Wikipedia:List of academic studies about Wikipedia: Difference between revisions
Typewriter (talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 1,567: | Line 1,567: | ||
|-- |
|-- |
||
| Joachim Schroer || Wikipedia: Auslösende und aufrechterhaltende Faktoren der freiwilligen Mitarbeit an einem Web-2.0-Project || PhD thesis || University of Würzburg || 2008 || German || |
| Joachim Schroer || Wikipedia: Auslösende und aufrechterhaltende Faktoren der freiwilligen Mitarbeit an einem Web-2.0-Project || PhD thesis || University of Würzburg || 2008 || German || |
||
|-- |
|||
| Mark W. Bell || [http://www.worldcat.org/oclc/127414808 The transformation of the encyclopedia : a textual analysis and comparison of the Encyclopædia Britannica and Wikipedia] || Master's thesis || Ball State University || 2007 || || |
|||
|-- |
|-- |
||
Revision as of 21:43, 24 July 2009
| Wikipedia in the media |
|---|
| Wikipedia as a topic |
| Wikipedia as a source |
Below is an incomplete list of academic conference presentations, peer-reviewed papers and other types of academic writing which focus on Wikipedia as their subject. Works that mention Wikipedia only in passing are unlikely to be listed.
Unpublished works of presumably academic quality are listed in a dedicated section. For non-academic research, as well as tools that may be useful in researching Wikipedia, see Wikipedia:Researching Wikipedia. For a WikiProject focussed on doing research on Wikipedia, see Wikipedia:WikiProject Wikidemia.
For academic papers using Wikipedia as a source, see Wikipedia:Wikipedia as an academic source, and the bibliography links listed at the bottom of this page. For teaching with Wikipedia, see Wikipedia:School and university projects. For researching with Wikipedia, see Wikipedia:Researching with Wikipedia. For non-academic works focused on Wikipedia, see Wikipedia:Wikipedia in the media.
Over time
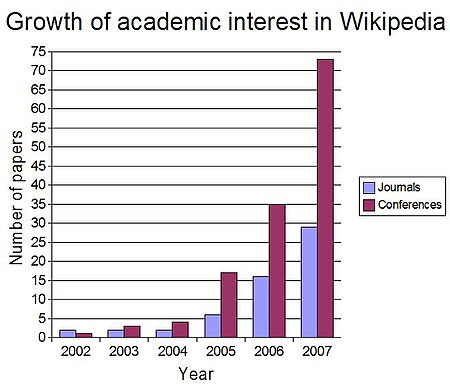
Conference presentations and papers
- See also: Wikimania conference series
- This table is sortable.
| Authors | Title | Conference / published in | Year | Online | Notes | Abstract | Keywords
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Andrew Krizhanovsky and Feiyu Lin | Related terms search based on WordNet / Wiktionary and its application in Ontology Matching | RCDL | 2009 | [1] | Wikokit |
A set of ontology matching algorithms (for finding correspondences between concepts) is based on a thesaurus that provides the source data for the semantic distance calculations. In this wiki era, new resources may spring up and improve this kind of semantic search. In the paper a solution of this task based on Russian Wiktionary is compared to WordNet based algorithms. Metrics are estimated using the test collection, containing 353 English word pairs with a relatedness score assigned by human evaluators. The experiment shows that the proposed method is capable in principle of calculating a semantic distance between pair of words in any language presented in Russian Wiktionary. The calculation of Wiktionary based metric had required the development of the open-source Wiktionary parser software. |
Wiktionary, semantic relatedness, information retrieval |
| Brent Hecht and Darren Gergle | Measuring Self-Focus Bias in Community-Maintained Knowledge Repositories | Communities and Technologies | 2009 | [2] | Uses a "hyperlingual approach" to demonstrate that each language of Wikipedia contains a massive amount of self-focus in its represented world knowledge. |
Self-focus is a novel way of understanding a type of bias in community-maintained Web 2.0 graph structures. It goes beyond previous measures of topical coverage bias by encapsulating both node- and edge-hosted biases in a single holistic measure of an entire community-maintained graph. We outline two methods to quantify self-focus, one of which is very computationally inexpensive, and present empirical evidence for the existence of self-focus using a “hyperlingual” approach that examines 15 different language editions of Wikipedia. We suggest applications of our methods and discuss the risks of ignoring self-focus bias in technological applications. |
hyperlingual, multi-lingual, self-focus |
| Michael D. Lieberman and Jimmy Lin | You Are Where You Edit: Locating Wikipedia Users Through Edit Histories | 3rd International Conference on Weblogs and Social Media (ICWSM) | 2009 | [3] |
Whether knowingly or otherwise, Wikipedia contributors reveal their interests and expertise through their contribution patterns. An analysis of Wikipedia edit histories shows that it is often possible to associate contributors with relatively small geographic regions, usually corresponding to where they were born or where they presently live. For many contributors, the geographic coordinates of pages they have edited are tightly clustered. Results suggest that a wealth of information about contributors can be gleaned from edit histories. This illustrates the efficacy of data mining on large, publicly-available datasets and raises potential privacy concerns. |
||
| Panciera, K.; Halfaker, A.; Terveen, L. | Wikipedians are born, not made: a study of power editors on Wikipedia | ACM 2009 International Conference on Group Work | 2009 | [4] | show that the amount of work done by Wikipedians and non-Wikipedians differs significantly from their very first day. |
we show that the amount of work done by Wikipedians and non-Wikipedians differs significantly from their very first day. Our results suggest a design opportunity: customizing the initial user experience to improve retention and channel new users’ intense energy. |
|
| Aniket Kittur, Ed H. Chi, Bongwon Suh | What’s in Wikipedia? Mapping Topics and Conflict Using Socially Annotated Category Structure | CHI 2009 | 2009 | [5] | blog summary, Signpost summary |
Wikipedia is an online encyclopedia which has undergone tremendous growth. However, this same growth has made it difficult to characterize its content and coverage. In this paper we develop measures to map Wikipedia using its socially annotated, hierarchical category structure. We introduce a mapping technique that takes advantage of socially-annotated hierarchical categories while dealing with the inconsistencies and noise inherent in the distributed way that they are generated. The technique is demonstrated through two applications: mapping the distribution of topics in Wikipedia and how they have changed over time; and mapping the degree of conflict found in each topic area. We also discuss the utility of the approach for other applications and datasets involving collaboratively annotated category hierarchies. |
Wikipedia, wiki, visualization, mapping, annotation, social computing, distributed collaboration, conflict. |
| Medelyan, O. and Milne, D. | Augmenting domain-specific thesauri with knowledge from Wikipedia | Proceedings of the NZ Computer Science Research Student Conference (NZCSRSC 2008), Christchurch, New Zealand. | 2008 | [6] | |||
| Medelyan, O. and Legg, C | Integrating Cyc and Wikipedia: Folksonomy meets rigorously defined common-sense | PProceedings of the first AAAI Workshop on Wikipedia and Artificial Intelligence (WIKIAI'08), Chicago, I.L. | 2008 | [7] | |||
| Medelyan, O, Witten, I.H., and Milne, D | Topic Indexing with Wikipedia. | PProceedings of the first AAAI Workshop on Wikipedia and Artificial Intelligence (WIKIAI'08), Chicago, I.L. | 2008 | [8] | |||
| Milne, David and Witten, Ian .H. | Learning to link with Wikipedia. | Proceedings of the first AAAI Workshop on Wikipedia and Artificial Intelligence (WIKIAI'08), Chicago, I.L. | 2008 | [9] | |||
| Milne, David and Witten, Ian .H. | An effective, low-cost measure of semantic relatedness obtained from Wikipedia links. | Proceedings of the first AAAI Workshop on Wikipedia and Artificial Intelligence (WIKIAI'08), Chicago, I.L. | 2008 | [10] |
This paper describes a new technique for obtaining measures of semantic relatedness. Like other recent approaches, it uses Wikipedia to provide structured world knowledge about the terms of interest. Our approach is unique in that it does so using the hyperlink structure of Wikipedia rather than its category hierarchy or textual content. Evaluation with manually defined measures of semantic relatedness reveals this to be an effective compromise between the ease of computation of the former approach and the accuracy of the latter. |
||
| Anuradha Jambunathan and Marco Ronchetti | Exploiting the collective intelligence contained in Wikipedia to automatically describe the content of a document | Proceedings of the Workshop on Collective Intelligence at the Third Asian Semantic Web Conference, in The Semantic Web: a view on data integration, reasoning, human factors, collective intelligence and technology adoption | 2008 | [11] |
The Wikipedia phenomenon is very interesting from the point of view of the collective, social effort to produce a large, strongly interlinked body of knowledge. It also offers, for the first time in history, a general source of information coded in electronic form and freely available to anyone. As such, it can be used as a reference for tools aiming at mining semantic meaning from generic documents. In this paper, we propose a clustering-based method that exploits some of the implicit knowledge built into Wikipedia to refine and ameliorate existing approaches. |
Semantic Relatedness, Semantic Analysis | |
| Bongwon Suh, Ed H. Chi, Aniket Kittur, Bryan A. Pendleton | Lifting the veil: improving accountability and social transparency in Wikipedia with wikidashboard | Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Proceeding of the twenty-sixth annual SIGCHI conference on Human factors in computing systems | 2008 | [12] |
Wikis are collaborative systems in which virtually anyone can edit anything. Although wikis have become highly popular in many domains, their mutable nature often leads them to be distrusted as a reliable source of information. Here we describe a social dynamic analysis tool called WikiDashboard which aims to improve social transparency and accountability on Wikipedia articles. Early reactions from users suggest that the increased transparency afforded by the tool can improve the interpretation, communication, and trustworthiness of Wikipedia articles. |
accountability, collaboration, social transparency, trust, visualization, wiki, wikidashboard, wikipedia | |
| Marcin Miłkowski | Automated Building of Error Corpora of Polish | Corpus Linguistics, Computer Tools, and Applications – State of the Art. PALC 2007, Peter Lang. Internationaler Verlag der Wissenschaften 2008, 631-639 | 2008 | [13] | The paper shows how to automatically develop error corpora out of revision history of documents. The idea is based on a hypothesis that minor edits in documents represent correction of typos, slips of the tongue, grammar, usage and style mistakes. This hypothesis has been confirmed by frequency analysis of revision history of articles in the Polish Wikipedia. Resources such as revision history in Wikipedia, Wikia, and other collaborative editing systems, can be turned into corpora of errors, just by extracting the minor edits. The most theoretically interesting aspect is that the corrections will represent the average speaker's intuitions about usage, and this seems to be a promising way of researching normativity in claims about proper or improper Polish. By processing the revision history, one can gain pairs of segments in the corpus: first representing the error, and the other representing the correction. Moreover, it is relatively easy to tag parts of speech, compare subsequent versions, and prepare a text file containing the resulting corpus. |
error corpora, normativity, revision history, corpora building | |
| Christopher Thomas, Pankaj Mehra, Roger Brooks, Amit Sheth | Growing Fields of Interest - Using an Expand and Reduce Strategy for Domain Model Extraction | IEEE/WIC International Conference on Web Intelligence, Sydney, Australia | 2008 | [14] |
Domain hierarchies are widely used as models underlying information retrieval tasks. Formal ontologies and taxonomies enrich such hierarchies further with properties and relationships associated with concepts and categories but require manual effort; therefore they are costly to maintain, and often stale. Folksonomies and vocabularies lack rich category structure and are almost entirely devoid of properties and relationships. Classification and extraction require the coverage of vocabularies and the alterability of folksonomies and can largely benefit from category relationships and other properties. With Doozer, a program for building conceptual models of information domains, we want to bridge the gap between the vocabularies and Folksonomies on the one side and the rich, expert-designed ontologies and taxonomies on the other. Doozer mines Wikipedia to produce tight domain hierarchies, starting with simple domain descriptions. It also adds relevancy scores for use in automated classification of information. The output model is described as a hierarchy of domain terms that can be used immediately for classifiers and IR systems or as a basis for manual or semi-automatic creation of formal ontologies. |
Wikipedia mining, Model creation
| |
| Benjamin K. Johnson | Incentives to Contribute in Online Collaboration: Wikipedia as Collective Action | International Communication Association, 58th Annual Conference, Montreal, Quebec | 2008 | [15] | Wikipedia is an online encyclopedia created by volunteers, and is an example of how developments in software platforms and the low cost of sharing and coordinating on the Internet are leading to a new paradigm of creative collaboration on a massive scale. The research presented here addresses the questions of why individuals choose to give away their time and effort and how the challenges associated with collective action are addressed by Wikipedia’s technologies, organization, and community. Interviews with editors of the encyclopedia were used to identify what personal gains and other motivations compel contributors, what challenges to collaboration exist, and what technological and social structures aid their ability to create a freely available repository of human knowledge. The paper suggests that the free encyclopedia is at once both a traditional instance of collective action requiring coordination and strong incentives and an instance of networked public goods that result through boundary crossing made possibly through extremely low barriers to sharing. |
collective action, motivation, coordination, incentives | |
| Sérgio Nunes, Cristina Ribeiro, Gabriel David | WikiChanges - Exposing Wikipedia Revision Activity | Proceedings of the 2008 International Symposium on Wikis (WikiSym '08) | 2008Fga | [16] | (pdf) |
Wikis are popular tools commonly used to support distributed collaborative work. Wikis can be seen as virtual scrapbooks that anyone can edit without having any specific technical know-how. The Wikipedia is a flagship example of a real-word application of wikis. Due to the large scale of Wikipedia it's difficult to easily grasp much of the information that is stored in this wiki. We address one particular aspect of this issue by looking at the revision history of each article. Plotting the revision activity in a timeline we expose the complete article's history in a easily understandable format. We present WikiChanges, a web-based application designed to plot an article's revision timeline in real time. It also includes a web browser extension that incorporates activity sparklines in the real Wikipedia. Finally, we introduce a revisions summarization task that addresses the need to understand what occurred during a given set of revisions. |
visualization, revision history |
| Travis Kriplean, Ivan Beschastnikh, David W. McDonald | Articulations of wikiwork: uncovering valued work in wikipedia through barnstars | Proceedings of the ACM 2008 conference on Computer supported cooperative work (CSCW '08) | 2008 | [17] | CSCW 2008 Best paper honorable mention (pdf) |
Successful online communities have complex cooperative arrangements, articulations of work, and integration practices. They require technical infrastructure to support a broad division of labor. Yet the research literature lacks empirical studies that detail which types of work are valued by participants in an online community. A content analysis of Wikipedia barnstars -- personalized tokens of appreciation given to participants -- reveals a wide range of valued work extending far beyond simple editing to include social support, administrative actions, and types of articulation work. Our analysis develops a theoretical lens for understanding how wiki software supports the creation of articulations of work. We give implications of our results for communities engaged in large-scale collaborations. |
articulation work, barnstars, commons-based peer production, online community
|
| Moira Burke, Robert Kraut | Mopping up: modeling wikipedia promotion decisions | Proceedings of the ACM 2008 conference on Computer supported cooperative work (CSCW '08) | 2008 | [18] |
This paper presents a model of the behavior of candidates for promotion to administrator status in Wikipedia. It uses a policy capture framework to highlight similarities and differences in the community's stated criteria for promotion decisions to those criteria actually correlated with promotion success. As promotions are determined by the consensus of dozens of voters with conflicting opinions and unwritten expectations, the results highlight the degree to which consensus is truly reached. The model is fast and easily computable on the fly, and thus could be applied as a self-evaluation tool for editors considering becoming administrators, as a dashboard for voters to view a nominee's relevant statistics, or as a tool to automatically search for likely future administrators. Implications for distributed consensus-building in online communities are discussed. |
administrators, collaboration, management, organizational behavior, policy capture, promotion | |
| Aniket Kittur, Robert Kraut | Harnessing the wisdom of crowds in wikipedia: quality through coordination | Proceedings of the ACM 2008 conference on Computer supported cooperative work (CSCW '08) | 2008 | [19] | CSCW 2008 Best paper honorable mention |
Wikipedia's success is often attributed to the large numbers of contributors who improve the accuracy, completeness and clarity of articles while reducing bias. However, because of the coordination needed to write an article collaboratively, adding contributors is costly. We examined how the number of editors in Wikipedia and the coordination methods they use affect article quality. We distinguish between explicit coordination, in which editors plan the article through communication, and implicit coordination, in which a subset of editors structure the work by doing the majority of it. Adding more editors to an article improved article quality only when they used appropriate coordination techniques and was harmful when they did not. Implicit coordination through concentrating the work was more helpful when many editors contributed, but explicit coordination through communication was not. Both types of coordination improved quality more when an article was in a formative stage. These results demonstrate the critical importance of coordination in effectively harnessing the "wisdom of the crowd" in online production environments. |
collaboration, collective intelligence, coordination, distributed cognition, social computing |
| Aniket Kittur, Bongwon Suh, Ed Chi | Can you ever trust a wiki?: impacting perceived trustworthiness in wikipedia | Proceedings of the ACM 2008 conference on Computer supported cooperative work (CSCW '08) | 2008 | [20] | CSCW 2008 Best short paper award |
Wikipedia has become one of the most important information resources on the Web by promoting peer collaboration and enabling virtually anyone to edit anything. However, this mutability also leads many to distrust it as a reliable source of information. Although there have been many attempts at developing metrics to help users judge the trustworthiness of content, it is unknown how much impact such measures can have on a system that is perceived as inherently unstable. Here we examine whether a visualization that exposes hidden article information can impact readers' perceptions of trustworthiness in a wiki environment. Our results suggest that surfacing information relevant to the stability of the article and the patterns of editor behavior can have a significant impact on users' trust across a variety of page types. |
collaboration, social computing, stability, trust, visualization |
| Masahiro Ito, Kotaro Nakayama, Takahiro Hara, Shojiro Nishio | Association Thesaurus Construction Methods based on Link Co-occurrence Analysis for Wikipedia | Conference on Information and Knowledge Management (CIKM 2008) | 2008 | [21] | Wikipedia-Lab | Wikipedia, a huge scale Web based encyclopedia, attracts great attention as an invaluable corpus for knowledge extraction because it has various impressive characteristics such as a huge number of articles, live updates, a dense link structure, brief anchor texts and URL identification for concepts. We have already proved that we can use Wikipedia to construct a huge scale accurate association thesaurus. The association thesaurus we constructed covers almost 1.3 million concepts and its accuracy is proved in detailed experiments. However, we still need scalable methods to analyze the huge number of Web pages and hyperlinks among articles in the Web based encyclopedia. In this paper, we propose a scalable method for constructing an association thesaurus from Wikipedia based on link co-occurrences. Link co-occurrence analysis is more scalable than link structure analysis because it is a one-pass process. We also propose integration method of tfidf and link co-occurrence analysis. Experimental results show that both our proposed methods are more accurate and scalable than conventional methods. Furthermore, the integration of tfidf achieved higher accuracy than using only link co-occurrences. |
Wikipedia Mining, Association Thesaurus, Link Co-occurrence, Semantic Relatedness |
| Amitava Dutta, Rahul Roy and Priya Seetharaman | Wikipedia Usage Patterns: The Dynamics of Growth | International Conference on Information Systems (ICIS 2008) | 2008 | [22] |
Wikis have attracted attention as a powerful technological platform on which to harness the potential benefits of collective knowledge. Current literature identifies different behavioral factors that modulate the interaction between contributors and wikis. Some inhibit growth while others enhance it. However, while these individual factors have been identified in the literature, their collective effects have not yet been identified. In this paper, we use the system dynamics methodology, and a survey of Wikipedia users, to propose a holistic model of the interaction among different factors and their collective impact on Wikipedia growth. The model is simulated to examine its ability to replicate observed growth patterns of Wikipedia metrics. Results indicate that the model is a reasonable starting point for understanding observed Wiki growth patterns. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first attempt in the literature to synthesize a holistic model of the forces underlying Wiki growth. |
Wikipedia, behavioral factors, system dynamics, simulation, survey data | |
| Wan Muhammad Salehuddin Wan Hassan and Khairulmizam Samsudin | Delta-encoding for document revision control system of Wikipedia | Sixth IEEE Student Conference on Research and Development (SCOReD 2008) | 2008 | [23] |
A revision control system keep track of changes for multiple versions of the same unit of information. It is often used in engineering and software development to manage storing, retrieval, logging, identification and merging of source files and electronic documents. Changes to these documents are noted by incrementing an associated number or letter code and associated historically with the person making the change. Revision control system is an important component of collaborative software platform that allows several member of a development team to work concurrently on an electronic document. Wikipedia, a free content encyclopedia is an example of a successful application of collaborative technology. A poorly implemented document revision control system will affect the performance and cause difficulty in managing Wikipedia huge amount of electronic data. In this work, efficiency of the current revision control system of Wikipedia will be evaluated. Feasibility of delta-encoding to address the current limitation of Wikipedia document revision control system will be presented. |
revision control, document revision, delta-encoding | |
| Joel Nothman, James R. Curran and Tara Murphy | Transforming Wikipedia into Named Entity Training Data | Australian Language Technology Workshop | 2008 | [24] |
Statistical named entity recognisers require costly hand-labelled training data and, as a result, most existing corpora are small. We exploit Wikipedia to create a massive corpus of named entity annotated text. We transform Wikipedia’s links into named entity annotations by classifying the target articles into common entity types (e.g. person, organisation and location). Comparing to MUC, CONLL and BBN corpora, Wikipedia generally performs better than other cross-corpus train/test pairs. |
named-entities, training corpora | |
| Johannes Schoning, Brent Hecht, Martin Raubal, Antonio Kruger, Meri Marsh, and Michael Rohs | Improving Interaction with Virtual Globes through Spatial Thinking: Helping Users Ask "Why?" | Intelligent User Interfaces (IUI) | 2008 | [25] |
abstract |
virtual globes, spatial thinking, multi-touch interaction, wall-size interfaces, artificial intelligence, wikipedia, semantic relatedness | |
| Brent Hecht and Johannes Schoning | Mapping the Zeitgeist | Fifth International Conference on Geographic Information Science (GIScience) | 2008 | [26] |
abstract |
zeitgeist, semantic relatedness, spatialization, spatial wikipedia | |
| Brent Hecht and Martin Raubal | Geographically explore semantic relations in world knowledge | 11th AGILE International Conference on Geographic Information Science | 2008 | [27] |
Methods to determine the semantic relatedness (SR) value between two lexically expressed entities abound in the field of natural language processing (NLP). The goal of such efforts is to identify a single measure that summarizes the number and strength of the relationships between the two entities. In this paper, we present GeoSR, the first adaptation of SR methods to the context of geographic data exploration. By combining the first use of a knowledge repository structure that is replete with non-classical relations, a new means of explaining those relations to users, and the novel application of SR measures to a geographic reference system, GeoSR allows users to geographically navigate and investigate the world knowledge encoded in Wikipedia. There are numerous visualization and interaction paradigms possible with GeoSR; we present one implementation as a proof-of-concept and discuss others. Although, Wikipedia is used as the knowledge repository for our implementation, GeoSR will also work with any knowledge repository having a similar set of properties. |
semantic relatendess, network analysis, non-classical relations, geography, wikipedia | |
| Darren Hardy | Discovering behavioral patterns in collective authorship of place-based information | Internet Research 9.0: Rethinking Community, Rethinking Place (to appear) | 2008 | [28] | While current GIS research has focused on technological issues of visualization and data organization, the emergence of new forms of collective authorship suggest we need new information frameworks and behaviors. How do individuals contribute place-based information to a digital commons? What are the authorship dynamics of such collective effort? For my research, I will use spatial data mining methods to characterize authorship behavior on a corpus of 1 million geotagged articles across 20 languages from Wikipedia. |
geotagging, peer production, Wikipedia, bots | |
| Andrew Krizhanovsky | Index wiki database: design and experiments | FLINS'08, Corpus Linguistics'08, AIS/CAD'08 | 2008 | [29] | Synarcher |
With the fantastic growth of Internet usage, information search in documents of a special type called a "wiki page" that is written using a simple markup language, has become an important problem. This paper describes the software architectural model for indexing wiki texts in three languages (Russian, English, and German) and the interaction between the software components (GATE, Lemmatizer, and Synarcher). The inverted file index database was designed using visual tool DBDesigner. The rules for parsing Wikipedia texts are illustrated by examples. Two index databases of Russian Wikipedia (RW) and Simple English Wikipedia (SEW) are built and compared. The size of RW is by order of magnitude higher than SEW (number of words, lexemes), though the growth rate of number of pages in SEW was found to be 12% higher than in Russian, and the rate of acquisition of new words in SEW lexicon was 6% higher during a period of five months (from September 2007 to February 2008). The Zipf's law was tested with both Russian and Simple Wikipedias. The entire source code of the indexing software and the generated index databases are freely available under GPL. |
corpus linguistics, inverted index, Zipf's law, information retrieval |
| Torsten Zesch, Christof Muller and Iryna Gurevych | Extracting Lexical Semantic Knowledge from Wikipedia and Wiktionary | LREC'08 | 2008 | [30] |
Recently, collaboratively constructed resources such as Wikipedia and Wiktionary have been discovered as valuable lexical semantic knowledge bases with a high potential in diverse Natural Language Processing (NLP) tasks. Collaborative knowledge bases however significantly differ from traditional linguistic knowledge bases in various respects, and this constitutes both an asset and an impediment for research in NLP. This paper addresses one such major impediment, namely the lack of suitable programmatic access mechanisms to the knowledge stored in these large semantic knowledge bases. We present two application programming interfaces for Wikipedia and Wiktionary which are especially designed for mining the rich lexical semantic information dispersed in the knowledge bases, and provide efficient and structured access to the available knowledge. As we believe them to be of general interest to the NLP community, we have made them freely available for research purposes. |
||
| Michael Roth and Sabine Schulte im Walde | Corpus Co-Occurrence, Dictionary and Wikipedia Entries as Resources for Semantic Relatedness Information | LREC'08 | 2008 | [31] |
Distributional, corpus-based descriptions have frequently been applied to model aspects of word meaning. However, distributional models that use corpus data as their basis have one well-known disadvantage: even though the distributional features based on corpus co-occurrence were often successful in capturing meaning aspects of the words to be described, they generally fail to capture those meaning aspects that refer to world knowledge, because coherent texts tend not to provide redundant information that is presumably available knowledge. The question we ask in this paper is whether dictionary and encyclopaedic resources might complement the distributional information in corpus data, and provide world knowledge that is missing in corpora. As test case for meaning aspects, we rely on a collection of semantic associates to German verbs and nouns. Our results indicate that a combination of the knowledge resources should be helpful in work on distributional descriptions. |
||
| Laura Kassner, Vivi Nastase and Michael Strube | Acquiring a Taxonomy from the German Wikipedia | LREC'08 | 2008 | [32] |
This paper presents the process of acquiring a large, domain independent, taxonomy from the German Wikipedia. We build upon a previously implemented platform that extracts a semantic network and taxonomy from the English version of the Wikipedia. We describe two accomplishments of our work: the semantic network for the German language in which isa links are identified and annotated, and an expansion of the platform for easy adaptation for a new language. We identify the platform’s strengths and shortcomings, which stem from the scarcity of free processing resources for languages other than English. We show that the taxonomy induction process is highly reliable - evaluated against the German version of WordNet, GermaNet, the resource obtained shows an accuracy of 83.34%. |
