Metamodeling: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Notsoimp2012 (talk | contribs) More discussions on metamodels. |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
== Overview == |
== Overview == |
||
Metamodel or surrogate model is model of model, i.e. a simplified model of an actual model of a circuit, system, or software like entity. <ref> O. Garitselov, S. P. Mohanty, and E. Kougianos, “[http://www.cse.unt.edu/~smohanty/Publications_Journals/2012/Mohanty_IEEE-TSM-2012Feb.pdf A Comparative Study of Metamodels for Fast and Accurate Simulation of Nano-CMOS Circuits]”, IEEE Transactions on Semiconductor Manufacturing (TSM), Vol. 25, No. 1, February 2012, pp. 26--36. </ref> <ref> [http://www.cse.unt.edu/~smohanty/Presentations/2012/Mohanty_SRC-TxACE_Talk_2012-04-27.pdf Ultra-Fast Design Exploration of Nanoscale Circuits through Metamodeling], Invited Talk, Semiconductor Research Corportation (SRC), Texas Analog Center for Excellence (TxACE), 27th April 2012. </ref> Metamodel can be an mathematical relation or algorithm representing input and output relations. A [[model (abstract)|model]] is an abstraction of phenomena in the [[Real life (reality)|real world]]; a metamodel is yet another abstraction, highlighting properties of the model itself. A model conforms to its metamodel in the way that a computer program conforms to the grammar of the programming language in which it is written. Various types of metamodels include polynomial equations, neural network, Kriging, etc. <ref> [http://www.cse.unt.edu/~smohanty/Presentations/2012/Mohanty_SRC-TxACE_Talk_2012-04-27.pdf Ultra-Fast Design Exploration of Nanoscale Circuits through Metamodeling], Invited Talk, Semiconductor Research Corportation (SRC), Texas Analog Center for Excellence (TxACE), 27th April 2012. </ref> "Metamodeling" is the construction of a collection of "concepts" (things, terms, etc.) within a certain domain. Metamodeling typically involves studying the output and input relationships and then fitting right metamodels to represent that behavior. <ref> O. Garitselov, S. P. Mohanty, and E. Kougianos, “[http://www.cse.unt.edu/~smohanty/Publications_Journals/2012/Mohanty_IEEE-TSM-2012Feb.pdf A Comparative Study of Metamodels for Fast and Accurate Simulation of Nano-CMOS Circuits]”, IEEE Transactions on Semiconductor Manufacturing (TSM), Vol. 25, No. 1, February 2012, pp. 26--36. </ref> |
|||
"Metamodeling" is the construction of a collection of "concepts" (things, terms, etc.) within a certain domain. A [[model (abstract)|model]] is an abstraction of phenomena in the [[Real life (reality)|real world]]; a metamodel is yet another abstraction, highlighting properties of the model itself. A model conforms to its metamodel in the way that a computer program conforms to the grammar of the programming language in which it is written. |
|||
Common uses for metamodels are: |
Common uses for metamodels are: |
||
Revision as of 19:40, 31 July 2014
This article needs additional citations for verification. (June 2008) |
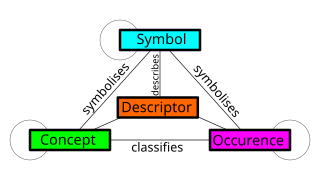
Metamodeling or meta-modeling is the analysis, construction and development of the frames, rules, constraints, models and theories applicable and useful for modeling a predefined class of problems. As its name implies, this concept applies the notions of meta- and modeling in software engineering and systems engineering.
