Elasmosaurus: Difference between revisions
Preliminarily adding some citations that will be used soon. |
Citation bot (talk | contribs) m Add: pmc, pmid, title, year, bibcode, author pars. 1-1. You can use this bot yourself. Report bugs here. |
||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
==Description== |
==Description== |
||
[[File:ElasmosaurusDB15.jpg|thumb|left|Restoration with size comparison]] |
[[File:ElasmosaurusDB15.jpg|thumb|left|Restoration with size comparison]] |
||
At 10.3 meters (38 ft) in length,<ref name="gorman2016">{{cite journal | first1 = J.P. | last1 = O'Gorman | title = A Small Body Sized Non-Aristonectine Elasmosaurid (Sauropterygia, Plesiosauria) from the Late Cretaceous of Patagonia with Comments on the Relationships of the Patagonian and Antarctic Elasmosaurids | journal = Ameghiniana | volume = 53 | issue = 3 | pages = |
At 10.3 meters (38 ft) in length,<ref name="gorman2016">{{cite journal | first1 = J.P. | last1 = O'Gorman | title = A Small Body Sized Non-Aristonectine Elasmosaurid (Sauropterygia, Plesiosauria) from the Late Cretaceous of Patagonia with Comments on the Relationships of the Patagonian and Antarctic Elasmosaurids | journal = Ameghiniana | volume = 53 | issue = 3 | pages = 245–268 | url = http://www.bioone.org/doi/abs/10.5710/AMGH.29.11.2015.2928 | doi = 10.5710/AMGH.29.11.2015.2928 | year = 2016}}</ref> ''Elasmosaurus'' was among the largest plesiosaurs. It differs from all other plesiosaurs by having six teeth per [[premaxilla]] (the bones at the tip of the snout) and 72 [[cervical vertebrae|neck]] (cervical) [[vertebra]]e.<ref name=Sachs2005>{{cite journal|author=Sachs, S.|year=2005|title=Redescription of ''Elasmosaurus platyurus'', Cope 1868 (Plesiosauria: Elasmosauridae) from the Upper Cretaceous (lower Campanian) of Kansas, U.S.A|journal=Paludicola|volume=5|issue=3|pages=92–106|url=https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Sven_Sachs2/publication/260421820_Redescription_of_Elasmosaurus_platyurus_Cope_1868_Plesiosauria_Elasmosauridae_from_the_Upper_Cretaceous_Lower_Campanian_of_Kansas_USA/links/0deec531221b71772a000000/Redescription-of-Elasmosaurus-platyurus-Cope-1868-Plesiosauria-Elasmosauridae-from-the-Upper-Cretaceous-Lower-Campanian-of-Kansas-USA.pdf}}</ref> |
||
The snout was rounded and almost formed a semi-circle when viewed from above, and the [[premaxillae]] (which form the front of the upper jaw) bore a low keel at the midline. It is uncertain how many teeth ''Elasmosaurus'' had, due to the fragmentary fossils. It probably had six teeth in each premaxilla, and the teeth preserved there were formed like large fangs. The two teeth at the front were smaller than the succeeding ones, and were located between the first two teeth in the [[dentaries]] of the lower jaws. The known teeth of the front part of the lower jaw are large fangs, and the teeth at the back of the jaws appear to have been smaller. The [[mandibular symphysis]] (where the two halves of the lower jaw connected) was well-[[ossified]], with no visible [[suture (anatomy)|suture]]. The skull was relatively flat, with a number of long pointed teeth. The lower jaws were joined at the tip to a point between the fourth and fifth teeth.<ref name=Sachs2005/> The neck vertebrae immediately following the skull were long and low, and had longitudinal lateral crests. Like most elasmosaurids, ''Elasmosaurus'' had around three pectoral vertebrae. The tail included at least 18 vertebrae.<ref name=Brown1993>{{cite journal|author=Brown, D. S.|year=1993|title=A taxonomic reappraisal of the families Elasmosauridae and Cryptoclididae (Reptilia: Plesiosauroidea)|journal=Révue de Paléobiologie|volume=7|pages= |
The snout was rounded and almost formed a semi-circle when viewed from above, and the [[premaxillae]] (which form the front of the upper jaw) bore a low keel at the midline. It is uncertain how many teeth ''Elasmosaurus'' had, due to the fragmentary fossils. It probably had six teeth in each premaxilla, and the teeth preserved there were formed like large fangs. The two teeth at the front were smaller than the succeeding ones, and were located between the first two teeth in the [[dentaries]] of the lower jaws. The known teeth of the front part of the lower jaw are large fangs, and the teeth at the back of the jaws appear to have been smaller. The [[mandibular symphysis]] (where the two halves of the lower jaw connected) was well-[[ossified]], with no visible [[suture (anatomy)|suture]]. The skull was relatively flat, with a number of long pointed teeth. The lower jaws were joined at the tip to a point between the fourth and fifth teeth.<ref name=Sachs2005/> The neck vertebrae immediately following the skull were long and low, and had longitudinal lateral crests. Like most elasmosaurids, ''Elasmosaurus'' had around three pectoral vertebrae. The tail included at least 18 vertebrae.<ref name=Brown1993>{{cite journal|author=Brown, D. S.|year=1993|title=A taxonomic reappraisal of the families Elasmosauridae and Cryptoclididae (Reptilia: Plesiosauroidea)|journal=Révue de Paléobiologie|volume=7|pages=9–16}}</ref><ref name=Carpenter1999>{{cite journal|author=Carpenter, K.|year=1999|title=Revision of North American elasmosaurs from the Cretaceous of the western interior|journal=Paludicola|volume=2|issue=2|pages=148–173}}</ref> |
||
The [[pectoral girdle]] featured a long bar,<ref name=Brown1993/><ref name=Carpenter1999/> not present in juveniles. The [[scapula]] had margins of approximately equal length for the joint with the [[coracoid]] and the articular surface for the upper arm.<ref name=Sachs2005/> The [[anatomical terms of location|anterior]] edge of the pelvic girdle was made up of three almost straight edges directed to the front and sides of the animal. The [[ischium|ischia]], a pair of bones that formed the posterior part of the pelvis, were joined along their medial surfaces.<ref name=Sachs2005/> The limbs of ''Elasmosaurus'', like those of other plesiosaurs, were modified into approximately equally sized rigid paddles.<ref name="Everhart135">Everhart p. 135</ref> |
The [[pectoral girdle]] featured a long bar,<ref name=Brown1993/><ref name=Carpenter1999/> not present in juveniles. The [[scapula]] had margins of approximately equal length for the joint with the [[coracoid]] and the articular surface for the upper arm.<ref name=Sachs2005/> The [[anatomical terms of location|anterior]] edge of the pelvic girdle was made up of three almost straight edges directed to the front and sides of the animal. The [[ischium|ischia]], a pair of bones that formed the posterior part of the pelvis, were joined along their medial surfaces.<ref name=Sachs2005/> The limbs of ''Elasmosaurus'', like those of other plesiosaurs, were modified into approximately equally sized rigid paddles.<ref name="Everhart135">Everhart p. 135</ref> |
