Nicotinamide mononucleotide: Difference between revisions
Citation bot (talk | contribs) Alter: template type. Add: pmid, doi, page, issue, volume, journal, pmc, year, authors 1-6. Removed proxy/dead URL that duplicated identifier. | Use this bot. Report bugs. | Suggested by Headbomb | #UCB_toolbar |
→Dietary sources: added more authoritative citation |
||
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
== Dietary sources == |
== Dietary sources == |
||
NMN is found in fruits and vegetables such as [[edamame]], [[broccoli]], [[cabbage]], [[cucumber]] and [[avocado]] at about 1mg per 100g.<ref>{{Cite web|last=Ryan|first=Finn|date=2016-12-06|title=5 Anti-Aging Food Types You Should Already Be Eating|url=https://www.bicycling.com/health-nutrition/g20011748/5-anti-aging-food-types-you-should-already-be-eating/|access-date=2022-01-20|website=Bicycling|language=en-US}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|date=2019-01-07|title=Scientists identify new fuel-delivery route for cells|url=https://medicine.wustl.edu/news/scientists-identify-new-fuel-delivery-route-for-cells/|access-date=2022-01-20|website=Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis|language=en}}</ref> |
NMN is found in fruits and vegetables such as [[edamame]], [[broccoli]], [[cabbage]], [[cucumber]] and [[avocado]] at about 1mg per 100g.<ref name="Mills et al., Cell Metab 2016">{{cite journal |last1=Mills |first1=KF |last2=Yoshida |first2=S |last3=Stein |first3=LR |last4=Grozio |first4=A |last5=Kubota |first5=S |last6=Sasaki |first6=Y |last7=Redpath |first7=P |last8=Migaud |first8=ME |last9=Apte |first9=RS |last10=Uchida |first10=K |last11=Yoshino |first11=J |last12=Imai |first12=SI |title=Long-Term Administration of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Mitigates Age-Associated Physiological Decline in Mice. |journal=Cell metabolism |date=13 December 2016 |volume=24 |issue=6 |pages=795-806 |doi=10.1016/j.cmet.2016.09.013 |pmid=28068222}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|last=Ryan|first=Finn|date=2016-12-06|title=5 Anti-Aging Food Types You Should Already Be Eating|url=https://www.bicycling.com/health-nutrition/g20011748/5-anti-aging-food-types-you-should-already-be-eating/|access-date=2022-01-20|website=Bicycling|language=en-US}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|date=2019-01-07|title=Scientists identify new fuel-delivery route for cells|url=https://medicine.wustl.edu/news/scientists-identify-new-fuel-delivery-route-for-cells/|access-date=2022-01-20|website=Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis|language=en}}</ref> |
||
==References== |
==References== |
||
Revision as of 23:58, 6 December 2022
You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in Japanese. (September 2018) Click [show] for important translation instructions.
|
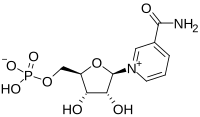
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3-Carbamoyl-1-[5-O-(hydroxyphosphinato)-β-D-ribofuranosyl]pyridinium
| |
| Preferred IUPAC name
[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(3-Carbamoylpyridin-1-ium-1-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methyl hydrogen phosphate | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 3570187 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.012.851 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C11H15N2O8P | |
| Molar mass | 334.221 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Nicotinamide mononucleotide ("NMN" and "β-NMN") is a nucleotide derived from ribose, nicotinamide, nicotinamide riboside and niacin.[1] Humans have enzymes that can use NMN to generate nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH).[1] In mice, NMN has been proposed to enter cells via the small intestines within 10 minutes converting to NAD+ through the Slc12a8 transporter.[2] However this observation has been challenged,[3] and remains unsettled.[4]
Because NADH is a cofactor for processes inside mitochondria, for sirtuins, and for PARP, NMN has been studied in animal models as a potential neuroprotective and anti-aging agent.[5][6] Dietary supplement companies have aggressively marketed NMN products claiming those benefits.[7] Single-dose administration of up to 500 mg was shown safe in men in a study at Keio University School of Medicine, Shinjuku, Tokyo, Japan.[8] One 2021 clinical trial found that NMN improved muscular insulin sensitivity in prediabetic women,[9] and another found that it improved aerobic capacity in amateur runners.[10]
Nicotinamide riboside (NR) kinase enzymes are essential for exogenously administered utilization of NR and NMN.[11][12] Some research suggests when administered exogenously, NMN must be converted to NR in order to enter a cell and be re-phosphorylated back to NMN.[11]

The molecular structures of NMN and NR are roughly the same, except NMN has an added phosphate group, making it a larger molecule. Some scientists believe NMN is too large to cross cellular membranes and must convert to NR before entering cells, where NAD+ biosynthesis occurs. Otherwise, NMN would need to be transported into cells by a transporter specific for NMN, possibly such as Slc12a8.[13]
Both NR and NMN are vulnerable to extracellular degradation by CD38 enzyme,[12] which can be inhibited by compounds such as CD38-IN-78c.[14]
Dietary sources
NMN is found in fruits and vegetables such as edamame, broccoli, cabbage, cucumber and avocado at about 1mg per 100g.[15][16][17]
References
- ^ a b Bogan KL, Brenner C (2008). "Nicotinic acid, nicotinamide, and nicotinamide riboside: a molecular evaluation of NAD+ precursor vitamins in human nutrition". Annual Review of Nutrition. 28: 115–30. doi:10.1146/annurev.nutr.28.061807.155443. PMID 18429699.
