tons of carbon dioxide equivalent emissions by 2100 and 35 by 2300 per every degree of warming. This would have a warming impact of 0.04°C per every full degree of warming by 2100, and 0.11°C per every full degree of warming by 2300. It also suggested that at between 3 and 6 degrees of warming (with the most likely figure around 4 degrees) a large-scale collapse of permafrost areas could become irreversible, adding between 175 and 350 billion tons of CO<sup>2</sup> equivalent emissions, or 0.2 - 0.4 degrees, over about 50 years (with a range between 10 and 300 years.)<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Armstrong McKay |first1=David|last2=Abrams |first2=Jesse |last3=Winkelmann |first3=Ricarda |last4=Sakschewski |first4=Boris |last5=Loriani |first5=Sina |last6=Fetzer |first6=Ingo|last7=Cornell|first7=Sarah |last8=Rockström |first8=Johan |last9=Staal |first9=Arie |last10=Lenton |first10=Timothy |date=9 September 2022 |title=Exceeding 1.5°C global warming could trigger multiple climate tipping points |url=https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.abn7950 |journal=Science |language=en |volume=377 |issue=6611 |doi=10.1126/science.abn7950 |issn=0036-8075}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=Armstrong McKay |first=David |date=9 September 2022 |title=Exceeding 1.5°C global warming could trigger multiple climate tipping points – paper explainer |url=https://climatetippingpoints.info/2022/09/09/climate-tipping-points-reassessment-explainer/ |access-date=2 October 2022 |website=climatetippingpoints.info |language=en}}</ref> |
|||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
Revision as of 23:30, 8 October 2022
| Part of a series on the |
| Carbon cycle |
|---|
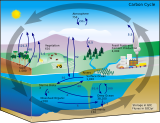 |
The permafrost carbon cycle or Arctic carbon cycle is a sub-cycle of the larger global carbon cycle. Permafrost is defined as subsurface material that remains below 0o C (32o F) for at least two consecutive years. Because permafrost soils remain frozen for long periods of time, they store large amounts of carbon and other nutrients within their frozen framework during that time. Permafrost represents a large carbon reservoir that is seldom considered when determining global terrestrial carbon reservoirs. Recent and ongoing scientific research however, is changing this view.[1]
The permafrost carbon cycle deals with the transfer of carbon from permafrost soils to terrestrial vegetation and microbes, to the atmosphere, back to vegetation, and finally back to permafrost soils through burial and sedimentation due to cryogenic processes. Some of this carbon is transferred to the ocean and other portions of the globe through the global carbon cycle. The cycle includes the exchange of carbon dioxide and methane between terrestrial components and the atmosphere, as well as the transfer of carbon between land and water as methane, dissolved organic carbon, dissolved inorganic carbon, particulate inorganic carbon and particulate organic carbon.[2]
Storage
Soils, in general, are the largest reservoirs of carbon in terrestrial ecosystems. This is also true for soils in the Arctic that are underlain by permafrost. In 2003, Tarnocai, et al. used the Northern and Mid Latitudes Soil Database to make a determination of carbon stocks in cryosols—soils containing permafrost within two meters of the soil surface.[3] Permafrost affected soils cover nearly 9% of the earth's land area, yet store between 25 and 50% of the soil organic carbon. These estimates show that permafrost soils are an important carbon pool.[4] These soils not only contain large amounts of carbon, but also sequester carbon through cryoturbation and cryogenic processes.[3][5]
Processes
Carbon is not produced by permafrost. Organic carbon derived from terrestrial vegetation must be incorporated into the soil column and subsequently be incorporated into permafrost to be effectively stored. Because permafrost responds to climate changes slowly, carbon storage removes carbon from the atmosphere for long periods of time. Radiocarbon dating techniques reveal that carbon within permafrost is often thousands of years old.[6][7] Carbon storage in permafrost is the result of two primary processes.
- The first process that captures carbon and stores it is syngenetic permafrost growth.[8] This process is the result of a constant active layer where thickness and energy exchange between permafrost, active layer, biosphere, and atmosphere, resulting in the vertical increase of the soil surface elevation. This aggradation of soil is the result of aeolian or fluvial sedimentation and/or peat formation. Peat accumulation rates are as high as 0.5mm/yr while sedimentation may cause a rise of 0.7mm/yr. Thick silt deposits resulting from abundant loess deposition during the last glacial maximum form thick carbon-rich soils known as yedoma.[9] As this process occurs, the organic and mineral soil that is deposited is incorporated into the permafrost as the permafrost surface rises.