||
[[File:Elasmosaurusskull.jpg|thumb|Reconstructed skull and neck, [[North American Museum of Ancient Life]]]] |
[[File:Elasmosaurusskull.jpg|thumb|Reconstructed skull and neck, [[North American Museum of Ancient Life]]]] |
||
Certain aspects of the anatomy of ''Elasmosaurus'' were fairly [[Synapomorphy|derived]] among elasmosaurids, and plesiosaurs in general.<ref name=Sachs2005/> As noted, ''Elasmosaurus'' can be distinguished by its six premaxillary teeth and 72 cervical vertebrae.<ref name=Sachs2005/> Primitively, plesiosaurs and most elasmosaurids had five teeth per premaxilla. Some elasmosaurids had more: ''[[Terminonatator]]'' had nine<ref name="Sato2003">{{cite journal|author=Sato, T.|year=2003|title=''Terminonatator ponteixensis'', a new elasmosaur (Reptilia:Sauropterygia) from the Upper Cretaceous of Saskatchewan"|journal=Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology|volume=23|issue=1|pages=89–103}}</ref> and ''[[Aristonectes]]'' had 10 to 13.<ref>{{cite journal|author=Gasparini, Z., Bardet, N., Martin, J.E. and Fernandez, M.S.|year=2003|title=The elasmosaurid plesiosaur ''Aristonectes'' Cabreta from the Latest Cretaceous of South America and Antarctica|journal=Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology|volume=23|issue=1|pages= |
Certain aspects of the anatomy of ''Elasmosaurus'' were fairly [[Synapomorphy|derived]] among elasmosaurids, and plesiosaurs in general.<ref name=Sachs2005/> As noted, ''Elasmosaurus'' can be distinguished by its six premaxillary teeth and 72 cervical vertebrae.<ref name=Sachs2005/> Primitively, plesiosaurs and most elasmosaurids had five teeth per premaxilla. Some elasmosaurids had more: ''[[Terminonatator]]'' had nine<ref name="Sato2003">{{cite journal|author=Sato, T.|year=2003|title=''Terminonatator ponteixensis'', a new elasmosaur (Reptilia:Sauropterygia) from the Upper Cretaceous of Saskatchewan"|journal=Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology|volume=23|issue=1|pages=89–103}}</ref> and ''[[Aristonectes]]'' had 10 to 13.<ref>{{cite journal|author=Gasparini, Z., Bardet, N., Martin, J.E. and Fernandez, M.S.|year=2003|title=The elasmosaurid plesiosaur ''Aristonectes'' Cabreta from the Latest Cretaceous of South America and Antarctica|journal=Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology|volume=23|issue=1|pages=104–115|doi=10.1671/0272-4634(2003)23[104:TEPACF]2.0.CO;2}}</ref> In addition, most plesiosaurs had fewer than 60 cervical vertebrae.<ref name=Sachs2005/> Aside from ''Elasmosaurus'', plesiosaurs that exceeded 60 cervicals include ''[[Styxosaurus]]'', ''[[Hydralmosaurus]]'', ''[[Thalassomedon]]'', and ''[[Albertonectes]]''.<ref name=Albertonectes>{{Cite journal | last1 = Kubo | first1 = T. | last2 = Mitchell | first2 = M. T. | last3 = Henderson | first3 = D. M. | doi = 10.1080/02724634.2012.658124 | title = ''Albertonectes vanderveldei'', a new elasmosaur (Reptilia, Sauropterygia) from the Upper Cretaceous of Alberta | journal = Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology | volume = 32 | issue = 3 | pages = 557–572| year = 2012 | pmid = | pmc = }}</ref> |
||
''Elasmosaurus'' and ''Albertonectes'' are the only known plesiosaurs with more than 70 cervical vertebrae.<ref name=Sachs2005/> ''Albertonectes'' has 75 vertebrate and is the only known genus to have more than ''Elasmosaurus''. The two plesiosaurs have the highest numbers of cervical vertebrae among vertebrates in general.<ref>{{cite journal|author=Sach, S.; Kear, B. P.; Everhart, M.|year=2013|title=Revised Vertebral Count in the "Longest-Necked Vertebrate" ''Elasmosaurus platyurus'' Cope 1868, and Clarification of the Cervical-Dorsal Transition in Plesiosauria|journal=PLoS ONE|volume=8|issue=8|page=e70877|doi=10.1371/journal.pone.0070877}}</ref> ''Elasmosaurus'' had roughly the same neck length as ''Thalassomedon''<ref name="Welles1943"/> because the latter has proportionally longer vertebrae.<ref>Everhart p. 130</ref> The presence of the pectoral bar is also considered an advanced feature.<ref name=Sachs2005/> The long, low [[axis (anatomy)|axis]] [[body of vertebra|centrum]] differs from the condition seen in most other plesiosaurs, which have centra that are either shorter in length than height, or about equidimensional.<ref name=Sachs2005/> ''Styxosaurus'' and ''Hydralmosaurus'' also have the condition present in ''Elasmosaurus''.<ref name="Welles1943">{{cite journal|author=Welles, S. P.|year=1943|title=Elasmosaurid plesiosaurs with descriptions of new material from California and Colorado|journal=Memoirs of the University of California|volume=13|pages= |
''Elasmosaurus'' and ''Albertonectes'' are the only known plesiosaurs with more than 70 cervical vertebrae.<ref name=Sachs2005/> ''Albertonectes'' has 75 vertebrate and is the only known genus to have more than ''Elasmosaurus''. The two plesiosaurs have the highest numbers of cervical vertebrae among vertebrates in general.<ref>{{cite journal|author=Sach, S.; Kear, B. P.; Everhart, M.|year=2013|title=Revised Vertebral Count in the "Longest-Necked Vertebrate" ''Elasmosaurus platyurus'' Cope 1868, and Clarification of the Cervical-Dorsal Transition in Plesiosauria|journal=PLoS ONE|volume=8|issue=8|page=e70877|doi=10.1371/journal.pone.0070877|bibcode=2013PLoSO...870877S}}</ref> ''Elasmosaurus'' had roughly the same neck length as ''Thalassomedon''<ref name="Welles1943"/> because the latter has proportionally longer vertebrae.<ref>Everhart p. 130</ref> The presence of the pectoral bar is also considered an advanced feature.<ref name=Sachs2005/> The long, low [[axis (anatomy)|axis]] [[body of vertebra|centrum]] differs from the condition seen in most other plesiosaurs, which have centra that are either shorter in length than height, or about equidimensional.<ref name=Sachs2005/> ''Styxosaurus'' and ''Hydralmosaurus'' also have the condition present in ''Elasmosaurus''.<ref name="Welles1943">{{cite journal|author=Welles, S. P.|year=1943|title=Elasmosaurid plesiosaurs with descriptions of new material from California and Colorado|journal=Memoirs of the University of California|volume=13|pages=125–254}}.</ref><ref name="Sachs2004">{{cite journal|author=Sachs, S.|year=2004|title=Redescription of ''Woolungasaurus glendowerensis'' (Plesiosauria: Elasmosauridae) from the Lower Cretaceous of Northeast Queensland|journal=Memoirs of the Quennsland Museum|volume=49|pages=215–233}}</ref> Another unusual feature of ''Elasmosaurus'' is the relatively equal lengths of the margins of the scapula, as mentioned above. Most plesiosaurs had longer margins for articulation with the coracoid than for articulation with the upper arm.<ref name="Sachs2004"/> |