- ^ Grozio, A; Mills, KF; Yoshino, J; Bruzzone, S; Sociali, G; Tokizane, K; Lei, HC; Cunningham, R; Sasaki, Y; Migaud, ME; Imai, SI (January 2019). "Slc12a8 is a nicotinamide mononucleotide transporter". Nature Metabolism. 1 (1): 47–57. doi:10.1038/s42255-018-0009-4. PMC 6530925. PMID 31131364.
- ^ Schmidt, MS; Brenner, C (July 2019). "Absence of evidence that Slc12a8 encodes a nicotinamide mononucleotide transporter". Nature Metabolism. 1 (7): 660–661. doi:10.1038/s42255-019-0085-0. PMID 32694648. S2CID 203899191.
- ^ Chini, CCS; Zeidler, JD; Kashyap, S; Warner, G; Chini, EN (1 June 2021). "Evolving concepts in NAD+ metabolism". Cell Metabolism. 33 (6): 1076–1087. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2021.04.003. PMC 8172449. PMID 33930322.
- ^ Brazill JM, Li C, Zhu Y, Zhai RG (June 2017). "+ synthase… It's a chaperone… It's a neuroprotector". Current Opinion in Genetics & Development. 44: 156–162. doi:10.1016/j.gde.2017.03.014. PMC 5515290. PMID 28445802.
- ^ Mills, Kathryn F.; Yoshida, Shohei; Stein, Liana R.; Grozio, Alessia; Kubota, Shunsuke; Sasaki, Yo; Redpath, Philip; Migaud, Marie E.; Apte, Rajendra S.; Uchida, Koji; Yoshino, Jun; Imai, Shin-Ichiro (13 December 2016). "Long-Term Administration of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Mitigates Age-Associated Physiological Decline in Mice". Cell Metabolism. 24 (6): 795–806. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2016.09.013. PMC 5668137. PMID 28068222.
- ^ Stipp D (March 11, 2015). "Beyond Resveratrol: The Anti-Aging NAD Fad". Scientific American Blog Network.
- ^ Irie, Junichiro; Inagaki, Emi; Fujita, Masataka; Nakaya, Hideaki; Mitsuishi, Masanori; Yamaguchi, Shintaro; Yamashita, Kazuya; Shigaki, Shuhei; Ono, Takashi; Yukioka, Hideo; Okano, Hideyuki (2020). "Effect of oral administration of nicotinamide mononucleotide on clinical parameters and nicotinamide metabolite levels in healthy Japanese men". Endocrine Journal. 67 (2): 153–160. doi:10.1507/endocrj.EJ19-0313. ISSN 0918-8959. PMID 31685720.
- ^ Yoshino, M; Yoshino, J; Kayser, BD; Patti, GJ; Franczyk, MP; Mills, KF; Sindelar, M; Pietka, T; Patterson, BW; Imai, SI; Klein, S (11 June 2021). "Nicotinamide mononucleotide increases muscle insulin sensitivity in prediabetic women". Science. 372 (6547): 1224–1229. Bibcode:2021Sci...372.1224Y. doi:10.1126/science.abe9985. PMC 8550608. PMID 33888596.
- ^ Liao, B.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhang, X.; Hao, X.; Hu, M. (2021). ""Nicotinamide mononucleotide supplementation enhances aerobic capacity in amateur runners: a randomized, double-blind study"". Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition. 18 (1): 54. doi:10.1186/s12970-021-00442-4. PMC 8265078. PMID 34238308.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ a b Fletcher RS, Lavery GG (October 2018). "The emergence of the nicotinamide riboside kinases in the regulation of NAD+ metabolism". Journal of Molecular Endocrinology. 61 (3): R107–R121. doi:10.1530/JME-18-0085. PMC 6145238. PMID 30307159.
- ^ a b Cambronne XA, Kraus WL (October 2020). "+ Synthesis and Functions in Mammalian Cells". Trends in Biochemical Sciences. 45 (10): 858–873. doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2020.05.010. PMC 7502477. PMID 32595066.
- ^ a b "NMN vs NR: The Differences Between These 2 NAD+ Precursors". www.nmn.com. Retrieved 2021-01-11.
- ^ Tarragó, MG; Chini, CCS; Kanamori, KS; Warner, GM; Caride, A; de Oliveira, GC; Rud, M; Samani, A; Hein, KZ; Huang, R; Jurk, D; Cho, DS; Boslett, JJ; Miller, JD; Zweier, JL; Passos, JF; Doles, JD; Becherer, DJ; Chini, EN (1 May 2018). "A Potent and Specific CD38 Inhibitor Ameliorates Age-Related Metabolic Dysfunction by Reversing Tissue NAD+ Decline". Cell Metabolism. 27 (5): 1081–1095.e10. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2018.03.016. PMC 5935140. PMID 29719225.
- ^ Mills, KF; Yoshida, S; Stein, LR; Grozio, A; Kubota, S; Sasaki, Y; Redpath, P; Migaud, ME; Apte, RS; Uchida, K; Yoshino, J; Imai, SI (13 December 2016). "Long-Term Administration of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Mitigates Age-Associated Physiological Decline in Mice". Cell metabolism. 24 (6): 795–806. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2016.09.013. PMID 28068222.
- ^ Ryan, Finn (2016-12-06). "5 Anti-Aging Food Types You Should Already Be Eating". Bicycling. Retrieved 2022-01-20.
- ^ "Scientists identify new fuel-delivery route for cells". Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. 2019-01-07. Retrieved 2022-01-20.