||
| Jordi Atserias, Hugo Zaragoza, Massimiliano Ciaramita and Giuseppe Attardi | Semantically Annotated Snapshot of the English Wikipedia | LREC'08 | 2008 | [33] |
This paper describes SW1, the first version of a semantically annotated snapshot of the English Wikipedia. In recent years Wikipedia has become a valuable resource for both the Natural Language Processing (NLP) community and the Information Retrieval (IR) community. Although NLP technology for processing Wikipedia already exists, not all researchers and developers have the computational resources to process such a volume of information. Moreover, the use of different versions of Wikipedia processed differently might make it difficult to compare results. The aim of this work is to provide easy access to syntactic and semantic annotations for researchers of both NLP and IR communities by building a reference corpus to homogenize experiments and make results comparable. These resources, a semantically annotated corpus and a “entity containment” derived graph, are licensed under the GNU Free Documentation License and available from http://www.yr-bcn.es/semanticWikipedia |
||
| Adrian Iftene and Alexandra Balahur-Dobrescu | Named Entity Relation Mining using Wikipedia | LREC'08 | 2008 | [34] |
Discovering relations among Named Entities (NEs) from large corpora is both a challenging, as well as useful task in the domain of Natural Language Processing, with applications in Information Retrieval (IR), Summarization (SUM), Question Answering (QA) and Textual Entailment (TE). The work we present resulted from the attempt to solve practical issues we were confronted with while building systems for the tasks of Textual Entailment Recognition and Question Answering, respectively. The approach consists in applying grammar induced extraction patterns on a large corpus - Wikipedia - for the extraction of relations between a given Named Entity and other Named Entities. The results obtained are high in precision, determining a reliable and useful application of the built resource. |
||
| Gaoying Cui, Qin Lu, Wenjie Li and Yirong Chen | Corpus Exploitation from Wikipedia for Ontology Construction | LREC'08 | 2008 | [35] |
Ontology construction usually requires a domain-specific corpus for building corresponding concept hierarchy. The domain corpus must have a good coverage of domain knowledge. Wikipedia(Wiki), the world’s largest online encyclopaedic knowledge source, is open-content, collaboratively edited, and free of charge. It covers millions of articles and still keeps on expanding continuously. These characteristics make Wiki a good candidate as domain corpus resource in ontology construction. However, the selected article collection must have considerable quality and quantity. In this paper, a novel approach is proposed to identify articles in Wiki as domain-specific corpus by using available classification information in Wiki pages. The main idea is to generate a domain hierarchy from the hyperlinked pages of Wiki. Only articles strongly linked to this hierarchy are selected as the domain corpus. The proposed approach makes use of linked category information in Wiki pages to produce the hierarchy as a directed graph for obtaining a set of pages in the same connected branch. Ranking and filtering are then done on these pages based on the classification tree generated by the traversal algorithm. The experiment and evaluation results show that Wiki is a good resource for acquiring a relative high quality domain-specific corpus for ontology construction. |
||
| Alexander E. Richman, Patrick Schone | Mining Wiki Resources for Multilingual Named Entity Recognition | ACL-08: HLT, pp. 1?9 | 2008 | [36] | In this paper, we describe a system by which the multilingual characteristics of Wikipedia can be utilized to annotate a large corpus of text with Named Entity Recognition (NER) tags requiring minimal human intervention and no linguistic expertise. This process, though of value in languages for which resources exist, is particularly useful for less commonly taught languages. We show how the Wikipedia format can be used to identify possible named entities and discuss in detail the process by which we use the Category structure inherent to Wikipedia to determine the named entity type of a proposed entity. We further describe the methods by which English language data can be used to bootstrap the NER process in other languages. We demonstrate the system by using the generated corpus as training sets for a variant of BBN's Identifinder in French, Ukrainian, Spanish, Polish, Russian, and Portuguese, achieving overall F-scores as high as 84.7% on independent, human-annotated corpora, comparable to a system trained on up to 40,000 words of human-annotated newswire. |
||
| Michael Kaisser | The QuALiM Question Answering Demo: Supplementing Answers with Paragraphs drawn from Wikipedia | ACL-08: HLT Demo Session, pp. 32?35 | 2008 | [37] | This paper describes the online demo of the QuALiM Question Answering system. While the system actually gets answers from the web by querying major search engines, during presentation answers are supplemented with relevant passages from Wikipedia. We believe that this additional information improves a user’s search experience. |
||
| Elif Yamangil, Rani Nelken | Mining Wikipedia Revision Histories for Improving Sentence Compression | ACL-08: HLT, Short Papers, pp. 137?140 | 2008 | [38] | A well-recognized limitation of research on supervised sentence compression is the dearth of available training data. We propose a new and bountiful resource for such training data, which we obtain by mining the revision history of Wikipedia for sentence compressions and expansions. Using only a fraction of the available Wikipedia data, we have collected a training corpus of over 380,000 sentence pairs, two orders of magnitude larger than the standardly used Ziff-Davis corpus. Using this newfound data, we propose a novel lexicalized noisy channel model for sentence compression, achieving improved results in grammaticality and compression rate criteria with a slight decrease in importance. |
||
| Fadi Biadsy, Julia Hirschberg, Elena Filatova | An Unsupervised Approach to Biography Production using Wikipedia | ACL-08: HLT, pp. 807?815 | 2008 | [39] | We describe an unsupervised approach to multi-document sentence-extraction based summarization for the task of producing biographies. We utilize Wikipedia to automatically construct a corpus of biographical sentences and TDT4 to construct a corpus of non-biographical sentences. We build a biographical-sentence classifier from these corpora and an SVM regression model for sentence ordering from the Wikipedia corpus. We evaluate our work on the DUC2004 evaluation data and with human judges. Overall, our system significantly outperforms all systems that participated in DUC2004, according to the ROUGE-L metric, and is preferred by human subjects. |
||
| Kai Wang, Chien-Liang Lin, Chun-Der Chen, and Shu-Chen Yang | The adoption of Wikipedia: a community- and information quality-based view | 12th Pacific Asia Conference on Information Systems (PACIS) | 2008 | [40] |
. |
TAM, Wikipedia, Critical Mass, Community identification, Information quality | |
| Carlo A. Curino, Hyun J. Moon, Letizia Tanca, Carlo Zaniolo | Schema Evolution in Wikipedia: toward a Web Information System Benchmark | International Conference on Enterprise Information System (ICEIS), | 2008 | [41] | Panta Rhei Project | Evolving the database that is at the core of an Information System represents a difficult maintenance problem that has only been studied in the framework of traditional information systems. However, the problem is likely to be even more severe in web information systems, where open-source software is often developed through the contributions and collaboration of many groups and individuals. Therefore, in this paper, we present an in-depth analysis of the evolution history of the Wikipedia database and its schema; Wikipedia is the best-known example of a large family of web information systems built using the open-source software MediaWiki. Our study is based on: (i) a set of Schema Modification Operators that provide a simple conceptual representation for complex schema changes, and (ii) simple software tools to automate the analysis. This framework allowed us to dissect and analyze the 4.5 years of Wikipedia history, which was short in time, but intense in terms of growth and evolution. Beyond confirming the initial hunch about the severity of the problem, our analysis suggests the need for developing better methods and tools to support graceful schema evolution. Therefore, we briefly discuss documentation and automation support systems for database evolution, and suggest that the Wikipedia case study can provide the kernel of a benchmark for testing and improving such systems. |
Schema Evolution, Benchmark, Schema Versioning, Query Rewriting
|
| Carlo A. Curino, Hyun J. Moon, Carlo Zaniolo | Graceful Database Schema Evolution: the PRISM Workbench | Very Large DataBases (VLDB), | 2008 | [] | Panta Rhei Project | Supporting graceful schema evolution represents an unsolved problem for traditional information systems that is further exacerbated in web information systems, such as Wikipedia and public scienti?c databases: in these pro jects based on multiparty cooperation the frequency of database schema changes has increased while tolerance for downtimes has nearly disappeared. As of today, schema evolution remains an error-prone and time-consuming undertaking, because the DB Administrator (DBA) lacks the methods and tools needed to manage and automate this endeavor by (i) pre- dicting and evaluating the e??ects of the proposed schema changes, (ii) rewriting queries and applications to operate on the new schema, and (iii) migrating the database. Our PRISM system takes a big ?rst step toward ad- dressing this pressing need by providing: (i) a language of Schema Modi?cation Operators to express concisely com- plex schema changes, (ii) tools that allow the DBA to eval- uate the e??ects of such changes, (iii) optimized translation of old queries to work on the new schema version, (iv) au- tomatic data migration, and (v) full documentation of in- tervened changes as needed to support data provenance, database ?ash back, and historical queries. PRISM solves these problems by integrating recent theoretical advances on mapping composition and invertibility, into a design that also achieves usability and scalability. Wikipedia and its 170+ schema versions provided an invaluable testbed for val- idating tools and their ability to support legacy queries. |
Schema Evolution, Graceful Evolution, Schema Versioning, Query Rewriting |
| Hyun J. Moon, Carlo A. Curino, Alin Deutsch, Chien-Yi Hou, Carlo Zaniolo | Managing and Querying Transaction-time Databases under Schema Evolution | Very Large DataBases (VLDB), | 2008 | [] | Panta Rhei Project | The old problem of managing the history of database in- formation is now made more urgent and complex by fast- spreading web information systems. Indeed, systems such as Wikipedia are faced with the challenge of managing the history of their databases in the face of intense database schema evolution. Our PRIMA system addresses this dif- ?cult problem by introducing two key pieces of new tech- nology. The ?rst is a method for publishing the history of a relational database in XML, whereby the evolution of the schema and its underlying database are given a uni- ?ed representation. This temporally grouped representation makes it easy to formulate sophisticated historical queries on any given schema version using standard XQuery. The second key piece of technology provided by PRIMA is that schema evolution is transparent to the user: she writes queries against the current schema while retrieving the data from one or more schema versions. The system then per- forms the labor-intensive and error-prone task of rewriting such queries into equivalent ones for the appropriate ver- sions of the schema. This feature is particularly relevant for historical queries spanning over potentially hundreds of di??erent schema versions. The latter one is realized by (i) introducing Schema Modi?cation Operators (SMOs) to represent the mappings between successive schema versions and (ii) an XML integrity constraint language (XIC) to efficiently rewrite the queries using the constraints established by the SMOs. The scalability of the approach has been tested against both synthetic data and real-world data from the Wikipedia DB schema evolution history. |
Schema Evolution, Transaction Time DB, Query Rewriting |
| Fogarolli Angela and Ronchetti Marco | Intelligent Mining and Indexing of Multi-Language e-Learning Material | Proc. of 1st International Symposium on Intelligent Interactive Multimedia Systems and Services, KES IIMS 2008, 9-11 July 2008 Piraeus, Greece Studies in Computational Intelligence, Springer-Verlag (2008). Note: to appear. | 2008 |
In this paper we describe a method to automatically discover important concepts and their relationships in e-Lecture material. The discovered knowledge is used to display semantic aware categorizations and query suggestions for facilitating navigation inside an unstructured multimedia repository of e-Lectures. We report about an implemented approach for dealing with learning materials referring to the same event in different languages. The information acquired from the speech is combined with the documents such as presentation slides which are temporally synchronized with the video for creating new knowledge through a mapping with a taxonomy representation such as Wikipedia. |
Content Retrieval, Content Filtering, Search over semi-structural Web sources, Multimedia, e-Learning
| ||
| Fogarolli Angela and Ronchetti Marco | Towards Bridging the Semantic-annotation-retrieval Gap in e-Learning | Proc. of International Conference on e-Society, 9-12 April 2008 Algarve, Portugal. IADIS | 2008 |
Semantic-based information retrieval is an area of ongoing work. In this paper we present a solution for giving semantic support to multimedia content information retrieval in an e-Learning environment where very often a large number of multimedia objects and information sources are used in combination. Semantic support is given through intelligent use of Wikipedia in combination with statistical Information Extraction techniques. |
Content Retrieval, Content Filtering, Search over semi-structural Web sources, Multimedia, e-Learning | ||
| Tyers, F. and Pienaar, J. | Extracting bilingual word pairs from Wikipedia | SALTMIL workshop at Language Resources and Evaluation Conference (LREC) 2008, (To appear) | 2008 | A bilingual dictionary or word list is an important resource for many purposes, among them, machine translation. For many language pairs these are either non-existent, or very often unavailable owing to licensing restrictions. We describe a simple, fast and computa- tionally inexpensive method for extracting bilingual dictionary entries from Wikipedia (using the interwiki link system) and assess the performance of this method with respect to four language pairs. Precision was found to be in the 69?92% region, but open to improvement. |
Under-resourced languages, Machine translation, Language resources, Bilingual terminology, Interwiki links | ||
| Fei Wu, Daniel S. Weld | Automatically Refining the Wikipedia Infobox Ontology | 17th International World Wide Web Conference (www-08) | 2008 | [42] | WWW '08: Best student paper honorable mention, The Intelligence in Wikipedia Project at University of Washington Google tech talk |
The combined efforts of human volunteers have recently extracted numerous facts fromWikipedia, storing them asmachine-harvestable object-attribute-value triples inWikipedia infoboxes. Machine learning systems, such as Kylin, use these infoboxes as training data, accurately extracting even more semantic knowledge from natural language text. But in order to realize the full power of this information, it must be situated in a cleanly-structured ontology. This paper introduces KOG, an autonomous system for refining Wikipedia’s infobox-class ontology towards this end. We cast the problem of ontology refinement as a machine learning problem and solve it using both SVMs and a more powerful joint-inference approach expressed in Markov Logic Networks. We present experiments demonstrating the superiority of the joint-inference approach and evaluating other aspects of our system. Using these techniques, we build a rich ontology, integratingWikipedia’s infobox-class schemata with WordNet. We demonstrate how the resulting ontology may be used to enhance Wikipedia with improved query processing and other features. |
Semantic Web, Ontology, Wikipedia, Markov Logic Networks |
| Maike Erdmann, Kotaro Nakayama, Takahiro Hara, Sojiro Nishio | An Approach for Extracting Bilingual Terminology from Wikipedia | 13th International Conference on Database Systems for Advanced Applications (DASFAA, To appear) | 2008 | [43] | Wikipedia-Lab work |
With the demand of bilingual dictionaries covering domain-specific terminology, research in the field of automatic dictionary extraction has become popular. However, accuracy and coverage of dictionaries created based on bilingual text corpora are often not sufficient for domain-specific terms. Therefore, we present an approach to extracting bilingual dictionaries from the link structure of Wikipedia, a huge scale encyclopedia that contains a vast amount of links between articles in different languages. Our methods analyze not only these interlanguage links but extract even more translation candidates from redirect page and link text information. In an experiment, we proved the advantages of our methods compared to a traditional approach of extracting bilingual terminology from parallel corpora. |
Wikipedia Mining, Bilingual Terminology, Link Structure Analysis |
| Kotaro Nakayama, Takahiro Hara, Sojiro Nishio | A Search Engine for Browsing the Wikipedia Thesaurus | 13th International Conference on Database Systems for Advanced Applications, Demo session (DASFAA, To appear) | 2008 | [44] | Wikipedia-Lab work |
Wikipedia has become a huge phenomenon on the WWW. As a corpus for knowledge extraction, it has various impressive characteristics such as a huge amount of articles, live updates, a dense link structure, brief link texts and URL identification for concepts. In our previous work, we proposed link structure mining algorithms to extract a huge scale and accurate association thesaurus from Wikipedia. The association thesaurus covers almost 1.3 million concepts and the significant accuracy is proved in detailed experiments. To prove its practicality, we implemented three features on the association thesaurus; a search engine for browsing Wikipedia Thesaurus, an XML Web service for the thesaurus and a Semantic Web support feature. We show these features in this demonstration. |
Wikipedia Mining, Association Thesaurus, Link Structure Analysis, XML Web Services |
| Kotaro Nakayama, Masahiro Ito, Takahiro Hara, Sojiro Nishio | Wikipedia Mining for Huge Scale Japanese Association Thesaurus Construction | International Symposium on Mining And Web (IEEE MAW) conjunction with IEEE AINA | 2008 | [45] | Wikipedia-Lab work |
. |
Wikipedia Mining, Association Thesaurus, Link Structure Analysis
|
| Minghua Pei, Kotaro Nakayama, Takahiro Hara, Sojiro Nishio | Constructing a Global Ontology by Concept Mapping using Wikipedia Thesaurus | International Symposium on Mining And Web (IEEE MAW) conjunction with IEEE AINA | 2008 | [46] | Wikipedia-Lab work |
. |
Wikipedia Mining, Association Thesaurus, Ontology Mapping, Global Ontology |
| Joachim Schroer, Guido Hertel | Voluntary engagement in an open web-based encyclopedia: From reading to contributing | 10th International General Online Research Conference, Hamburg, Germany | 2008 | [47] |
{{{2}}} |
wikipedia, contributors, motivation, instrumentality, intrinsic motivation | |
| Martin Potthast, Benno Stein, Maik Anderka | A Wikipedia-Based Multilingual Retrieval Model | 30th European Conference on IR Research, ECIR 2008, Glasgow | 2008 | [48] | This paper introduces CL-ESA, a new multilingual retrieval model for the analysis of cross-language similarity. The retrieval model exploits the multilingual alignment of Wikipedia: given a document d written in language L we construct a concept vector d for d, where each dimension i in d quantifies the similarity of d with respect to a document d*i chosen from the "L-subset" of Wikipedia. Likewise, for a second document d‘ written in language L‘, L≠L‘, we construct a concept vector d‘, using from the L‘-subset of the Wikipedia the topic-aligned counterparts d‘*i of our previously chosen documents. Since the two concept vectors d and d‘ are collection-relative representations of d and d‘ they are language-independent. I.e., their similarity can directly be computed with the cosine similarity measure, for instance. We present results of an extensive analysis that demonstrates the power of this new retrieval model: for a query document d the topically most similar documents from a corpus in another language are properly ranked. Salient property of the new retrieval model is its robustness with respect to both the size and the quality of the index document collection. |
multilingual retrieval model, explicit semantic analysis, wikipedia | |
| Martin Potthast, Benno Stein, Robert Gerling | Automatic Vandalism Detection in Wikipedia | 30th European Conference on IR Research, ECIR 2008, Glasgow | 2008 | [49] | ECIR 2008: Best poster award |
We present results of a new approach to detect destructive article revisions, so-called vandalism, in Wikipedia. Vandalism detection is a one-class classi?cation problem, where vandalism edits are the target to be identi?ed among all revisions. Interestingly, vandalism detection has not been addressed in the Information Retrieval literature by now. In this paper we discuss the characteristics of vandalism as humans recognize it and develop features to render vandalism detection as a machine learning task. We compiled a large number of vandalism edits in a corpus, which allows for the comparison of existing and new detection approaches. Using logistic regression we achieve 83% precision at 77% recall with our model. Compared to the rule-based methods that are urrently applied in Wikipedia, our approach increases the F-Measure performance by 49% while being faster at the same time. |
vandalism, machine learning, wikipedia |
| Ivan Beschastnikh, Travis Kriplean, David W. McDonald | Wikipedian Self-Governance in Action: Motivating the Policy Lens | Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Weblogs and Social Media, AAAI, March 31, 2008 (ICWSM '08) | 2008 | [50] | ICWSM '08: Best paper award |
While previous studies have used the Wikipedia dataset to provide an understanding of its growth, there have been few attempts to quantitatively analyze the establishment and evolution of the rich social practices that support this editing community. One such social practice is the enactment and creation of Wikipedian policies. We focus on the enactment of policies in discussions on the talk pages that accompany each article. These policy citations are a valuable micro-to-macro connection between everyday action, communal norms and the governance structure of Wikipedia. We find that policies are widely used by registered users and administrators, that their use is converging and stabilizing in and across these groups, and that their use illustrates the growing importance of certain classes of work, in particular source attribution. We also find that participation in Wikipedias governance structure is inclusionary in practice. |
policy use, governance, wikipedia |
| Andrea Forte, Amy Bruckman | Scaling Consensus: Increasing Decentralization in Wikipedia Governance | HICSS 2008, pp. 157-157. | 2008 | [51] |
How does "self-governance" happen in Wikipedia? Through in-depth interviews with eleven individuals who have held a variety of responsibilities in the English Wikipedia, we obtained rich descriptions of how various forces produce and regulate social structures on the site. Our analysis describes Wikipedia as an organization with highly refined policies, norms, and a technological architecture that supports organizational ideals of consensus building and discussion. We describe how governance in the site is becoming increasingly decentralized as the community grows and how this is predicted by theories of commons-based governance developed in offline contexts. The trend of decentralization is noticeable with respect to both content-related decision making processes and social structures that regulate user behavior. |
governance, wikipedia | |
| Zareen Syed, Tim Finin, and Anupam Joshi | Wikipedia as an Ontology for Describing Documents | Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Weblogs and Social Media, AAAI, March 31, 2008 | 2008 | [52] |
Identifying topics and concepts associated with a set of documents is a task common to many applications. It can help in the annotation and categorization of documents and be used to model a person's current interests for improving search results, business intelligence or selecting appropriate advertisements. One approach is to associate a document with a set of topics selected from a fixed ontology or vocabulary of terms. We have investigated using Wikipedia's articles and associated pages as a topic ontology for this purpose. The benefits are that the ontology terms are developed through a social process, maintained and kept current by the Wikipedia community, represent a consensus view, and have meaning that can be understood simply by reading the associated Wikipedia page. We use Wikipedia articles and the category and article link graphs to predict concepts common to a set of documents. We describe several algorithms to aggregate and refine results, including the use of spreading activation to select the most appropriate terms. While the Wikipedia category graph can be used to predict generalized concepts, the article links graph helps by predicting more specific concepts and concepts not in the category hierarchy. Our experiments demonstrate the feasibility of extending the category system with new concepts identified as a union of pages from the page link graph. |
ontology, wikipedia, information retrieval, text classification | |
| Felipe Ortega, Jesus M. Gonzalez-Barahona and Gregorio Robles | On the Inequality of Contributions to Wikipedia | HICSS 2008 | 2008 | [53] | Application of the Gini coefficient to measure the level of inequality of the contributions to the top ten language editions of Wikipedia. |
Wikipedia is one of the most successful examples of massive collaborative content development. However, many of the mechanisms and procedures that it uses are still unknown in detail. For instance, how equal (or unequal) are the contributions to it has been discussed in the last years, with no conclusive results. In this paper, we study exactly that aspect by using Lorenz curves and Gini coefficients, very well known instruments to economists. We analyze the trends in the inequality of distributions for the ten biggest language editions of Wikipedia, and their evolution over time. As a result, we have found large differences in the number of contributions by different authors (something also observed in free, open source software development), and a trend to stable patterns of inequality in the long run. |
wikipedia |
| Anne-Marie Vercoustre, James A. Thom and Jovan Pehcevski | Entity Ranking in Wikipedia | SAC’08 March 16-20, 2008, Fortaleza, Ceara, Brazil | 2008 | [54] | Application of the Gini coefficient to measure the level of inequality of the contributions to the top ten language editions of Wikipedia. |
The traditional entity extraction problem lies in the ability of extracting named entities from plain text using natural language processing techniques and intensive training from large document collections. Examples of named entities include organisations, people, locations, or dates. There are many research activities involving named entities; we are interested in entity ranking in the field of information retrieval. In this paper, we describe our approach to identifying and ranking entities from the INEX Wikipedia document collection. Wikipedia offers a number of interesting features for entity identification and ranking that we first introduce. We then describe the principles and the architecture of our entity ranking system, and introduce our methodology for evaluation. Our preliminary results show that the use of categories and the link structure of Wikipedia, together with entity examples, can significantly improve retrieval effectiveness. |
Entity Ranking, XML Retrieval, Test collection
|
| Brent Hecht, Michael Rohs, Johannes Schoning and Antonio Kruger | WikEye - Using Magic Lenses to Explore Georeferenced Wikipedia Content. | 3rd International Workshop on Pervasive Mobile Interaction Devices (PERMID) in Conjuncation with Pervasive Computing | 2007 | [55] |
abstract |
wikipedia data-mining, magic lens, augmented reality, markerless tracking
| |
| Marek Meyer, Christoph Rensing, Ralf Steinmetz | Categorizing Learning Objects Based On Wikipedia as Substitute Corpus | First International Workshop on Learning Object Discovery & Exchange (LODE'07), September 18, 2007, Crete, Greece | 2007 | [56] | Usage of Wikipedia as corpus for machine learning methods. |
As metadata is often not sufficiently provided by authors of Learning Resources, automatic metadata generation methods are used to create metadata afterwards. One kind of metadata is categorization, particularly the partition of Learning Resources into distinct subject cat- egories. A disadvantage of state-of-the-art categorization methods is that they require corpora of sample Learning Resources. Unfortunately, large corpora of well-labeled Learning Resources are rare. This paper presents a new approach for the task of subject categorization of Learning Re- sources. Instead of using typical Learning Resources, the free encyclope- dia Wikipedia is applied as training corpus. The approach presented in this paper is to apply the k-Nearest-Neighbors method for comparing a Learning Resource to Wikipedia articles. Different parameters have been evaluated regarding their impact on the categorization performance. |
Wikipedia, Categorization, Metadata, kNN, Classification, Substitute Corpus, Automatic Metadata Generation |
| Overell, Simon E., and Stefan Ruger | Geographic co-occurrence as a tool for GIR. | 4th ACM workshop on Geographical Information Retrieval. Lisbon, Portugal. | 2007 | [57] |
In this paper we describe the development of a geographic co-occurrence model and how it can be applied to geographic information retrieval. The model consists of mining co-occurrences of placenames from Wikipedia, and then mapping these placenames to locations in the Getty Thesaurus of Geographical Names. We begin by quantifying the accuracy of our model and compute theoretical bounds for the accuracy achievable when applied to placename disambiguation in free text. We conclude with a discussion of the improvement such a model could provide for placename disambiguation and geographic relevance ranking over traditional methods. |
Wikipedia, disambiguation, geographic information retrieval | |
| Torsten Zesch, Iryna Gurevych | Analysis of the Wikipedia Category Graph for NLP Applications. | Proceedings of the TextGraphs-2 Workshop (NAACL-HLT) | 2007 | [58] |
In this paper, we discuss two graphs in Wikipedia (i) the article graph, and (ii) the category graph. We perform a graphtheoretic analysis of the category graph, and show that it is a scale-free, small world graph like other well-known lexical semantic networks. We substantiate our findings by transferring semantic relatedness algorithms defined on WordNet to the Wikipedia category graph. To assess the usefulness of the category graph as an NLP resource, we analyze its coverage and the performance of the transferred semantic relatedness algorithms. |
nlp, relatedness, semantic, wikipedia | |
| Antonio Toral and Rafael Munozh | Towards a Named Entity Wordnet (NEWN) | Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Recent Advances in Natural Language Processing (RANLP). Borovets (Bulgaria). pp. 604-608 . September 2007 | 2007 | [59] | poster? | ||
| Ulrik Brandes and Jurgen Lerner | Visual Analysis of Controversy in User-generated Encyclopedias | Proc. IEEE Symp. Visual Analytics Science and Technology (VAST ' 07), to appear. | 2007 | [60] |