||
==History of discovery== |
==History of discovery== |
||
[[File:Cope Elasmosaurus.jpg|thumb|left|1869 "head-on-the-wrong-end" reconstruction; Cope did not include the "hind" (actually front) paddles in this figure in part due to his erroneous belief that ''Elasmosaurus'' was propelled by its extremely long “tail” (neck)]] |
[[File:Cope Elasmosaurus.jpg|thumb|left|1869 "head-on-the-wrong-end" reconstruction; Cope did not include the "hind" (actually front) paddles in this figure in part due to his erroneous belief that ''Elasmosaurus'' was propelled by its extremely long “tail” (neck)]] |
||
''Elasmosaurus platyurus'' was described in March, 1868 by [[Edward Drinker Cope]]<ref name="Cope 1868">{{cite journal|author=Cope, E. D.|year= 1868|title=Remarks on a new enaliosaurian, ''Elasmosaurus platyurus''|journal=Proceedings of the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia|volume=20|pages= |
''Elasmosaurus platyurus'' was described in March, 1868 by [[Edward Drinker Cope]]<ref name="Cope 1868">{{cite journal|author=Cope, E. D.|year= 1868|title=Remarks on a new enaliosaurian, ''Elasmosaurus platyurus''|journal=Proceedings of the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia|volume=20|pages=92–93}}</ref> from a [[fossil]] discovered and collected by Dr. Theophilus Turner, a military doctor, in western [[Kansas]], United States. Although other specimens of elasmosaurs have been found in various locations in [[North America]], Carpenter (1999) determined that ''Elasmosaurus platyurus'' was the only representative of the genus.<ref name=Carpenter1999/><ref>{{cite journal|last1=Williston|first1=S. W.|title=North American plesiosaurs ''Elasmosaurus'', ''Cimoliasaurus'', and ''Polycotylus''|journal=American Journal of Science|date=1906|volume=s4-21|issue=123|pages=221–236|doi=10.2475/ajs.s4-21.123.221}}</ref> |
||
Turner found the remains of the species in Pierre Shale sediments along a [[Right-of-way (transportation)|right-of-way]] passage of a Pacific Union railroad close to [[McAllaster, Kansas]] in 1867. Turner give some parts to the [[John LeConte]], would was working for the railroad company as part of a survey crew. LeConte then delivered them to Cope, who was in Philadelphia. Recognizing then as the remains of a plesiosaur, Cope wrote to Turner asking him to deliver the rest of the specimen. Cope finally got them in mid-March 1868 and two weeks later reported that it was a previously unknown species of plesiosaur, which he named ''Elasmosaurus platyurus'' (Greek for flat-tailed, thin-plate reptile). Cope mistakenly believed that the cervical vertebrae were caudal vertebrate and the long neck was the tail, thereby putting the head on the wrong end. Two years later [[Joseph Leidy]], who mentored Cope, noted the error in his article published in the [[Transactions of the American Philosophical Society]]. Embarrassed by this revelation, Cope immediately printed a notice and offered to replaced the copies of [[Manuscript_(publishing)#Preprint|preprint]] of his paper. [[Othniel Charles Marsh|O. C. Marsh]] quoted the text of the notice in his 1890 article for the ''[[New York Herald]]''.<ref>Everhart pp. 121–123</ref><ref>{{cite journal|last1=Davidson|first1=J. P.|title=Bonehead mistakes: The background in scientific literature and illustrations for Edward Drinker Cope's first restoration of ''Elasmosaurus platyurus''|journal=Proceedings of the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia|date=2002|volume=152|issue=1|pages=215–240|doi=10.1635/0097-3157(2002)152[0215:HPOVBM]2.0.CO;2}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal|url=http://www.palarch.nl/2005/07/everhart-mj-2005-elasmosaurid-remains-from-the-pierre-shale-upper-cretaceous-of-western-kansas-possible-missing-elements-of-the-type-specimen-of-elasmosaurus-platyurus-cope-1868-%E2%80%93-pal/}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal|last1=Cope|first1=E. D.|title=1868. Remarks on a new enaliosaurian, Elasmosaurus platyurus. Proceedings of the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia 20:92-93.|date=1841|url=https://archive.org/details/cbarchive_50660_copeed1868remarksonanewenalios1841}}</ref><ref>http://oceansofkansas.com/Cope1870a.html</ref> |
Turner found the remains of the species in Pierre Shale sediments along a [[Right-of-way (transportation)|right-of-way]] passage of a Pacific Union railroad close to [[McAllaster, Kansas]] in 1867. Turner give some parts to the [[John LeConte]], would was working for the railroad company as part of a survey crew. LeConte then delivered them to Cope, who was in Philadelphia. Recognizing then as the remains of a plesiosaur, Cope wrote to Turner asking him to deliver the rest of the specimen. Cope finally got them in mid-March 1868 and two weeks later reported that it was a previously unknown species of plesiosaur, which he named ''Elasmosaurus platyurus'' (Greek for flat-tailed, thin-plate reptile). Cope mistakenly believed that the cervical vertebrae were caudal vertebrate and the long neck was the tail, thereby putting the head on the wrong end. Two years later [[Joseph Leidy]], who mentored Cope, noted the error in his article published in the [[Transactions of the American Philosophical Society]]. Embarrassed by this revelation, Cope immediately printed a notice and offered to replaced the copies of [[Manuscript_(publishing)#Preprint|preprint]] of his paper. [[Othniel Charles Marsh|O. C. Marsh]] quoted the text of the notice in his 1890 article for the ''[[New York Herald]]''.<ref>Everhart pp. 121–123</ref><ref>{{cite journal|last1=Davidson|first1=J. P.|title=Bonehead mistakes: The background in scientific literature and illustrations for Edward Drinker Cope's first restoration of ''Elasmosaurus platyurus''|journal=Proceedings of the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia|date=2002|volume=152|issue=1|pages=215–240|doi=10.1635/0097-3157(2002)152[0215:HPOVBM]2.0.CO;2|year=2002}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal|url=http://www.palarch.nl/2005/07/everhart-mj-2005-elasmosaurid-remains-from-the-pierre-shale-upper-cretaceous-of-western-kansas-possible-missing-elements-of-the-type-specimen-of-elasmosaurus-platyurus-cope-1868-%E2%80%93-pal/}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal|last1=Cope|first1=E. D.|title=1868. Remarks on a new enaliosaurian, Elasmosaurus platyurus. Proceedings of the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia 20:92-93.|date=1841|url=https://archive.org/details/cbarchive_50660_copeed1868remarksonanewenalios1841}}</ref><ref>http://oceansofkansas.com/Cope1870a.html</ref> |