- The second process responsible for storing carbon is cryoturbation, the mixing of soil due to freeze-thaw cycles. Cryoturbation moves carbon from the surface to depths within the soil profile. Frost heaving is the most common form of cryoturbation. Eventually, carbon that originates at the surface moves deep enough into the active layer to be incorporated into permafrost. When cryoturbation and the deposition of sediments act together carbon storage rates increase.[9]
Current estimates
It is estimated that the total soil organic carbon (SOC) stock in northern circumpolar permafrost region equals around 1,460-1,600 Pg.[5] (1 Pg = 1 Gt = 1015g)[10][11] With the Tibetan Plateau carbon content included, the total carbon pools in the permafrost of the Northern Hemisphere is likely to be around 1832 Gt.[12] This estimation of the amount of carbon stored in permafrost soils is more than double the amount currently in the atmosphere.[1]
Soil column in the permafrost soils is generally broken into three horizons, 0–30 cm, 0–100 cm, and 1–300 cm. The uppermost horizon (0–30 cm) contains approximately 200 Pg of organic carbon. The 0–100 cm horizon contains an estimated 500 Pg of organic carbon, and the 0–300 cm horizon contains an estimated 1024 Pg of organic carbon. These estimates more than doubled the previously known carbon pools in permafrost soils.[3][4][5] Additional carbon stocks exist in yedoma (400 Pg), carbon rich loess deposits found throughout Siberia and isolated regions of North America, and deltaic deposits (240 Pg) throughout the Arctic. These deposits are generally deeper than the 3 m investigated in traditional studies.[5] Many concerns arise because of the large amount of carbon stored in permafrost soils. Until recently, the amount of carbon present in permafrost was not taken into account in climate models and global carbon budgets.[1][9]
Carbon release from the permafrost
Carbon is continually cycling between soils, vegetation, and the atmosphere. As climate change increases mean annual air temperatures throughout the Arctic, it extends permafrost thaw and deepens the active layer, exposing old carbon that has been in storage for decades to millennia to biogenic processes which facilitate its entrance into the atmosphere. In general, the volume of permafrost in the upper 3 m of ground is expected to decrease by about 25% per 1 °C of global warming.[13] According to the IPCC Sixth Assessment Report, there is high confidence that global warming over the last few decades has led to widespread increases in permafrost temperature.[14] Observed warming was up to 3 °C in parts of Northern Alaska (early 1980s to mid-2000s) and up to 2 °C in parts of the Russian European North (1970-2020), and active layer thickness has increased in the European and Russian Arctic across the 21st century and at high elevation areas in Europe and Asia since the 1990s.[14][15] In Yukon, the zone of continuous permafrost might have moved 100 kilometres (62 mi) poleward since 1899, but accurate records only go back 30 years. Based on high agreement across model projections, fundamental process understanding, and paleoclimate evidence, it is virtually certain that permafrost extent and volume will continue to shrink as global climate warms.[13]
Carbon emissions from permafrost thaw contribute to the same warming which facilitates the thaw, making it a positive climate change feedback. The amount of carbon that will be released from warming conditions depends on depth of thaw, carbon content within the thawed soil, physical changes to the environment[7] and microbial and vegetation activity in the soil. Microbial respiration is the primary process through which old permafrost carbon is re-activated and enters the atmosphere. The rate of microbial decomposition within organic soils, including thawed permafrost, depends on environmental controls, such as soil temperature, moisture availability, nutrient availability, and oxygen availability.[9]
Altogether, the likelihood of the entire carbon pool mobilizing and entering the atmosphere is low despite the large volumes stored in the soil. Although temperatures will fit does not imply complete loss of permafrost and mobilization of the entire carbon pool. Much of the ground underlain by permafrost will remain frozen even if warming temperatures increase the thaw depth or increase thermokarsting and permafrost degradation.[4] However, once permafrost area thaws, it will not go back to being permafrost for centuries even if the temperature increase reversed, making it one of the best-known examples of tipping points in the climate system.