Wikipedia is a large and rapidly growing Web-based collaborative authoring environment, where anyone on the Internet can create, modify, and delete pages about encyclopedic topics. A remarkable property of some Wikipedia pages is that they are written by up to thousands of authors who may have contradicting opinions. In this paper we show that a visual analysis of the “who revises whom”- network gives deep insight into controversies. We propose a set of analysis and visualization techniques that reveal the dominant authors of a page, the roles they play, and the alters they confront. Thereby we provide tools to understand howWikipedia authors collaborate in the presence of controversy. |
social network controversy editing visualisation wikipedia | |
| V Jijkoun, M de Rijke | WiQA: Evaluating Multi-lingual Focused Access to Wikipedia | Proceedings EVIA, 2007 | 2007 | [61] |
We describe our experience with WiQA 2006, a pilot task aimed at studying question answering using Wikipedia. Going beyond traditional factoid questions, the task considered at WiQA 2006 was to identify?given an source article from Wikipedia?snippets from other Wikipedia articles, possibly in languages different from the language of the source article, that add new and important information to the source article, and that do so without repetition. A total of 7 teams took part, submitting 20 runs. Our main findings are two-fold: (i) while challenging, the tasks considered at WiQA are do-able as participants achieved precision@10 scores in the .5 range and MRR scores upwards of .5; (ii) on the bilingual task, substantially higher scores were achieved than on the monolingual tasks. |
||
| Martin Potthast | Wikipedia in the pocket: indexing technology for near-duplicate detection and high similarity search | SIGIR '07: Proceedings of the 30th annual international ACM SIGIR conference on Research and development in information retrieval | 2007 | [62] |
We develop and implement a new indexing technology which allows us to use complete (and possibly very large) documents as queries, while having a retrieval performance comparable to a standard term query. Our approach aims at retrieval tasks such as near duplicate detection and high similarity search. To demonstrate the performance of our technology we have compiled the search index "Wikipedia in the Pocket", which contains about 2 million English and German Wikipedia articles.1 This index--along with a search interface--fits on a conventional CD (0.7 gigabyte). The ingredients of our indexing technology are similarity hashing and minimal perfect hashing. |
wikipedia | |
| Minier, Zsolt Bodo, Zalan Csato, Lehel | Wikipedia-Based Kernels for Text Categorization | Symbolic and Numeric Algorithms for Scientific Computing, 2007. SYNASC. International Symposium on | 2007 | [63] |
In recent years several models have been proposed for text categorization. Within this, one of the widely applied models is the vector space model (VSM), where independence between indexing terms, usually words, is assumed. Since training corpora sizes are relatively small - compared to what would be required for a realistic number of words - the generalization power of the learning algorithms is low. It is assumed that a bigger text corpus can boost the representation and hence the learning process. Based on the work of Gabrilovich and Markovitch [6], we incorporate Wikipedia articles into the system to give word distributional representation for documents. The extension with this new corpus causes dimensionality increase, therefore clustering of features is needed. We use Latent Semantic Analysis (LSA), Kernel Principal Component Analysis (KPCA) and Kernel Canonical Correlation Analysis (KCCA) and present results for these experiments on the Reuters corpus. |
||
| Thomas, Christopher Sheth, Amit P. | Semantic Convergence of Wikipedia Articles | Web Intelligence, IEEE/WIC/ACM International Conference on | 2007 | [64] |
Social networking, distributed problem solving and human computation have gained high visibility. Wikipedia is a well established service that incorporates aspects of these three fields of research. For this reason it is a good object of study for determining quality of solutions in a social setting that is open, completely distributed, bottom up and not peer reviewed by certified experts. In particular, this paper aims at identifying semantic convergence of Wikipedia articles; the notion that the content of an article stays stable regardless of continuing edits. This could lead to an automatic recommendation of good article tags but also add to the usability of Wikipedia as a Web Service and to its reliability for information extraction. The methods used and the results obtained in this research can be generalized to other communities that iteratively produce textual content. |
||
| Rada Mihalcea | Using Wikipedia for Automatic Word Sense Disambiguation | Proceedings of NAACL HLT, 2007 | 2007 | [65] |
This paper describes a method for generating sense-tagged data using Wikipedia as a source of sense annotations. Through word sense disambiguation experiments, we show that the Wikipedia-based sense annotations are reliable and can be used to construct accurate sense classifiers. |
||
| J Yu, JA Thom, A Tam | Ontology evaluation using wikipedia categories for browsing | Proceedings of the sixteenth ACM conference on Conference on information and knowledge management | 2007 | [66] |
Ontology evaluation is a maturing discipline with methodologies and measures being developed and proposed. However, evaluation methods that have been proposed have not been applied to specific examples. In this paper, we present the state-of-the-art in ontology evaluation - current methodologies, criteria and measures, analyse appropriate evaluations that are important to our application - browsing in Wikipedia, and apply these evaluations in the context of ontologies with varied properties. Specifically, we seek to evaluate ontologies based on categories found in Wikipedia. |
browsing, ontology evaluation, user studies, wikipedia | |
| Reagle, Joseph M. | Do as I do: authorial leadership in wikipedia | WikiSym '07: Proceedings of the 2007 international symposium on Wikis | 2007 | [67] / [68] |
In seemingly egalitarian collaborative on-line communities, like Wikipedia, there is often a paradoxical, or perhaps merely playful, use of the title "Benevolent Dictator" for leaders. I explore discourse around the use of this title so as to address how leadership works in open content communities. I first review existing literature on "emergent leadership" and then relate excerpts from community discourse on how leadership is understood, performed, and discussed by Wikipedians. I conclude by integrating concepts from existing literature and my own findings into a theory of "authorial" leadership. |
Wikipedia, authorial, benevolent dictator, leadership | |
| Martin Wattenberg, Fernanda B. Viegas and Katherine Hollenbach | Visualizing Activity on Wikipedia with Chromograms | Human-Computer Interaction ? INTERACT 2007 | 2007 | [69] |
To investigate how participants in peer production systems allocate their time, we examine editing activity on Wikipedia, the well-known online encyclopedia. To analyze the huge edit histories of the site’s administrators we introduce a visualization technique, the chromogram, that can display very long textual sequences through a simple color coding scheme. Using chromograms we describe a set of characteristic editing patterns. In addition to confirming known patterns, such reacting to vandalism events, we identify a distinct class of organized systematic activities. We discuss how both reactive and systematic strategies shed light on self-allocation of effort in Wikipedia, and how they may pertain to other peer-production systems. |
Wikipedia - Visualization - Peer Production - Visualization | |
| A Kittur, E Chi, BA Pendleton, B Suh, T Mytkowicz | Power of the Few vs. Wisdom of the Crowd: Wikipedia and the Rise of the Bourgeoisie | 25th Annual ACM Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI 2007); 2007 April 28 - May 3; San Jose; CA. | 2007 | [70] |
Wikipedia has been a resounding success story as a collaborative system with a low cost of online participation. However, it is an open question whether the success of Wikipedia results from a “wisdom of crowds” type of effect in which a large number of people each make a small number of edits, or whether it is driven by a core group of “elite” users who do the lion’s share of the work. In this study we examined how the influence of “elite” vs. “common” users changed over time in Wikipedia. The results suggest that although Wikipedia was driven by the influence of “elite” users early on, more recently there has been a dramatic shift in workload to the “common” user. We also show the same shift in del.icio.us, a very different type of social collaborative knowledge system. We discuss how these results mirror the dynamics found in more traditional social collectives, and how they can influence the design of new collaborative knowledge systems. |
Wikipedia, Wiki, collaboration, collaborative knowledge systems, social tagging, delicious. | |
| Meiqun Hu, Ee-Peng Lim, Aixin Sun, Hady W Lauw, Ba-Quy Vuong | On improving wikipedia search using article quality | WIDM '07: Proceedings of the 9th annual ACM international workshop on Web information and data management | 2007 | [71] |
Wikipedia is presently the largest free-and-open online encyclopedia collaboratively edited and maintained by volunteers. While Wikipedia offers full-text search to its users, the accuracy of its relevance-based search can be compromised by poor quality articles edited by non-experts and inexperienced contributors. In this paper, we propose a framework that re-ranks Wikipedia search results considering article quality. We develop two quality measurement models, namely Basic and Peer Review, to derive article quality based on co-authoring data gathered from articles' edit history. Compared withWikipedia's full-text search engine, Google and Wikiseek, our experimental results showed that (i) quality-only ranking produced by Peer Review gives comparable performance to that of Wikipedia and Wikiseek; (ii) Peer Review combined with relevance ranking outperforms Wikipedia's full-text search significantly, delivering search accuracy comparable to Google. |
quality, wikipedia | |
| Wilkinson, Dennis M. and Huberman, Bernardo A. | Cooperation and quality in wikipedia | WikiSym '07: Proceedings of the 2007 international symposium on Wikis. | 2007 | [72] |
The rise of the Internet has enabled collaboration and cooperation on anunprecedentedly large scale. The online encyclopedia Wikipedia, which presently comprises 7.2 million articles created by 7.04 million distinct editors, provides a consummate example. We examined all 50 million edits made tothe 1.5 million English-language Wikipedia articles and found that the high-quality articles are distinguished by a marked increase in number of edits, number of editors, and intensity of cooperative behavior, as compared to other articles of similar visibility and age. This is significant because in other domains, fruitful cooperation has proven to be difficult to sustain as the size of the collaboration increases. Furthermore, in spite of the vagaries of human behavior, we show that Wikipedia articles accrete edits according to a simple stochastic mechanism in which edits beget edits. Topics of high interest or relevance are thus naturally brought to the forefront of quality. |
Wikipedia, collaborative authoring, cooperation, groupware | |
| DPT Nguyen, Y Matsuo, M Ishizuka | Subtree Mining for Relation Extraction from Wikipedia | Proc. of NAACL/HLT 2007 | 2007 | [73] |
In this study, we address the problem of extracting relations between entities fromWikipedia’s English articles. Our proposed method first anchors the appearance of entities in Wikipedia’s articles using neither Named Entity Recognizer (NER) nor coreference resolution tool. It then classifies the relationships between entity pairs using SVM with features extracted from the web structure and subtrees mined from the syntactic structure of text. We evaluate our method on manually annotated data from actual Wikipedia articles. |
||
| Bongwon Suh, Ed H Chi, Bryan A Pendleton, Aniket Kittur | Us vs. Them: Understanding Social Dynamics in Wikipedia with Revert Graph Visualizations | Visual Analytics Science and Technology, 2007. VAST 2007. IEEE Symposium on (2007), pp. 163-170. | 2007 | [74] |
Wikipedia is a wiki-based encyclopedia that has become one of the most popular collaborative on-line knowledge systems. As in any large collaborative system, as Wikipedia has grown, conflicts and coordination costs have increased dramatically. Visual analytic tools provide a mechanism for addressing these issues by enabling users to more quickly and effectively make sense of the status of a collaborative environment. In this paper we describe a model for identifying patterns of conflicts in Wikipedia articles. The model relies on users' editing history and the relationships between user edits, especially revisions that void previous edits, known as "reverts". Based on this model, we constructed Revert Graph, a tool that visualizes the overall conflict patterns between groups of users. It enables visual analysis of opinion groups and rapid interactive exploration of those relationships via detail drill-downs. We present user patterns and case studies that show the effectiveness of these techniques, and discuss how they could generalize to other systems. |
motivation, social-network, wikipedia | |
| Kittur, Aniket and Suh, Bongwon and Pendleton, Bryan A. and Chi, Ed H. | He says, she says: conflict and coordination in Wikipedia | CHI '07: Proceedings of the SIGCHI conference on Human factors in computing systems | 2007 | [75] |
Wikipedia, a wiki-based encyclopedia, has become one of the most successful experiments in collaborative knowledge building on the Internet. As Wikipedia continues to grow, the potential for conflict and the need for coordination increase as well. This article examines the growth of such non-direct work and describes the development of tools to characterize conflict and coordination costs in Wikipedia. The results may inform the design of new collaborative knowledge systems. |
Wiki, Wikipedia, collaboration, conflict, user model, visualization, web-based interaction | |
| Davide Buscaldi and Paolo Rosso | A Comparison of Methods for the Automatic Identification of Locations in Wikipedia | Proceedings of GIR’07 | 2007 | [76] |
In this paper we compare two methods for the automatic identification of geographical articles in encyclopedic resources such asWikipedia. The methods are aWordNet-basedmethod that uses a set of keywords related to geographical places, and a multinomial Na¨?ve Bayes classificator, trained over a randomly selected subset of the English Wikipedia. This task may be included into the broader task of Named Entity classification, a well-known problem in the field of Natural Language Processing. The experiments were carried out considering both the full text of the articles and only the definition of the entity being described in the article. The obtained results show that the information contained in the page templates and the category labels is more useful than the text of the articles. |
Algorithms, Measurement, Performance, text analysis, language models | |
| Li, Yinghao and Wing and Kei and Fu | Improving weak ad-hoc queries using wikipedia asexternal corpus | SIGIR '07: Proceedings of the 30th annual international ACM SIGIR conference on Research and development in information retrieval | 2007 | [77] |
In an ad-hoc retrieval task, the query is usually short and the user expects to find the relevant documents in the first several result pages. We explored the possibilities of using Wikipedia's articles as an external corpus to expand ad-hoc queries. Results show promising improvements over measures that emphasize on weak queries. |
Wikipedia, external corpus, pseudo-relevance feedback | |
| Y Watanabe, M Asahara, Y Matsumoto | A Graph-based Approach to Named Entity Categorization in Wikipedia Using Conditional Random Fields | Proceedings of the 2007 Joint Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and Computational Natural Language Learning (EMNLP-CoNLL) | 2007 | [78] |
This paper presents a method for categorizing named entities in Wikipedia. In Wikipedia, an anchor text is glossed in a linked HTML text. We formalize named entity categorization as a task of categorizing anchor texts with linked HTML texts which glosses a named entity. Using this representation, we introduce a graph structure in which anchor texts are regarded as nodes. In order to incorporate HTML structure on the graph, three types of cliques are defined based on the HTML tree structure. We propose a method with Conditional Random Fields (CRFs) to categorize the nodes on the graph. Since the defined graph may include cycles, the exact inference of CRFs is computationally expensive. We introduce an approximate inference method using Treebased Reparameterization (TRP) to reduce computational cost. In experiments, our proposed model obtained significant improvements compare to baseline models that use Support Vector Machines. |
||
| Simone Braun and Andreas Schmidt | Wikis as a Technology Fostering Knowledge Maturing: What we can learn from Wikipedia | 7th International Conference on Knowledge Management (IKNOW '07),Special Track on Integrating Working and Learning in Business (IWL), 2007. | 2007 | [79] |
The knowledge maturing theory opens an important macro perspective within the new paradigm of work-integrated learning. Especially wikis are interesting socio-technical systems to foster maturing activities by overcoming typical barriers. But so far, the theory has been mainly based on anecdotal evidence collected from various projects and observations. In this paper, we want to present the results of a qualitative and quantitative study of Wikipedia with respect to maturing phenomena, identifying instruments and measures indicating maturity. The findings, generalized to enterprise wikis, open the perspective on what promotes maturing on a method level and what can be used to spot maturing processes on a technology level. |
knowledge management wiki wikipedia | |
| Linyun Fu and Haofen Wang and Haiping Zhu and Huajie Zhang and Yang Wang and Yong Yu | Making More Wikipedians: Facilitating Semantics Reuse for Wikipedia Authoring | Proceedings of the 6th International Semantic Web Conference and 2nd Asian Semantic Web Conference (ISWC/ASWC2007), Busan, South Korea, 4825: 127--140, 2007. | 2007 | [80] |
Wikipedia, a killer application in Web 2.0, has embraced the power of collaborative editing to harness collective intelligence. It can also serve as an ideal Semantic Web data source due to its abundance, influence, high quality and well-structuring. However, the heavy burden of up-building and maintaining such an enormous and ever-growing online encyclopedic knowledge base still rests on a very small group of people. Many casual users may still feel difficulties in writing high quality Wikipedia articles. In this paper, we use RDF graphs to model the key elements in Wikipedia authoring, and propose an integrated solution to make Wikipedia authoring easier based on RDF graph matching, expecting making more Wikipedians. Our solution facilitates semantics reuse and provides users with: 1) a link suggestion module that suggests and auto-completes internal links between Wikipedia articles for the user; 2) a category suggestion module that helps the user place her articles in correct categories. A prototype system is implemented and experimental results show significant improvements over existing solutions to link and category suggestion tasks. The proposed enhancements can be applied to attract more contributors and relieve the burden of professional editors, thus enhancing the current Wikipedia to make it an even better Semantic Web data source. |
semanticWeb web2.0 wikipedia | |
| Soren Auer and Chris Bizer and Jens Lehmann and Georgi Kobilarov and Richard Cyganiak and Zachary Ives | DBpedia: A Nucleus for a Web of Open Data | Proceedings of the 6th International Semantic Web Conference and 2nd Asian Semantic Web Conference (ISWC/ASWC2007), Busan, South Korea, 4825: 715--728, 2007. | 2007 | [81] |
DBpedia is a community effort to extract structured information from Wikipedia and to make this information available on the Web. DBpedia allows you to ask sophisticated queries against datasets derived from Wikipedia and to link other datasets on the Web to Wikipedia data. We describe the extraction of the DBpedia datasets, and how the resulting information can be made available on the Web for humans and machines. We describe some emerging applications from the DBpedia community and show how website operators can reduce costs by facilitating royalty-free DBpedia content within their sites. Finally, we present the current status of interlinking DBpedia with other open datasets on the Web and outline how DBpedia could serve as a nucleus for an emerging Web of open data sources. |
information retrieval mashup semantic Web wikipedia | |
| Simone P. Ponzetto and Michael Strube | An API for Measuring the Relatedness of Words in Wikipedia | Companion Volume to the Proceedings of the 45th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, : 23--30, 2007. | 2007 | [82] |
We present an API for computing the semantic relatedness of words in Wikipedia. |
api, relatedness semantic\_web, sematic, wikipedia | |
| Ponzetto, Simone P. and Strube, Michael | Deriving a Large Scale Taxonomy from Wikipedia | Proceedings of the 22nd National Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, B.C., 22-26 July | 2007 | [83] |
We take the category system in Wikipedia as a conceptual network. We label the semantic relations between categories us- ing methods based on connectivity in the network and lexico- syntactic matching. As a result we are able to derive a large scale taxonomy containing a large amount of subsumption, i.e. isa, relations. We evaluate the quality of the created resource by comparing it with ResearchCyc, one of the largest manually annotated ontologies, as well as computing seman- tic similarity between words in benchmarking datasets. able to derive a large scale taxonomy. |
api, relatedness semantic web, sematic, wikipedia | |
| Simone Paolo Ponzetto | Creating a Knowledge Base from a Collaboratively Generated Encyclopedia | Proceedings of the NAACL-HLT 2007 Doctoral Consortium, pp 9-12, Rochester, NY, April 2007 | 2007 | [84] |
We present our work on using Wikipedia as a knowledge source for Natural Language Processing. We first describe our previous work on computing semantic relatedness from Wikipedia, and its application to a machine learning based coreference resolution system. Our results suggest that Wikipedia represents a semantic resource to be treasured for NLP applications, and accordingly present the work directions to be explored in the future. |
||
| Ralf Schenkel, Fabian Suchanek and Gjergji Kasneci | YAWN: A Semantically Annotated Wikipedia XML Corpus | BTW2007 | 2007 | [85] |
The paper presents YAWN, a system to convert the well-known and widely used Wikipedia collection into an XML corpus with semantically rich, self-explaining tags. We introduce algorithms to annotate pages and links with concepts from the WordNet thesaurus. This annotation process exploits categorical information in Wikipedia, which is a high-quality, manually assigned source of information, extracts additional information from lists, and utilizes the invocations of templates with named parameters. We give examples how such annotations can be exploited for high-precision queries. |
||
| Hugo Zaragoza, Henning Rode, Peter Mika, Jordi Atserias, Massimiliano Ciaramita & Giuseppe Attardi | Ranking Very Many Typed Entities on Wikipedia | CIKM ‘07: Proceedings of the Sixteenth ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management | 2007 | [86] |
We discuss the problem of ranking very many entities of different types. In particular we deal with a heterogeneous set of types, some being very generic and some very speci??c. We discuss two approaches for this problem: i) exploiting the entity containment graph and ii) using a Web search engine to compute entity relevance. We evaluate these approaches on the real task of ranking Wikipedia entities typed with a state-of-the-art named-entity tagger. Results show that both approaches can greatly increase the performance of methods based only on passage retrieval. |
||
| Soren Auer and Jens Lehmann | What Have Innsbruck and Leipzig in Common? Extracting Semantics from Wiki Content | Proceedings of 4th European Semantic Web Conference; published in The Semantic Web: Research and Applications, pages 503-517 | 2007 | [87] |
WWikis are established means for the collaborative authoring, versioning and publishing of textual articles. The Wikipedia project, for example, succeeded in creating the by far largest encyclopedia just on the basis of a wiki. Recently, several approaches have been proposed on how to extend wikis to allow the creation of structured and semantically enriched content. However, the means for creating semantically enriched structured content are already available and are, although unconsciously, even used by Wikipedia authors. In this article, we present a method for revealing this structured content by extracting information from template instances. We suggest ways to efficiently query the vast amount of extracted information (e.g. more than 8 million RDF statements for the English Wikipedia version alone), leading to astonishing query answering possibilities (such as for the title question). We analyze the quality of the extracted content, and propose strategies for quality improvements with just minor modifications of the wiki systems being currently used. |
||
| George Bragues | Wiki-Philosophizing in a Marketplace of Ideas: Evaluating Wikipedia's Entries on Seven Great Minds | Social Science Research Network Working Paper Series (April 2007) | 2007 | [88] |
A very conspicuous part of the new participatory media, Wikipedia has emerged as the Internet's leading source of all-purpose information, the volume and range of its articles far surpassing that of its traditional rival, the Encyclopedia Britannica. This has been accomplished by permitting virtually anyone to contribute, either by writing an original article or editing an existing one. With almost no entry barriers to the production of information, the result is that Wikipedia exhibits a perfectly competitive marketplace of ideas. It has often been argued that such a marketplace is the best guarantee that quality information will be generated and disseminated. We test this contention by examining Wikipedia's entries on seven top Western philosophers. These entries are evaluated against the consensus view elicited from four academic reference works in philosophy. Wikipedia's performance turns out to be decidedly mixed. Its average coverage rate of consensus topics is 52%, while the median rate is 56%. A qualitative analysis uncovered no outright errors, though there were significant omissions. The online encyclopedia's harnessing of the marketplace of ideas, though not unimpressive, fails to emerge as clearly superior to the traditional alternative of relying on individual expertise for information. |
quality, wikipedia | |
| Gang Wang and Yong Yu and Haiping Zhu | PORE: Positive-Only Relation Extraction from Wikipedia Text | Proceedings of the 6th International Semantic Web Conference and 2nd Asian Semantic Web Conference (ISWC/ASWC2007), Busan, South Korea | 2007 | [89] |
Extracting semantic relations is of great importance for the creation of the Semantic Web content. It is of great benefit to semi-automatically extract relations from the free text of Wikipedia using the structured content readily available in it. Pattern matching methods that employ information redundancy cannot work well since there is not much redundancy information in Wikipedia, compared to the Web. Multi-class classification methods are not reasonable since no classification of relation types is available in Wikipedia. In this paper, we propose PORE (Positive-Only Relation Extraction), for relation extraction from Wikipedia text. The core algorithm B-POL extends a state-of-the-art positive-only learning algorithm using bootstrapping, strong negative identification, and transductive inference to work with fewer positive training examples. We conducted experiments on several relations with different amount of training data. The experimental results show that B-POL can work effectively given only a small amount of positive training examples and it significantly outperforms the original positive learning approaches and a multi-class SVM. Furthermore, although PORE is applied in the context of Wikipedia, the core algorithm B-POL is a general approach for Ontology Population and can be adapted to other domains. |
annotation iswc, knowledge-extraction nlp semantic-web text-mining wikipedia | |
| Fei Wu, Daniel S. Weld | Autonomously semantifying wikipedia | Proceedings of the sixteenth ACM conference on Conference on information and knowledge management | 2007 | [90] | CIKM-07: Best paper award, The Intelligence in Wikipedia Project at University of Washington |
Berners-Lee's compelling vision of a Semantic Web is hindered by a chicken-and-egg problem, which can be best solved by a bootstrapping method - creating enough structured data to motivate the development of applications. This paper argues that autonomously "Semantifying Wikipedia" is the best way to solve the problem. We choose Wikipedia as an initial data source, because it is comprehensive, not too large, high-quality, and contains enough manually-derived structure to bootstrap an autonomous, self-supervised process. We identify several types of structures which can be automatically enhanced in Wikipedia (e.g., link structure, taxonomic data, infoboxes, etc.), and we describea prototype implementation of a self-supervised, machine learning system which realizes our vision. Preliminary experiments demonstrate the high precision of our system's extracted data - in one case equaling that of humans. |
Information Extraction, Wikipedia, Semantic Web |
| Viegas, Fernanda | The Visual Side of Wikipedia | System Sciences, 2007. HICSS 2007. 40th Annual Hawaii International Conference on | 2007 | [91] | HICSS '07: Best paper honorable mention |
Critical social theorists often emphasize the control and surveillance aspects of information systems, building upon a characterization of information technology as a tool for increased rationalization. The emancipatory potential of information systems is often overlooked. In this paper, we apply the Habermasian ideal of rational discourse to Wikipedia as an illustration of the emancipatory potential of information systems. We conclude that Wikipedia does embody an approximation of rational discourse, while several challenges remain |
|
| Sean Hansen, Nicholas Berente, Kalle Lyytinen | Wikipedia as Rational Discourse: An Illustration of the Emancipatory Potential of Information Systems | Proceedings of Hawaiian International Conference of Systems Sciences Big Island, Hawaii.) | 2007 | [92] | HICSS '07: Best paper award |
The name “Wikipedia” has been associated with terms such as collaboration, volunteers, reliability, vandalism, and edit-war. Fewer people might think of “images,” “maps,” “diagrams,” “illustrations” in this context. This paper presents the burgeoning but underexplored visual side of the online encyclopedia. A survey conducted with image contributors to Wikipedia reveals key differences in collaborating around images as opposed to text. The results suggest that, even though image editing is a more isolated activity, somewhat shielded from vandalism, the sense of community is an important motivation for image contributors. By examining how contributors are appropriating text-oriented wiki technology to support collective editing around visual materials, this paper reveals the potential and some of the limitations of wikis in the realm of visual collaboration. |
|
| Fissaha Adafre, Sisay, Jijkoun, Valentin, de Rijke, Maarten | Fact Discovery in Wikipedia | Web Intelligence, IEEE/WIC/ACM International Conference on | 2007 | [93] |