||
==Classification== |
==Classification== |
||
While numerous species of ''Elasmosaurus'' have been named since its discovery, a 1999 review by Ken Carpenter showed that only one, the [[type species]] ''Elasmosaurus platyurus'', could be considered valid. Various other species assigned to the genus are either [[nomen dubium|dubious]] or have been classified in other genera. For example, ''E. serpentinus'' has been reclassified as ''[[Hydralmosaurus]]'', ''E. morgani'' as ''[[Libonectes]]'', and ''E. snowii'' as ''[[Styxosaurus]]''.<ref name=Carpenter1999/><ref>{{cite journal|doi=10.5962/bhl.title.5289}}</ref> |
While numerous species of ''Elasmosaurus'' have been named since its discovery, a 1999 review by Ken Carpenter showed that only one, the [[type species]] ''Elasmosaurus platyurus'', could be considered valid. Various other species assigned to the genus are either [[nomen dubium|dubious]] or have been classified in other genera. For example, ''E. serpentinus'' has been reclassified as ''[[Hydralmosaurus]]'', ''E. morgani'' as ''[[Libonectes]]'', and ''E. snowii'' as ''[[Styxosaurus]]''.<ref name=Carpenter1999/><ref>{{cite journal|doi=10.5962/bhl.title.5289|title=A specimen of Elasmosaurus serpentinus / by Elmer S. Riggs --|year=1939|last1=Riggs|first1=Elmer S}}</ref> |
||
By the early part of the [[Late Cretaceous]], there were two distinct groups of plesiosaurs left.<ref>Everhart, p. 129</ref> ''Elasmosaurus'' is the [[type genus]] for one of these groups, the [[Elasmosauridae|elasmosaurids]] which had extremely long necks with relatively short heads, in contrast to the [[polycotylid]]s which had shorter necks and relatively larger heads. Late Cretaceous elasmosaurids from the Western Interior of North America have few features that separate them and are morphologically [[basal (phylogenetics)|primitive]].<ref name=Carpenter1999/> However, as noted above, ''Elasmosaurus'' and some others have some derived features. It has been suggested that ''Elasmosaurus'' was closely related to ''Hydralmosaurus'' and ''Styxosaurus'' due to these advanced features.<ref name=Sachs2005/> |
By the early part of the [[Late Cretaceous]], there were two distinct groups of plesiosaurs left.<ref>Everhart, p. 129</ref> ''Elasmosaurus'' is the [[type genus]] for one of these groups, the [[Elasmosauridae|elasmosaurids]] which had extremely long necks with relatively short heads, in contrast to the [[polycotylid]]s which had shorter necks and relatively larger heads. Late Cretaceous elasmosaurids from the Western Interior of North America have few features that separate them and are morphologically [[basal (phylogenetics)|primitive]].<ref name=Carpenter1999/> However, as noted above, ''Elasmosaurus'' and some others have some derived features. It has been suggested that ''Elasmosaurus'' was closely related to ''Hydralmosaurus'' and ''Styxosaurus'' due to these advanced features.<ref name=Sachs2005/> |
||
[[File:Elasmosaur.jpg |thumb|Reconstructed skeleton, [[Canadian Museum of Nature]]]] |
[[File:Elasmosaur.jpg |thumb|Reconstructed skeleton, [[Canadian Museum of Nature]]]] |
||
The following [[cladogram]] shows the placement of ''Elasmosaurus'' within Elasmosauridae following an analysis by Rodrigo A. Otero, 2016:<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Otero|first1=R. A.|title=Taxonomic reassessment of ''Hydralmosaurus'' as ''Styxosaurus'': new insights on the elasmosaurid neck evolution throughout the Cretaceous|journal=PeerJ|date=2016|volume=4|pages=e1777|doi=10.7717/peerj.1777}}</ref> |
The following [[cladogram]] shows the placement of ''Elasmosaurus'' within Elasmosauridae following an analysis by Rodrigo A. Otero, 2016:<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Otero|first1=R. A.|title=Taxonomic reassessment of ''Hydralmosaurus'' as ''Styxosaurus'': new insights on the elasmosaurid neck evolution throughout the Cretaceous|journal=PeerJ|date=2016|volume=4|pages=e1777|doi=10.7717/peerj.1777|pmid=27019781|pmc=4806632}}</ref> |
||
{{clade| style=font-size:85%; line-height:85%; |
{{clade| style=font-size:85%; line-height:85%; |
||
| Line 82: | Line 82: | ||
[[File:Elasmosaurus NT.jpg|thumb|Restoration showing two individuals swimming with straight necks]] |
[[File:Elasmosaurus NT.jpg|thumb|Restoration showing two individuals swimming with straight necks]] |
||
===Habits=== |
===Habits=== |
||
''Elasmosaurus'' is believed to have lived mostly in open ocean.<ref name="Everhart140"/> The unusual body structure of elasmosaurs would have limited the speed in which they could swim and their paddles may have moved in manner similar to birds wings but could not twist and were thus held rigidly.<ref name="Everhart136"/> The paddles, as with other plesiosaurs, are so rigid and specialized for swimming that they could not have come on land to lay eggs like [[sea turtle]]s. Thus they most likely gave live birth to their young like [[sea snake]]s.<ref name="Everhart140">Everhart, pp. 140</ref> Evidence for [[viviparity]] in plesiosaurs came in the form of a fossil of an adult ''[[Polycotylus]]'' with a single fetus inside. It was unearthed in Kansas during the 1980s and was in storage at the Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County until it was described in 2011.<ref name="Okeefe2011">{{cite journal|author=O'Keefe, F. R. and Chiappe, L. M.|year=2011|title=Viviparity and K-selected life history in a Mesozoic marine plesiosaur (Reptilia, Sauropterygia)|journal=Science|volume=333|issue=6044|pages=870–873|doi=10.1126/science.1205689}}</ref> |
