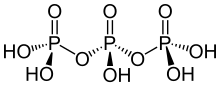
Triphosphoric acid
Appearance
This article needs additional citations for verification. (December 2014) |
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Diphosphono hydrogen phosphate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.752 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| H5P3O10 | |
| Molar mass | 257.95 g/mol |
| Acidity (pKa) | small, small, 2.30, 6.50, 9.24 |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Corrosive (C) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Triphosphoric acid (also tripolyphosphoric acid), with formula H5P3O10, is a condensed form of phosphoric acid. In the family of phosphoric acids, it is the next polyphosphoric acid after pyrophosphoric acid, H4P2O7, also called diphosphoric acid.
Compounds such as ATP (adenosine triphosphate) are esters of triphosphoric acid.
Triphosphoric acid has not been obtained in crystalline form. The equilibrium mixture with an overall composition corresponding to H5P3O10 contains about 18% of triphosphoric acid. A solution of the pure species can be obtained by ion exchange of the sodium salt, sodium triphosphate, at 0 °C.[1]
Various pKa values are reported, 1.0 ; 2.2 ; 2.3 ; 5.7 ; 8.5,[1] 1.0 ; 2.2 ; 2.3 ; 3.7 ; 8.5 [2]
References
- ^ a b Corbridge, D. (1995). "Chapter 3: Phosphates". Studies in inorganic Chemistry vol. 20. Elsevier Science B.V. pp. 169–305. ISBN 0-444-89307-5. Retrieved January 30, 2015. – via ScienceDirect (Subscription may be required or content may be available in libraries.)
- ^ Holleman, Arnold Frederik; Wiberg, Egon (2001), Wiberg, Nils (ed.), Inorganic Chemistry, translated by Eagleson, Mary; Brewer, William, San Diego/Berlin: Academic Press/De Gruyter, p. 729, ISBN 0-12-352651-5