We address the task of extracting focused salient information items, relevant and important for a given topic, from a large encyclopedic resource. Specifically, for a given topic (a Wikipedia article) we identify snippets from other articles in Wikipedia that contain important information for the topic of the original article, without duplicates. We compare several methods for addressing the task, and find that a mixture of content-based, link-based, and layout-based features outperforms other methods, especially in combination with the use of so-called reference corpora that capture the key properties of entities of a common type. |
nlp, relatedness, semantic, wikipedia | |
| Li, Bing Chen, Qing-Cai Yeung, Daniel S. Ng, Wing W.Y. Wang, Xiao-Long | Exploring Wikipedia and Query Log's Ability for Text Feature Representation | Machine Learning and Cybernetics, 2007 International Conference on | 2007 | [94] |
The rapid increase of internet technology requires a better management of web page contents. Many text mining researches has been conducted, like text categorization, information retrieval, text clustering. When machine learning methods or statistical models are applied to such a large scale of data, the first step we have to solve is to represent a text document into the way that computers could handle. Traditionally, single words are always employed as features in Vector Space Model, which make up the feature space for all text documents. The single-word based representation is based on the word independence and doesn't consider their relations, which may cause information missing. This paper proposes Wiki-Query segmented features to text classification, in hopes of better using the text information. The experiment results show that a much better F1 value has been achieved than that of classical single-word based text representation. This means that Wikipedia and query segmented feature could better represent a text document. |
||
| Wei Che Huang, Andrew Trotman, and Shlomo Geva | Collaborative Knowledge Management: Evaluation of Automated Link Discovery in the Wikipedia | SIGIR 2007 Workshop on Focused Retrieval, July 27, 2007, Amsterdam | 2007 | [95] |
Using the Wikipedia as a corpus, the Link-the-Wiki track, launched by INEX in 2007, aims at producing a standard procedure and metrics for the evaluation of (automated) link discovery at different element levels. In this paper, we describe the preliminary procedure for the assessment, including the topic selection, submission, pooling and evaluation. Related techniques are also presented such as the proposed DTD, submission format, XML element retrieval and the concept of Best Entry Points (BEPs). Due to the task required by LTW, it represents a considerable evaluation challenge. We propose a preliminary procedure of assessment for this stage of the LTW and also discuss the further issues for improvement. Finally, an efficiency measurement is introduced for investigation since the LTW task involves two studies: the selection of document elements that represent the topic of request and the nomination of associated links that can access different levels of the XML document. |
Wikipedia, Link-the-Wiki, INEX, Evaluation, DTD, Best Entry Point | |
| Morten Rask | The Richness and Reach of Wikinomics: Is the Free Web-Based Encyclopedia Wikipedia Only for the Rich Countries? | Proceedings of the Joint Conference of The International Society of Marketing Development and the Macromarketing Society, June 2-5, 2007 | 2007 | [96] |
In this paper, a model of the patterns of correlation in Wikipedia, reach and richness, lays the foundation for studying whether or not the free web-based encyclopedia Wikipedia is only for developed countries. Wikipedia is used in this paper, as an illustrative case study for the enormous rise of the so-called Web 2.0 applications, a subject which has become associated with many golden promises: Instead of being at the outskirts of the global economy, the development of free or low-cost internet-based content and applications, makes it possible for poor, emerging, and transition countries to compete and collaborate on the same level as developed countries. Based upon data from 12 different Wikipedia language editions, we find that the central structural effect is on the level of human development in the current country. In other words, Wikipedia is in general, more for rich countries than for less developed countries. It is suggested that policy makers make investments in increasing the general level of literacy, education, and standard of living in their country. The main managerial implication for businesses, that will expand their social network applications to other countries, is to use the model of the patterns of correlation in Wikipedia, reach and richness, as a market screening and monitoring model. |
Digital divide, Developing countries, Internet, Web 2.0, Social networks, Reach and richness, Wikipedia, Wikinomics, culture, language | |
| Kotaro Nakayama, Takahiro Hara, Sojiro Nishio | A Thesaurus Construction Method from Large Scale Web Dictionaries | 21st IEEE International Conference on Advanced Information Networking and Applications (AINA) | 2007 | [97] |
Wikipedia-Lab work |
Web-based dictionaries, such as Wikipedia, have become dramatically popular among the internet users in past several years. The important characteristic of Web-based dictionary is not only the huge amount of articles, but also hyperlinks. Hyperlinks have various information more than just providing transfer function between pages. In this paper, we propose an efficient method to analyze the link structure of Web-based dictionaries to construct an association thesaurus. We have already applied it to Wikipedia, a huge scale Web-based dictionary which has a dense link structure, as a corpus. We developed a search engine for evaluation, then conducted a number of experiments to compare our method with other traditional methods such as co-occurrence analysis. |
Wikipedia Mining, Association Thesaurus, Link Structure Analysis, Link Text, Synonyms |
| Sergio Ferrandez, Antonio Toral, Oscar Ferrandez, Antonio Ferrandez and Rafael Munoz | Applying Wikipedia’s Multilingual Knowledge to Cross?Lingual Question Answering | Lecture Notes in Computer Science | 2007 | [98] |
The application of the multilingual knowledge encoded in Wikipedia to an open?domain Cross?Lingual Question Answering system based on the Inter Lingual Index (ILI) module of EuroWordNet is proposed and evaluated. This strategy overcomes the problems due to ILI’s low coverage on proper nouns (Named Entities). Moreover, as these are open class words (highly changing), using a community?based up?to?date resource avoids the tedious maintenance of hand?coded bilingual dictionaries. A study reveals the importance to translate Named Entities in CL?QA and the advantages of relying on Wikipedia over ILI for doing this. Tests on questions from the Cross?Language Evaluation Forum (CLEF) justify our approach (20% of these are correctly answered thanks to Wikipedia’s Multilingual Knowledge). |
||
| G Urdaneta, G Pierre, M van Steen | A Decentralized Wiki Engine for Collaborative Wikipedia Hosting | 3rd International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technology (WEBIST), March 2007 | 2007 | [99] |
This paper presents the design of a decentralized system for hosting large-scale wiki web sites like Wikipedia, using a collaborative approach. Our design focuses on distributing the pages that compose the wiki across a network of nodes provided by individuals and organizations willing to collaborate in hosting the wiki. We present algorithms for placing the pages so that the capacity of the nodes is not exceeded and the load is balanced, and algorithms for routing client requests to the appropriate nodes. We also address fault tolerance and security issues. |
||
| M Hu, EP Lim, A Sun, HW Lauw, BQ Vuong | Measuring article quality in wikipedia: models and evaluation | Proceedings of the sixteenth ACM conference on Conference on information and knowledge management | 2007 | [100] |
Wikipedia has grown to be the world largest and busiest free encyclopedia, in which articles are collaboratively written and maintained by volunteers online. Despite its success as a means of knowledge sharing and collaboration, the public has never stopped criticizing the quality of Wikipedia articles edited by non-experts and inexperienced contributors. In this paper, we investigate the problem of assessing the quality of articles in collaborative authoring of Wikipedia. We propose three article quality measurement models that make use of the interaction data between articles and their contributors derived from the article edit history. Our B<scp>asic</scp> model is designed based on the mutual dependency between article quality and their author authority. The P<scp>eer</scp>R<scp>eview</scp> model introduces the review behavior into measuring article quality. Finally, our P<scp>rob</scp>R<scp>eview</scp> models extend P<scp>eer</scp>R<scp>eview</scp> with partial reviewership of contributors as they edit various portions of the articles. We conduct experiments on a set of well-labeled Wikipedia articles to evaluate the effectiveness of our quality measurement models in resembling human judgement |
article quality, authority, collaborative authoring, peer review, wikipedia | |
| Rodrigo B. Almeida, Barzan Mozafari, Junghoo Cho | On the Evolution of Wikipedia | Proc. of the Int. Conf. on Weblogs and Social Media, 2007 | 2007 | [101] |
A recent phenomenon on the Web is the emergence and pro- liferation of new social media systems allowing social inter- action between people. One of the most popular of these systems is Wikipedia that allows users to create content in a collaborative way. Despite its current popularity, not much is known about how users interact with Wikipedia and how it has evolved over time. In this paper we aim to provide a first, extensive study of the user behavior on Wikipedia and its evolution. Compared to prior studies, our work differs in several ways. First, previ- ous studies on the analysis of the user workloads (for systems such as peer-to-peer systems [10] and Web servers [2]) have mainly focused on understanding the users who are accessing information. In contrast, Wikipedia’s provides us with the opportunity to understand how users create and maintain in- formation since it provides the complete evolution history of its content. Second, the main focus of prior studies is eval- uating the implication of the user workloads on the system performance, while our study is trying to understand the evo- lution of the data corpus and the user behavior themselves. Our main findings include that (1) the evolution and up- dates of Wikipedia is governed by a self-similar process, not by the Poisson process that has been observed for the general Web [4, 6] and (2) the exponential growth of Wikipedia is mainly driven by its rapidly increasing user base, indicating the importance of its open editorial policy for its current suc- cess. We also find that (3) the number of updates made to the Wikipedia articles exhibit a power-law distribution, but the distribution is less skewed than those obtained from other studies. |
Wikipedia, user behavior, social systems | |
| David Milne | Computing Semantic Relatedness using Wikipedia Link Structure | Proc. of NZCSRSC, 2007 | 2007 | [102] |
This paper describes a new technique for obtaining measures of semantic relatedness. Like other recent approaches, it uses Wikipedia to provide a vast amount of structured world knowledge about the terms of interest. Our system, the Wikipedia Link Vector Model or WLVM, is unique in that it does so using only the hyperlink structure of Wikipedia rather than its full textual content. To evaluate the algorithm we use a large, widely used test set of manually defined measures of semantic relatedness as our bench-mark. This allows direct comparison of our system with other similar techniques. |
Wikipedia, Data Mining, Semantic Relatedness | |
| Dat P.T. Nguyen, Yutaka Matsuo and Mitsuru Ishizuka | Relation Extraction from Wikipedia Using Subtree Mining | AAAI ‘07 | 2007 | [103] |
The exponential growth and reliability of Wikipedia have made it a promising data source for intelligent systems. The first challenge of Wikipedia is to make the encyclopedia machine-processable. In this study, we address the problem of extracting relations among entities from Wikipedia’s English articles, which in turn can serve for intelligent systems to satisfy users’ information needs. Our proposed method first anchors the appearance of entities in Wikipedia articles using some heuristic rules that are supported by their encyclopedic style. Therefore, it uses neither the Named Entity Recognizer (NER) nor the Coreference Resolution tool, which are sources of errors for relation extraction. It then classifies the relationships among entity pairs using SVM with features extracted from the web structure and subtrees mined from the syntactic structure of text. The innovations behind our work are the following: a) our method makes use of Wikipedia characteristics for entity allocation and entity classification, which are essential for relation extraction; b) our algorithm extracts a core tree, which accurately reflects a relationship between a given entity pair, and subsequently identifies key features with respect to the relationship from the core tree. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach through evaluation of manually annotated data from actual Wikipedia articles. |
||
| David Milne, Ian H. Witten and David M. Nichols | A Knowledge-Based Search Engine Powered by Wikipedia | CIKM ‘07 | 2007 | [104] |
This paper describes a new technique for obtaining measures of semantic relatedness. Like other recent approaches, it uses Wikipedia to provide a vast amount of structured world knowledge about the terms of interest. Our system, the Wikipedia Link Vector Model or WLVM, is unique in that it does so using only the hyperlink structure of Wikipedia rather than its full textual content. To evaluate the algorithm we use a large, widely used test set of manually defined measures of semantic relatedness as our bench-mark. This allows direct comparison of our system with other similar techniques. |
Information Retrieval, Query Expansion, Wikipedia, Data Mining, Thesauri. | |
| Torsten Zesch, Iryna Gurevych, Max Muhlhauser | Comparing Wikipedia and German Wordnet by Evaluating Semantic Relatedness on Multiple Datasets. | Proceedings of Human Language Technologies: The Annual Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics (NAACL-HLT) | 2007 | [105] |
We evaluate semantic relatedness measures on different German datasets showing that their performance depends on: (i) the definition of relatedness that was underlying the construction of the evaluation dataset, and (ii) the knowledge source used for computing semantic relatedness. We analyze how the underlying knowledge source in?uences the performance of a measure. Finally, we investigate the combination of wordnets and Wikipedia to improve the performance of semantic relatedness measures. |
||
| Jun'ichi Kazama and Kentaro Torisawa | Exploiting Wikipedia as External Knowledge for Named Entity Recognition | Joint Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and Computational Natural Language Learning, : 698--707, 2007. | 2007 | [106] |
We explore the use of Wikipedia as external knowledge to improve named entity recognition (NER). Our method retrieves the corresponding Wikipedia entry for each candidate word sequence and extracts a category label from the first sentence of the entry, which can be thought of as a definition part. These category labels are used as features in a CRF-based NE tagger. We demonstrate using the CoNLL 2003 dataset that the Wikipedia category labels extracted by such a simple method actually improve the accuracy of NER. |
named-entities wikipedia | |
| D. P. T. Nguyen and Y. Matsuo and M. Ishizuka | Exploiting Syntactic and Semantic Information for Relation Extraction from Wikipedia | IJCAI Workshop on Text-Mining \\& Link-Analysis (TextLink 2007), 2007. | 2007 | [107] |
The exponential growth of Wikipedia recently attracts the attention of a large number of researchers and practitioners. However, one of the current challenges on Wikipedia is to make the encyclopedia processable for machines. In this paper, we deal with the problem of extracting relations between entities from Wikipedia’s English articles, which can straightforwardly be transformed into Semantic Web meta data. We propose a novel method to exploit syntactic and semantic information for relation extraction. We mine frequent subsequences from the path between an entity pair in the syntactic and semantic structure in order to explore key patterns reflecting the relationship between the pair. In addition, our method can utilize the nature of Wikipedia to automatically obtain training data. The preliminary results of our experiments strongly support our hyperthesis that analyzing language in higher level is better for relation extraction on Wikipedia and show that our method is promising for text understanding. |
knowledge-extraction wikipedia | |
| . A. Thom and J. Pehcevski and A. M. Vercoustre | Use of Wikipedia Categories in Entity Ranking | Proceedings of the 12th Australasian Document Computing Symposium, Melbourne, Australia, 2007. | 2007 | [108] |
Wikipedia is a useful source of knowledge that has many applications in language processing and knowledge representation. The Wikipedia category graph can be compared with the class hierarchy in an ontology; it has some characteristics in common as well as some differences. In this paper, we present our approach for answering entity ranking queries from the Wikipedia. In particular, we explore how to make use of Wikipedia categories to improve entity ranking effectiveness. Our experiments show that using categories of example entities works significantly better than using loosely defined target categories. |
named-entities wikipedia | |
| S. Cucerzan | Large-Scale Named Entity Disambiguation Based on Wikipedia Data | EMNLP 2007: Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, June 28-30, 2007, Prague, Czech Republic, 2007. | 2007 | [109] |
This paper presents a large-scale system for the recognition and semantic disambiguation of named entities based on information extracted from a large encyclopedic collection and Web search results. It describes in detail the disambiguation paradigm employed and the information extraction process from Wikipedia. Through a process of maximizing the agreement between the contextual information extracted from Wikipedia and the context of a document, as well as the agreement among the category tags associated with the candidate entities, the implemented system shows high disambiguation accuracy on both news stories and Wikipedia articles. |
named-entities wikipedia | |
| Anne-Marie Vercoustre and Jovan Pehcevski and James A. Thom | Using Wikipedia Categories and Links in Entity Ranking | Pre-proceedings of the sixth International Workshop of the Initiative for the Evaluation of XML Retrieval (INEX 2007), 2007. | 2007 | [110] |
This paper describes the participation of the INRIA group in the INEX 2007 XML entity ranking and ad hoc tracks. We developed a system for ranking Wikipedia entities in answer to a query. Our approach utilises the known categories, the link structure of Wikipedia, as well as the link co-occurrences with the examples (when provided) to improve the effectiveness of entity ranking. Our experiments on the training data set demonstrate that the use of categories and the link structure of Wikipedia, together with entity examples, can significantly improve entity retrieval effectiveness. We also use our system for the ad hoc tasks by inferring target categories from the title of the query. The results were worse than when using a full-text search engine, which confirms our hypothesis that ad hoc retrieval and entity retrieval are two different tasks. |
information-retrieval link-mining wikipedia | |
| Kotaro Nakayama and Takahiro Hara and Shojiro Nishio | Wikipedia Mining for an Association Web Thesaurus Construction | Web Information Systems Engineering (WISE) 2007 France | 2007 | [111] | Wikipedia-Lab work |
Wikipedia has become a huge phenomenon on the WWW. As a corpus for knowledge extraction, it has various impressive characteristics such as a huge amount of articles, live updates, a dense link structure, brief link texts and URL identification for concepts. In this paper, we propose an efficient link mining method pfibf (Path Frequency - Inversed Backward link Frequency) and the extension method “forward / backward link weighting (FB weighting)” in order to construct a huge scale association thesaurus. We proved the effectiveness of our proposed methods compared with other conventional methods such as cooccurrence analysis and TF-IDF. |
dblp, thesaurus wikipedia |
| Klaus Stein, Claudia Hess | Does it matter who contributes: a study on featured articles in the german wikipedia | Proceedings of the 18th conference on Hypertext and hypermedia | 2007 | [112] |
The considerable high quality of Wikipedia articles is often accredited to the large number of users who contribute to Wikipedia's encyclopedia articles, who watch articles and correct errors immediately. In this paper, we are in particular interested in a certain type of Wikipedia articles, namely, the featured articles - articles marked by a community's vote as being of outstanding quality. The German Wikipedia has the nice property that it has two types of featured articles: excellent and worth reading. We explore on the German Wikipedia whether only the mere number of contributors makes the difference or whether the high quality of featured articles results from having experienced authors contributing with a reputation for high quality contributions. Our results indicate that it does matter who contributes. |
Wikipedia, collaborative working, measures of quality and reputation, statistical analysis of Wikipedia, wiki | |
| Patrick AS Sinclair, Kirk Martinez, Paul H Lewis | Dynamic link service 2.0: using wikipedia as a linkbase | Proceedings of the 18th conference on Hypertext and hypermedia | 2007 | [113] |
This paper describes how a Web 2.0 mashup approach, reusing technologies and services freely available on the web, have enabled the development of a dynamic link service system that uses Wikipedia as its linkbase. |
dynamic link service, wikipedia | |
| Tunsch, Thomas | Museen und Wikipedia | Gesellschaft zur Forderung angewandter Informatik, EVA Conferences International (eds). EVA 2007 Berlin, die 14. Berliner Veranstaltung der Internationalen EVA-Serie Electronic Imaging & the Visual Arts. Berlin: Gesellschaft zur Forderung angewandter Informatik, EVA Conferences International. (7th?9th Nov 2007). 87. 15?21 | 2007 | [114] | German | ||
| Suchanek Fabian M., Gjergji Kasneci, Gerhard Weikum | YAGO: A Core of Semantic Knowledge Unifying WordNet and Wikipedia | Proceedings of the 16th international conference on World Wide Web | 2007 | [115] |
We present YAGO, a light-weight and extensible ontology with high coverage and quality. YAGO builds on entities and relations and currently contains more than 1 million entities and 5 million facts. This includes the Is-A hierarchy as well as non-taxonomic relations between entities (such as HASONEPRIZE). The facts have been automatically extracted from Wikipedia and unified with WordNet, using a carefully designed combination of rule-based and heuristic methods described in this paper. The resulting knowledge base is a major step beyond WordNet: in quality by adding knowledge about individuals like persons, organizations, products, etc. with their semantic relationships - and in quantity by increasing the number of facts by more than an order of magnitude. Our empirical evaluation of fact correctness shows an accuracy of about 95%. YAGO is based on a logically clean model, which is decidable, extensible, and compatible with RDFS. Finally, we show how YAGO can be further extended by state-of-the-art information extraction techniques. |
||
| Andras Csomai and Rada Mihalcea | Wikify! Linking Educational Materials to Encyclopedic Knowledge | Proceedings of the International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education (AIED 2007), 2007. | 2007 | [116] |
This paper describes a system that automatically links study materials to encyclopedic knowledge, and shows how the availability of such knowledge within easy reach of the learner can improve both the quality of the knowledge acquired and the time needed to obtain such knowledge. |
E-NLP WSD keywords significance_testing terminology wikipedia | |
| Rainer Hammwohner | Semantic Wikipedia - Checking the Premises | The Social Semantic Web 2007 - Proceedings of the 1st Conference on Social Semantic Web, 2007. | 2007 | [117] |
Enhancing Wikipedia by means of semantic representations seems to be a promising issue. From a formal or technical point of view there are no major obstacles in the way. Nevertheless, a close look at Wikipedia, its structure and contents reveals that some questions have to be answered in advance. This paper will deal with these questions and present some first results based on empirical findings. |
semantic, statistics, tagging, wikipedia | |
| Torsten Zesch, Iryna Gurevych, Max Muhlhauser | Analyzing and Accessing Wikipedia as a Lexical Semantic Resource. | Biannual Conference of the Society for Computational Linguistics and Language Technology pp. 213-221 | 2007 | [118] |
We analyze Wikipedia as a lexical semantic resource and compare it with conventional resources, such as dictionaries, thesauri, semantic wordnets, etc. Diffrent parts of Wikipedia record different aspects of these resources. We show that Wikipedia contains a vast amount of knowledge about, e.g., named entities, domain specific terms, and rare word senses. If Wikipedia is to be used as a lexical semantic resource in large-scale NLP tasks, efficient programmatic access to the knowledge therein is required. We review existing access mechanisms and show that they are limited with respect to performance and the provided access functions. Therefore, we introduce a general purpose, high performance Java-based Wikipedia API that overcomes these limitations. |
named-entities, wikipedia | |
| Somnath Banerjee | Boosting Inductive Transfer for Text Classification Using Wikipedia | Sixth International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA) | 2007 | [119] |
Inductive transfer is applying knowledge learned on one set of tasks to improve the performance of learning a new task. Inductive transfer is being applied in improving the generalization performance on a classification task using the models learned on some related tasks. In this paper, we show a method of making inductive transfer for text classification more effective using Wikipedia. We map the text documents of the different tasks to a feature space created using Wikipedia, thereby providing some background knowledge of the contents of the documents. It has been observed here that when the classifiers are built using the features generated from Wikipedia they become more effective in transferring knowledge. An evaluation on the daily classification task on the Reuters RCV1 corpus shows that our method can significantly improve the performance of inductive transfer. Our method was also able to successfully overcome a major obstacle observed in a recent work on a similar setting. |
classification, knowledge-extraction, wikipedia
| |
| Brent Hecht, Nicole Starosielski, and Drew Dara-Abrams | Generating Educational Tourism Narratives from Wikipedia | Association for the Advancement of Artifical Intelligence Fall Symposium on Intelligent Narrative Technologies (AAAI-INT) | 2007 | [120] | notes | We present a narrative theory-based approach to data mining that generates cohesive stories from a Wikipedia corpus. This approach is based on a data mining-friendly view of narrative derived from narratology, and uses a prototype mining algorithm that implements this view. Our initial test case and focus is that of field-based educational tour narrative generation, for which we have successfully implemented a proof-of-concept system called Minotour. This system operates on a client-server model, in which the server mines a Wikipedia database dump to generate narratives between any two spatial features that have associated Wikipedia articles. The server then delivers those narratives to mobile device clients. |
narrative theory, data mining, educational tourism
|
| Travis Kriplean, Ivan Beschastnikh, David W. McDonald, and Scott A. Golder | Community, Consensus, Coercion, Control: CS*W or How Policy Mediates Mass Participation | GROUP 2007 -- ACM Conference on Supporting Group Work. | 2007 | [121] | How Wikipedia participants apply and interpret policies on the talk pages that accompany each encyclopedia article. |
When large groups cooperate, issues of conflict and control surface because of differences in perspective. Managing such diverse views is a persistent problem in cooperative group work. The Wikipedian community has responded with an evolving body of policies that provide shared principles, processes, and strategies for collaboration. We employ a grounded approach to study a sample of active talk pages and examine how policies are employed as contributors work towards consensus. Although policies help build a stronger community, we find that ambiguities in policies give rise to power plays. This lens demonstrates that support for mass collaboration must take into account policy and power. |
Wikipedia, collaborative authoring, community, policy, power |
| Felipe Ortega and Jesus M. Gonzalez-Barahona | Quantitative Analysis of the Wikipedia Community of Users | WikiSym 2007, 21-23 October. Montreal, Canada. | 2007 | [122] | Identification of the core group of very active users who leads most of the contribution process to the English Wikipedia. It extends the proposed research methodology to other language editions as well. |
Many activities of editors in Wikipedia can be traced using its database dumps, which register detailed information about every single change to every article. Several researchers have used this information to gain knowledge about the production process of articles, and about activity patterns of authors. In this analysis, we have focused on one of those previous works, by Kittur et al. First, we have followed the same methodology with more recent and comprehensive data. Then, we have extended this methodology to precisely identify which fraction of authors are producing most of the changes in Wikipedia's articles, and how the behaviour of these authors evolves over time. This enabled us not only to validate some of the previous results, but also to find new interesting evidences. We have found that the analysis of sysops is not a good method for estimating different levels of contributions, since it is dependent on the policy for electing them (which changes over time and for each language). Moreover, we have found new activity patterns classifying authors by their contributions during specific periods of time, instead of using their total number of contributions over the whole life of Wikipedia. Finally, we present a tool that automates this extended methodology, implementing a quick and complete quantitative analysis of every language edition in Wikipedia. |
wikipedia |
| Felipe Ortega, Jesus M. Gonzalez-Barahona and Gregorio Robles | The Top Ten Wikipedias: A quantitative analysis using WikiXRay | ICSOFT 2007, July 2007. Barcelona, Spain | 2007 | [123] | Presents initial quantitative results and conclusions about the content creation process in the top ten language editions of Wikipedia. |
In a few years, Wikipedia has become one of the information systems with more public (both producers and consumers) of the Internet. Its system and information architecture is relatively simple, but has proven to be capable of supporting the largest and more diverse community of collaborative authorship worldwide. In this paper, we analyze in detail this community, and the contents it is producing. Using a quantitative methodology based on the analysis of the public Wikipedia databases, we describe the main characteristics of the 10 largest language editions, and the authors that work in them. The methodology (which is almost completely automated) is generic enough to be used on the rest of the editions, providing a convenient framework to develop a complete quantitative analysis of the Wikipedia. Among other parameters, we study the evolution of the number of contributions and articles, their size, and the differences in contributions by different authors, inferring some relationships between contribution patterns and content. These relationships reflect (and in part, explain) the evolution of the different language editions so far, as well as their future trends. |
