Subgrade: Difference between revisions
m Reverted edits by 47.15.34.4 (talk) to last version by JMF |
More general info and a source. |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
[[File:Section through railway track and foundation.png|450px|thumb|right|Section through railway track and foundation showing the sub-grade]] |
[[File:Section through railway track and foundation.png|450px|thumb|right|Section through railway track and foundation showing the sub-grade]] |
||
In [[transport engineering]], '''subgrade''' is the native material underneath a constructed [[road]],<ref name="idiot">http://www.highwaysmaintenance.com/drainage.htm The Idiots' Guide to Highways Maintenance ''highwaysmaintenence.com''</ref> [[Road surface|pavement]] or [[Track (rail transport)|railway track]] (US: railroad track). It is also called '''formation level'''. |
In [[transport engineering]], '''subgrade''' is the native material underneath a constructed [[road]],<ref name="idiot">http://www.highwaysmaintenance.com/drainage.htm The Idiots' Guide to Highways Maintenance ''highwaysmaintenence.com''</ref> [[Road surface|pavement]] or [[Track (rail transport)|railway track]] (US: railroad track). It is also called '''formation level'''. |
||
The subgrade provides support to the subbase level and acts as an integral load-bearing layer. Failure of the subgrade can cause depressions and rutting of the upper base and surface courses. These in turn can lead to water pooling in deformations and cause vehicle [[aquaplaning]] among other issues.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Ruts Cause Hydroplaning Accidents |url=https://www.atlantaeng.com/ruts_cause_hydroplaning.html |access-date=2024-02-09 |website=www.atlantaeng.com}}</ref> |
|||
The term can also refer to imported material that has been used to build an [[Embankment (transportation)|embankment]]. |
The term can also refer to imported material that has been used to build an [[Embankment (transportation)|embankment]]. |
||
| Line 8: | Line 10: | ||
==Construction== |
==Construction== |
||
Subgrades are commonly compacted before the construction of a road, pavement or railway track |
Subgrades are commonly compacted before the construction of a road, pavement or railway track. This is to ensure their ability to absorb the loads being transferred down from the upper layers, increasing the life and wear of the surface courses. |
||
== See also == |
== See also == |
||
Latest revision as of 09:49, 9 February 2024
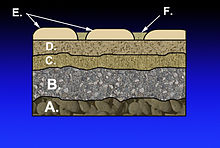

In transport engineering, subgrade is the native material underneath a constructed road,[1] pavement or railway track (US: railroad track). It is also called formation level.
The subgrade provides support to the subbase level and acts as an integral load-bearing layer. Failure of the subgrade can cause depressions and rutting of the upper base and surface courses. These in turn can lead to water pooling in deformations and cause vehicle aquaplaning among other issues.[2]
The term can also refer to imported material that has been used to build an embankment.
Construction
[edit]Subgrades are commonly compacted before the construction of a road, pavement or railway track. This is to ensure their ability to absorb the loads being transferred down from the upper layers, increasing the life and wear of the surface courses.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ http://www.highwaysmaintenance.com/drainage.htm The Idiots' Guide to Highways Maintenance highwaysmaintenence.com
- ^ "Ruts Cause Hydroplaning Accidents". www.atlantaeng.com. Retrieved 2024-02-09.
