History of the Mediterranean region: Difference between revisions
m Date/fix the maintenance tags or gen fixes |
→Middle Ages: Byzantine Empire |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Refimprove|date=May 2007}} |
{{Refimprove|date=May 2007}} |
||
The '''history of the [[Mediterranean region]]''' is the [[history]] of the interaction of the cultures and peoples of the lands surrounding the [[Mediterranean Sea]] —the central [[superhighway]] of transport, trade and cultural exchange between diverse peoples. Its history is important to understanding the origin and development of the [[Mesopotamia]]n, [[Ancient Egypt|Egyptian]], [[Phoenicia]]n, [[History of ancient Israel and Judah|Jewish]], [[Ancient Greece|Greek]], [[Ancient Rome|Latin]], [[Arab]] |
The '''history of the [[Mediterranean region]]''' is the [[history]] of the interaction of the cultures and peoples of the lands surrounding the [[Mediterranean Sea]] —the central [[superhighway]] of transport, trade and cultural exchange between diverse peoples. Its history is important to understanding the origin and development of the [[Mesopotamia]]n, [[Ancient Egypt|Egyptian]], [[Persian Empire|Persian]], [[Phoenicia]]n, [[History of ancient Israel and Judah|Jewish]], [[Ancient Greece|Greek]], [[Ancient Rome|Latin]], [[Arab]] and [[Turkish people|Turkish]] cultures — and hence is important to understanding the development of [[Western world|Western civilization]] as we understand it today. |
||
==Dawn of Civilization== |
==Dawn of Civilization== |
||
{{see|Fertile Crescent|Mesopotamia|Ancient Egypt|History of the Levant}} |
|||
[[Image:Fertile Crescent map.png|thumb|right|The Fertile Crescent in the 2nd millennium BC]] |
[[Image:Fertile Crescent map.png|thumb|right|The Fertile Crescent in the 2nd millennium BC]] |
||
Two of the first human civilizations began in the Mediterranean area. Civilization first developed in [[Mesopotamia]] beginning with [[Sumer]] in the [[4th millennium BC]]. Soon after, the [[Nile River]] valley was unified under the [[Pharaoh]]s in the 4th millennium BC, and civilization quickly spread through the [[Fertile Crescent]] to the east coast of the sea and throughout the [[Levant]], which happens to make the Mediterranean countries of [[Syria]], [[Lebanon]], |
Two of the first human civilizations began in the eastern Mediterranean area. Civilization first developed in [[Mesopotamia]] beginning with [[Sumer]] in the [[4th millennium BC]]. Soon after, the [[Nile River]] valley was unified under the [[Pharaoh]]s in the 4th millennium BC, and civilization quickly spread through the [[Fertile Crescent]] to the east coast of the sea and throughout the [[Levant]], which happens to make the Mediterranean countries of [[Ancient Egypt|Egypt]], [[Syria]], [[Lebanon]], [[Israel]] part of the [[cradle of civilization]]. These areas shared similar climates and geographies, but it was more difficult to spread technologies and crops, such as flax, lentil, peas, barley, and cotton to other portions of the Mediterranean basin. |
||
In time, large empires developed in [[Anatolia|Asia Minor]], such as the [[Hittites]]. The main expansion was delayed until ships sturdy enough the cross the sea were developed. [[Cyprus]] and the other islands developed, and the [[Minoan civilization]] flourished on the island of [[Crete]]. While the river valley civilizations always had larger populations, the trading societies on the coast of the sea soon became the most prosperous, and rose to power. |
In time, large empires developed in [[Anatolia|Asia Minor]], such as the [[Hittites]]. The main expansion was delayed until ships sturdy enough the cross the sea were developed. [[Cyprus]] and the other islands developed, and the [[Minoan civilization]] flourished on the island of [[Crete]]. While the river valley civilizations always had larger populations, the trading societies on the coast of the sea soon became the most prosperous, and rose to power. |
||
==Classical Antiquity== |
==Classical Antiquity== |
||
{{main|Classical antiquity}} |
|||
| ⚫ | The two most notable of these were the [[Ancient Greece|Greek]] city states and the [[Phoenicia]]ns. The Greeks expanded throughout the [[Black Sea]] and south through the [[Red Sea]]. The Phoenicians spread through the western Mediterranean including [[North Africa]] and the [[Iberian Peninsula]]. The Phoenician heartland in the Levant was still dominated by powers rooted east in Mesopotamia or [[Iran|Persia]], and the Phoenicians often provided the naval forces of the [[Persian Empire]]. |
||
{{see|Persian Empire|Hellenistic civilization|Carthage|Roman Empire}} |
|||
| ⚫ | The two most notable of these were the [[Ancient Greece|Greek]] city states and the [[Phoenicia]]ns. The Greeks expanded throughout the [[Black Sea]] and south through the [[Red Sea]]. The Phoenicians spread through the western Mediterranean including [[North Africa]] and the [[Iberian Peninsula]]. The Phoenician heartland in the Levant was still dominated by powers rooted east in Mesopotamia or [[Iran|Persia]], and the Phoenicians often provided the naval forces of the [[Achaemenid Empire|Achaemenid]] [[Persian Empire]]. |
||