wikipedia |
| Reid Priedhorsky, Jilin Chen, Shyong (Tony) K. Lam, Katherine Panciera, Loren Terveen, John Riedl | Creating, Destroying, and Restoring Value in Wikipedia | Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of Minnesota | 2007 | [124] | Introduces the notion that the impact of an edit is best measured by the number of times the edited version is viewed. |
Wikipedia's brilliance and curse is that any user can edit any of the encyclopedia entries. We introduce the notion of the impact of an edit, measured by the number of times the edited version is viewed. Using several datasets, including recent logs of all article views, we show that an overwhelming majority of the viewed words were written by frequent editors and that this majority is increasing. Similarly, using the same impact measure, we show that the probability of a typical article view being damaged is small but increasing, and we present empirically grounded classes of damage. Finally, we make policy recommendations for Wikipedia and other wikis in light of these findings. |
wikipedia |
| Somnath Banerjee, Krishnan Ramanathan, Ajay Gupta | Clustering Short Texts using Wikipedia | The 30th Annual International ACM SIGIR Conference | 2007 | [125] |
Subscribers to the popular news or blog feeds (RSS/Atom) often face the problem of information overload as these feed sources usually deliver large number of items periodically. One solution to this problem could be clustering similar items in the feed reader to make the information more manageable for a user. Clustering items at the feed reader end is a challenging task as usually only a small part of the actual article is received through the feed. In this paper, we propose a method of improving the accuracy of clustering short texts by enriching their representation with additional features from Wikipedia. Empirical results indicate that this enriched representation of text items can substantially improve the clustering accuracy when compared to the conventional bag of words representation. |
cultering, rss | |
| R. Almeida, B. Mozafari, and J. Junghoo | On the Evolution of Wikipedia | Proceedings of ICWSM 2007, International Conference on Weblogs and Social Media, 2007 | 2007 | [126] |
A recent phenomenon on the Web is the emergence and proliferation of new social media systems allowing social interaction between people. One of the most popular of these systems is Wikipedia that allows users to create content in a collaborative way. Despite its current popularity, not much is known about how users interact with Wikipedia and how it has evolved over time. In this paper we aim to provide a first, extensive study of the user behavior on Wikipedia and its evolution. Compared to prior studies, our work differs in several ways. First, previous studies on the analysis of the user workloads (for systems such as peer-to-peer systems [10] and Web servers [2]) have mainly focused on understanding the users who are accessing information. In contrast, Wikipedia’s provides us with the opportunity to understand how users create and maintain information since it provides the complete evolution history of its content. Second, the main focus of prior studies is evaluating the implication of the user workloads on the system performance, while our study is trying to understand the evolution of the data corpus and the user behavior themselves. Our main findings include that (1) the evolution and updates of Wikipedia is governed by a self-similar process, not by the Poisson process that has been observed for the general Web [4, 6] and (2) the exponential growth of Wikipedia is mainly driven by its rapidly increasing user base, indicating the importance of its open editorial policy for its current success. We also find that (3) the number of updates made to the Wikipedia articles exhibit a power-law distribution, but the distribution is less skewed than those obtained from other studies. |
Wikipedia, user behavior, social systems | |
| Enric Senabre Hidalgo | Stigmergy, meritocracy and vandalism in peer-production: how can wikis grow | Towards a Social Science of Web 2.0 | 2007 | [127] | All links have rotten? Abstract? | ||
| Adler, B. Thomas, and de Alfaro, Luca | A Content-Driven Reputation System for the Wikipedia | Proceedings of WWW 2007, the 16th International World Wide Web Conference, ACM Press, 2007 | 2007 | [128] |
We present a content-driven reputation system for Wikipedia authors. In our system, authors gain reputation when the edits they perform to Wikipedia articles are preserved by subsequent authors, and they lose reputation when their edits are rolled back or undone in short order. Thus, author reputation is computed solely on the basis of content evolution; user-to-user comments or ratings are not used. The author reputation we compute could be used to flag new contributions from low-reputation authors, or it could be used to allow only authors with high reputation to contribute to controversial or critical pages. A reputation system for the Wikipedia could also provide an incentive for high-quality contributions. We have implemented the proposed system, and we have used it to analyze the entire Italian and French Wikipedias, consisting of a total of 691,551 pages and 5,587,523 revisions. Our results show that our notion of reputation has good predictive value: changes performed by low-reputation authors have a significantly larger than average probability of having poor quality, as judged by human observers, and of being later undone, as measured by our algorithms. |
wikipedia | |
| Gabrilovich, Evgeniy and Shaul Markovitch | Computing Semantic Relatedness using Wikipedia-based Explicit Semantic Analysis. | Proceedings of the 20th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI), Hyderabad, India, January 2007. | 2007 | [129] |
{{{2}}} |
semantic, text-mining, wikipedia | |
| Tunsch, Thomas: | Museum Documentation and Wikipedia.de: Possibilities, opportunities and advantages for scholars and museums | J. Trant and D. Bearman (eds). Museums and the Web 2007: Proceedings. Toronto: Archives & Museum Informatics, published March 31, 2007 at http://www.archimuse.com/mw2007/papers/tunsch/tunsch.html | 2007 | [130] | post-conference communication: museums.wikia.com |
The importance of Wikipedia for the documentation and promotion of museum holdings is gaining acceptance, and the number of references to articles is growing. However, the museum world still pays little attention to the Wikipedia project as a collaborative community with intentions, structures, and special features. Although these observations are based on museums in Germany and focus on the German Wikipedia, they are just as important and applicable to other museums and other editions of Wikipedia. Universities and libraries have already taken advantage of the Wikipedia and have established functional links. In that the mission of museums is closely related to that of universities and libraries, the value of Wikipedia for museum professionals is worthy of consideration. This paper provides the complete study to serve as reference for the selected topics to be discussed in the professional forum. Keywords: Wikipedia, documentation, collaborative, community, scholars, interconnections |
Wikipedia; documentation; collaborative; community; scholars; interconnections |
| Viegas, Fernanda, Martin Wattenberg, Jesse Kriss, Frank van Ham | Talk Before You Type: Coordination in Wikipedia | Proceedings of Hawaiian International Conference of Systems Sciences Big Island, Hawaii. | 2007 | [131] |
Wikipedia, the online encyclopedia, has attracted attention both because of its popularity and its unconventional policy of letting anyone on the internet edit its articles. This paper describes the results of an empirical analysis of Wikipedia and discusses ways in which the Wikipedia community has evolved as it hasgrown. We contrast our findings with an earlier study [11] and present three main results. First, the community maintains a strong resilience to malicious editing, despite tremendous growth and high traffic. Second, the fastest growing areas of Wikipedia are devoted to coordination and organization. Finally, we focus on a particular set of pages used to coordinate work, the “Talk” pages. By manually coding the content of a subset of these pages, we find that these pages serve many purposes, notably supporting strategic planning of edits and enforcement of standard guidelines and conventions. Our results suggest that despite the potential for anarchy, the Wikipedia community places a strong emphasis on group coordination, policy, and process. |
empirical study, visualization, wiki, wikipedia | |
| Ollivier, Yann, and Senellart, Pierre | Finding Related Pages Using Green Measures: An Illustration with Wikipedia. | Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI 2007) | 2007 | [132] |
We introduce a new method for finding nodes semantically related to a given node in a hyperlinked graph: the Green method, based on a classical Markov chain tool. It is generic, adjustment-free and easy to implement. We test it in the case of the hyperlink structure of the English version of Wikipedia, the on-line encyclopedia. We present an extensive comparative study of the performance of our method versus several other classical methods in the case of Wikipedia. The Green method is found to have both the best average results and the best robustness. |
PageRank, Markov chain, Green measure, Wikipedia | |
| Pedersen, Niels M. L. & Anders Due | Wikipedia - viden som social handlen. | Paper presented at The 3. Nordic Conference on Rhetoric, May 19-20, Oslo, Norway | 2006 | [133] | Danish | ||
| Rafaeli, Sheizaf, Ariel, Yaron and Hayat, Tsahi | Wikipedians Sense of (Virtual) Community. | Presented at The eighth International Conference General Online Research (GOR06): Bielefeld, Germany | 2006 | [134] | English | ||
| Sigurbjornsson, Borkur, Kamps, Jaap, and de Rijke, Maarten | Focused Access to Wikipedia | Proceedings DIR-2006 | 2006 | [135] |
Wikipedia is a "free" online encyclopedia. It contains millions of entries in many languages and is growing at a fast pace. Due to its volume, search engines play an important role in giving access to the information in Wikipedia. The "free" availability of the collection makes it an attractive corpus for in formation retrieval experiments. In this paper we describe the evaluation of a searchengine that provides focused search access to Wikipedia, i.e., a search engine which gives direct access to individual sections of Wikipedia pages. The main contributions of this paper are twofold. First, we introduce Wikipedia as a test corpus for information retrieval experiments in general and for semi-structured retrieval in particular. Second, we demonstrate that focused XML retrieval methods can be applied to a wider range of problems than searching scientific journals in XML format, including accessing reference works. |
document structure, visualization, information searching | |
| Rudiger Gleim, Alexander Mehler and Matthias Dehmer | Web Corpus Mining by Instance of Wikipedia | Proc. 2nd Web as Corpus Workshop at EACL 2006 | 2006 | [136] |
In this paper we present an approach to structure learning in the area of web documents. This is done in order to approach the goal of webgenre tagging in the area of web corpus linguistics. A central outcome of the paper is that purely structure oriented approaches to web document classification provide an information gain which may be utilized in combined approaches of web content and structure analysis. |
||
| Martin Hepp and Daniel Bachlechner and Katharina Siorpaes | Harvesting Wiki Consensus - Using Wikipedia Entries as Ontology Elements | Proceedings of the First Workshop on Semantic Wikis -- From Wiki to Semantics, co-located with the 3rd Annual European Semantic Web Conference (ESWC 2006), 2006. | 2006 | [137] |
One major obstacle towards adding machine-readable annotation to existing Web content is the lack of domain ontologies. While FOAF and Dublin Core are popular means for expressing relationships between Web resources and between Web resources and literal values, we widely lack unique identifiers for common concepts and instances. Also, most available ontologies have a very weak community grounding in the sense that they are designed by single individuals or small groups of individuals, while the majority of potential users is not involved in the process of proposing new ontology elements or achieving consensus. This is in sharp contrast to natural language where the evolution of the vocabulary is under the control of the user community. At the same time, we can observe that, within Wiki communities, especially Wikipedia, a large number of users is able to create comprehensive domain representations in the sense of unique, machine-feasible, identifiers and concept definitions which are sufficient for humans to grasp the intension of the concepts. The English version of Wikipedia contains now more than one million entries and thus the same amount of URIs plus a human-readable description. While this collection is on the lower end of ontology expressiveness, it is likely the largest living ontology that is available today. In this paper, we (1) show that standard Wiki technology can be easily used as an ontology development environment for named classes, reducing entry barriers for the participation of users in the creation and maintenance of lightweight ontologies, (2) prove that the URIs of Wikipedia entries are surprisingly reliable identifiers for ontology concepts, and (3) demonstrate the applicability of our approach in a use case. |
2006 ezweb folksonomy ontology wikipedia | |
| Razvan Bunescu and Marius Pasca | Using Encyclopedic Knowledge for Named Entity Disambiguation | 11th Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics, : 9--16, 2006. | 2006 | [138] | Despite not mentioning Wikipedia in title or abstract, the paper discusses it as one of the main examples. |
We present a new method for detecting and disambiguating named entities in open domain text. A disambiguation SVM kernel is trained to exploit the high coverage and rich structure of the knowledge encoded in an online encyclopedia. The resulting model significantly outperforms a less informed baseline. |
disambiguation named-entities wikipedia |
| Angela Beesley | How and why Wikipedia works | WikiSym '06: Proceedings of the 2006 international symposium on Wikis | 2006 | [139] |
This talk discusses the inner workings of Wikipedia. Angela will address the roles, processes, and sociology that make up the project, with information on what happens behind the scenes and how the community builds and defends its encyclopedia on a daily basis. The talk will give some insight into why Wikipedia has worked so far and why we believe it will keep working in the the future despite the many criticisms that can be made of it. It is hoped that this review inspires further Wikipedia research. For this, please also see our Wikipedia Research workshop on Wednesday, which is open to walk-ins. |
Design, Theory | |
| Simon Overell and Stefan Ruger | Identifying and Grounding Descriptions of Places | SIGIR Workshop on Geographic Information Retrieval, | 2006 | [140] |
In this paper we test the hypothesis Given a piece of text describing an object or concept our combined disambiguation method can disambiguate whether it is a place and ground it to a Getty Thesaurus of Geographical Names unique identifier with significantly more accuracy than na¨?ve methods. We demonstrate a carefully engineered rule-based place name disambiguation system and give Wikipedia as a worked example with hand-generated ground truth and bench mark tests. This paper outlines our plans to apply the co-occurrence models generated with Wikipedia to solve the problem of disambiguating place names in text using supervised learning techniques. |
Geographic Information Retrieval, Disambiguation, Wikipedia | |
| A. Toral and R. Munoz | A proposal to automatically build and maintain gazetteers for Named Entity Recognition by using Wikipedia | EACL 2006, 2006. | 2006 | [141] |
This paper describes a method to automatically create and maintain gazetteers for Named Entity Recognition (NER). This method extracts the necessary information from linguistic resources. Our approach is based on the analysis of an on-line encyclopedia entries by using a noun hierarchy and optionally a PoS tagger. An important motivation is to reach a high level of language independence. This restricts the techniques that can be used but makes the method useful for languages with few resources. The evaluation carried out proves that this approach can be successfully used to build NER gazetteers for location (F 78%) and person (F 68%) categories. |
gazetteers, named-entities wikipedia | |
| Ofer Arazy, Wayne Morgan and Raymond Patterson | Wisdom of the Crowds: Decentralized Knowledge Construction in Wikipedia | 16th Annual Workshop on Information Technologies & Systems (WITS) | 2006 | [142] |
Recently, Nature published an article comparing the quality of Wikipedia articles to those of Encyclopedia Britannica (Giles 2005). The article, which gained much public attention, provides evidence for Wikipedia quality, but does not provide an explanation of the underlying source of that quality. Wikipedia, and wikis in general, aggregate information from a large and diverse author-base, where authors are free to modify any article. Building upon Surowiecki's (2005) Wisdom of Crowds, we develop a model of the factors that determine wiki content quality. In an empirical study of Wikipedia, we find strong support for our model. Our results indicate that increasing size and diversity of the author-base improves content quality. We conclude by highlighting implications for system design and suggesting avenues for future research. |
Wikipedia, Wisdom of the Crowds, Collective Intelligence, information quality | |
| Aurelie Herbelot and Ann Copestake | Acquiring Ontological Relationships from Wikipedia Using RMRS | Proc.of the ISWC 2006 Workshop on Web Content Mining with Human Language Technologies, 2006. | 2006 | [143] |
We investigate the extraction of ontologies from biological text using a semantic representation derived from a robust parser. The use of a semantic representation avoids the problems that traditional pattern-based approaches have with complex syntactic constructions and long-distance dependencies. The discovery of taxonomic relationships is explored in a corpus consisting of 12,200 animal-related articles from the online encyclopaedia Wikipedia. The semantic representation used is Robust Minimal Recursion Semantics (RMRS). Initial experiments show good results in systematising extraction across a variety of hyponymic constructions. |
linguistics ontology semantic text-mining wikipedia | |
| Zhang, Yuejiao | Wiki means more: hyperreading in Wikipedia | HYPERTEXT '06: Proceedings of the seventeenth conference on Hypertext and hypermedia | 2006 | [144] |
Based on the open-sourcing technology of wiki, Wikipedia has initiated a new fashion of hyperreading. Reading Wikipedia creates an experience distinct from reading a traditional encyclopedia. In an attempt to disclose one of the site's major appeals to the Web users, this paper approaches the characteristics of hyperreading activities in Wikipedia from three perspectives. Discussions are made regarding reading path, user participation, and navigational apparatus in Wikipedia. |
Hypertext, Hypermedia, Human Factors, Theory | |
| Schonhofen, Peter | Identifying Document Topics Using the Wikipedia Category Network | WI '06: Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE/WIC/ACM International Conference on Web Intelligence | 2006 | [145] |
In the last few years the size and coverage of Wikipe- dia, a freely available on-line encyclopedia has reached the point where it can be utilized similar to an ontology or tax- onomy to identify the topics discussed in a document. In this paper we will show that even a simple algorithm that exploits only the titles and categories of Wikipedia articles can characterize documents by Wikipedia categories sur- prisingly well. We test the reliability of our method by pre- dicting categories ofWikipedia articles themselves based on their bodies, and by performing classification and cluster- ing on 20 Newsgroups and RCV1, representing documents by their Wikipedia categories instead of their texts. |
Retrieval models, Algorithms | |
| Sangweon Suh and Harry Halpin and Ewan Klein | Extracting Common Sense Knowledge from Wikipedia | Proc. of the ISWC2006 Workshop on Web Content Mining with Human Language technology, 2006. | 2006 | [146] |
Much of the natural language text found on the web contains various kinds of generic or “common sense” knowledge, and this information has long been recognized by artificial intelligence as an important supplement to more formal approaches to building Semantic Web knowledge bases. Consequently, we are exploring the possibility of automatically identifying “common sense” statements from unrestricted natural language text and mapping them to RDF. Our hypothesis is that common sense knowledge is often expressed in the form of generic statements such as Coffee is a popular beverage, and thus our work has focussed on the challenge of automatically identifying generic statements. We have been using the Wikipedia xml corpus as a rich source of common sense knowledge. For evaluation, we have been using the existing annotation of generic entities and relations in the ace 2005 corpus. |
linguistics semantic text-mining wcmhlt2006, wikipedia | |
| Gabriel Weaver, Barbara Strickland, Gregory Crane | Quantifying the accuracy of relational statements in Wikipedia: a methodology | JCDL '06: Proceedings of the 6th ACM/IEEE-CS joint conference on Digital libraries | 2006 | [147] |
An initial evaluation of the English Wikipedia indicates that it may provide accurate data for disambiguating and finding relations among named entities. |
Wikipedia, link analysis, named-entity recognition | |
| David Milne and Olena Medelyan and Ian H. Witten | Mining Domain-Specific Thesauri from Wikipedia: A case study | ACM International Conference on Web Intelligence (WI 2006 Main Conference Proceedings)(WI'06) | 2006 | [148] |
Domain-specific thesauri are high-cost, high-maintenance, high-value knowledge structures. We show how the classic thesaurus structure of terms and links can be mined automatically from Wikipedia, a vast, open encyclopedia. In a comparison with a professional thesaurus for agriculture (Agrovoc) we find that Wikipedia contains a substantial proportion of its domain-specific concepts and semantic relations; furthermore it has impressive coverage of a collection of contemporary documents in the domain. Thesauri derived using these techniques are attractive because they capitalize on existing public efforts and tend to reflect contemporary language usage better than their costly, painstakingly-constructed manual counterparts. |
datamining information-retrieval semantic text-mining wikipedia | |
| Wissner-Gross, A. D. | Preparation of Topical Reading Lists from the Link Structure of Wikipedia | Advanced Learning Technologies, 2006. Sixth International Conference on (2006), pp. 825-829. | 2006 | [149] |
Personalized reading preparation poses an important challenge for education and continuing education. Using a PageRank derivative and graph distance ordering, we show that personalized background reading lists can be generated automatically from the link structure of Wikipedia. We examine the operation of our new tool in professional, student, and interdisciplinary researcher learning models. Additionally, we present desktop and mobile interfaces for the generated reading lists. |
information-retrieval, link-mining, wikipedia | |
| Spek, Sander and Postma, Eric and Herik, Jaap van den | Wikipedia: organisation from a bottom-up approach | Paper presented at the Research in Wikipedia-workshop of WikiSym 2006, Odense, Denmark. | 2006 | [150] |
Wikipedia can be considered as an extreme form of a self-managing team, as a means of labour division. One could expect that this bottom-up approach, with the absence of top-down organisational control, would lead to a chaos, but our analysis shows that this is not the case. In the Dutch Wikipedia, an integrated and coherent data structure is created, while at the same time users succeed in distributing roles by self-selection. Some users focus on an area of expertise, while others edit over the whole encyclopedic range. This constitutes our conclusion that Wikipedia, in general, is a successful example of a self-managing team. |
wikipedia | |
| S. P. Ponzetto and M. Strube | Exploiting semantic role labeling, WordNet and Wikipedia for coreference resolution | Proceedings of the main conference on Human Language Technology Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association of Computational Linguistics, : 192--199, 2006. | 2006 | [151] |
In this paper we present an extension of a machine learning based coreference resolution system which uses features induced from different semantic knowledge sources. These features represent knowledge mined from WordNet and Wikipedia, as well as information about semantic role labels. We show that semantic features indeed improve the performance on different referring expression types such as pronouns and common nouns. |
coreference, semantic wikipedia | |
| Krotzsch, Markus, Denny Vrandecic, Max Volkel | Semantic Wikipedia | International World Wide Web Conference. Proceedings of the 15th international conference on World Wide Web | 2006 | [152] | no open content found |
Wikipedia is the world's largest collaboratively edited source of encyclopaedic knowledge. But in spite of its utility, its contents are barely machine-interpretable. Structural knowledge, e.,g. about how concepts are interrelated, can neither be formally stated nor automatically processed. Also the wealth of numerical data is only available as plain text and thus can not be processed by its actual meaning. We provide an extension to be integrated in Wikipedia, that allows the typing of links between articles and the specification of typed data inside the articles in an easy-to-use manner. Enabling even casual users to participate in the creation of an open semantic knowledge base, Wikipedia has the chance to become a resource of semantic statements, hitherto unknown regarding size, scope, openness, and internationalisation. These semantic enhancements bring to Wikipedia benefits of today's semantic technologies: more specific ways of searching and browsing. Also, the RDF export, that gives direct access to the formalised knowledge, opens Wikipedia up to a wide range of external applications, that will be able to use it as a background knowledge base. In this paper, we present the design, implementation, and possible uses of this extension. | |
| Denoyer, Ludovic, Patrick Gallinari | The Wikipedia XML corpus | SIGIR Conference Proceedings. Volume 40 , Issue 1 (June 2006). WORKSHOP SESSION: INEX. Pages: 64 - 69 Year of Publication: 2006 ISSN:0163-5840 | 2006 | [153] | no open content found |
Wikipedia is a well known free content, multilingual encyclopedia written collaboratively by contributors around the world. Anybody can edit an article using a wiki markup language that offers a simplified alternative to HTML. This encyclopedia is composed of millions of articles in different languages. |
Hypertext, Hypermedia, XML |
| Michael Strube and Simone Paolo Ponzetto | WikiRelate! Computing Semantic Relatedness Using Wikipedia. | 21. AAAI / 18. IAAI 2006, 2006. | 2006 | [154] |
Wikipedia provides a knowledge base for computing word relatedness in a more structured fashion than a search engine and with more coverage than WordNet. In this work we present experiments on using Wikipedia for computing semantic relatedness and compare it to WordNet on various benchmarking datasets. Existing relatedness measures perform better using Wikipedia than a baseline given by Google counts, and we show that Wikipedia outperforms WordNet when applied to the largest available dataset designed for that purpose. The best results on this dataset are obtained by integrating Google, WordNet and Wikipedia based measures. We also show that including Wikipedia improves the performance of an NLP application processing naturally occurring texts. |
Wikipedia ontology relatedness semantic_web | |
| Sergey Chernov and Tereza Iofciu and Wolfgang Nejdl and Xuan Zhou | Extracting Semantic Relationships between Wikipedia Categories | 1st Workshop on Semantic Wikis:, 2006. | 2006 | [155] |
The Wikipedia is the largest online collaborative knowledge sharing system, a free encyclopedia. Built upon traditional wiki architectures, its search capabilities are limited to title and full-text search. We suggest that semantic information can be extracted from Wikipedia by analyzing the links between categories. The results can be used for building a semantic schema for Wikipedia which could improve its search capabilities and provide contributors with meaningful suggestions for editing theWikipedia pages.We analyze relevant measures for inferring the semantic relationships between page categories of Wikipedia. Experimental results show that Connectivity Ratio positively correlates with the semantic connection strength. |
semantic wikipedia | |
| McGuinness, Deborah L., Honglei Zeng, Paulo Pinheiro da Silva, Li Ding, Dhyanesh Narayanan, Mayukh Bhaowal | Investigations into Trust for Collaborative Information Repositories: A Wikipedia Case Study | Proceedings of the Workshop on Models of Trust for the Web | 2006 | [156] |
As collaborative repositories grow in popularity and use, issues concerning the quality and trustworthiness of information grow. Some current popular repositories contain contributions from a wide variety of users, many of which will be unknown to a potential end user. Additionally the content may change rapidly and information that was previously contributed by a known user may be updated by an unknown user. End users are now faced with more challenges as they evaluate how much they may want to rely on information that was generated and updated in this manner. A trust management layer has become an important requirement for the continued growth and acceptance of collaboratively developed and maintained information resources. In this paper, we will describe our initial investigations into designing and implementing an extensible trust management layer for collaborative and/or aggregated repositories of information. We leverage our work on the Inference Web explanation infrastructure and exploit and expand the Proof Markup Language to handle a simple notion of trust. Our work is designed to support representation, computation, and visualization of trust information. We have grounded our work in the setting of Wikipedia. In this paper, we present our vision, expose motivations, relate work to date on trust representation, and present a trust computation algorithm with experimental results. We also discuss some issues encountered in our work that we found interesting. |
Trust, Wikipedia, Inference Web, Proof Markup Language, Open Editing. | |
| Gabrilovich, Evgeniy and Shaul Markovitch | Overcoming the Brittleness Bottleneck using Wikipedia: Enhancing Text Categorization with Encyclopedic Knowledge. | Proceedings of the 21st National Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI-06), pp. 1301-1306. | 2006 | [157] |
When humans approach the task of text categorization, they interpret the specific wording of the document in the much larger context of their background knowledge and experience. On the other hand, state-of-the-art information retrieval systems are quite brittle?they traditionally represent documents as bags of words, and are restricted to learning from individual word occurrences in the (necessarily limited) training set. For instance, given the sentence “Wal-Mart supply chain goes real time”, how can a text categorization system know that Wal-Mart manages its stock with RFID technology? And having read that “Ciprofloxacin belongs to the quinolones group”, how on earth can a machine know that the drug mentioned is an antibiotic produced by Bayer? In this paper we present algorithms that can do just that. We propose to enrich document representation through automatic use of a vast compendium of human knowledge?an encyclopedia. We apply machine learning techniques to Wikipedia, the largest encyclopedia to date, which surpasses in scope many conventional encyclopedias and provides a cornucopia of world knowledge. EachWikipedia article represents a concept, and documents to be categorized are represented in the rich feature space of words and relevant Wikipedia concepts. Empirical results confirm that this knowledge-intensive representation brings text categorization to a qualitatively new level of performance across a diverse collection of datasets. |