''Elasmosaurus'' is believed to have lived mostly in open ocean.<ref name="Everhart140"/> The unusual body structure of elasmosaurs would have limited the speed in which they could swim and their paddles may have moved in manner similar to birds wings but could not twist and were thus held rigidly.<ref name="Everhart136"/> The paddles, as with other plesiosaurs, are so rigid and specialized for swimming that they could not have come on land to lay eggs like [[sea turtle]]s. Thus they most likely gave live birth to their young like [[sea snake]]s.<ref name="Everhart140">Everhart, pp. 140</ref> Evidence for [[viviparity]] in plesiosaurs came in the form of a fossil of an adult ''[[Polycotylus]]'' with a single fetus inside. It was unearthed in Kansas during the 1980s and was in storage at the Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County until it was described in 2011.<ref name="Okeefe2011">{{cite journal|author=O'Keefe, F. R. and Chiappe, L. M.|year=2011|title=Viviparity and K-selected life history in a Mesozoic marine plesiosaur (Reptilia, Sauropterygia)|journal=Science|volume=333|issue=6044|pages=870–873|doi=10.1126/science.1205689|bibcode=2011Sci...333..870O}}</ref> |
||
===Neck structure and function=== |
===Neck structure and function=== |
||
| Line 94: | Line 94: | ||
===Feeding=== |
===Feeding=== |
||
[[Image:Gastroliths.jpg|thumb|upright|Plesiosaur gastroliths from the [[Tropic, Utah|Tropic]] [[Shale]].]] |
[[Image:Gastroliths.jpg|thumb|upright|Plesiosaur gastroliths from the [[Tropic, Utah|Tropic]] [[Shale]].]] |
||
The flexion ranges of ''Elasmosaurus'' would have allowed them to employ a number of hunting methods including "[[benthic]] grazing" which would have involved swimming close to the bottom and using the head and neck to dig for prey on the sea floor. Elasmosaurs may also have been active hunters in the [[pelagic zone]] and retracted their necks back to launch a strike or used side-swip motions to stun or kill prey with their laterally projected teeth (like [[sawshark]]s).<ref name="Zammit2008">{{cite journal|author=Zammit M., Daniels, C. B. and Kear, B. P.|year=2008|title=Elasmosaur (Reptilia: Sauropterygia) neck flexibility: Implications for feeding strategies|journal=Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology - Part A: Molecular & Integrative Physiology|volume=150|issue=2|pages= |
The flexion ranges of ''Elasmosaurus'' would have allowed them to employ a number of hunting methods including "[[benthic]] grazing" which would have involved swimming close to the bottom and using the head and neck to dig for prey on the sea floor. Elasmosaurs may also have been active hunters in the [[pelagic zone]] and retracted their necks back to launch a strike or used side-swip motions to stun or kill prey with their laterally projected teeth (like [[sawshark]]s).<ref name="Zammit2008">{{cite journal|author=Zammit M., Daniels, C. B. and Kear, B. P.|year=2008|title=Elasmosaur (Reptilia: Sauropterygia) neck flexibility: Implications for feeding strategies|journal=Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology - Part A: Molecular & Integrative Physiology|volume=150|issue=2|pages=124–130|doi=10.1016/j.cbpa.2007.09.004|pmid=17933571}}</ref> |
||
It is possible that ''Elasmosaurus'' and its kin stalked schools of fish, concealing themselves below and moving the head slowly up as they approached. The eyes of the animal were located at the top of the head and allowed them to see directly upward. This [[stereoscopic vision]] would help it find small prey. Hunting from below would also have helped by silhouetting the prey in the sunlight while concealing ''Elasmosaurus'' in the dark waters below. Elasmosaurs probably ate small [[bony fish]] and [[marine invertebrates]], as their small, non-[[Cranial kinesis|kinetic]] skulls would have limited the prey they could eat. The long, slender teeth were adapted for seizing prey and not tearing, and hence it was swallowed whole.<ref>Everhart 133–135</ref> It swallowed [[gastrolith|small stones]] to aid its [[digestion]].<ref name="Everhart136">Everhart, pp. 136-137</ref> |
It is possible that ''Elasmosaurus'' and its kin stalked schools of fish, concealing themselves below and moving the head slowly up as they approached. The eyes of the animal were located at the top of the head and allowed them to see directly upward. This [[stereoscopic vision]] would help it find small prey. Hunting from below would also have helped by silhouetting the prey in the sunlight while concealing ''Elasmosaurus'' in the dark waters below. Elasmosaurs probably ate small [[bony fish]] and [[marine invertebrates]], as their small, non-[[Cranial kinesis|kinetic]] skulls would have limited the prey they could eat. The long, slender teeth were adapted for seizing prey and not tearing, and hence it was swallowed whole.<ref>Everhart 133–135</ref> It swallowed [[gastrolith|small stones]] to aid its [[digestion]].<ref name="Everhart136">Everhart, pp. 136-137</ref> |
||
Revision as of 00:00, 27 September 2017
| Elasmosaurus Temporal range: Late Cretaceous,
| |
|---|---|

| |
| Reconstructed skeleton in the Rocky Mountain Dinosaur Resource Center | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Superorder: | †Sauropterygia |
| Order: | †Plesiosauria |
| Family: | †Elasmosauridae |
| Genus: | †Elasmosaurus Cope, 1868 |
| Species: | †E. platyurus
|
| Binomial name | |
| †Elasmosaurus platyurus Cope, 1868
| |
Elasmosaurus (/ɪˌlæzməˈsɔːrəs, -moʊ-/;[1] from Greek ελασμος elasmos 'thin plate' (referring to thin plates in its pelvic girdle) + σαυρος sauros 'lizard') is a genus of plesiosaur with an extremely long neck that lived in the Late Cretaceous period (Campanian stage), 80.5 million years ago.[2]
Description

At 10.3 meters (38 ft) in length,[3] Elasmosaurus was among the largest plesiosaurs. It differs from all other plesiosaurs by having six teeth per premaxilla (the bones at the tip of the snout) and 72 neck (cervical) vertebrae.[4]
The snout was rounded and almost formed a semi-circle when viewed from above, and the premaxillae (which form the front of the upper jaw) bore a low keel at the midline. It is uncertain how many teeth Elasmosaurus had, due to the fragmentary fossils. It probably had six teeth in each premaxilla, and the teeth preserved there were formed like large fangs. The two teeth at the front were smaller than the succeeding ones, and were located between the first two teeth in the dentaries of the lower jaws. The known teeth of the front part of the lower jaw are large fangs, and the teeth at the back of the jaws appear to have been smaller. The mandibular symphysis (where the two halves of the lower jaw connected) was well-ossified, with no visible suture. The skull was relatively flat, with a number of long pointed teeth. The lower jaws were joined at the tip to a point between the fourth and fifth teeth.[4] The neck vertebrae immediately following the skull were long and low, and had longitudinal lateral crests. Like most elasmosaurids, Elasmosaurus had around three pectoral vertebrae. The tail included at least 18 vertebrae.[5][6]