A 1993 study suggested that while the tundra was a carbon sink until the end of 1970s, it had already transitioned to a net carbon source by the time the study concluded.[16] The 2019 Arctic Report Card estimated that Arctic permafrost releases between 0.3 and 0.6 Pg C per year.[11] That same year, a study settled on the 0.6 Pg C figure, as the net difference between the annual emissions of 1,66 Pg C during the winter season (October–April), and the model-estimated vegetation carbon uptake of 1 Pg C during the growing season. It estimated that RCP 8.5, a scenario of continually accelerating greenhouse gas emissions, winter CO2 emissions from the norther permafrost domain would increase 41% by 2100. Under the "intermediate" scenario RCP 4.5, where greenhouse gas emissions peak and plateau within the next two decades, before gradually declining for the rest of the century (a rate of mitigation deeply insufficient to meet the Paris Agreement goals) permafrost carbon emissions would increase by 17%. [17] In 2022, this was challenged by a study which used a record of atmospheric observations between 1980 to 2017, and found that permafrost regions have been gaining carbon on net, as process-based models underestimated net CO2 uptake in the permafrost regions and overestimated it in the forested regions, where increased respiration in response to warming offsets more of the gains then was previously understood. [18]
Notably, estimates of carbon release alone do not fully represent the impact of permafrost thaw on climate change. This is because carbon can either be released as carbon dioxide (CO2) or methane (CH4). Aerobic respiration releases carbon dioxide, while anaerobic respiration releases methane. This is a substantial difference, as while biogenic methane lasts less than 12 years in the atmosphere, its global warming potential is around 80 times larger than that of CO2 over a 20-year period and between 28 and 40 times larger over a 100-year period.
Carbon dioxide emissions
Most of the permafrost soil are oxic and provide a suitable environment for aerobic microbial respiration. As such, carbon dioxide emissions account for the overwhelming majority of permafrost emissions and of the Arctic emissions in general. [19] There's some debate over whether the observed emissions from permafrost soils primarily constitute microbial respiration of ancient carbon, or simply greater respiration of modern-day carbon (i.e. leaf litter), due to warmer soils intensifying microbial metabolism. Studies published in the early 2020s indicate that while soil microbiota still primarily consumes and respires modern carbon when plants grow during the spring and summer, these microorganisms then sustain themselves on ancient carbon during the winter, releasing it into the atmosphere. [20][21]
On the other hand, former permafrost areas consistently see increased vegetation growth, or primary production, as plants can set down deeper roots in the thawed soil and grow larger and uptake more carbon. This is generally the main counteracting feedback on permafrost carbon emissions. However, in areas with streams and other waterways, more of their leaf litter enters those waterways, increasing their dissolved organic carbon content. Leaching of soil organic carbon from permafrost soils is also accelerated by warming climate and by erosion along river and stream banks freeing the carbon from the previously frozen soil.[6] Moreover, thawed areas become more vulnerable to wildfires, which alter landscape and release large quantities of stored organic carbon through combustion. As these fires burn, they remove organic matter from the surface. Removal of the protective organic mat that insulates the soil exposes the underlying soil and permafrost to increased solar radiation, which in turn increases the soil temperature, active layer thickness, and changes soil moisture. Changes in the soil moisture and saturation alter the ratio of oxic to anoxic decomposition within the soil.[22]
A hypothesis promoted by Sergey Zimov is that the reduction of herds of large herbivores has increased the ratio of energy emission and energy absorption tundra (energy balance) in a manner that increases the tendency for net thawing of permafrost.[23] He is testing this hypothesis in an experiment at Pleistocene Park, a nature reserve in northeastern Siberia.[24] On the other hand, warming allows the beavers to extend their habitat further north, where their dams impair boat travel, impact access to food, affect water quality, and endanger downstream fish populations.[25] Pools formed by the dams store heat, thus changing local hydrology and causing localized permafrost thaw.[25]
Methane emissions
Global warming in the Arctic accelerates methane release from both existing stores and methanogenesis in rotting biomass.[26] Methanogenesis requires thoroughly anaerobic environments, which slows down the mobilization of old carbon. A 2015 Nature review estimated that the cumulative emissions from thawed anaerobic permafrost sites were 75-85% lower than the cumulative emissions from aerobic sites, and that even there, methane emissions amounted to only 3% to 7% of CO2 emitted in situ. While they represented between 25% to 45% of the CO2's potential impact on climate over a 100-year timescale, the review concluded that aerobic permafrost thaw still had a greater warming impact overall.[27] In 2018, however, another study in Nature Climate Change found that at many anaerobic sites, methane production was equivalent to CO2 production, substantially raising the overall warming impact they represented. [28]