information-retrieval, text-mining, wikipedia | |
| Grassineau, Benjamin | Wikipedia et le relativisme democratique | OMNSH | 2006 | [158] | French | ||
| Krizhanovsky, Andrew | Synonym search in Wikipedia: Synarcher. | 11-th International Conference "Speech and Computer" SPECOM'2006. Russia, St. Petersburg, June 25-29, pp. 474-477 | 2006 | [159] |
The program Synarcher for synonym (and related terms) search in the text corpus of special structure (Wikipedia) was developed. The results of the search are presented in the form of graph. It is possible to explore the graph and search for graph elements interactively. Adapted HITS algorithm for synonym search, program architecture, and program work evaluation with test examples are presented in the paper. The proposed algorithm can be applied to a query expansion by synonyms (in a search engine) and a synonym dictionary forming. |
HITS, Semantic relatedness | |
| Fissaha Adafre, Sisay and de Rijke, Maarten | Finding Similar Sentences across Multiple Languages in Wikipedia | EACL 2006 Workshop on New Text?Wikis and Blogs and Other Dynamic Text Sources | 2006 | [160] |
We investigate whether theWikipedia corpus is amenable to multilingual analysis that aims at generating parallel corpora. We present the results of the application of two simple heuristics for the identification of similar text across multiple languages inWikipedia. Despite the simplicity of the methods, evaluation carried out on a sample ofWikipedia pages shows encouraging results. |
nlp, wikipedia | |
| Fissaha Adafre, Sisay and de Rijke, Maarten | Exploratory Search in Wikipedia | Proceedings SIGIR 2006 workshop on Evaluating Exploratory Search Systems (EESS) | 2006 | [161] |
We motivate the need for studying the search, discovery and retrieval requirements of Wikipedia users. Based on a sample from an experimental Wikipedia search engine, we hypothesize that the fraction of Wikipedia searches that are exploratory in nature is at least the same as that of general web searches. We also describe a questionnaire for eliciting search, discovery and retrieval requirements from Wikipedia users. |
Wikipedia, interfaces, exploratory search | |
| Forte, Andrea, Amy Bruckman | From Wikipedia to the classroom: exploring online publication and learning | International Conference on Learning Sciences. Proceedings of the 7th international conference on Learning sciences | 2006 | [162] |
Wikipedia represents an intriguing new publishing paradigm?can it be used to engage students in authentic collaborative writing activities? How can we design wiki publishing tools and curricula to support learning among student authors? We suggest that wiki publishing environments can create learning opportunities that address four dimensions of authenticity: personal, real world, disciplinary, and assessment. We have begun a series of design studies to investigate links between wiki publishing experiences and writing-to-learn. The results of an initial study in an undergraduate government course indicate that perceived audience plays an important role in helping students monitor the quality of writing; however, students’ perception of audience on the Internet is not straightforward. This preliminary iteration resulted in several guidelines that are shaping efforts to design and implement new wiki publishing tools and curricula for students and teachers. |
wikipedia, teaching | |
| Maria R. Casado and Enrique Alfonseca and Pablo Castells | From Wikipedia to Semantic Annotations: automatic relationship extraction | 1st Workshop on Semantic Wikis:, 2006. | 2006 | [163] | all links have rotted? | annotation semantic text-mining wikipedia | |
| Buriol L.S., Castillo C., Donato D., Leonardi S., Millozzi S. | Temporal Analysis of the Wikigraph. | To appear in Proceedings of the Web Intelligence Conference (WI), Hong Kong 2006. Published by IEEE CS Press. | 2006 | [164] |
Wikipedia (www.wikipedia.org) is an online encyclopedia, available in more than 100 languages and comprising over 1 million articles in its English version. If we consider each Wikipedia article as a node and each hyperlink between articles as an arc we have a “Wikigraph”, a graph that represents the link structure of Wikipedia. The Wikigraph differs from other Web graphs studied in the literature by the fact that there are timestamps associated with each node. The timestamps indicate the creation and update dates of each page, and this allows us to do a detailed analysis of the Wikipedia evolution over time. In the first part of this study we characterize this evolution in terms of users, editions and articles; in the second part, we depict the temporal evolution of several topological properties of the Wikigraph. The insights obtained from the Wikigraphs can be applied to large Web graphs from which the temporal data is usually not available. |
analysis, wiki | |
| Caldarelli, Guido; Capocci, Andrea; Servedio, Vito; Buriol, Luciana; Donato, Debora; Leonardi, Stefano | Preferential attachment in the growth of social networks: the case of Wikipedia | American Physical Society. APS March Meeting, March 13-17, 2006 | 2006 | [165] |
Here we present experimental data and a model in order to describe the evolution of a socio-technological system. The case of study presented is that of the online free encyclopedia Wikipedia, for which we have the complete series of pages addition during time. The varioius entries and the hyperlinks between them can be described as a graph. We find scale-invariant behaviour in the distribution of the degree and a topology similar to that of the World Wide Web. By using the information on dynamics we are able to model and reproduce the features of this system. We also find that regardless the fact that any user has the possibility of global reshape, still Wikipedia has a growth described by local rules as that of the preferential attachment. |
link mining, small world, web, wikipedia | |
| Caldarelli, Guido; Capocci, Andrea; Servedio, Vito; Buriol, Luciana; Donato, Debora; Leonardi, Stefano | Preferential attachment in the growth of social networks: the case of Wikipedia | American Physical Society. APS March Meeting, March 13-17, 2006 | 2006 | [166] |
Here we present experimental data and a model in order to describe the evolution of a socio-technological system. The case of study presented is that of the online free encyclopedia Wikipedia, for which we have the complete series of pages addition during time. The varioius entries and the hyperlinks between them can be described as a graph. We find scale-invariant behaviour in the distribution of the degree and a topology similar to that of the World Wide Web. By using the information on dynamics we are able to model and reproduce the features of this system. We also find that regardless the fact that any user has the possibility of global reshape, still Wikipedia has a growth described by local rules as that of the preferential attachment. |
||
| Mehler, Alexander | Text Linkage in the Wiki Medium - A Comparative Study | Proceedings of the EACL 2006 Workshop on New Text - Wikis and blogs and other dynamic text sources, Trento, Italy, April 3-7, pp. 1-8 | 2006 | [167] | Despite not mentioning Wikipedia in title or abstract, the paper discusses it as one of the main examples. |
We analyze four different types of document networks with respect to their small world characteristics. These characteristics allow distinguishing wiki-based systems from citation and more traditional text-based networks augmented by hyperlinks. The study provides evidence that a more appropriate network model is needed which better reflects the specifics of wiki systems. It puts emphasize on their topological differences as a result of wikirelated linking compared to other textbased networks. |
wikipedia |
| Mainguy Gaell | Wikipedia and science publishing. Has the time come to end the liaisons dangereuses? | paper presented at the 3rd NATO-UNESCO Advanced Research Workshop Science Education: Talent Recruitment and Public Understanding. Balatonfured, Hungary, 20-22 October 2006 | 2006 | [168] |
Structuring information into knowledge is an important challenge for the 21st century. The emergence of internet and the diffusion of collaborative practices provide new tools with which to build and share knowledge. Scientists are seeking efficient ways to get recognition and to diffuse their work while Wikipedia is seeking well grounded contributors to shape in-depth articles. Science publishing and Wikipedia are thus profoundly modifying access to knowledge and may provide suitable conditions for a reorganization of the academic landscape. |
Science publishing, Wikipedia, open access, knowledge management | |
| Ma, Cathy | The Social, Cultural, Economical Implications of the Wikipedia | Paper submitted to Computers and Writing Online 2005 | 2005 | [169] |
Wikipedia is a non-profit online project that aims at building an encyclopedia for everyone. It has attracted thousands of users to contribute and collaborate on a voluntary base. In this paper I argue that Wikipedia poses a new model of collaboration founded on three assumptions trust, openness and reduced barrier of participation as opposed to more conventional models of collaboration based on authority and hierarchy. With this new-found social structure in mind, the cultural implications of the Wikipedia will be discussed in relation to the notion of Commons-Based Peer Production (CBPP) as proposed by Benkler in 2002, concluded with an analysis of the challenges that are facing the Wikipedia project, the problem of credibility building and vandalism control. |
||
| Denise Anthony, Sean Smith, & Tim Williamson | Explaining Quality in Internet Collective Goods: Zealots and Good Samaritans in the Case of Wikipedia | Fall 2005 Innovation & Enterpreneurship Seminar at MIT | 2005 | [170] |
One important innovation in information and communication technology developed over the past decade was organizational rather than merely technological. Open source production is remarkable because it converts a private commodity (typically software) into a public good. A number of studies examine the factors motivating contributions to open source production goods, but we argue it is important to understand the causes of high quality contributions to such goods. In this paper, we analyze quality in the open source online encyclopedia Wikipedia. We find that, for users who create an online persona through a registered user name, the quality of contributions increases as the number of contributions increase, consistent with the idea of experts motivated by reputation and committed to the Wikipedia community. Unexpectedly, however, we find the highest quality contributions come from the vast numbers of anonymous “Good Samaritans” who contribute infrequently. Our findings that Good Samaritans as well as committed “Zealots” contribute high quality content to Wikipedia suggest that open source production is remarkable as much for its organizational as its technological innovation that enables vast numbers of anonymous one-time contributors to create high quality, essentially public goods. |
||
| Stvilia, B., Twidale, M. B., Gasser, L., Smith, L. C. | Information quality in a community-based encyclopedia | Knowledge Management: Nurturing Culture, Innovation, and Technology - Proceedings of the 2005 International Conference on Knowledge Management (pp. 101-113) | 2005 | [171] |
We examine the Information Quality aspects of Wikipedia. By a study of the discussion pages and other process-oriented pages within the Wikipedia project, it is possible to determine the information quality dimensions that participants in the editing process care about, how they talk about them, what tradeoffs they make between these dimensions and how the quality assessment and improvement process operates. This analysis helps in understanding how high quality is maintained in a project where anyone may participate with no prior vetting. It also carries implications for improving the quality of more conventional datasets. |
information quality, negotiations | |
| Stvilia, B., Twidale, M. B., Gasser, L., Smith, L. C. | Assessing information quality of a community-based encyclopedia | Proceedings of the International Conference on Information Quality - ICIQ 2005. Cambridge, MA. 442-454 | 2005 | [172] |
Effective information quality analysis needs powerful yet easy ways to obtain metrics. The English version of Wikipedia provides an extremely interesting yet challenging case for the study of Information Quality dynamics at both macro and micro levels. We propose seven IQ metrics which can be evaluated automatically and test the set on a representative sample of Wikipedia content. The methodology of the metrics construction and the results of tests, along with a number of statistical characterizations of Wikipedia articles, their content construction, process metadata and social context are reported. |
information quality | |
| Ruiz M. Casado and Enrique Alfonseca and Pablo Castells | Automatic Extraction of Semantic Relationships for WordNet by Means of Pattern Learning from Wikipedia | Natural Language Processing and Information Systems: 10th International Conference on Applications of Natural Language to Information Systems, NLDB 2005, Alicante, Spain, June 15-17, 2005: Proceedings, 2005 | 2005 | [173] |
This paper describes an automatic approach to identify lexical patterns which represent semantic relationships between concepts, from an on-line encyclopedia. Next, these patterns can be applied to extend existing ontologies or semantic networks with new relations. The experiments have been performed with the Simple English Wikipedia and WordNet 1.7. A new algorithm has been devised for automatically generalising the lexical patterns found in the encyclopedia entries. We have found general patterns for the hyperonymy, hyponymy, holonymy and meronymy relations and, using them, we have extracted more than 1200 new relationships that did not appear in WordNet originally. The precision of these relationships ranges between 0.61 and 0.69, depending on the relation. |
learning, semantic wikipedia | |
| Emigh, William and Herring, Susan C. | Collaborative Authoring on the Web: A Genre Analysis of Online Encyclopedias | Paper presented at the 39th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences. ≪ Collaboration Systems and Technology Track ≫, Hawai. | 2005 | [174] |
This paper presents the results of a genre analysis of two web-based collaborative authoring environments, Wikipedia and Everything2, both of which are intended as repositories of encyclopedic knowledge and are open to contributions from the public. Using corpus linguistic methods and factor analysis of word counts for features of formality and informality, we show that the greater the degree of post-production editorial control afforded by the system, the more formal and standardized the language of the collaboratively-authored documents becomes, analogous to that found in traditional print encyclopedias. Paradoxically, users who faithfully appropriate such systems create homogeneous entries, at odds with the goal of open-access authoring environments to create diverse content. The findings shed light on how users, acting through mechanisms provided by the system, can shape (or not) features of content in particular ways. We conclude by identifying sub-genres of webbased collaborative authoring environments based on their technical affordances. |
collaboration | |
| Rafaeli, Sheizaf, Hayat, Tsahi and Ariel, Yaron | Wikipedia Participants and "Ba": Knowledge Building and Motivations. | Paper Presented at Cyberculture 3rd Global Conference. Prague, Czech Republic | 2005 | [175] | English | ||
| Rafaeli, Sheizaf, Hayat, Tsahi and Ariel, Yaron | Wikipedians' sense of community, motivations, and knowledge building. | Proceedings of Wikimania 2005 - The First International Wikimedia Conference, Frankfurt, Germany | 2005 | [176] | English |
In this paper, we examine the discursive situation of Wikipedia. The primary goal is to explore principle ways of analyzing and characterizing the various forms of communicative user interaction using Foucault"s discourse theory. First, the communicative situation of Wikipedia is addressed and a list of possible forms of communication is compiled. Second, the current research on the linguistic features of Wikis, especially Wikipedia, is reviewed. Third, some key issues of Foucault"s theory are explored: the notion of "discourse", the discursive formation, and the methods of archaeology and genealogy, respectively. Finally, first steps towards a qualitative discourse analysis of the English Wikipedia are elaborated. The paper argues, that Wikipedia can be understood as a discursive formation that regulates and structures the production of statements. Most of the discursive regularities named by Foucault are established in the collaborative writing processes of Wikipedia, too. Moreover, the editing processes can be described in Foucault"s terms as discursive knowledge production. |
|
| Krotzsch, Markus, Denny Vrandecic, Max Volkel | Wikipedia and the Semantic Web The Missing Links | Wikimania'05 | 2005 | [177] | Follow-up? [178] |
Wikipedia is the biggest collaboratively created source of encyclopaedic knowledge. Growing beyond the borders of any traditional encyclopaedia, it is facing new problems of knowledge management: The current excessive usage of article lists and categories witnesses the fact that 19th century content organization technologies like inter-article references and indices are no longer su#cient for today's needs. Rather, it is necessary to allow knowledge processing in a computer assisted way, for example to intelligently query the knowledge base. To this end, we propose the introduction of typed links as an extremely simple and unintrusive way for rendering large parts of Wikipedia machine readable. We provide a detailed plan on how to achieve this goal in a way that hardly impacts usability and performance, propose an implementation plan, and discuss possible difficulties on Wikipedia's way to the semantic future of the World Wide Web. The possible gains of thisendeavor are huge; we sketch them by considering some immediate applications that semantic technologies can provide to enhance browsing, searching, and editing Wikipedia. |
Semantic web, Wikipedia |
| Buntine, Wray | Static Ranking of Web Pages, and Related Ideas | Open Source Web Information Retrieval | 2005 | [179] | Link-based analysis | ||
| Voss, Jakob | Measuring Wikipedia. | Proceedings International Conference of the International Society for Scientometrics and Informetrics : 10th, Stockholm (Sweden) | 2005 | [180] |
Wikipedia, an international project that uses Wiki software to collaboratively create an encyclopaedia, is becoming more and more popular. Everyone can directly edit articles and every edit is recorded. The version history of all articles is freely available and allows a multitude of examinations. This paper gives an overview on Wikipedia research. Wikipedia’s fundamental components, i.e. articles, authors, edits, and links, as well as content and quality are analysed. Possibilities of research are explored including examples and first results. Several characteristics that are found in Wikipedia, such as exponential growth and scale-free networks are already known in other context. However the Wiki architecture also possesses some intrinsic specialities. General trends are measured that are typical for all Wikipedias but vary between languages in detail. |
social web, wikipedia | |
| Bellomi, Francesco and Roberto Bonato | Network Analysis for Wikipedia | Proceedings of Wikimania 2005, Frankfurt, Germany. | 2005 | [181] |
Network analysis is concerned with properties related to connectivity and distances in graphs, with diverse applications like citation indexing and information retrieval on the Web. HITS (Hyperlink-Induced Topic Search) is a network analysis algorithm that has been successfully used for ranking web pages related to a common topic according to their potential relevance. HITS is based on the notions of hub and authority: a good hub is a page that points to several good authorities; a good authority is a page that is pointed at by several good hubs. HITS exclusively relies on the hyperlink relations existing among the pages, to define the two mutually reinforcing measures of hub and authority. It can be proved that for each page these two weights converge to fixed points, the actual hub and authority values for the page. Authority is used to rank pages resulting from a given query (and thus potentially related to a given topic) in order of relevance. The hyperlinked structure of Wikipedia and the ongoing, incremental editing process behind it make it an interesting and unexplored target domain for network analysis techniques. In particular, we explored the relevance of the notion of HITS's authority on this encyclopedic corpus. We've developed a crawler that extensively scans through the structure of English language Wikipedia articles, and that keeps track for each entry of all other Wikipedia articles pointed at in its de ̄nition. The result is a directed graph (roughly 500000 nodes, and more than 8 millions links), which consists for the most part of a big loosely connected component. Then we applied the HITS algorithm to the latter, thus getting a hub and authority weight associated to every entry. First results seem to be meaningful in characterizing the notion of authority in this peculiar domain. Highest-rank authorities seem to be for the most part lexical elements that denote particular and concrete rather than universal and abstract entities. More precisely, at the very top of the authority scale there are concepts used to structure space and time like country names, city names and other geopolitical entities (such as United States and many European countries), historical periods and landmark events (World War II, 1960s). "Television", "scientifc classification" and "animal" are the first three most authoritative common nouns. We will also present the first results issued from the application of well-known PageRank algorithm (Google's popular ranking metrics detailed in [2]) to the Wikipedia entries collected by our crawler. |
link-mining, wikipedia | |
| Reagle, Joseph M. | A Case of Mutual Aid: Wikipedia, Politeness, and Perspective Taking | Proceedings of Wikimania 2005?The First International Wikimedia Conference, Frankfurt, Germany. | 2005 | [182] |
The anarchist Peter Kropotkin once wrote that “Mutual aid is as much a law of animal life as mutual struggle” (1902). At the time, he was responding to arguments arising from Darwin's The Origin of Species: that in nature and society individual creatures ceaselessly struggle against each other for dominance. Kropotkin took pains to explain and provide examples of how animals and humans survive by cooperating with each other. Interestingly, Kropotkin also contributed the article on anarchism to the 1911 Encyclopadia Britannica, a collaborative product of the Scottish Enlightenment and a precursor to the Wikipedia, a collaborative, on-line, and free encyclopedia. This paper explores the character of “mutual aid” and interdependent decision making within the Wikipedia. I provide a brief introduction to Wikipedia, the key terms associated with group decision making, and the Wikipedia dispute resolution process. I then focus on the cultural norms (e.g., “good faith”) within Wikipedia that frame participation as a cooperative endeavor. In particular, I argue that the “neutral point of view policy” policy is not a source of conflict, as it is often perceived to be, but a resolution shaping norm. However, the naive understanding that this policy is about an unbiased neutrality is also problematic. I conclude by identifying some notions from negotiation literature that may be inappropriate or require adaptation to the Wikipedia case. |
collaboration, collective action, mutual aid, wiki, wikipedia | |
| Fissaha Adafre, Sisay and de Rijke, Maarten | Discovering Missing Links in Wikipedia | Proceedings of the Workshop on Link Discovery: Issues, Approaches and Applications (LinkKDD-2005) | 2005 | [183] |
In this paper we address the problem of discovering missing hypertext links in Wikipedia. The method we propose consists of two steps: first, we compute a cluster of highly similar pages around a given page, and then we identify candidate links from those similar pages that might be missing on the given page. The main innovation is in the algorithm that we use for identifying similar pages, LTRank, which ranks pages using co-citation and page title information. Both LTRank and the link discovery method are manually evaluated and show acceptable results, especially given the simplicity of the methods and conservativeness of the evaluation criteria. |
missing links, wikipedia, clustering, system issues | |
| Bryant, Susan, Andrea Forte and Amy Bruckman | Becoming Wikipedian: Transformation of participation in a collaborative online encyclopedia | Proceedings of GROUP International Conference on Supporting Group Work, 2005. pp 1.-10. | 2005 | [184] |
Traditional activities change in surprising ways when computermediated communication becomes a component of the activity system. In this descriptive study, we leverage two perspectives on social activity to understand the experiences of individuals who became active collaborators in Wikipedia, a prolific, cooperatively-authored online encyclopedia. Legitimate peripheral participation provides a lens for understanding participation in a community as an adaptable process that evolves over time. We use ideas from activity theory as a framework to describe our results. Finally, we describe how activity on the Wikipedia stands in striking contrast to traditional publishing and suggests a new paradigm for collaborative systems. |
community, incentives, wikipedia | |
| Ahn, David, Jijkoun, Valentin, Mishne, Gilad, Muller, Karin, de Rijke, Maarten, and Schlobach, Stefan | Using Wikipedia at the TREC QA Track | The Thirteenth Text Retrieval Conference (TREC 2004) | 2005 | [185] |
We describe our participation in the TREC 2004 Question Answering track. We provide a detailed account of the ideas underlying our approach to the QA task, especially to the so-called "other" questions. This year we made essential use of Wikipedia, the free online encyclopedia, both as a source of answers to factoid questions and as an importance model to help us identify material to be returned in response to "other" questions. |
question-answering, semantic text-mining, wikipedia | |
| Augur, Naomi, Ruth Raitman and Wanlei Zhou | Teaching and learning online with wikis | 21st Annual Conference of the Australasian Society for Computers in Learning in Tertiary Education. Perth, Australia: Australasian Society for Computers in Learning in Tertiary Education (ASCILITE). (5th?8th Dec 2004). 95?104. | 2004 | [186] | Despite Wikipedia not being mentioned in title or abstract, it is a common example and heavily discussed in article itself. |
Wikis are fully editable websites; any user can read or add content to a wiki site. This functionality means that wikis are an excellent tool for collaboration in an online environment. This paper presents wikis as a useful tool for facilitating online education. Basic wiki functionality is outlined and different wikis are reviewed to highlight the features that make them a valuable technology for teaching and learning online. Finally, the paper discuses a wiki project underway at Deakin University. This project uses a wiki to host an icebreaker exercise which aims to facilitate ongoing interaction between members of online learning groups. Wiki projects undertaken in America are outlined and future wiki research plans are also discussed. These wiki projects illustrate how e-learning practitioners can and are moving beyond their comfort zone by using wikis to enhance the process of teaching and learning online. |
wiki, teaching |
| Bellomi F., Bonato R. | Lexical Authorities in an Encyclopedic Corpus: a Case Study with Wikipedia. | Paper presented at the International Colloquium on ‘Word structure and lexical systems: models and applications’, December 16 - 18, 2004, University of Pavia, Pavia, Italy. | 2004 | [187] | Blog description only? | link-mining, wikipedia | |
| Lih, Andrew | Wikipedia as Participatory Journalism: Reliable Sources? | Paper presented at the 5th International Symposium on Online Journalism, April 16 - 17, 2004, Austin, Texas, United States. | 2004 | [188] |
Wikipedia is an Internet-based, user contributed encyclopedia that is collaboratively edited, and utilizes the wiki concept ? the idea that any user on the Internet can change any page within the Web site, even anonymously. Paradoxically, this seemingly chaotic process has created a highly regarded reference on the Internet. Wikipedia has emerged as the largest example of participatory journalism to date ? facilitating many-to-many communication among users editing articles, all working towards maintaining a neutral point of view ? Wikipedia’s mantra. This study examines the growth of Wikipedia and analyzes the crucial technologies and community policies that have enabled the project to prosper. It also analyzes Wikipedia’s articles that have been cited in the news media, and establishes a set of metrics based on established encyclopedia taxonomies and analyzes the trends in Wikipedia being used as a source. |
wikipedia, journalism | |
| Viegas, F. B., Wattenberg, M. and Dave, K. | Studying cooperation and conflict between authors with history flow visualizations | CHI 2004, 575-582. | 2004 | [189] |
The Internet has fostered an unconventional and powerful style of collaboration: “wiki” web sites, where every visitor has the power to become an editor. In this paper we investigate the dynamics of Wikipedia, a prominent, thriving wiki. We make three contributions. First, we introduce a new exploratory data analysis tool, the history flow visualization, which is effective in revealing patterns within the wiki context and which we believe will be useful in other collaborative situations as well. Second, we discuss several collaboration patterns highlighted by this visualization tool and corroborate them with statistical analysis. Third, we discuss the implications of these patterns for the design and governance of online collaborative social spaces. We focus on the relevance of authorship, the value of community surveillance in ameliorating antisocial behavior, and how authors with competing perspectives negotiate their differences. |
collaborative writing, social informatics, visualization, wikis | |
| Smolenski, Nikola | Wikipedia in Serbian language and Cyrillic script. | Presentation at scientific-technical conference "Contemporary informatic technologies - Internet and Cyrillic script", November 25, Bijeljina. | 2003 | [190] | Serbian? | ||
| Moller, Erik | Loud and clear: How Internet media can work. | Presentation at Open Cultures conference, June 5 - 6, Vienna. | 2003 | [191] | Video and no abstract? | ||
| Winkler, Stefan | Selbstorganisation der Kommunikation Wissenschaft - Offentlichkeit im virtuellen Raum, Koblenz, Forschungsstelle Wissenstransfer. | ? | 2003 | German | |||
| Primo, Alex Fernando Teixeira and Recuero, Raquel da Cunha | Hipertexto cooperativo: Uma analise da escrita coletiva a partir dos blogs e da Wikipedia. | Paper presented at Seminario Internacional da Comunicacao. ≪ Da aldeia global ao ciberespaco: Tecnologias do imaginario como extensao do homem ≫, Porto Alegre | 2003 | [192] | Portuguese |
O artigo tem o objetivo de analisar e discutir as caracteristicas da escrita coletiva, segundo o conceito de hipertexto cooperativo. A partir disso, discute-se como os blogs e a wikipedia (uma enciclopedia digital construida online) viabilizam a concretizacao de uma uma "web viva", ou seja, redigida e interligada pelos proprios internautas. |
Peer-reviewed journal articles
- This table is sortable.