To the north of Greece, in [[Macedon]], Greek technological and organizational skill was forged with a long history of cavalry warfare. Under [[Alexander the Great]], this force turned east, and in a series of three decisive battles, routed the Persian forces and took their empire, which included Egypt and the Phoenician lands. The major centres of the Mediterranean at the time became part of Alexander's empire as a result. His empire quickly disintegrated, and the Middle East, Egypt, and Greece were soon again independent. Alexander's conquests spread Greek knowledge and ideas throughout the region. |
To the north of Greece, in [[Macedon]], Greek technological and organizational skill was forged with a long history of cavalry warfare. Under [[Alexander the Great]], this force turned east, and in a series of three decisive battles, routed the Persian forces and took their empire, which included Egypt and the Phoenician lands. The major centres of the Mediterranean at the time became part of Alexander's empire as a result. His empire quickly disintegrated, and the Middle East, Egypt, and Greece were soon again independent. Alexander's conquests spread Greek knowledge and ideas throughout the region. |
||
[[Image:Europe map 220BC.PNG|thumb|200px|The Mediterranean region in 220 BC]] |
[[Image:Europe map 220BC.PNG|thumb|200px|The Mediterranean region in 220 BC]] |
||
These eastern powers soon began to be overshadowed by those further west. In North Africa the former Phoenician colony of [[Carthage]] rose to dominate its surroundings with an empire that contained many of the former Phoenician holdings. However, it was a city on the [[Italian peninsula]], [[Rome]], that would eventually dominate the entire Mediterranean basin. Spreading first through Italy, Rome defeated Carthage in the [[Punic Wars]], becoming the leading force in the region. The Romans soon spread east taking Greece, and the Greek heritage played an important role in the Roman Empire. By this point the coastal trading cultures were thoroughly dominant over the inland river valleys that had once been the heart of the great powers. Egyptian power moved from the Nile cities to the coastal ones, especially [[Alexandria]]. Mesopotamia became a fringe border region between the Roman Empire and the Persians. |
These eastern powers soon began to be overshadowed by those further west. In North Africa the former Phoenician colony of [[Carthage]] rose to dominate its surroundings with an empire that contained many of the former Phoenician holdings. However, it was a city on the [[Italian peninsula]], [[Rome]], that would eventually dominate the entire Mediterranean basin. Spreading first through Italy, Rome defeated Carthage in the [[Punic Wars]], becoming the leading force in the region. The Romans soon spread east taking Greece, and the Greek heritage played an important role in the Roman Empire. By this point the coastal trading cultures were thoroughly dominant over the inland river valleys that had once been the heart of the great powers. Egyptian power moved from the Nile cities to the coastal ones, especially [[Alexandria]]. Mesopotamia became a fringe border region between the Roman Empire and the Persians. |
||
| Line 19: | Line 24: | ||
==Middle Ages== |
==Middle Ages== |
||
{{main|Middle Ages|Islamic Golden Age}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
{{see|Byzantine Empire|Muslim conquests|Caliphate|Arab Empire|Ottoman Empire}} |
|||
| ⚫ | Another power was rising in the east, that of [[Islam]], whilst the Byzantine and Persian |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | Another power was rising in the east, that of [[Islam]], whilst the Byzantine and Persian empires were both weakened by centuries of stalemate warfare during the [[Roman-Persian Wars]]. In a series of rapid [[Muslim conquests]], the [[Arab]] armies motivated by Islam and led by the [[Caliph]]s and skilled military commanders swept through much of the Middle East; reducing Byzantine lands by half and completely engulfing the Persians. In Anatolia the expansion was blocked by the still capable Byzantines. The Byzantine governors and indigenous kingdoms of North Africa could not mount such a resistance, and the Muslim conquerors swept through the region, and at the far west crossed the sea taking [[Iberian Peninsula|Iberia]] before being halted in southern [[France]] by the [[Franks]]. |
||
Much of North Africa became a peripheral area to the main Muslim centres in the Middle East, but Iberia ([[Al Andalus]]) and Morocco soon broke from this distant control and founded one of the world's most advanced societies at the time, along with [[Baghdad]] in the eastern Mediterranean. |
Much of North Africa became a peripheral area to the main Muslim centres in the Middle East, but Iberia ([[Al Andalus]]) and Morocco soon broke from this distant control and founded one of the world's most advanced societies at the time, along with [[Baghdad]] in the eastern Mediterranean. |
||
| Line 31: | Line 39: | ||
==Modern Era== |
==Modern Era== |
||
{{see|Ottoman Empire|Portuguese Empire|Spanish Empire}} |
|||
