Sauroniops
| Sauroniops Temporal range: Cenomanian,
| |
|---|---|
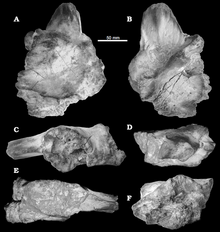
| |
| Holotype specimen, a left frontal bone (MPM 2594) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Dinosauria |
| Clade: | Saurischia |
| Clade: | Theropoda |
| Family: | †Carcharodontosauridae |
| Genus: | †Sauroniops Cau et al., 2012[1] |
| Type species | |
| †Sauroniops pachytholus Cau et al., 2012[1]
| |
Sauroniops is a genus of carnivorous basal carcharodontosaurid theropod dinosaur known from the Late Cretaceous (Cenomanian stage) of Morocco.[1]
Discovery

In the early twenty-first century a collector donated a dinosaur skull bone to the Italian Museo Paleontologico di Montevarchi. He had acquired the specimen from a Moroccan fossil dealer, who again had bought the piece from local fossil hunters near Taouz. Its exact provenance is therefore uncertain. Later research showed that it presented a new species that was in 2012 reported and described by Andrea Cau, Fabio Marco Dalla Vecchia and Matteo Fabbri.[2]
The same year, 2012, the specimen was, by the same authors, formally named in a subsequent publication as the type species Sauroniops pachytholus. The generic name has the intended meaning of "Eye of Sauron", a powerful entity from The Lord of the Rings fantasy novel by J.R.R. Tolkien, combining his name with a Classical Greek ὄψ, ops, "eye". Like in the novels the corporeal presence of Sauron had largely been limited to a single searching eye, Sauroniops is only known from a single bone above the eye socket. The specific name is derived from Greek παχύς, pachys, "thick", and θόλος, tholos, "round building with conical roof", in reference to the thick vaulted skull roof.[1]
The holotype, specimen MPM 2594, had probably been recovered from the Kem Kem Group, dating to the Cenomanian. It consists of a left frontal bone.[1]
A later study in 2020 suggested that Sauroniops was a junior synonym of Carcharodontosaurus saharicus,[3] though this statement has been criticized by Cau.[4]
A 2022 study published by Paterna and Cau reevaluated the reasoning of the 2020 study for considering Sauroniops a synonym of Carcharodontosaurus, and found most of the supposed shared features were based on misinterpretations of the Sauroniops holotype. Accordingly, having also found several additional features distinguishing the two taxa, they dismissed the synonymy between Carcharodontosaurus and Sauroniops.[5]
Description

Sauroniops was a large bipedal predator. The describers established several unique traits, differentiating Sauroniops from its relatives, such as Carcharodontosaurus which is found in the same layers. The nasal bone has an area of contact with the frontal bone over 40% of the latter's length. The frontal has in the left front corner a thick vaulted area. On the front upper rim the frontal has a trapezoid facet to contact the prefrontal, which is no part of the upper rim of the eye socket, and is separated from the facet for the lacrimal bone by a thin vertical ridge. The contact area with the lacrimal is D-shaped, extremely large and has four times the height of the facet with the postorbital bone. On the rear inner side of the frontal an elevated rim is present that is joint to the front vaulted area by a saddle-shaped depression and more towards the front midline of the skull continues in a series of rugosities.[1]
The frontal has a preserved length of 186 millimetres. Near the contact with the lacrimal the bone is extremely thickened to a height of seventy-three millimetres and vaulted; a second thick area is present at the rear separated from the first by a hollow surface. Such a thickening of the skull roof is more typical of the Abelisauridae in which group however, it is the postorbital that shows the phenomenon. The authors explained the thickening as an adaptation for display or to strengthen the skull for intraspecific head-butting.[1]
The holotype of Sauroniops was originally interpreted as belonging to a derived member of the Carcharodontosauridae. A more extensive cladistic analysis in the naming paper showed a more basal position in the same group as a sister species of Eocarcharia. The similarities to the abelisaurids would then be convergences.[1]
See also
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h Cau, Andrea; Dalla Vecchia, Fabio M.; Fabbri, Matteo (March 2013). "A thick-skulled theropod (Dinosauria, Saurischia) from the Upper Cretaceous of Morocco with implications for carcharodontosaurid cranial evolution". Cretaceous Research. 40: 251–260. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2012.09.002.
- ^ Cau, Andrea; Dalla Vecchia, Fabio Marco; Fabbri, Matteo (2012). "Evidence of a New Carcharodontosaurid from the Upper Cretaceous of Morocco". Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 57 (3): 661–665. doi:10.4202/app.2011.0043.
- ^ Ibrahim, Nizar; Sereno, Paul C.; Varricchio, David J.; Martill, David M.; Dutheil, Didier B.; Unwin, David M.; Baidder, Lahssen; Larsson, Hans C. E.; Zouhri, Samir; Kaoukaya, Abdelhadi (2020-04-21). "Geology and paleontology of the Upper Cretaceous Kem Kem Group of eastern Morocco". ZooKeys (928): 1–216. doi:10.3897/zookeys.928.47517. ISSN 1313-2970. PMC 7188693. PMID 32362741.
- ^ Cau, Andrea (15 October 2020). "Sauroniops non è Carcharodontosaurus". Theropoda.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ Paterna A, Cau A (2022). "New giant theropod material from the Kem Kem Compound Assemblage (Morocco) with implications on the diversity of the mid-Cretaceous carcharodontosaurids from North Africa". Historical Biology: An International Journal of Paleobiology. doi:10.1080/08912963.2022.2131406.