The pectoral girdle featured a long bar,[5][6] not present in juveniles. The scapula had margins of approximately equal length for the joint with the coracoid and the articular surface for the upper arm.[4] The anterior edge of the pelvic girdle was made up of three almost straight edges directed to the front and sides of the animal. The ischia, a pair of bones that formed the posterior part of the pelvis, were joined along their medial surfaces.[4] The limbs of Elasmosaurus, like those of other plesiosaurs, were modified into approximately equally sized rigid paddles.[7]

Certain aspects of the anatomy of Elasmosaurus were fairly derived among elasmosaurids, and plesiosaurs in general.[4] As noted, Elasmosaurus can be distinguished by its six premaxillary teeth and 72 cervical vertebrae.[4] Primitively, plesiosaurs and most elasmosaurids had five teeth per premaxilla. Some elasmosaurids had more: Terminonatator had nine[8] and Aristonectes had 10 to 13.[9] In addition, most plesiosaurs had fewer than 60 cervical vertebrae.[4] Aside from Elasmosaurus, plesiosaurs that exceeded 60 cervicals include Styxosaurus, Hydralmosaurus, Thalassomedon, and Albertonectes.[10]
Elasmosaurus and Albertonectes are the only known plesiosaurs with more than 70 cervical vertebrae.[4] Albertonectes has 75 vertebrate and is the only known genus to have more than Elasmosaurus. The two plesiosaurs have the highest numbers of cervical vertebrae among vertebrates in general.[11] Elasmosaurus had roughly the same neck length as Thalassomedon[12] because the latter has proportionally longer vertebrae.[13] The presence of the pectoral bar is also considered an advanced feature.[4] The long, low axis centrum differs from the condition seen in most other plesiosaurs, which have centra that are either shorter in length than height, or about equidimensional.[4] Styxosaurus and Hydralmosaurus also have the condition present in Elasmosaurus.[12][14] Another unusual feature of Elasmosaurus is the relatively equal lengths of the margins of the scapula, as mentioned above. Most plesiosaurs had longer margins for articulation with the coracoid than for articulation with the upper arm.[14]
History of discovery

Elasmosaurus platyurus was described in March, 1868 by Edward Drinker Cope[15] from a fossil discovered and collected by Dr. Theophilus Turner, a military doctor, in western Kansas, United States. Although other specimens of elasmosaurs have been found in various locations in North America, Carpenter (1999) determined that Elasmosaurus platyurus was the only representative of the genus.[6][16]
Turner found the remains of the species in Pierre Shale sediments along a right-of-way passage of a Pacific Union railroad close to McAllaster, Kansas in 1867. Turner give some parts to the John LeConte, would was working for the railroad company as part of a survey crew. LeConte then delivered them to Cope, who was in Philadelphia. Recognizing then as the remains of a plesiosaur, Cope wrote to Turner asking him to deliver the rest of the specimen. Cope finally got them in mid-March 1868 and two weeks later reported that it was a previously unknown species of plesiosaur, which he named Elasmosaurus platyurus (Greek for flat-tailed, thin-plate reptile). Cope mistakenly believed that the cervical vertebrae were caudal vertebrate and the long neck was the tail, thereby putting the head on the wrong end. Two years later Joseph Leidy, who mentored Cope, noted the error in his article published in the Transactions of the American Philosophical Society. Embarrassed by this revelation, Cope immediately printed a notice and offered to replaced the copies of preprint of his paper. O. C. Marsh quoted the text of the notice in his 1890 article for the New York Herald.[17][18][19][20][21]
Classification
While numerous species of Elasmosaurus have been named since its discovery, a 1999 review by Ken Carpenter showed that only one, the type species Elasmosaurus platyurus, could be considered valid. Various other species assigned to the genus are either dubious or have been classified in other genera. For example, E. serpentinus has been reclassified as Hydralmosaurus, E. morgani as Libonectes, and E. snowii as Styxosaurus.[6][22]
By the early part of the Late Cretaceous, there were two distinct groups of plesiosaurs left.[23] Elasmosaurus is the type genus for one of these groups, the elasmosaurids which had extremely long necks with relatively short heads, in contrast to the polycotylids which had shorter necks and relatively larger heads. Late Cretaceous elasmosaurids from the Western Interior of North America have few features that separate them and are morphologically primitive.[6] However, as noted above, Elasmosaurus and some others have some derived features. It has been suggested that Elasmosaurus was closely related to Hydralmosaurus and Styxosaurus due to these advanced features.[4]

The following cladogram shows the placement of Elasmosaurus within Elasmosauridae following an analysis by Rodrigo A. Otero, 2016:[24]
| Elasmosauridae |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Paleobiology

Habits
Elasmosaurus is believed to have lived mostly in open ocean.[25] The unusual body structure of elasmosaurs would have limited the speed in which they could swim and their paddles may have moved in manner similar to birds wings but could not twist and were thus held rigidly.[26] The paddles, as with other plesiosaurs, are so rigid and specialized for swimming that they could not have come on land to lay eggs like sea turtles. Thus they most likely gave live birth to their young like sea snakes.[25] Evidence for viviparity in plesiosaurs came in the form of a fossil of an adult Polycotylus with a single fetus inside. It was unearthed in Kansas during the 1980s and was in storage at the Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County until it was described in 2011.[27]
Neck structure and function