The growing naval prowess of the European powers confronted further rapid Ottoman expansion in the region when the [[Battle of Lepanto]] checked the power of the Ottoman navy. However, as [[Braudel]] argued forcefully, this only slowed the Ottoman expansion instead of ending it. The prized island of [[Cyprus]] became Ottoman in 1571. The last resistance in [[Tunisia]] ended in 1574 and almost a generation long siege in [[Crete]] pushed Venetians out of this strategic island in 1669. A balance of power was then established between [[Spain]] and [[Ottoman Empire]] until 18th century, each dominating their respective half of Mediterranean, reducing Italian navies as naval powers became increasingly more irrelevant. Furthermore, the Ottoman Empire had succeeded in their objective of extending muslim rule across the North African coast. |
The growing naval prowess of the European powers confronted further rapid Ottoman expansion in the region when the [[Battle of Lepanto]] checked the power of the Ottoman navy. However, as [[Braudel]] argued forcefully, this only slowed the Ottoman expansion instead of ending it. The prized island of [[Cyprus]] became Ottoman in 1571. The last resistance in [[Tunisia]] ended in 1574 and almost a generation long siege in [[Crete]] pushed Venetians out of this strategic island in 1669. A balance of power was then established between [[Spain]] and [[Ottoman Empire]] until 18th century, each dominating their respective half of Mediterranean, reducing Italian navies as naval powers became increasingly more irrelevant. Furthermore, the Ottoman Empire had succeeded in their objective of extending muslim rule across the North African coast. |
||
Revision as of 08:11, 14 June 2007
This article needs additional citations for verification. (May 2007) |
The history of the Mediterranean region is the history of the interaction of the cultures and peoples of the lands surrounding the Mediterranean Sea —the central superhighway of transport, trade and cultural exchange between diverse peoples. Its history is important to understanding the origin and development of the Mesopotamian, Egyptian, Persian, Phoenician, Jewish, Greek, Latin, Arab and Turkish cultures — and hence is important to understanding the development of Western civilization as we understand it today.
Dawn of Civilization
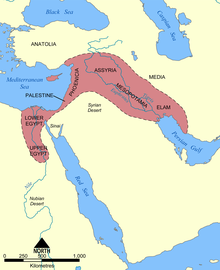
Two of the first human civilizations began in the eastern Mediterranean area. Civilization first developed in Mesopotamia beginning with Sumer in the 4th millennium BC. Soon after, the Nile River valley was unified under the Pharaohs in the 4th millennium BC, and civilization quickly spread through the Fertile Crescent to the east coast of the sea and throughout the Levant, which happens to make the Mediterranean countries of Egypt, Syria, Lebanon, Israel part of the cradle of civilization. These areas shared similar climates and geographies, but it was more difficult to spread technologies and crops, such as flax, lentil, peas, barley, and cotton to other portions of the Mediterranean basin.
In time, large empires developed in Asia Minor, such as the Hittites. The main expansion was delayed until ships sturdy enough the cross the sea were developed. Cyprus and the other islands developed, and the Minoan civilization flourished on the island of Crete. While the river valley civilizations always had larger populations, the trading societies on the coast of the sea soon became the most prosperous, and rose to power.
Classical Antiquity
The two most notable of these were the Greek city states and the Phoenicians. The Greeks expanded throughout the Black Sea and south through the Red Sea. The Phoenicians spread through the western Mediterranean including North Africa and the Iberian Peninsula. The Phoenician heartland in the Levant was still dominated by powers rooted east in Mesopotamia or Persia, and the Phoenicians often provided the naval forces of the Achaemenid Persian Empire.
To the north of Greece, in Macedon, Greek technological and organizational skill was forged with a long history of cavalry warfare. Under Alexander the Great, this force turned east, and in a series of three decisive battles, routed the Persian forces and took their empire, which included Egypt and the Phoenician lands. The major centres of the Mediterranean at the time became part of Alexander's empire as a result. His empire quickly disintegrated, and the Middle East, Egypt, and Greece were soon again independent. Alexander's conquests spread Greek knowledge and ideas throughout the region.

These eastern powers soon began to be overshadowed by those further west. In North Africa the former Phoenician colony of Carthage rose to dominate its surroundings with an empire that contained many of the former Phoenician holdings. However, it was a city on the Italian peninsula, Rome, that would eventually dominate the entire Mediterranean basin. Spreading first through Italy, Rome defeated Carthage in the Punic Wars, becoming the leading force in the region. The Romans soon spread east taking Greece, and the Greek heritage played an important role in the Roman Empire. By this point the coastal trading cultures were thoroughly dominant over the inland river valleys that had once been the heart of the great powers. Egyptian power moved from the Nile cities to the coastal ones, especially Alexandria. Mesopotamia became a fringe border region between the Roman Empire and the Persians.
