Gulf of Finland: Difference between revisions
Undid revision 276078334 by 207.165.137.250 (talk) rv vandalism |
|||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
== Geography == |
== Geography == |
||
The Gulf of |
The Gulf of Finland has an area of {{convert|29500|km2|sqmi|abbr=on}}, its length is {{convert|428|km|mi|abbr=on}} and it is up to {{convert|120|km|mi|abbr=on}} wide. The width at the mouth of the gulf is {{convert|75|km|mi|abbr=on}} and the distance from [[Porkkala]] to [[Rohuneeme]], outside [[Tallinn]], is {{convert|52|km|mi|abbr=on}}. The gulf narrows in the east, eventually becoming the {{convert|10|–|28|km|mi|sing=on}} wide [[Gulf of Kronstadt]]. The largest bay on the northern coast is the [[Gulf of Vyborg]], and in the south [[Narva Bay]]. |
||
There are several islands in the Gulf of Finland. [[Hogland]], [[Tyters]], [[Lavansaari]] and [[Seiskari]] are the largest of these, and there are countless islands along the very splintered northern shoreline all the way from the west to the Gulf of Vyborg in the east. The deepest parts of the gulf can be found at the mouth of the gulf, where there is a deep with a depth of {{convert|80|–|100|m}}. There are even depths of over {{convert|100|m|ft|spell=us}} at the southern coast, while the depth at the northern coast never exceeds {{convert|60|m|ft|spell=us}}. Much of the northern shoreline is quite shallow and rocky, making it difficult, even dangerous to navigate coastal waters there without accurate charts. The deepest point, {{convert|121|m|ft|abbr=on}}, is at the Estonian coast, just northeast of Tallinn. About 5% of the water mass in the Baltic Sea is located in the Gulf of Finland. |
There are several islands in the Gulf of Finland. [[Hogland]], [[Tyters]], [[Lavansaari]] and [[Seiskari]] are the largest of these, and there are countless islands along the very splintered northern shoreline all the way from the west to the Gulf of Vyborg in the east. The deepest parts of the gulf can be found at the mouth of the gulf, where there is a deep with a depth of {{convert|80|–|100|m}}. There are even depths of over {{convert|100|m|ft|spell=us}} at the southern coast, while the depth at the northern coast never exceeds {{convert|60|m|ft|spell=us}}. Much of the northern shoreline is quite shallow and rocky, making it difficult, even dangerous to navigate coastal waters there without accurate charts. The deepest point, {{convert|121|m|ft|abbr=on}}, is at the Estonian coast, just northeast of Tallinn. About 5% of the water mass in the Baltic Sea is located in the Gulf of Finland. |
||
Revision as of 18:32, 9 March 2009
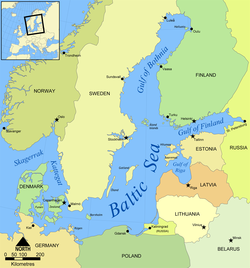
The Gulf of Finland (Finnish: Suomenlahti, Russian: Финский залив, Finskiy zaliv, Swedish: Finska viken, Estonian: Soome laht) is the easternmost arm of the Baltic Sea that extends between Finland (to the north) and Estonia (to the south) all the way to Saint Petersburg in Russia, where the river Neva drains into it. Other major cities around the gulf include Helsinki and Tallinn. The eastern parts of the Gulf of Finland belong to Russia and some of Russia's most important oil harbours are located farthest in, near Saint Petersburg (including Primorsk). As the seaway to Saint Petersburg, the Gulf of Finland has been and continues to be of considerable strategic importance to Russia. Some of the environmental problems affecting the Baltic Sea are at their most pronounced in the shallow, cul-de-sac gulf.
Geography
The Gulf of Finland has an area of 29,500 km2 (11,400 sq mi), its length is 428 km (266 mi) and it is up to 120 km (75 mi) wide. The width at the mouth of the gulf is 75 km (47 mi) and the distance from Porkkala to Rohuneeme, outside Tallinn, is 52 km (32 mi). The gulf narrows in the east, eventually becoming the 10–28-kilometre (6.2–17.4 mi) wide Gulf of Kronstadt. The largest bay on the northern coast is the Gulf of Vyborg, and in the south Narva Bay.
There are several islands in the Gulf of Finland. Hogland, Tyters, Lavansaari and Seiskari are the largest of these, and there are countless islands along the very splintered northern shoreline all the way from the west to the Gulf of Vyborg in the east. The deepest parts of the gulf can be found at the mouth of the gulf, where there is a deep with a depth of 80–100 metres (260–330 ft). There are even depths of over 100 meters (330 ft) at the southern coast, while the depth at the northern coast never exceeds 60 meters (200 ft). Much of the northern shoreline is quite shallow and rocky, making it difficult, even dangerous to navigate coastal waters there without accurate charts. The deepest point, 121 m (397 ft), is at the Estonian coast, just northeast of Tallinn. About 5% of the water mass in the Baltic Sea is located in the Gulf of Finland.
The ocean currents tend to move clockwise on the northern hemisphere (due to the Coriolis effect), and therefore the currents are moving eastwards in near the Finnish coast, and westwards near the Estonian coast. The already low salinity of the gulf's waters is even lower in the eastern end, since the large river Neva has its outlet there.
Environmental problems
The severe eutrophication of the Gulf of Finland is the biggest problem for the sea – algal blooms, which occur during summers, can cover large areas.
Cities and Towns
Major Islands

- Bolshoy Tyuters (Tytärsaari)
- Hogland (Suursaari)
- Kotlin Island
- Lavansari (Lavansaari)
- Naissaar
- Grachevo (Seiskari)
- Pakri Islands