Like most plesiosaurs, and in stark contrast to many common media depictions, Elasmosaurus was incapable of raising anything more than its head above the water. The weight of its long neck placed the center of gravity behind the front flippers. Thus Elasmosaurus could only have raised its head and neck above the water if in shallow water, where it could rest its body on the bottom. The weight of the neck, the limited musculature, and the limited movement between the vertebrae would have prevented Elasmosaurus from raising its head and neck very high as well. The head and shoulders of the Elasmosaurus most likely acted as a rudder. If the animal moved the anterior part of the body in a certain direction, it would cause the rest of the body to move in that direction. Thus, Elasmosaurus could not have swum in one direction while moving its head and neck either horizontally or vertically in a different direction.[28]
One study found that the necks of elasmosaurs were capable of 75–177˚ of ventral movement, 87–155° of dorsal movement, and 94–176° of lateral movement, depending on the amount of tissue between the vertebrae, which likely increased in rigidness towards the back of the neck. The researchers concluded that lateral and vertical arches and shallow S-shaped curves were feasible in contrast to the "swan-like" S-shape neck postures which required more than 360° of vertical flexion.[29]
It has also been suggested that the long necks of plesiosaurs served as a snorkel and allowed then to breathe air while the body remained underwater. This is disputed as there would be large hydrostatic pressure differences, particularly for the extremely long-necked elasmosaurs. The neck anatomy of elasmosaurs was capable of making a gentle slop to allow them to breathe at the surface but would have required them to make energy expensive swimming at the sub-surface. In addition, the longer neck would also have increased dead space and the animals may have required larger lungs. The neck could have had other vulnerabilities; it could have been targeted by predators.[30]
Feeding

The flexion ranges of Elasmosaurus would have allowed them to employ a number of hunting methods including "benthic grazing" which would have involved swimming close to the bottom and using the head and neck to dig for prey on the sea floor. Elasmosaurs may also have been active hunters in the pelagic zone and retracted their necks back to launch a strike or used side-swip motions to stun or kill prey with their laterally projected teeth (like sawsharks).[29]
It is possible that Elasmosaurus and its kin stalked schools of fish, concealing themselves below and moving the head slowly up as they approached. The eyes of the animal were located at the top of the head and allowed them to see directly upward. This stereoscopic vision would help it find small prey. Hunting from below would also have helped by silhouetting the prey in the sunlight while concealing Elasmosaurus in the dark waters below. Elasmosaurs probably ate small bony fish and marine invertebrates, as their small, non-kinetic skulls would have limited the prey they could eat. The long, slender teeth were adapted for seizing prey and not tearing, and hence it was swallowed whole.[31] It swallowed small stones to aid its digestion.[26]
Paleoecology
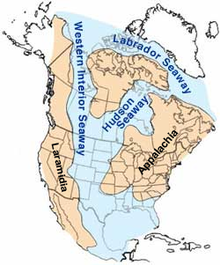
Elasmosaurus fossils have been found in the Campanian-age Upper Cretaceous Pierre Shale of western Kansas. The Pierre Shale represents a period of marine deposition from the Western Interior Seaway, a shallow continental sea that submerged much of central North America during the Cretaceous.[32] At its largest, the Western Interior Seaway stretched from the Rockies east to the Appalachians, some 1,000 km (620 mi) wide. At its deepest, it may have been only 800 or 900 metres (2,600 or 3,000 ft) deep, shallow in terms of seas. Two great continental watersheds drained into it from east and west, diluting its waters and bringing resources in eroded silt that formed shifting delta systems along its low-lying coasts. There was little sedimentation on the eastern shores of the Seaway; the western boundary, however, consisted of a thick clastic wedge eroded eastward from the Sevier orogenic belt.[33][34] The western shore was thus highly variable, depending on variations in sea level and sediment supply.[33]
While the soft, muddy sea floor likely got very little sunlight, it teamed with life due to steady rains of organic debris from plankton and other organisms up the water column. The bottom was dominated by large Inoceramus clams which were covered with oysters and there was little biodiversity. Clam shells would have accumulated over the centuries in layers under the floor surface, these would have provided shelter for small fish. Other invertebrates known to have lived the sea include cephalopods, like squids and ammonites, and Baculites and the crinoid Uintacrinus.[35]
Large fish known to have inhabited the sea include the bony fishes; Pachyrhizodus, Enchodus, Cimolichthys, Saurocephalus, Saurodon, Gillicus, Ichthyodectes, Xiphactinus, Protosphyraena and Martinichthys,[36] and the sharks; Cretoxyrhina, Cretolamna, Scapanorhynchus, Pseudocorax and Squalicorax.[37] In addition to Elasmosaurus, marine reptiles present include fellow plesiosaurs; Hydralmosaurus, Libonectes, Styxosaurus, Thalassomedon, Terminonatator, Polycotylus, Brachauchenius, Dolichorhynchops and Trinacromerum[38]; the mosasaurs; Mosasaurus, Halisaurus, Prognathodon, Tylosaurus, Ectenosaurus, Globidens, Clidastes, Platecarpus and Plioplatecarpus[39] and the sea turtles; Archelon, Protostega, Porthochelys and Toxochelys.[40] The flightless aquatic bird Hesperornis also made its home there.[41] In addition, the pterosaurs; Pteranodon and Nyctosaurus[42] and the bird Ichthyornis.[41], flew in the skies above.
See also
References
- ^ "Elasmosaurus". Oxford Dictionaries UK English Dictionary. Oxford University Press. n.d. Retrieved 2016-01-21.
- ^ Carpenter, K. 2003. "Vertebrate Biostratigraphy of the Smoky Hill Chalk (Niobrara Formation) and the Sharon Springs Member (Pierre Shale)." High-Resolution Approaches in Stratigraphic Paleontology, 21: 421-437. doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-9053-0
- ^ O'Gorman, J.P. (2016). "A Small Body Sized Non-Aristonectine Elasmosaurid (Sauropterygia, Plesiosauria) from the Late Cretaceous of Patagonia with Comments on the Relationships of the Patagonian and Antarctic Elasmosaurids". Ameghiniana. 53 (3): 245–268. doi:10.5710/AMGH.29.11.2015.2928.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k Sachs, S. (2005). "Redescription of Elasmosaurus platyurus, Cope 1868 (Plesiosauria: Elasmosauridae) from the Upper Cretaceous (lower Campanian) of Kansas, U.S.A" (PDF). Paludicola. 5 (3): 92–106.