For several centuries the Mediterranean was a "Roman Lake," surrounded on all sides by the empire. One portion of the empire was Judea, and in time, a religion founded in that region, Christianity, spread throughout the empire and eventually became its official faith. The empire began to crumble, however, and collapsed in the fifth century. Temporarily the east was again dominant as the Byzantine Empire formed from the eastern half of the Roman one. The western part of the empire, Gaul, Iberia, and the Maghreb were invaded by nomadic horse peoples from the Eurasian steppe. These conquerors soon became settled, and adopted many of the local customs, forming many small and warring kingdoms.
Middle Ages

Another power was rising in the east, that of Islam, whilst the Byzantine and Persian empires were both weakened by centuries of stalemate warfare during the Roman-Persian Wars. In a series of rapid Muslim conquests, the Arab armies motivated by Islam and led by the Caliphs and skilled military commanders swept through much of the Middle East; reducing Byzantine lands by half and completely engulfing the Persians. In Anatolia the expansion was blocked by the still capable Byzantines. The Byzantine governors and indigenous kingdoms of North Africa could not mount such a resistance, and the Muslim conquerors swept through the region, and at the far west crossed the sea taking Iberia before being halted in southern France by the Franks.
Much of North Africa became a peripheral area to the main Muslim centres in the Middle East, but Iberia (Al Andalus) and Morocco soon broke from this distant control and founded one of the world's most advanced societies at the time, along with Baghdad in the eastern Mediterranean.
Europe was reviving, however, as more organized and centralized states began to form in the later Middle Ages. Motivated by religion and dreams of conquest, the kings of Europe launched a number of Crusades to try to roll back Muslim power and retake the holy land. The Crusades were unsuccessful in this goal, but they were far more effective in weakening the already tottering Byzantine Empire that began to lose increasing amounts of territory to the Ottoman Turks. They also rearranged the balance of power in the Muslim world as Egypt once again emerged as a major power in the eastern Mediterranean.
Europe continued to increase in power as the Renaissance began in Northern Italy. The Islamic states had never been major naval powers, and trade from the east to Europe was soon in the hands of Italian traders, especially the Venetians, who profited immensely from it.
Ottoman power continued to grow, and in 1453 , the Byzantine Empire was extinguished with the fall of Constantinople. The Ottomans already controlled Greece and much of the Balkans, and soon also began to spread through North Africa. North Africa had grown wealthy from the trade across the Sahara Desert, but the Portuguese, who, along with other Christian powers, had been engaged in a long campaign to evict the Muslims from Iberia, had found a method to circumvent this trade by trading directly with West Africa. This was enabled by a new type of ships, the caravel, that made trade in the rough Atlantic waters profitable for the first time. The reduction in the Saharan trade weakened North Africa, and made them an easy target for the Ottomans.
Modern Era
The growing naval prowess of the European powers confronted further rapid Ottoman expansion in the region when the Battle of Lepanto checked the power of the Ottoman navy. However, as Braudel argued forcefully, this only slowed the Ottoman expansion instead of ending it. The prized island of Cyprus became Ottoman in 1571. The last resistance in Tunisia ended in 1574 and almost a generation long siege in Crete pushed Venetians out of this strategic island in 1669. A balance of power was then established between Spain and Ottoman Empire until 18th century, each dominating their respective half of Mediterranean, reducing Italian navies as naval powers became increasingly more irrelevant. Furthermore, the Ottoman Empire had succeeded in their objective of extending muslim rule across the North African coast.
The development of oceanic shipping began to affect the entire Mediterranean, however. While once all trade from the east had passed through the region, the circumnavigation of Africa allowed gold, spices, and dyes to be imported directly to the Atlantic ports of western Europe. The Americas were also a source of extreme wealth to the western powers, from which some of the Mediterranean states were largely cut off. The base of European power thus shifted northward and the once wealthy Italy became a peripheral area dominated by foreigners. The Ottoman Empire also began a slow decline that saw its North African possessions gain de facto independence and its European holdings gradually reduced by the increasing power of Austria and Russia.
By the nineteenth century the Northern European states were vastly more powerful, and began to colonize North Africa. France spread its power south by taking Algeria in 1830 . Britain gained control of Egypt in 1882 . The Ottoman Empire finally collapsed in the First World War, and its holdings were carved up among France and Britain, but the Turkish regions quickly regained their independence, becoming the independent state of Turkey.
See also
Further reading
- Fernand Braudel, The Mediterranean in the Age of Philip II
References
HISTORY OF THE MEDITERRANEAN at historyworld.net