Since methanogenesis requires anaerobic environments, it is frequently associated with Arctic lake environments, where the emergence of bubbles of methane can be observed.[29][30] Lake produced by the thaw of particularly ice-rich permafrost are known as thermokarst lakes. Another process which frequently results in substantial methane emissions is the erosion of permafrost-stabilized hillsides and their ultimate collapse. [31] Altogether, these two processes - hillside collapse and thermokarst lake formation - are known as abrupt thaw, as they can rapidly expose substantial volumes of soil to microbial respiration in a matter of days, as opposed to the gradual, cm by cm, thaw of formerly frozen soil which dominates across most permafrost environments. This rapidity was illustrated in 2019, when three permafrost sites which would have been safe from thawing under the "intermediate" Representative Concentration Pathway 4.5 for 70 more years had undergone abrupt thaw. [32]
Until recently, Permafrost carbon feedback (PCF) modeling had mainly focused on gradual permafrost thaw, due to the difficulty of modelling abrupt thaw, and because of the flawed assumptions about the rates of methane production.[33] Nevertheless, a study from 2018, by using field observations, radiocarbon dating, and remote sensing to account for thermokarst lakes, determined that abrupt thaw will more than double permafrost carbon emissions by 2100.[34] And a second study from 2020, showed that under a high RCP 8.5 scenario, abrupt thaw carbon emissions across 2.5 million km2 are projected to provide the same feedback as gradual thaw of near-surface permafrost across the whole 18 million km2 it occupies.[33] Thus, compared to just gradual thaw, abrupt thaw increases carbon emissions by ~125–190%.[33][34]
However, there is still scientific debate about the rate and the trajectory of methane production in the thawed permafrost environments. For instance, a 2017 paper suggested that even in the thawing peatlands with frequent thermokarst lakes, less than 10% of methane emissions can be attributed to the old, thawed carbon, and the rest is anaerobic decomposition of modern carbon. [35] A follow-up study in 2018 had even suggested that increased uptake of carbon due to rapid peat formation in the thermokarst wetlands would compensate for the increased methane release.[36] Another 2018 paper suggested that permafrost emissions are limited following thermokarst thaw, but are substantially greater in the aftermath of wildfires.[37] In 2022, a paper demonstrated that peatland methane emissions from permafrost thaw are initially quite high (82 milligrams of methane per square meter per day), but decline by nearly three times as the permafrost bog matures, suggesting a reduction in methane emissions in several decades to a century following abrupt thaw.[38]
Subsea permafrost
Subsea permafrost occurs beneath the seabed and exists in the continental shelves of the polar regions.[39] Thus, it can be defined as "the unglaciated continental shelf areas exposed during the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM, ~26 500 BP) that are currently inundated". Large stocks of organic matter (OM) and methane (CH4) are accumulated below and within the subsea permafrost deposits.This source of methane is different from methane clathrates, but contributes to the overall outcome and feedbacks in the Earth's climate system.[40]
The size of today's subsea permafrost has been estimated at around 2 million km2 (~1/5 of the terrestrial permafrost domain size), which constitutes a 30-50% reduction since the LGM. Containing around 560 GtC in OM and 45 GtC in CH4, with a current release of 18 and 38 MtC per year respectively, which is due to the warming and thawing that the subsea permafrost domain has been experiencing since after the LGM (~14000 years ago). In fact, because the subsea permafrost systems responds at millennial timescales to climate warming, the current carbon fluxes it is emitting to the water are in response to climatic changes occurring after the LGM. Therefore, human-driven climate change effects on subsea permafrost will only be seen hundreds or thousands of years from today. According to predictions under a business-as-usual emissions scenario RCP 8.5, by 2100, 43 GtC could be released from the subsea permafrost domain, and 190 GtC by the year 2300. Whereas for the low emissions scenario RCP 2.6, 30% less emissions are estimated. This constitutes a significant anthropogenic-driven acceleration of carbon release in the upcoming centuries.[40]
Cumulative
In 2011, preliminary computer analyses suggested that permafrost emissions could be equivalent to around 15% of anthropogenic emissions.[41]
A 2018 perspectives article discussing tipping points in the climate system at 2 degrees of warming suggested that at 2 degrees Celsius of global warming, permafrost thaw would add a further 0.09 °C to global temperatures by 2100, with a range between 0.04°C and 0.16°C [42] In 2021, another study estimated that in a future where zero emissions were reached following a emission of a further 1000 Pg C into the atmosphere (a scenario where temperatures ordinarily stay stable after the last emission, or start to decline slowly) permafrost carbon would add 0.06°C (with a range between 0.02°C and 0.14°C) 50 years after the last anthropogenic emission, 0.09°C (with a range between 0.04°C to 0.21°C) 100 years later and 0.27°C (ranging between 0.12 to 0.49°C) 500 years later.[43] However, neither study was able to take abrupt thaw into account.