- ^ a b Brown, D. S. (1993). "A taxonomic reappraisal of the families Elasmosauridae and Cryptoclididae (Reptilia: Plesiosauroidea)". Révue de Paléobiologie. 7: 9–16.
- ^ a b c d e Carpenter, K. (1999). "Revision of North American elasmosaurs from the Cretaceous of the western interior". Paludicola. 2 (2): 148–173.
- ^ Everhart p. 135
- ^ Sato, T. (2003). "Terminonatator ponteixensis, a new elasmosaur (Reptilia:Sauropterygia) from the Upper Cretaceous of Saskatchewan"". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 23 (1): 89–103.
- ^ Gasparini, Z., Bardet, N., Martin, J.E. and Fernandez, M.S. (2003). "The elasmosaurid plesiosaur Aristonectes Cabreta from the Latest Cretaceous of South America and Antarctica". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 23 (1): 104–115. doi:10.1671/0272-4634(2003)23[104:TEPACF]2.0.CO;2.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Kubo, T.; Mitchell, M. T.; Henderson, D. M. (2012). "Albertonectes vanderveldei, a new elasmosaur (Reptilia, Sauropterygia) from the Upper Cretaceous of Alberta". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 32 (3): 557–572. doi:10.1080/02724634.2012.658124.
- ^ Sach, S.; Kear, B. P.; Everhart, M. (2013). "Revised Vertebral Count in the "Longest-Necked Vertebrate" Elasmosaurus platyurus Cope 1868, and Clarification of the Cervical-Dorsal Transition in Plesiosauria". PLoS ONE. 8 (8): e70877. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...870877S. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0070877.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ a b Welles, S. P. (1943). "Elasmosaurid plesiosaurs with descriptions of new material from California and Colorado". Memoirs of the University of California. 13: 125–254..
- ^ Everhart p. 130
- ^ a b Sachs, S. (2004). "Redescription of Woolungasaurus glendowerensis (Plesiosauria: Elasmosauridae) from the Lower Cretaceous of Northeast Queensland". Memoirs of the Quennsland Museum. 49: 215–233.
- ^ Cope, E. D. (1868). "Remarks on a new enaliosaurian, Elasmosaurus platyurus". Proceedings of the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia. 20: 92–93.
- ^ Williston, S. W. (1906). "North American plesiosaurs Elasmosaurus, Cimoliasaurus, and Polycotylus". American Journal of Science. s4-21 (123): 221–236. doi:10.2475/ajs.s4-21.123.221.
- ^ Everhart pp. 121–123
- ^ Davidson, J. P. (2002). "Bonehead mistakes: The background in scientific literature and illustrations for Edward Drinker Cope's first restoration of Elasmosaurus platyurus". Proceedings of the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia. 152 (1): 215–240. doi:10.1635/0097-3157(2002)152[0215:HPOVBM]2.0.CO;2.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) - ^ http://www.palarch.nl/2005/07/everhart-mj-2005-elasmosaurid-remains-from-the-pierre-shale-upper-cretaceous-of-western-kansas-possible-missing-elements-of-the-type-specimen-of-elasmosaurus-platyurus-cope-1868-%E2%80%93-pal/.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help); Missing or empty|title=(help) - ^ Cope, E. D. (1841). "1868. Remarks on a new enaliosaurian, Elasmosaurus platyurus. Proceedings of the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia 20:92-93".
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ http://oceansofkansas.com/Cope1870a.html
- ^ Riggs, Elmer S (1939). "A specimen of Elasmosaurus serpentinus / by Elmer S. Riggs --". doi:10.5962/bhl.title.5289.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Everhart, p. 129
- ^ Otero, R. A. (2016). "Taxonomic reassessment of Hydralmosaurus as Styxosaurus: new insights on the elasmosaurid neck evolution throughout the Cretaceous". PeerJ. 4: e1777. doi:10.7717/peerj.1777. PMC 4806632. PMID 27019781.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ a b Everhart, pp. 140
- ^ a b Everhart, pp. 136-137
- ^ O'Keefe, F. R. and Chiappe, L. M. (2011). "Viviparity and K-selected life history in a Mesozoic marine plesiosaur (Reptilia, Sauropterygia)". Science. 333 (6044): 870–873. Bibcode:2011Sci...333..870O. doi:10.1126/science.1205689.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Everhart, pp. 132-133
- ^ a b Zammit M., Daniels, C. B. and Kear, B. P. (2008). "Elasmosaur (Reptilia: Sauropterygia) neck flexibility: Implications for feeding strategies". Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology - Part A: Molecular & Integrative Physiology. 150 (2): 124–130. doi:10.1016/j.cbpa.2007.09.004. PMID 17933571.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Noè, L. F.; Taylor, M. A.; Gómez-Pérez, M. (2017). "An integrated approach to understanding the role of the long neck in plesiosaurs" (PDF). Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 62 (1): 137–162. doi:10.4202/app.00334.2016.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Everhart 133–135
- ^ Everhart, p. 6
- ^ a b Stanley, Steven M. (1999). Earth System History. New York: W.H. Freeman and Company. pp. 487–489. ISBN 0-7167-2882-6.
- ^ Monroe, James S.; Wicander, Reed (2009). The Changing Earth: Exploring Geology and Evolution (5th ed.). Belmont, CA: Brooks/Cole, Cengage Learning. p. 605. ISBN 0495554804.
- ^ Everhart, pp. 28–38
- ^ Everhart, pp. 78, 82–84, 88, 93
- ^ Everhart, p. 58
- ^ Everhart, pp. 125, 129, 132–133, 144
- ^ Everhart, p. 160
- ^ Everhart, pp. 108–109
- ^ a b Everhart, p. 221
- ^ Everhart, p. 210
General sources
- Everhart, M. J. (2005). Oceans of Kansas - A Natural History of the Western Interior Sea. Indiana University. ISBN 0-253-34547-2.
External links
 Media related to Elasmosaurus at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Elasmosaurus at Wikimedia Commons- Elasmosaurus platyurus on Oceans of Kansas
- Elasmosaurus The Plesiosaur Directory - Elasmosaurus
- Where the Elasmosaurs roam: Separating fact from fiction