Overview
Metamodel or surrogate model is model of model, i.e. a simplified model of an actual model of a circuit, system, or software like entity. [2] [3] Metamodel can be an mathematical relation or algorithm representing input and output relations. A model is an abstraction of phenomena in the real world; a metamodel is yet another abstraction, highlighting properties of the model itself. A model conforms to its metamodel in the way that a computer program conforms to the grammar of the programming language in which it is written. Various types of metamodels include polynomial equations, neural network, Kriging, etc. [4] "Metamodeling" is the construction of a collection of "concepts" (things, terms, etc.) within a certain domain. Metamodeling typically involves studying the output and input relationships and then fitting right metamodels to represent that behavior. [5]
Common uses for metamodels are:
- As a schema for semantic data that needs to be exchanged or stored
- As a language that supports a particular method or process
- As a language to express additional semantics of existing information
- As a mechanism to create tools that work with a broad class of models at run time
- As a schema for modeling and automatically exploring sentences of a language with applications to automated test synthesis
Because of the "meta" character of metamodeling, both the praxis and theory of metamodels are of relevance to metascience[disambiguation needed], metaphilosophy, metatheories and systemics, and meta-consciousness. The concept can be useful in mathematics, and has practical applications in computer science and computer engineering/software engineering, which are the main focus of this article.
Metamodeling topics
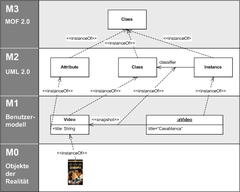

Definition
In software engineering, the use of models is more and more recommended. This should be contrasted with the classical code-based development techniques. A model always conforms to a unique metamodel. One of the currently most active branch of Model Driven Engineering is the approach named model-driven architecture proposed by OMG. This approach is based on the utilization of a language to write metamodels called the Meta Object Facility or MOF. Typical metamodels proposed by OMG are UML, SysML, SPEM or CWM. ISO has also published the standard metamodel ISO/IEC 24744.[7] All the languages presented below could be defined as MOF metamodels.
Metadata modeling
Metadata modeling is a type of metamodeling used in software engineering and systems engineering for the analysis and construction of models applicable and useful to some predefined class of problems. (see also: data modeling).
Model transformations
One important move in Model Driven Engineering is the systematic use of Model Transformation Languages. The OMG has proposed a standard for this called QVT for Queries/Views/Transformations. QVT is based on the Meta-Object Facility or MOF. Among many other Model Transformation Languages (MTLs), some examples of implementations of this standard are AndroMDA, VIATRA, Tefkat, MT[disambiguation needed], ManyDesigns Portofino.
Relationship to ontologies
Meta-models are closely related to ontologies. Both are often used to describe and analyze the relations between concepts[8]
- Ontologies: express something meaningful within a specified universe or domain of discourse by utilizing a grammar for using vocabulary. The grammar specifies what it means to be a well-formed statement, assertion, query, etc. (formal constraints) on how terms in the ontology’s controlled vocabulary can be used together.[9]
- Meta-modeling: can be considered as an explicit description (constructs and rules) of how a domain-specific model is built. In particular, this comprises a formalized specification of the domain-specific notations. Typically, metamodels are – and always should follow - a strict rule set.[10] “A valid metamodel is an ontology, but not all ontologies are modeled explicitly as metamodels”.[9]
Types of metamodels
For software engineering, several types of models (and their corresponding modeling activities) can be distinguished:
- Metadata modeling (MetaData Model)
- Meta-Process Modeling (MetaProcess Model)
- Executable Meta-Modeling (combining both of the above and much more, as in the general purpose tool Kermeta)
- Model Transformation Language (see below)
Zoos of metamodels
A library of similar metamodels has been called a Zoo of metamodels.[11] There are several types of meta-model zoos.[12] Some are expressed in ECore. Others are written in MOF 1.4 - XMI 1.2. The metamodels expressed in UML-XMI1.2 may be uploaded in Poseidon for UML, a UML CASE tool.
See also
- Business reference model
- Data governance
- Model Driven Engineering (MDE)
- Model-driven architecture (MDA)
- Domain Specific Language (DSL)
- Domain-Specific Modeling (DSM)
- Generic Eclipse Modeling System (GEMS)
- Kermeta (Kernel Meta-modeling)
- MetaCASE tool (tools for creating tools for Computer-aided software engineering tools)
- Method engineering
- MODAF Meta-Model
- MOF Queries/Views/Transformations (MOF QVT)
- Object Process Methodology
- Requirements analysis
- Surrogate model
- Transformation language
- VIATRA (Viatra)
- XML transformation language (XML TL)
References
- ^ David R. Soller et al. (2001) Progress Report on the National Geologic Map Database, Phase 3: An Online Database of Map Information Digital Mapping Techniques '01 -- Workshop Proceedings U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 01-223.