| Authors | Title | Publisher | Year | Online | Notes | Abstract | Keywords |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Michaël R. Laurenta and Tim J. Vickers | Seeking Health Information Online: Does Wikipedia Matter? | Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association 16:471-479 | 2009 | [193] | English Wikipedia as a prominent source of online health information compared to other health information providers studied in this paper, based on its search engine ranking and page view statistics |
{{{2}}} |
Health informatics, Health education, Internet |
| Kristine L. Callis, Lindsey R. Christ, Julian Resasco, David W. Armitage, Jeremy D. Ash, Timothy T. Caughlin, Sharon F. Clemmensen, Stella M. Copeland, Timothy J. Fullman, Ryan L. Lynch, Charley Olson, Raya A. Pruner, Ernane H.M. Vieira-Neto, Raneve West-Singh, Emilio M. Bruna | Improving Wikipedia: educational opportunity and professional responsibility | Trends in Ecology & Evolution 24(4):177-179 | 2009 | Note Wikipedia as a science-society interface making it a professional responsibility for scientists to improve content on it | Ecology | ||
| Guido Urdaneta, Guillaume Pierre, Maarten van Steen | Wikipedia Workload Analysis for Decentralized Hosting | Elsevier Computer Networks 53(11), pp. 1830-1845. | 2009 | [194] |
We study an access trace containing a sample of Wikipedia’s traffic over a 107-day period aiming to identify appropriate replication and distribution strategies in a fully decentralized hosting environment. We perform a global analysis of the whole trace, and a detailed analysis of the requests directed to the English edition of Wikipedia. In our study, we classify client requests and examine aspects such as the number of read and save operations, significant load variations and requests for nonexisting pages. We also review proposed decentralized wiki architectures and discuss how they would handle Wikipedia’s workload. We conclude that decentralized architectures must focus on applying techniques to efficiently handle read operations while maintaining consistency and dealing with typical issues on decentralized systems such as churn, unbalanced loads and malicious participating nodes. |
Workload analysis; Wikipedia; Decentralized hosting; P2P | |
| Deborah Perron Tollefsen | WIKIPEDIA and the Epistemology of Testimony | Episteme, volume 6, number 1, pp. 8-24 | 2009 | [195] | Summarized in the Wikipedia Signpost |
In “Group Testimony” (2007) I argued that the testimony of a group cannot be understood (or at least cannot always be understood) in a summative fashion; as the testimony of some or all of the group members. In some cases, it is the group itself that testifies. I also argued that one could extend standard reductionist accounts of the justification of testimonial belief to the case of testimonial belief formed on the basis of group testimony. In this paper, I explore the issue of group testimony in greater detail by focusing on one putative source of testimony, that of Wikipedia. My aim is to the answer the following questions: Is Wikipedia a source of testimony? And if so, what is the nature of that source? Are we to understand Wikipedia entries as a collection of testimonial statements made by individuals, some subset of individuals, or is Wikipedia itself (the organization or the Wikipedia community) the entity that testifies? If Wikipedia itself is a source of testimony, what resources do we have for assessing the trustworthiness of such an unusual epistemic source? In answering these questions I hope to further elucidate the nature of collective epistemic agency (Tollefsen 2006), of which group testimony is a paradigm example. |
|
| K. Brad Wray | The Epistemic Cultures of Science and WIKIPEDIA: A Comparison | Episteme, volume 6, number 1, pp. 38-51 | 2009 | [196] | Summarized in the Wikipedia Signpost |
I compare the epistemic culture of Wikipedia with the epistemic culture of science, with special attention to the culture of collaborative research in science. The two cultures differ markedly with respect to (1) the knowledge produced, (2) who produces the knowledge, and (3) the processes by which knowledge is produced. Wikipedia has created a community of inquirers that are governed by norms very different from those that govern scientists. Those who contribute to Wikipedia do not ground their claims on their reputations as knowers, for they stand to lose nothing if and when their contributions are found to be misleading or false. And the immediacy of the medium encourages gossip and jokes. Hence, though we have some reason to believe that an invisible hand aids scientists in realizing their epistemic goals, we cannot ground our confidence in what is reported on Wikipedia on the fact that an invisible hand ensures quality. Nor is the information on Wikipedia aptly justified in a manner similar to the way testimony can be justified. |
|
| Lawrence M. Sanger | The Fate of Expertise after WIKIPEDIA | Episteme, volume 6, number 1, pp. 52-73 | 2009 | [197] | Summarized in the Wikipedia Signpost |
Wikipedia has challenged traditional notions about the roles of experts in the Internet Age. Section 1 sets up a paradox. Wikipedia is a striking popular success, and yet its success can be attributed to the fact that it is wide open and bottom-up. How can such a successful knowledge project disdain expertise? Section 2 discusses the thesis that if Wikipedia could be shown by an excellent survey of experts to be fantastically reliable, then experts would not need to be granted positions of special authority. But, among other problems, this thesis is self-stultifying. Section 3 explores a couple ways in which egalitarian online communities might challenge the occupational roles or the epistemic leadership roles of experts. There is little support for the notion that the distinctive occupations that require expertise are being undermined. It is also implausible that Wikipedia and its like might take over the epistemic leadership roles of experts. Section 4 argues that a main reason that Wikipedia’s articles are as good as they are is that they are edited by knowledgeable people to whom deference is paid, although voluntarily. But some Wikipedia articles suffer because so many aggressive people drive off people more knowledgeable than they are; so there is no reason to think that Wikipedia’s articles will continually improve. Moreover, Wikipedia’s commitment to anonymity further drives off good contributors. Generally, some decisionmaking role for experts is not just consistent with online knowledge communities being open and bottom-up, it is recommended as well. |
|
| P. D. Magnus | On Trusting WIKIPEDIA | Episteme, volume 6, number 1, pp. 74-90 | 2009 | [198] | Summarized in the Wikipedia Signpost |
Given the fact that many people use Wikipedia, we should ask: Can we trust it? The empirical evidence suggests that Wikipedia articles are sometimes quite good but that they vary a great deal. As such, it is wrong to ask for a monolithic verdict on Wikipedia. Interacting with Wikipedia involves assessing where it is likely to be reliable and where not. I identify five strategies that we use to assess claims from other sources and argue that, to a greater of lesser degree, Wikipedia frustrates all of them. Interacting responsibly with something like Wikipedia requires new epistemic methods and strategies. |
|
| Piotr Konieczny | Governance, Organization, and Democracy on the Internet: The Iron Law and the Evolution of Wikipedia | Sociological Forum, Volume 24, Issue 1, Pages 162-192, 31 Jan 2009 | 2009 | [199] (issue ToC) |
This study examines whether the Iron Law of Oligarchy exists in Wikipedia by analyzing how a key policy of the website regarding verifiability evolved into its current form. The study describes the decision-making processes of Wikipedia and shows that there are many factors preventing or slowing the development of oligarchy on Wikipedia. The study provides data advancing theoretical concepts related to the Iron Law of Oligarchy and the evolution of virtual communities and organizations; results and knowledge gained can also improve Wikipedia policies related to verifiability. Michels wrote: "who says organization, says oligarchy." I argue that we should follow this with a caveat: "who says wiki-organization, says no to oligarchy." |
community, democracy, Internet, oligarchy, iron law, organization, Wikipedia | |
| Ryan McGrady | Gaming against the greater good | First Monday, Volume 14, Number 2 - 2 February 2009 | 2009 | [200] |
Wikipedia has grown to be one of the most visited Web sites in the world. Despite its influence on popular culture and the way we think about knowledge production and consumption, the conversation about why and how it works —or whether it’s credible at all — is ongoing. This paper began as an examination of what the concept of “authority” means in Wikipedia and what role rhetoric might play in manufacturing this authority. But Wikipedia’s editors have functioned well as a community, having collaboratively developed a comprehensive set of social norms designed to place the project before any individual. Hence ideas like authority and rhetoric have only marginal roles in day–to–day activities. This paper takes an in–depth look at these norms and how they work, paying particular attention to a relatively new guideline that exemplifies the spirit of the Wikipedia community — “Gaming the system.”. |
||
| Fogarolli A. & Ronchetti M. | Extracting Semantics from Multimedia Content using Wikipedia | Special Issue of Scalable Computing: Practice and Experience v. 1895-1767 | 2009 | [201] |
Semantic-based information retrieval is an area of ongoing work. In this paper we present a solution for giving semantic support to multimedia content information retrieval in an e-Learning environment where very often a large number of multimedia objects and information sources are used in combination. Semantic support is given through intelligent use of Wikipedia in combination with statistical Information Extraction techniques. |
Content retrieval and filtering: search over semi-structural Web sources, Multimedia, Wikipedia, e-Learning | |
| Sean Hansen, Nicholas Berente, Kalle Lyytinen | Wikipedia, Critical Social Theory, and the Possibility of Rational Discourse | The Information Society, Volume 25, Number 1, January 2009 , pp. 38-59 | 2009 | [202] |
Information systems researchers that apply critical social perspectives frequently emphasize the potential for information technology to serve as a mechanism for increased rationalization, domination, and control. Such theorists often overlook or discount the liberating aspects of information systems. In this study, we apply the ideal of rational discourse developed by Jurgen Habermas to the phenomenon of Wikipedia in an effort to explore empirically the emancipatory potential of information systems. We contend that Wikipedia embodies an approximation of the necessary conditions for rational discourse. While several challenges persist, the example of Wikipedia illustrates the positive potential of information systems in supporting the emergence of more emancipatory forms of communication. The corresponding implications for researchers and design professionals alike are discussed. |
communicative action; critical social theory; discursive action; Habermas; rational discourse; social computing; Wikipedia | |
| Erik W. Black | Wikipedia and academic peer review: Wikipedia as a recognised medium for scholarly publication? | Online Information Review 32(1):73-88 | 2008 | doi:10.1108/14684520810865994 | |||
| Don Fallis | Toward an Epistemology of Wikipedia | Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, Vol. 59, No. 10, pp. 1662-1674 | 2008 | [203] |
Wikipedia (the "free online encyclopedia that anyone can edit") is having a huge impact on how a great many people gather information about the world. So, it is important for epistemologists and information scientists to ask whether or not people are likely to acquire knowledge as a result of having access to this information source. In other words, is Wikipedia having good epistemic consequences? After surveying the various concerns that have been raised about the reliability of Wikipedia, this paper argues that the epistemic consequences of people using Wikipedia as a source of information are likely to be quite good. According to several empirical studies, the reliability of Wikipedia compares favorably to the reliability of traditional encyclopedias. Furthermore, the reliability of Wikipedia compares even more favorably to the reliability of those information sources that people would be likely to use if Wikipedia did not exist (viz., websites that are as freely and easily accessible as Wikipedia). In addition, Wikipedia has a number of other epistemic virtues (e.g., power, speed, and fecundity) that arguably outweigh any deficiency in terms of reliability. Even so, epistemologists and information scientists should certainly be trying to identify changes (or alternatives) to Wikipedia that will bring about even better epistemic consequences. This paper suggests that, in order to improve Wikipedia, we need to clarify what our epistemic values are and we need a better understanding of why Wikipedia works as well as it does. |
Encyclopedias, Epistemic Values, Mass Collaboration, Reliability, Social Epistemology, Verifiability, Wikipedia, Wisdom of Crowds | |
| Jon W. Huss III, Camilo Orozco, James Goodale, Chunlei Wu, Serge Batalov, Tim J. Vickers, Faramarz Valafar, Andrew I. Su | A Gene Wiki for Community Annotation of Gene Function | PLoS Biology | 2008 | [204] | Gene Wiki, biology, gene annotation | ||
| Yair Amichai–Hamburger, Naama Lamdan, Rinat Madiel, Tsahi Hayat | Personality Characteristics of Wikipedia Members | CyberPsychology & Behaviour | 2008 | [205] | Full article PDF |
Wikipedia is an online, free access, volunteer-contributed encyclopedia. This article focuses on the Wikipedians’ (Wikipedia users) personality characteristics, studying Wikipedians’ conceptions of Real-Me and BFI dimensions. To survey these aspects, we posted links to two online web questionnaires; one was targeted at Wikipedians and the second to non-Wikipedia users. One hundred and thirty-nine subjects participated in the study, of which 69 were active Wikipedia members. It was found that Wikipedia members locate their real me on the Internet more frequently as compared to non-Wikipedia members. Variance analysis revealed significant differences between Wikipedia members and non-Wikipedia members in agreeableness, openness, and conscientiousness, which were lower for the Wikipedia members. An interaction was found between Wikipedia membership and gender: introverted women were more likely to be Wikipedia members as compared with extroverted women. The results of this study are discussed with special emphasis on the understanding of the motivators of Wikipedia members. |
personality, Big Five Questionnaire
|
| Clauson, Kevin A; Hyla H Polen, Maged N Kamel Boulos & Joan H Dzenowagis | Scope, Completeness, and Accuracy of Drug Information in Wikipedia | The Annals of Pharmacotherapy | 2008 | [206] |
{{{2}}} |
drug information, eHealth, Wikipedia | |
| Olena Medelyan, Catherine Legg, David Milne and Ian H. Witten | Mining Meaning from Wikipedia | CoRR, vol. abs/0809.4530 | 2008 | [207] | An excellent survey paper |
Wikipedia is a goldmine of information; not just for its many readers, but also for the growing community of researchers who recognize it as a resource of exceptional scale and utility. It represents a vast investment of manual effort and judgment: a huge, constantly evolving tapestry of concepts and relations that is being applied to a host of tasks. This article provides a comprehensive description of this work. It focuses on research that extracts and makes use of the concepts, relations, facts and descriptions found in Wikipedia, and organizes the work into four broad categories: applying Wikipedia to natural language processing; using it to facilitate information retrieval and information extraction; and as a resource for ontology building. The article addresses how Wikipedia is being used as is, how it is being improved and adapted, and how it is being combined with other structures to create entirely new resources. We identify the research groups and individuals involved, and how their work has developed in the last few years. We provide a comprehensive list of the open-source software they have produced. We also discuss the implications of this work for the long-awaited semantic web. |
Wikipedia, Semantic Relatedness, NLP, IR |
| Katherine Ehmann, Andrew Large, and Jamshid Beheshti | Collaboration in context: Comparing article evolution among subject disciplines in Wikipedia | First Monday, volume 13, issue 10. | 2008 | [208] |
This exploratory study examines the relationships between article and Talk page contributions and their effect on article quality in Wikipedia. The sample consisted of three articles each from the hard sciences, soft sciences, and humanities, whose talk page and article edit histories were observed over a five–month period and coded for contribution types. Richness and neutrality criteria were then used to assess article quality and results were compared within and among subject disciplines. This study reveals variability in article quality across subject disciplines and a relationship between Talk page discussion and article editing activity. Overall, results indicate the initial article creator’s critical role in providing a framework for future editing as well as a remarkable stability in article content over time. |
Wikipedia, open source, encyclopedias, reference materials, information sources, article quality, article development | |
| Joachim Schroer and Guido Hertel | Voluntary engagement in an open web-based encyclopedia: Wikipedians, and why they do it. | Media Psychology, volume 12, issue 1, 96-120 | 2009 | [209] [210] |
The online encyclopedia Wikipedia is a highly successful “Open Content” project, written and maintained completely by volunteers. Little is known, however, about the motivation of these volunteers. Results from an online survey among 106 contributors to the German Wikipedia project are presented. Both motives derived from social sciences (perceived benefits, identification with Wikipedia, etc.) as well as perceived task characteristics (autonomy, skill variety, etc.) were assessed as potential predictors of contributors’ satisfaction and self-reported engagement. Satisfaction ratings were particularly determined by perceived benefits, identification with the Wikipedia community, and task characteristics. Engagement was particularly determined by high tolerance for opportunity costs and by task characteristics, the latter effect being partially mediated by intrinsic motivation. Relevant task characteristics for contributors’ engagement and satisfaction were perceived autonomy, task significance, skill variety, and feedback. Models from social sciences and work psychology complemented each other by suggesting that favorable task experiences might counter perceived opportunity costs in Wikipedia contributors. Moreover, additional data reported by Wikipedia authors indicate the importance of generativity motives. |
Volunteerism, Wikipedia, Open Content, Open Source, Intrinsic Motivation, Task
Characteristics, Generativity | |
| Lucy Holman Rector | Comparison of Wikipedia and other encyclopedias for accuracy, breadth, and depth in historical articles | Reference Services Review Volume: 36 Issue: 1 Page: 7 - 22 DOI: 10.1108/00907320810851998 | 2008 | [211] |
This paper seeks to provide reference librarians and faculty with evidence regarding the comprehensiveness and accuracy of Wikipedia articles compared with respected reference resources. |
Encyclopaedias, Reference services | |
| Sheizaf Rafaeli and Yaron Ariel | Online motivational factors: Incentives for participation and contribution in Wikipedia. | Psychological aspects of cyberspace: Theory, research, applications pp. 243-267 | 2008 | [212] | Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. | motivations, users, user generated content UGC | |
| Matthijs den Besten and Jean-Michel Dalle | Keep it Simple: A Companion for Simple Wikipedia? | Industry & Innovation 15(2):169-178 | 2008 | [213] |
In this paper, we inquire about some of the ways in which the community around Simple Wikipedia—an offspring of Wikipedia, the notorious free online encyclopedia—manages the online collaborative production of reliable knowledge. We focus on how it keeps its collection of articles “simple” and easy to read. We find that the labeling of pages as “unsimple” by core members of the community plays a significant but seemingly insufficient role. We suggest that the nature of this mode of decentralized knowledge production and the structure of Wiki-technology might call for the implementation of an editorial companion to the community. |
readability, companions, quality assurance | |
| Diomidis Spinellis and Panagiotis Louridas | The Collaborative Organization of Knowledge | Communications of the ACM 51(8):68–73 | 2008 | [214] |
Wikipedia is an ongoing endeavor to create a free encyclopedia through an open computer-mediated collaborative effort. A longitudinal study of Wikipedia's evolution shows that although Wikipedia's scope is increasing, its coverage is not deteriorating. This can be explained by the fact that referring to an non-existing entry typically leads to the establishment of an article for it. Wikipedia's evolution also demonstrates the creation of a large real world scale-free graph through a combination of incremental growth and preferential attachment. |
Wikipedia, references, growth, coverage, scale-free graph | |
| Müller, C., Meuthrath, B., Baumgraß, A. | Analyzing Wiki-based Networks to Improve Knowledge Processes in Organizations | Journal of Universal Computer Science, 14(4) | 2008 | [215] |
Increasingly wikis are used to support existing corporate knowledge exchange processes. They are an appropriate software solution to support knowledge processes. However, it is not yet proven whether wikis are an adequate knowledge management tool or not. This paper presents a new approach to analyze existing knowledge exchange processes in wikis based on network analysis. Because of their dynamic characteristics four perspectives on wiki networks are introduced to investigate the interrelationships between people, information, and events in a wiki information space. As an analysis method the Social Network Analysis (SNA) is applied to uncover existing structures and temporal changes. A scenario data set of an analysis conducted with a corporate wiki is presented. The outcomes of this analysis were utilized to improve the existing corporate knowledge processes. |
collaboration network, knowledge work, network analysis, social software, wiki | |
| Stvilia, B., Gasser, L. | An activity theoretic model for information quality change | First Monday, 13(4) | 2008 | [216] |
To manage information quality (IQ) effectively, one needs to know how IQ changes over time, what causes it to change, and whether the changes can be predicted. In this paper we analyze the structure of IQ change in Wikipedia, an open, collaborative general encyclopedia. We found several patterns in Wikipedia’s IQ process trajectories and linked them to article types. Drawing on the results of our analysis, we develop a general model of IQ change that can be used for reasoning about IQ dynamics in many different settings, including traditional databases and information repositories. |
Wikipedia, Activity Theory, Information Quality | |
| Stvilia, B., Twidale, M., Smith, L. C., Gasser, L. | Information quality work organization in Wikipedia | JASIST, 59(6), 983–1001 | 2008 | [217] |
The classic problem within the information quality (IQ) research and practice community has been the problem of defining IQ. It has been found repeatedly that IQ is context sensitive and cannot be described, measured, and assured with a single model. There is a need for empirical case studies of IQ work in different systems to develop a systematic knowledge that can then inform and guide the construction of context-specific IQ models. This article analyzes the organization of IQ assurance work in a large-scale, open, collaborative encyclopedia—Wikipedia. What is special about Wikipedia as a resource is that the quality discussions and processes are strongly connected to the data itself and are accessible to the general public. This openness makes it particularly easy for researchers to study a particular kind of collaborative work that is highly distributed and that has a particularly substantial focus, not just on error detection, but also on error correction. We believe that the study of those evolving debates and processes and of the IQ assurance model as a whole has useful implications for the improvement of quality in other more conventional databases. |
Collaborative Quality Control, Collaborative Content Creation, Information Quality, Distributed Collective Practices | |
| Marek Meyer, Christoph Rensing and Ralf Steinmetz | Using community-generated contents as a substitute corpus for metadata generation. | International Journal of Advanced Media and Communications, Vol. 2, No. 1, 2008 | 2008 | [218] |
Metadata is crucial for reuse of Learning Resources. However, in the area of e-Learning, suitable training corpora for automatic classification methods are hardly available. This paper proposes the use of community-generated substitute corpora for classification methods. As an example for such a substitute corpus, the free online Encyclopaedia Wikipedia is used as a training corpus for domain-independent classification and keyword extraction of Learning Resources. |
e-learning, classification, categorization, metadata generation, Wikipedia, substitute corpus, online learning, learning resourses, reuse | |
| Shaul Oreg and Oded Nov | Exploring motivations for contributing to open source initiatives: The roles of contribution context and personal values. | Computers in Human Behavior, volume 24, issue 5, 2055-2073 | 2008 | [219] |
We explore contextual and dispositional correlates of the motivation to contribute to open source initiatives. We examine how the context of the open source project, and the personal values of contributors, are related to the types of motivations for contributing. A web-based survey was administered to 300 contributors in two prominent open source contexts: software and content. As hypothesized, software contributors placed a greater emphasis on reputation-gaining and self-development motivations, compared with content contributors, who placed a greater emphasis on altruistic motives. Furthermore, the hypothesized relationships were found between contributors' personal values and their motivations for contributing. |
Personal values; Motivations; Open source; Wikipedia | |
| Alexander Halavais, Derek Lackaff | An Analysis of Topical Coverage of Wikipedia | Journal of Computer-Mediated Communication, Vol. 13, No. 2. (2008), pp. 429-440. | 2008 | [220] |
Many have questioned the reliability and accuracy of Wikipedia. Here a different issue, but one closely related: how broad is the coverage of Wikipedia? Differences in the interests and attention of Wikipedia’s editors mean that some areas, in the traditional sciences, for example, are better covered than others. Two approaches to measuring this coverage are presented. The first maps the distribution of topics on Wikipedia to the distribution of books published. The second compares the distribution of topics in three established, field-specific academic encyclopedias to the articles found in Wikipedia. Unlike the top-down construction of traditional encyclopedias, Wikipedia’s topical coverage is driven by the interests of its users, and as a result, the reliability and completeness of Wikipedia is likely to be different depending on the subject-area of the article. |
collaboration, measurement, wiki, wikipedia | |
| Beate Elvebakk | Philosophy democratized? A comparison between Wikipedia and two other Web–based philosophy resources | First Monday, volume 13, issue 2 | 2008 | [221] | This article compares the individuals categorized as twentieth century philosophers in Wikipedia with the selection found in two major edited and widely used online philosophy resources, The Stanford Encyclopaedia of Philosophy (http://plato.stanford.edu), and the Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy (http://www.iep.utm.edu). These are both free online resources, but unlike Wikipedia, they are written and edited by members of the academic community, and thus sanctioned by the established communities. The individuals presented as twentieth century philosophers are compared along the parameters of year of birth, gender, and national and disciplinary backgrounds. The results show that although the types of academics listed in Wikipedia are generally similar to those in the other encyclopaedias, their relative youth and their very numbers may still serve to give the user a very different impression on philosophy as a field. Contents. |
||
| Luyt, Brendan, Tay Chee Hsien,Aaron, Lim Hai Thian, Cheng Kian Hong | Improving Wikipedia's accuracy: Is edit age a solution? | Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, volume 59, issue 2 | 2008 | [222] |
Wikipedia is fast becoming a key information source for many despite criticism that it is unreliable and inaccurate. A number of recommendations have been made to sort the chaff from the wheat in Wikipedia, among which is the idea of color-coding article segment edits according to age (Cross, 2006). Using data collected as part of a wider study published in Nature, this article examines the distribution of errors throughout the life of a select group of Wikipedia articles. The survival time of each error edit in terms of the edit counts and days was calculated and the hypothesis that surviving material added by older edits is more trustworthy was tested. Surprisingly, we find that roughly 20% of errors can be attributed to surviving text added by the first edit, which confirmed the existence of a first-mover effect (Viegas, Wattenberg, & Kushal, 2004) whereby material added by early edits are less likely to be removed. We suggest that the sizable number of errors added by early edits is simply a result of more material being added near the beginning of the life of the article. Overall, the results do not provide support for the idea of trusting surviving segments attributed to older edits because such edits tend to add more material and hence contain more errors which do not seem to be offset by greater opportunities for error correction by later edits. |
error correction; Internet information resources; editing; accuracy; temporal currency | |
| Nielsen, Finn Årup | Scientific citations in Wikipedia | First Monday, volume 12, issue 8 | 2007 | [223] |
The Internet–based encyclopædia Wikipedia has grown to become one of the most visited Web sites on the Internet, but critics have questioned the quality of entries. An empirical study of Wikipedia found errors in a 2005 sample of science entries. Biased coverage and lack of sources are among the “Wikipedia risks.” This paper describes a simple assessment of these aspects by examining the outbound links from Wikipedia articles to articles in scientific journals with a comparison against journal statistics from Journal Citation Reports such as impact factors. The results show an increasing use of structured citation markup and good agreement with citation patterns seen in the scientific literature though with a slight tendency to cite articles in high–impact journals such as Nature and Science. These results increase confidence in Wikipedia as a reliable information resource for science in general. |