In 2020, a study of the northern permafrost peatlands (a smaller subset of the entire permafrost area, covering 3.7 million km2 out of the estimated 18 million km2[40]) would amount to ∼1% of anthropogenic radiative forcing by 2100, and that this proportion remains the same in all warming scenarios considered, from 1.5°C to 6°C. It had further suggested that after 200 more years, those peatlands would have absorbed more carbon than what they had emitted into the atmosphere.[44]
In 2021, a group of prominent permafrost researchers like Merritt Turetsky had presented their collective estimate of permafrost emissions as part of an effort to advocate for a 50% reduction in anthropogenic emissions by 2030 as a necessary milestone to help reach net zero by 2050. Their figures included abrupt thaw, and compared the combined permafrost emissions by 2100 to the cumulative historical emissions of Canada if 1.5 degrees target was met, but to those of the European Union if the warming reached 2 degrees, as 2 million more square kilometers of permafrost would be lost. If the warming was allowed to exceed 4 degrees, then permafrost emissions would match the cumulative emissions of the United States or China, and would be equivalent to the today's remaining budget for staying within a 1.5 degrees target. [45]
The IPCC Sixth Assessment Report estimates that carbon dioxide and methane released from permafrost could amount to the equivalent of 14-175 billion tonnes of carbon dioxide per 1oC of warming.[14] For comparison, by 2019 the anthropogenic emission of all carbon dioxide into the atmosphere stood around 40 billion tonnes.[14]
An updated 2022 assessment of climate tipping points concluded that abrupt permafrost thaw would add 50% to gradual thaw rates, and would add 14 billion tons of carbon dioxide equivalent emissions by 2100 and 35 by 2300 per every degree of warming. This would have a warming impact of 0.04°C per every full degree of warming by 2100, and 0.11°C per every full degree of warming by 2300. It also suggested that at between 3 and 6 degrees of warming (with the most likely figure around 4 degrees) a large-scale collapse of permafrost areas could become irreversible, adding between 175 and 350 billion tons of CO2 equivalent emissions, or 0.2 - 0.4 degrees, over about 50 years (with a range between 10 and 300 years.)[46][47]
See also
References
- ^ a b c Zimov SA, Schuur EA, Chapin FS (June 2006). "Climate change. Permafrost and the global carbon budget". Science. 312 (5780): 1612–3. doi:10.1126/science.1128908. PMID 16778046. S2CID 129667039.
- ^ McGuire, A.D., Anderson, L.G., Christensen, T.R., Dallimore, S., Guo, L., Hayes, D.J., Heimann, M., Lorenson, T.D., Macdonald, R.W., and Roulet, N. (2009). "Sensitivity of the carbon cycle in the Arctic to climate change". Ecological Monographs. 79 (4): 523–555. doi:10.1890/08-2025.1. hdl:11858/00-001M-0000-000E-D87B-C.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c Tarnocai, C., Kimble, J., Broll, G. (2003). "Determining carbon stocks in Cryosols using the Northern and Mid Latitudes Soil Database" (PDF). In Phillips, Marcia; Springman, Sarah M; Arenson, Lukas U (eds.). Permafrost : Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Permafrost, Zurich, Switzerland, 21–25 July 2003. London: Momenta. pp. 1129–34. ISBN 978-90-5809-584-8.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c Bockheim, J.G. & Hinkel, K.M. (2007). "The importance of "Deep" organic carbon in permafrost-affected soils of Arctic Alaska". Soil Science Society of America Journal. 71 (6): 1889–92. Bibcode:2007SSASJ..71.1889B. doi:10.2136/sssaj2007.0070N. Archived from the original on 17 July 2009. Retrieved 5 June 2010.
- ^ a b c d Tarnocai, C., Canadell, J.G., Schuur, E.A.G., Kuhry, P., Mazhitova, G., and Zimov, S. (2009). "Soil organic carbon pools in the northern circumpolar permafrost region". Global Biogeochemical Cycles. 23 (2): GB2023. Bibcode:2009GBioC..23.2023T. doi:10.1029/2008GB003327.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Guo, L., Chien-Lu Ping, and Macdonald, R.W. (July 2007). "Mobilization pathways of organic carbon from permafrost to arctic rivers in a changing climate. ". Geophysical Research Letters. 34 (13): L13603. Bibcode:2007GeoRL..3413603G. doi:10.1029/2007GL030689.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Nowinski NS, Taneva L, Trumbore SE, Welker JM (January 2010). "Decomposition of old organic matter as a result of deeper active layers in a snow depth manipulation experiment". Oecologia. 163 (3): 785–92. Bibcode:2010Oecol.163..785N. doi:10.1007/s00442-009-1556-x. PMC 2886135. PMID 20084398.
- ^ Anderson, D. A.; Bray, M. T.; French, H. M.; Shur, Y. (1 October 2004). "Syngenetic permafrost growth: cryostratigraphic observations from the CRREL tunnel near Fairbanks, Alaska". Permafrost and Periglacial Processes. 15 (4): 339–347. doi:10.1002/ppp.486. ISSN 1099-1530.