- ^ O. Garitselov, S. P. Mohanty, and E. Kougianos, “A Comparative Study of Metamodels for Fast and Accurate Simulation of Nano-CMOS Circuits”, IEEE Transactions on Semiconductor Manufacturing (TSM), Vol. 25, No. 1, February 2012, pp. 26--36.
- ^ Ultra-Fast Design Exploration of Nanoscale Circuits through Metamodeling, Invited Talk, Semiconductor Research Corportation (SRC), Texas Analog Center for Excellence (TxACE), 27th April 2012.
- ^ Ultra-Fast Design Exploration of Nanoscale Circuits through Metamodeling, Invited Talk, Semiconductor Research Corportation (SRC), Texas Analog Center for Excellence (TxACE), 27th April 2012.
- ^ O. Garitselov, S. P. Mohanty, and E. Kougianos, “A Comparative Study of Metamodels for Fast and Accurate Simulation of Nano-CMOS Circuits”, IEEE Transactions on Semiconductor Manufacturing (TSM), Vol. 25, No. 1, February 2012, pp. 26--36.
- ^ FEA (2005) FEA Records Management Profile, Version 1.0. December 15, 2005.
- ^ International Organization for Standardization / International Electrotechnical Commission, 2007. ISO/IEC 24744. Software Engineering - Metamodel for Development Methodologies.
- ^ E. Söderström, et al. (2001) "Towards a Framework for Comparing Process Modelling Languages", in: Lecture Notes In Computer Science; Vol. 2348. Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Advanced Information Systems Engineering. Pages: 600 – 611, 2001
- ^ a b
Pidcock, Woody (2003), What are the differences between a vocabulary, a taxonomy, a thesaurus, an ontology, and a meta-model?
{{citation}}: Cite has empty unknown parameters:|doi_brokendate=,|laydate=,|coauthors=,|editorn-link=,|nopp=,|separator=,|laysummary=,|editorn-first=,|month=,|chapterurl=,|editorn=,|author-separator=,|lastauthoramp=, and|editorn-last=(help) - ^
Ernst, Johannes (2002), What is metamodeling, and what is it good for?
{{citation}}: Cite has empty unknown parameters:|doi_brokendate=,|laydate=,|coauthors=,|editorn-link=,|nopp=,|separator=,|laysummary=,|editorn-first=,|month=,|chapterurl=,|editorn=,|author-separator=,|lastauthoramp=, and|editorn-last=(help) - ^ Jean-Marie Favre: Towards a Basic Theory to Model Driven Engineering..
- ^ AtlanticZoo.
Further reading
- J. Bezivin, On the Unification Power of Models, in: Software and System Modeling (SoSym) 4(2):171—188.
- Booch, G., Rumbaugh, J., Jacobson, I. (1999), The Unified Modeling Language User Guide, Redwood City, CA: Addison Wesley Longman Publishing Co., Inc.
- J. P. van Gigch, System Design Modeling and Metamodeling, Plenum Press, New York, 1991
- Gopi Bulusu, hamara.in, 2004 Model Driven Transformation
- P. C. Smolik, Mambo Metamodeling Environment, Doctoral Thesis, Brno University of Technology. 2006
- Gonzalez-Perez, C. and B. Henderson-Sellers, 2008. Metamodelling for Software Engineering. Chichester (UK): Wiley. 210 p. ISBN 978-0-470-03036-3
- M.A. Jeusfeld, M. Jarke, and J. Mylopoulos, 2009. Metamodeling for Method Engineering. Cambridge (USA): The MIT Press. 424 p. ISBN 978-0-262-10108-0
- G. Caplat Modèles & Métamodèles, 2008 - ISBN 978-2-88074-749-7 Template:Fr
- Fill, H.-G., Karagiannis, D., 2013. On the Conceptualisation of Modelling Methods Using the ADOxx Meta Modelling Platform, Enterprise Modelling and Information Systems Architectures, Vol. 8, Issue 1, 4-25.