- ^ a b c d Schuur, E.A.G., Bockheim, J., Canadell, J.G., Euskirchen, E., Field, C.B., Goryachkin, S.V., Hagemann, S., Kuhry, P., Lafleur, P.M., Lee, H., Mazhitova, G., Nelson, F.E., Rinke, A., Romanovsky, V.E., Skiklomanov, N., Tarnocai, C., Venevsky, S., Vogel, J.G., and Zimov, S.A. (2008). "Vulnerability of Permafrost Carbon to Climate Change: Implications for the Global Carbon Cycle". BioScience. 58 (8): 701–714. doi:10.1641/B580807.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Hugelius, G.; Strauss, J.; Zubrzycki, S.; Harden, J. W.; Schuur, E. A. G.; Ping, C.-L.; Schirrmeister, L.; Grosse, G.; Michaelson, G. J.; Koven, C. D.; O'Donnell, J. A. (1 December 2014). "Estimated stocks of circumpolar permafrost carbon with quantified uncertainty ranges and identified data gaps". Biogeosciences. 11 (23): 6573–6593. Bibcode:2014BGeo...11.6573H. doi:10.5194/bg-11-6573-2014. ISSN 1726-4189. S2CID 14158339.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ a b "Permafrost and the Global Carbon Cycle". Arctic Program. Retrieved 18 May 2021.
- ^ http://www.the-cryosphere.net/9/479/2015/tc-9-479-2015.pdf [bare URL PDF]
- ^ a b IPCC AR6 WG1 Ch9 2021, p. 1283
- ^ a b c d Fox-Kemper, B.; Hewitt, H.T.; Xiao, C.; Aðalgeirsdóttir, G.; Drijfhout, S.S.; Edwards, T.L.; Golledge, N.R.; Hemer, M.; Kopp, R.E.; Krinner, G.; Mix, A. (2021). Masson-Delmotte, V.; Zhai, P.; Pirani, A.; Connors, S.L.; Péan, C.; Berger, S.; Caud, N.; Chen, Y.; Goldfarb, L. (eds.). "Ocean, Cryosphere and Sea Level Change". Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK and New York, NY, USA: 1237, 1238–1239, 1320. doi:10.1017/9781009157896.011 (inactive 9 July 2022).
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of July 2022 (link) - ^ "Working Group I Contribution to the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report Climate Change 2013 - Summary for Policymakers - Template Lab". 10 November 2015. Archived from the original on 18 January 2017. Retrieved 16 January 2017.
- ^ Oechel, Walter C.; Hastings, Steven J.; Vourlrtis, George; Jenkins, Mitchell; et al. (1993). "Recent change of Arctic tundra ecosystems from a net carbon dioxide sink to a source". Nature. 361 (6412): 520–523. Bibcode:1993Natur.361..520O. doi:10.1038/361520a0. S2CID 4339256.
- ^ Natali, Susan M.; Watts, Jennifer D.; Rogers, Brendan M.; Potter, Stefano; Ludwig, Sarah M.; Selbmann, Anne-Katrin; Sullivan, Patrick F.; Abbott, Benjamin W.; Arndt, Kyle A.; Birch, Leah; Björkman, Mats P. (21 October 2019). "Large loss of CO2 in winter observed across the northern permafrost region". Nature Climate Change. 9 (11): 852–857. Bibcode:2019NatCC...9..852N. doi:10.1038/s41558-019-0592-8. hdl:10037/17795. ISSN 1758-678X. PMC 8781060. PMID 35069807. S2CID 204812327.
- ^ Liu, Zhihua; Kimball, John S.; Ballantyne, Ashley P.; Parazoo, Nicholas C.; Wang, Wen J.; Bastos, Ana; Chandra, Naveen; Natali, Susan M.; Watts, Jennifer D.; Rogers, Brendan M.; Ciais, Philippe; Yu, Kailiang; Virkkala, Anna-Maria; Chevallier, Frederic; Peters, Wouter; Patra, Prabir K. (21 October 2019). "Respiratory loss during late-growing season determines the net carbon dioxide sink in northern permafrost regions". Nature Communications. 13. doi:10.1038/s41467-022-33293-x.
- ^ Miner, Kimberley R.; Turetsky, Merritt R.; Malina, Edward; Bartsch, Annett; Tamminen, Johanna; McGuire, A. David; Fix, Andreas; Sweeney, Colm; Elder, Clayton D.; Miller, Charles E. (11 January 2022). "Permafrost carbon emissions in a changing Arctic". Nature Reviews Earth & Environment. 13: 55–67. doi:10.1038/s43017-021-00230-3.
- ^ Estop-Aragonés, Cristian; Olefeldt, David; et al. (2 September 2020). "Assessing the Potential for Mobilization of Old Soil Carbon After Permafrost Thaw: A Synthesis of 14C Measurements From the Northern Permafrost Region". Global Biogeochemical Cycles. 34 (9). doi:10.1029/2020GB006672.
- ^ Pedron, Shawn A.; Welker, J. M.; Euskirchen, E. S.; Klein, E. S.; Walker, J. C.; Xu, X.; Czimczik, C. I. (14 March 2022). "Closing the Winter Gap—Year-Round Measurements of Soil CO2 Emission Sources in Arctic Tundra". Geophysical Research Letters. 49 (6). doi:10.1029/2021GL097347.
- ^ Meyers-Smith, I.H., McGuire, A.D., Harden, J.W., Chapin, F.S. (2007). "Influence of disturbance on carbon exchange in a permafrost collapse and adjacent burned forest" (PDF). Journal of Geophysical Research. 112 (G4): G04017. Bibcode:2007JGRG..11204017M. doi:10.1029/2007JG000423.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ S.A. Zimov, N.S. Zimov, A.N. Tikhonov, F.S. Chapin III (2012). "Mammoth steppe: a high-productivity phenomenon" (PDF). In: Quaternary Science Reviews, vol. 57, 4 December 2012, p. 42 fig.17. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 17 October 2014.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Sergey A. Zimov (6 May 2005): "Pleistocene Park: Return of the Mammoth's Ecosystem." Archived 2017-02-20 at the Wayback Machine In: Science, pages 796–798. Article also to be found in www.pleistocenepark.ru/en/ – Materials. Archived 2016-11-03 at the Wayback Machine Retrieved 5 May 2013.
- ^ a b Milman, Oliver (4 January 2022). "Dam it: beavers head north to the Arctic as tundra continues to heat up". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 4 January 2022.
- ^ Walter, K. M.; Chanton, J. P.; Chapin, F. S.; Schuur, E. A. G.; Zimov, S. A. (2008). "Methane production and bubble emissions from arctic lakes: Isotopic implications for source pathways and ages". Journal of Geophysical Research. 113: G00A08. Bibcode:2008JGRG..11300A08W. doi:10.1029/2007JG000569.
- ^ Schuur, E. A. G.; McGuire, A. D.; Schädel, C.; Grosse, G.; Harden, J. W.; et al. (9 April 2015). "Climate change and the permafrost carbon feedback". Nature. 520: 171–179. doi:10.1038/nature14338.
- ^ Pfeiffer, Eva-Maria; Grigoriev, Mikhail N.; Liebner, Susanne; Beer, Christian; Knoblauch, Christian (April 2018). "Methane production as key to the greenhouse gas budget of thawing permafrost". Nature Climate Change. 8 (4): 309–312. Bibcode:2018NatCC...8..309K. doi:10.1038/s41558-018-0095-z. ISSN 1758-6798. S2CID 90764924.
- ^ Walter, KM; Zimov, SA; Chanton, JP; Verbyla, D; et al. (7 September 2006). "Methane bubbling from Siberian thaw lakes as a positive feedback to climate warming". Nature. 443 (7107): 71–75. Bibcode:2006Natur.443...71W. doi:10.1038/nature05040. PMID 16957728. S2CID 4415304.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Gillis, Justin (16 December 2011). "As Permafrost Thaws, Scientists Study the Risks". The New York Times. Retrieved 17 December 2011.
- ^ Turetsky, Merritt R. (30 April 2019). "Permafrost collapse is accelerating carbon release". Nature. 569 (7754): 32–34. Bibcode:2019Natur.569...32T. doi:10.1038/d41586-019-01313-4. PMID 31040419.
- ^ Reuters (18 June 2019). "Scientists shocked by Arctic permafrost thawing 70 years sooner than predicted". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 2 July 2019.
{{cite news}}:|last=has generic name (help) - ^ a b c Turetsky, Merritt R.; Abbott, Benjamin W.; Jones, Miriam C.; Anthony, Katey Walter; Olefeldt, David; Schuur, Edward A. G.; Grosse, Guido; Kuhry, Peter; Hugelius, Gustaf; Koven, Charles; Lawrence, David M. (February 2020). "Carbon release through abrupt permafrost thaw". Nature Geoscience. 13 (2): 138–143. Bibcode:2020NatGe..13..138T. doi:10.1038/s41561-019-0526-0. ISSN 1752-0894. S2CID 213348269.
- ^ a b Walter Anthony, Katey; Schneider von Deimling, Thomas; Nitze, Ingmar; Frolking, Steve; Emond, Abraham; Daanen, Ronald; Anthony, Peter; Lindgren, Prajna; Jones, Benjamin; Grosse, Guido (15 August 2018). "21st-century modeled permafrost carbon emissions accelerated by abrupt thaw beneath lakes". Nature Communications. 9 (1): 3262. Bibcode:2018NatCo...9.3262W. doi:10.1038/s41467-018-05738-9. ISSN 2041-1723. PMC 6093858. PMID 30111815.
- ^ Cooper, M.; Estop-Aragonés, C.; Fisher, J.; et al. (26 June 2017). "Limited contribution of permafrost carbon to methane release from thawing peatlands". Nature Climate Change. 7: 507–511. doi:10.1038/nclimate3328.
- ^ Estop-Aragonés, Cristian; Cooper, Mark D.A.; Fisher, James P.; et al. (March 2018). "Limited release of previously-frozen C and increased new peat formation after thaw in permafrost peatlands". Soil Biology and Biochemistry. 118: 115–129. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2017.12.010.
- ^ Estop-Aragonés, Cristian; et al. (13 August 2018). "Respiration of aged soil carbon during fall in permafrost peatlands enhanced by active layer deepening following wildfire but limited following thermokarst". Environmental Research Letters. 13. doi:10.1088/1748-9326/aad5f0.
- ^ Heffernan, Liam; Cavaco, Maria A.; Bhatia, Maya P.; Estop-Aragonés, Cristian; Knorr, Klaus-Holger; Olefeldt, David (24 June 2022). "High peatland methane emissions following permafrost thaw: enhanced acetoclastic methanogenesis during early successional stages". Biogeosciences. 19 (8): 3051–3071. doi:10.5194/bg-19-3051-2022.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ IPCC AR4 (2007). "Climate Change 2007: Working Group I: The Physical Science Basis". Archived from the original on 13 April 2014. Retrieved 12 April 2014.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c Sayedi, Sayedeh Sara; Abbott, Benjamin W; Thornton, Brett F; Frederick, Jennifer M; Vonk, Jorien E; Overduin, Paul; Schädel, Christina; Schuur, Edward A G; Bourbonnais, Annie; Demidov, Nikita; Gavrilov, Anatoly (1 December 2020). "Subsea permafrost carbon stocks and climate change sensitivity estimated by expert assessment". Environmental Research Letters. 15 (12): B027-08. Bibcode:2020AGUFMB027...08S. doi:10.1088/1748-9326/abcc29. ISSN 1748-9326. S2CID 234515282.
- ^ Gillis, Justin (16 December 2011). "As Permafrost Thaws, Scientists Study the Risks". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 19 May 2017. Retrieved 11 February 2017.
- ^ Schellnhuber, Hans Joachim; Winkelmann, Ricarda; Scheffer, Marten; Lade, Steven J.; Fetzer, Ingo; Donges, Jonathan F.; Crucifix, Michel; Cornell, Sarah E.; Barnosky, Anthony D. (2018). "Trajectories of the Earth System in the Anthropocene". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 115 (33): 8252–8259. Bibcode:2018PNAS..115.8252S. doi:10.1073/pnas.1810141115. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 6099852. PMID 30082409.
- ^ MacDougall, Andrew H. (10 September 2021). "Estimated effect of the permafrost carbon feedback on the zero emissions commitment to climate change". Biogeosciences. 18: 4937–4952. doi:10.5194/bg-18-4937-2021.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Hugelius, Gustaf; Loisel, Julie; Chadburn, Sarah; et al. (10 August 2020). "Large stocks of peatland carbon and nitrogen are vulnerable to permafrost thaw". Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary Sciences. 117 (34): 20438–20446. doi:10.1073/pnas.1916387117.
- ^ "Carbon Emissions from Permafrost". 50x30. 2021. Retrieved 8 October 2022.
- ^ Armstrong McKay, David; Abrams, Jesse; Winkelmann, Ricarda; Sakschewski, Boris; Loriani, Sina; Fetzer, Ingo; Cornell, Sarah; Rockström, Johan; Staal, Arie; Lenton, Timothy (9 September 2022). "Exceeding 1.5°C global warming could trigger multiple climate tipping points". Science. 377 (6611). doi:10.1126/science.abn7950. ISSN 0036-8075.
- ^ Armstrong McKay, David (9 September 2022). "Exceeding 1.5°C global warming could trigger multiple climate tipping points – paper explainer". climatetippingpoints.info. Retrieved 2 October 2022.