Wikipedia; impact factor; citation | |
| Willinsky, John | What open access research can do for Wikipedia | First Monday volume 12, issue 3 | 2007 | [224] | "The open access references that we were able to locate for the smaller sample of twenty entries in the course of the study have now been added to the relevant Wikipedia articles and clearly marked with a link to the “open access copy” (by Sarah Munro" |
This study examines the degree to which Wikipedia entries cite or reference research and scholarship, and whether that research and scholarship is generally available to readers. Working on the assumption that where Wikipedia provides links to research and scholarship that readers can readily consult, it increases the authority, reliability, and educational quality of this popular encyclopedia, this study examines Wikipedia’s use of open access research and scholarship, that is, peer-reviewed journal articles that have been made freely available online. This study demonstrates among a sample of 100 Wikipedia entries, which included 168 sources or references, only two percent of the entries provided links to open access research and scholarship. However, it proved possible to locate, using Google Scholar and other search engines, relevant examples of open access work for 60 percent of a sub-set of 20 Wikipedia entries. The results suggest that much more can be done to enrich and enhance this encyclopedia’s representation of the current state of knowledge. To assist in this process, the study provides a guide to help Wikipedia contributors locate and utilize open access research and scholarship in creating and editing encyclopedia entries. |
|
| Simone P. Ponzetto and Michael Strube | Knowledge Derived from Wikipedia for Computing Semantic Relatedness | Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 30: 181--212, 2007. | 2007 | [225] |
Wikipedia provides a semantic network for computing semantic relatedness in a more structured fashion than a search engine and with more coverage than WordNet. We present experiments on using Wikipedia for computing semantic relatedness and compare it to WordNet on various benchmarking datasets. Existing relatedness measures perform better using Wikipedia than a baseline given by Google counts, and we show that Wikipedia outperforms WordNet on some datasets. We also address the question whether and how Wikipedia can be integrated into NLP applications as a knowledge base. Including Wikipedia improves the performance of a machine learning based coreference resolution system, indicating that it represents a valuable resource for NLP applications. Finally, we show that our method can be easily used for languages other than English by computing semantic relatedness for a German dataset. |
knowledge, knowledge-extraction relatedness semantic semantic web, wikipedia
| |
| Firer-Blaess, S. | Wikipédia: histoire, communauté, gouvernance | homo-numericus.net | July-October 2007 | [226] [227][228][229] |
Depuis sa création, Wikipedia est un véritable sujet de polémiques, en particulier au sein des milieux académiques qui se sentent menacés par la popularité de cette encyclopédie ouverte, sans doute parce que, éditable et amendable par tous, elle remet en question ce qu'ils estiment relever d'un monopole légitime. Pour preuve, la récente « étude » diffusée par plusieurs étudiants de Science Po, cherchant à mettre en évidence la faillibilité de l'encyclopédie, sur la base d'erreurs qu'ils y ont volontairement introduits. Au delà d'interrogations un peu puériles sur la qualité ou l'absence de qualité intrinsèque de cette encyclopédie qu'on aborderait comme un « produit » fini, il peut être intéressant de se pencher sur le mode de fonctionnement de cette entreprise, considérée cette fois comme un système social, un lieu de coordination et de coopération entre plusieurs milliers de participants ; amendable par tous, éditable indéfiniment, Wikipédia n'est en effet jamais « finie » - pas plus que ne l'est le savoir d'ailleurs, en perpétuel renouvellement. De ce simple fait, il est bien plus pertinent de s'interroger sur la manière dont le travail de co-construction des connaissance s'accomplit en permanence, que sur la « verité » de tel ou tel énoncé qui y serait produit. C'est exactement ce que fait Sylvain Firer-Blaess dans cette série de trois articles qu'il a accepté de publier pour Homo Numericus. S'appuyant sur les travaux de Foucault, mais pas ceux auquel on s'attendrait, il développe une analyse politique percutante de Wikipedia comme lieu où s'exerce et refuse de s'exercer en même temps une certaine forme de pouvoir. Pour lui, et il l'expliquera dans ses deuxième et troisième parties de cette série, Wikipédia est traversé d'une tension qui lui est propre et qu'il tente de qualifier en démontant à la fois les moeurs et les mécanismes de régulation de cette communauté très particulière. Pour l'heure, il nous la présente, dans ses dimension techniques et historiques. Ce travail est issu d'un mémoire de fin d'étude présenté à l'IEP de Lyon. |
Wikipedia, History, Governance, Power Structure | |
| Nielsen, Finn Årup | Scientific Citations in Wikipedia | First Monday 12(8) | August 2007 | [230] | The Internet-based encyclopædia Wikipedia has grown to become one of the most visited Web sites on the Internet, but critics have questioned the quality of entries. An empirical study of Wikipedia found errors in a 2005 sample of science entries. Biased coverage and lack of sources are among the “Wikipedia risks.” The study here describes a simple assessment of these aspects by examining the outbound links from Wikipedia articles to articles in scientific journals with a comparison against journal statistics from Journal Citation Reports such as impact factors. The results show an increasing use of structured citation markup and good agreement with citation patterns seen in the scientific literature though with a slight tendency to cite articles in high-impact journals such as Nature and Science. These results increase confidence in Wikipedia as a reliable information resource for science in general. |
Wikipedia, Citations, Information Quality | |
| Wilkinson, Dennis M. and Bernardo A. Huberman | Assessing the value of cooperation in Wikipedia | First Monday, volume 12, number 4 (March 2007) | 2007 | [231] |
Since its inception six years ago, the online encyclopedia Wikipedia has accumulated 6.40 million articles and 250 million edits, contributed in a predominantly undirected and haphazard fashion by 5.77 million unvetted volunteers. Despite the apparent lack of order, the 50 million edits by 4.8 million contributors to the 1.5 million articles in the English–language Wikipedia follow strong certain overall regularities. We show that the accretion of edits to an article is described by a simple stochastic mechanism, resulting in a heavy tail of highly visible articles with a large number of edits. We also demonstrate a crucial correlation between article quality and number of edits, which validates Wikipedia as a successful collaborative effort. |
cooperation, Wikipedia | |
| Nicolas Auray, Céline Poudat, Pascal Pons | Democratizing scientific vulgarization. The balance between cooperation and conflict in french Wikipedia | Observatorio (OBS*), Vol 1, No 3 (2007) | 2007 | [232] |
The free online encyclopedia project Wikipedia has become in less than six years one of the most prominent commons-based peer production example. The present study investigates the patterns of involvement and the patterns of cooperation within the French version of the encyclopaedia. In that respect, we consider different groups of users, highlighting the opposition between passerby contributors and core members, and we attempt to evaluate for each class of contributors the main motivations for their participation to the project. Then, we study the qualitative and quantitative patterns of cowriting and the correlation between size and quality of the production process. |
||
| Maria Ruiz-Casado, Enrique Alfonseca and Pablo Castells | Automatising the Learning of Lexical Patterns: an Application to the Enrichment of WordNet by Extracting Semantic Relationships from Wikipedia | Data & Knowledge Engineering Volume 61 , Issue 3 (June 2007) Pages 484-499 | 2007 | [233] |
This paper describes Koru, a new search interface that offers effective domain-independent knowledge-based information retrieval. Koru exhibits an understanding of the topics of both queries and documents. This allows it to (a) expand queries automatically and (b) help guide the user as they evolve their queries interactively. Its understanding is mined from the vast investment of manual effort and judgment that is Wikipedia. We show how this open, constantly evolving encyclopedia can yield inexpensive knowledge structures that are specifically tailored to expose the topics, terminology and semantics of individual document collections. We conducted a detailed user study with 12 participants and 10 topics from the 2005 TREC HARD track, and found that Koru and its underlying knowledge base offers significant advantages over traditional keyword search. It was capable of lending assistance to almost every query issued to it; making their entry more efficient, improving the relevance of the documents they return, and narrowing the gap between expert and novice seekers. |
Information extraction, Lexical patterns, Ontology and thesaurus acquisition, Relation extraction | |
| Neil L Waters | Why you can't cite Wikipedia in my class | Communications of the ACM Volume 50 , Issue 9 (September 2007) | 2007 | [234] |
The online encyclopedia's method of adding information risks conflating facts with popular opinion. |
education | |
| Fabian M. Suchanek, Gjergji Kasneci and Gerhard Weikum | Yago: A Large Ontology from Wikipedia and WordNet | forthcoming in Elsevier Journal of Web Semantics (?) | 2007 (?) | [235] |
This article presents YAGO, a large ontology with high coverage and precision. YAGO has been automatically derived from Wikipedia and WordNet. It comprises entities and relations, and currently contains more than 1.7 million entities and 15 million facts. These include the taxonomic Is-A hierarchy as well as semantic relations between entities. The facts for YAGO have been extracted from the category system and the infoboxes of Wikipedia and have been combined with taxonomic relations fromWordNet. Type checking techniques help us keep YAGO’s precision at 95% – as proven by an extensive evaluation study. YAGO is based on a clean logical model with a decidable consistency. Furthermore, it allows representing n-ary relations in a natural way while maintaining compatibility with RDFS. A powerful query model facilitates access to YAGO’s data. |
||
| Gang Wang and Huajie Zhang and Haofen Wang and Yong Yu | Enhancing Relation Extraction by Eliciting Selectional Constraint Features from Wikipedia | Natural Language Processing and Information Systems, : 329--340, 2007. | 2007 | [236] |
Selectional Con straints are usually checked for detecting semantic relations. Previous work usually defined the constraints manually based on hand crafted concept taxonomy, which is time-consuming and impractical for large scale relation extraction. Further, the determination of entity type (e.g. NER) based on the taxonomy cannot achieve sufficiently high accuracy. In this paper, we propose a novel approach to extracting relation instances using the features elicited from Wikipedia, a free online encyclopedia. The features are represented as selectional constraints and further employed to enhance the extrac tion of relations. We conduct case stud ies on the validation of the ex tracted instances for two common relations has Artist (album, artist) and has Director (film, director). Substantially high extraction precision (around 0.95) and validation accuracy (near 0.90) are obtained. |
cooperation, Wikipedia | |
| Pierpaolo Dondio and Stephen Barret | Computational Trust in Web Content Quality: A Comparative Evalutation on the Wikipedia Project | Informatica 31 (2007) 151–160 151 | 2007 | [237] |
The problem of identifying useful and trustworthy information on the World Wide Web is becoming increasingly acute as new tools such as wikis and blogs simplify and democratize publication. It is not hard to predict that in the future the direct reliance on this material will expand and the problem of evaluating the trustworthiness of this kind of content become crucial. The Wikipedia project represents the most successful and discussed example of such online resources. In this paper we present a method to predict Wikipedia articles trustworthiness based on computational trust techniques and a deep domain-specific analysis. Our assumption is that a deeper understanding of what in general defines high-standard and expertise in domains related to Wikipedia – i.e. content quality in a collaborative environment – mapped onto Wikipedia elements would lead to a complete set of mechanisms to sustain trust in Wikipedia context. We present a series of experiment. The first is a study-case over a specific category of articles; the second is an evaluation over 8 000 articles representing 65% of the overall Wikipedia editing activity. We report encouraging results on the automated evaluation of Wikipedia content using our domain-specific expertise method. Finally, in order to appraise the value added by using domain-specific expertise, we compare our results with the ones obtained with a pre-processed cluster analysis, where complex expertise is mostly replaced by training and automatic classification of common features. |
computational trust, Wikipedia, content-quality | |
| Martin Hepp and Daniel Bachlechner and Katharina Siorpaes | Harvesting Wiki Consensus: Using Wikipedia Entries as Vocabulary for Knowledge Management | IEEE Internet Computing, Volume: 11, Issue: 5 Sept.-Oct. 2007 p. 54-65 | 2007 | [238] |
Vocabularies that provide unique identifiers for conceptual elements of a domain can improve precision and recall in knowledge-management applications. Although creating and maintaining such vocabularies is generally hard, wiki users easily manage to develop comprehensive, informal definitions of terms, each one identified by a URI. Here, the authors show that the URIs of Wikipedia entries are reliable identifiers for conceptual entities. They also demonstrate how Wikipedia entries can be used for annotating Web resources and knowledge assets and give precise estimates of the amount of Wikipedia URIs in terms of the popular Proton ontology's top-level concepts. |
URIs Wikipedia knowledge management ontologies semantic knowledge management wikis | |
| Andrew Dalby | Wikipedia(s) on the language map of the world | English Today (2007), 23: 3-8 Cambridge University Press | 2007 | [239] |
This article will not try to describe the whole Wikimedia galaxy. It will stick to Wikipedia in English, and that's ambitious enough. The English-language Wikipedia, by far the biggest of them, now (28th November 2006) contains 1,506,659 articles. The German Wikipedia reached 500,000 articles on 23rd November (note in passing: the English Wikipedia has added that many articles to its total in just six months), while the French Wikipedia reached the 400,000 milestone on 27th November. The newest and smallest Wikipedia, number 250, is in the Lak language of Dagestan, in the Caucasus, with one article and 20 users. One more statistical measure will show how much Wikipedia matters. People who Google already know that for a great many Google searches one or more Wikipedia entries will turn up high on the first page of the results. They don't all know that Wikipedia now comes eleventh in alexa.com's traffic ranking of world websites. For a strictly non-commercial site with relatively academic content, that is astonishing success; what's more, the trend is steadily upwards, though it will be hard to overtake the top four: yahoo.com, msn.com, google.com, and the highly popular Chinese search engine, baidu.com. |
||
| A Bhole, B Fortuna, M Grobelnik, D Mladenić | Extracting Named Entities and Relating Them over Time Based on Wikipedia | Informatica, 2007 | 2007 | [240] | Based on conference paper (Conference on Data Mining and Data Warehouses (SiKDD 2007)) "Mining Wikipedia and Relating Named Entities over Time" [241] |
This paper presents an approach to mining information relating people, places, organizations and events extracted from Wikipedia and linking them on a time scale. The approach consists of two phases: (1) identifying relevant pages - categorizing the articles as containing people, places or organizations; (2) generating timeline - linking named entities and extracting events and their time frame. We illustrate the proposed approach on 1.7 million Wikipedia articles. |
text mining, document categorization, information extraction |
| K Nakayama, T Hara, S Nishio | Wikipedia: A New Frontier for AI Researches | JOURNAL- JAPANESE SOCIETY FOR ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE 2007, VOL 22; NUMB 5, pages 693-701 | 2007 | ||||
| Rubén Rosario Rodríguez | Liberating Epistemology: Wikipedia and the Social Construction of Knowledge | Religious Studies and Theology, Vol 26, No 2 (2007) | 2007 | [242] |
This investigation contends that postfoundationalist models of rationality provide a constructive alternative to the positivist models of scientific rationality that once dominated academic discourse and still shape popular views on science and religion. Wikipedia, a free online encyclopedia, has evolved organically into a cross-cultural, cross-contextual, interdisciplinary conversation that can help liberate epistemology—especially theological epistemology—from the stranglehold of Enlightenment foundationalism. U.S. Latino/a theology provides an alternative to the dominant epistemological perspective within academic theology that is in many ways analogous to the organic, conversational epistemology embodied by the Wikipedia online community. Accordingly, this investigation argues that the work of human liberation is better served by liberating epistemology from the more authoritarian aspects of the Enlightenment scientific tradition—especially popular positivist conceptions of rationality. |
||
| BS Noveck | Wikipedia and the Future of Legal Education | JOURNAL OF LEGAL EDUCATION, 2007 | 2007 | [243] | peer reviewed? | ||
| L Devgan, N Powe, B Blakey, M Makary | Wiki-Surgery? Internal validity of Wikipedia as a medical and surgical reference | Journal of the American College of Surgeons, Volume 205, Issue 3, Supplement 1, September 2007, Pages S76-S77 | 2007 | [244] |
{{{2}}} |
||
| Brendan Luyt, Wee Kwek, Ju Sim, Peng York | Evaluating the Comprehensiveness of Wikipedia: The Case of Biochemistry | Asian Digital Libraries. Looking Back 10 Years and Forging New Frontiers (2007), pp. 512-513. | 2007 | [245] |
In recent years, the world of encyclopedia publishing has been challenged as new collaborative models of online information gathering and sharing have developed. Most notable of these is Wikipedia. Although Wikipedia has a core group of devotees, it has also attracted critical comment and concern, most notably in regard to its quality. In this article we compare the scope of Wikipedia and Encyclopedia Britannica in the subject of biochemistry using a popular first year undergraduate textbook as a benchmark for concepts that should appear in both works, if they are to be considered comprehensive in scope. |
quality, wikipedia | |
| Fernanda B Viégas, Martin Wattenberg, Matthew Mckeon | The Hidden Order of Wikipedia | EOnline Communities and Social Computing (2007), pp. 445-454. | 2007 | [246] |
We examine the procedural side of Wikipedia, the well-known internet encyclopedia. Despite the lack of structure in the underlying wiki technology, users abide by hundreds of rules and follow well-defined processes. Our case study is the Featured Article (FA) process, one of the best established procedures on the site. We analyze the FA process through the theoretical framework of commons governance, and demonstrate how this process blends elements of traditional workflow with peer production. We conclude that rather than encouraging anarchy, many aspects of wiki technology lend themselves to the collective creation of formalized process and policy. |
wikipedia | |
| Oded Nov | What motivates Wikipedians? | Communications of the ACM Volume 50 , Issue 11 (November 2007) Pages: 60 - 64 ISSN:0001-0782 | 2007 | [247] |
In order to increase and enhance user-generated content contributions, it is important to understand the factors that lead people to freely share their time and knowledge with others. |
wikipedia | |
| Davide Buscaldi, Paolo Rosso | A Bag-of-Words Based Ranking Method for the Wikipedia Question Answering Task | Evaluation of Multilingual and Multi-modal Information Retrieval (2007), pp. 550-553. | 2007 | [248] |
This paper presents a simple approach to the Wikipedia Question Answering pilot task in CLEF 2006. The approach ranks the snippets, retrieved using the Lucene search engine, by means of a similarity measure based on bags of words extracted from both the snippets and the articles in wikipedia. Our participation was in the monolingual English and Spanish tasks. We obtained the best results in the Spanish one. |
answering, question, ranking, wikipedia | |
| Miro Lehtonen, Antoine Doucet | EXTIRP: Baseline Retrieval from Wikipedia | Comparative Evaluation of XML Information Retrieval Systems (2007), pp. 115-120. | 2007 | [249] |
The Wikipedia XML documents are considered an interesting challenge to any XML retrieval system that is capable of indexing and retrieving XML without prior knowledge of the structure. Although the structure of the Wikipedia XML documents is highly irregular and thus unpredictable, EXTIRP manages to handle all the well-formed XML documents without problems. Whether the high flexibility of EXTIRP also implies high performance concerning the quality of IR has so far been a question without definite answers. The initial results do not confirm any positive answers, but instead, they tempt us to define some requirements for the XML documents that EXTIRP is expected to index. The most interesting question stemming from our results is about the line between high-quality XML markup which aids accurate IR and noisy “XML spam” that misleads flexible XML search engines. |
retrieval, wikipedia | |
| Yang Wang, Haofen Wang, Haiping Zhu, Yong Yu | Exploit Semantic Information for Category Annotation Recommendation in Wikipedia | Natural Language Processing and Information Systems (2007), pp. 48-60. | 2007 | [250] |
Compared with plain-text resources, the ones in “semi-semantic” web sites, such as Wikipedia, contain high-level semantic information which will benefit various automatically annotating tasks on themself. In this paper, we propose a “collaborative annotating” approach to automatically recommend categories for a Wikipedia article by reusing category annotations from its most similar articles and ranking these annotations by their confidence. In this approach, four typical semantic features in Wikipedia, namely incoming link, outgoing link, section heading and template item, are investigated and exploited as the representation of articles to feed the similarity calculation. The experiment results have not only proven that these semantic features improve the performance of category annotating, with comparison to the plain text feature; but also demonstrated the strength of our approach in discovering missing annotations and proper level ones for Wikipedia articles. |
cooperation, Wikipedia | |
| Muchnik, Lev; Royi Itzhack; Sorin Solomon; and Yoram Louzoun | Self-emergence of knowledge trees: Extraction of the Wikipedia hierarchies | Physical Review E 76, 016106 | 2007 | [251] |
The rapid accumulation of knowledge and the recent emergence of new dynamic and practically unmoderated information repositories have rendered the classical concept of the hierarchal knowledge structure irrelevant and impossible to impose manually. This led to modern methods of data location, such as browsing or searching, which conceal the underlying information structure. We here propose methods designed to automatically construct a hierarchy from a network of related terms. We apply these methods to Wikipedia and compare the hierarchy obtained from the article network to the complementary acyclic category layer of the Wikipedia and show an excellent fit. We verify our methods in two networks with no a priori hierarchy (the E. Coli genetic regulatory network and the C. Elegans neural network) and a network of function libraries of modern computer operating systems that are intrinsically hierarchical and reproduce a known functional order. |
||
| Konieczny, Piotr | Wikis and Wikipedia as a Teaching Tool | International Journal of Instructional Technology and Distance Learning, January 2007 | 2007 | [252] |
Wikis are a very versatile and easy-to-use tool that is finding increasing applications in teaching and learning. This paper will illustrate how teaching academics can join the wiki revolution. First. it will introduce the common wikis and then focus on Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia, which has become one of the most popular Internet sites and offers unique opportunities for teachers and learners. It will describe how wikis and Wikipedia are used as a teaching tool and how to develop them further.Wikipedia can be used for various assignments: for example, students can be asked to reference an unreferenced article or create a completely new one. In doing so, students will see that writing an article is not a 'tedious assignment' but an activity that millions do 'for fun'. By submitting their work to Wikipedia students will see their work benefiting – and being improved upon – by the entire world. |
wikis, wikipedia, teaching, education, classroom | |
| O'Donnell, Daniel Paul | If I were "You": How Academics Can Stop Worrying and Learn to Love "the Encyclopedia that Anyone Can Edit" | The Heroic Age: A Journal of Early Medieval Northwestern Europe, Issue 10, May 2007, ISSN 1526-1867 | 2007 | [253] |
"Electronic Medievalia" column in the Saints and Sanctity issue. Sections include: Time Magazine and the Participatory Web, Academic Resistance, Why the Participatory Web Works, Why Don't We Like It, Why We Can't Do Anything About It, and A New Model of Scholarship: The Wikipedia as Community Service | ||
| # Pentzold, Christian, Sebastian Seidenglanz, Claudia Fraas, Peter Ohler | Wikis. Bestandsaufnahme eines Forschungsfeldes und Skizzierung eines integrativen Anlayserahmens. | In: Medien und Kommunikationswissenschaft. 55(1), 61-79. | 2007 | ||||
| Martin Ebner | Wikipedia Hype oder Zukunftshoffnung für die Hochschullehre | E-Learning: Strategische Implementierungen und Studiengang, Tagungsband zur 13. FNMA-Tagung, Verlag Forum Neue Medien Austria S. 139-146 | 2007 | [254] | German | ||
| Pfeil, Ulrike, Panayiotis Zaphiris, Chee Siang Ang | Cultural Differences in Collaborative Authoring of Wikipedia | Journal of Computer-Mediated Communication, 12(1), article 5 | 2006 | [255] |
This article explores the relationship between national culture and computer-mediated communication (CMC) in Wikipedia. The articles on the topic game from the French, German, Japanese, and Dutch Wikipedia websites were studied using content analysis methods. Correlations were investigated between patterns of contributions and the four dimensions of cultural influences proposed by Hofstede (Power Distance, Collectivism versus Individualism, Femininity versus Masculinity, and Uncertainty Avoidance). The analysis revealed cultural differences in the style of contributions across the cultures investigated, some of which are correlated with the dimensions identified by Hofstede. These findings suggest that cultural differences that are observed in the physical world also exist in the virtual world. |
collaboration, cultural, differences, wikipedia | |
| B.T. Adler, L. de Alfaro. | A Content-Driven Reputation System for the Wikipedia. | Technical report ucsc-crl-06-18, School of Engineering, University of California, Santa Cruz, November 2006 | 2006 | [256] |
On-line forums for the collaborative creation of bodies of information are a phenomenon of rising importance; the Wikipedia is one of the best-known examples. The open nature of such forums could benefit from a notion of reputation for its authors. Author reputation could be used to flag new contributions from low-reputation authors, and it could be used to allow only authors with good reputation to contribute to controversial or critical pages. A reputation system for the Wikipedia would also provide an incentive to give high-quality contributions. We present in this paper a novel type of content-driven reputation system for Wikipedia authors. In our system, authors gain reputation when the edits and text additions they perform to Wikipedia articles are long-lived, and they lose reputation when their changes are undone in short order. We have implemented the proposed system, and we have used it to analyze the entire Italian and French Wikipedias, consisting of a total of 691,551 pages and 5,587,523 revisions. Our results show that our notion of reputation has good predictive value: changes performed by low-reputation authors have a significantly larger than average probability of having poor quality, and of being undone. |
Wikipedia; reputation; user-generated content | |
| Zlatić V., M. Božičević, H. Štefančić, and M. Domazet | Wikipedias: Collaborative web-based encyclopedias as complex networks | Phys. Rev. E 74, 016115 | 2006 | [257] |
Wikipedia is a popular web-based encyclopedia edited freely and collaboratively by its users. In this paper we present an analysis of Wikipedias in several languages as complex networks. The hyperlinks pointing from one Wikipedia article to another are treated as directed links while the articles represent the nodes of the network. We show that many network characteristics are common to different language versions of Wikipedia, such as their degree distributions, growth, topology, reciprocity, clustering, assortativity, path lengths, and triad significance profiles. These regularities, found in the ensemble of Wikipedias in different languages and of different sizes, point to the existence of a unique growth process. We also compare Wikipedias to other previously studied networks. |
||
| Andrew Gregorowicz and Mark A. Kramer | Mining a Large-Scale Term-Concept Network from Wikipedia | Mitre Technical Report | 2006 | [258] |
Social tagging and information retrieval are challenged by the fact that the same item or idea can be expressed by different terms or words. To counteract the problem of variable terminology, researchers have proposed concept-based information retrieval. To date, however, most concept spaces have been either manually-produced taxonomies or special-purpose ontologies, too small for classifying arbitrary resources. To create a large set of concepts, and to facilitate terms to concept mapping, we introduce mine a network of concepts and terms from Wikipedia. Our algorithm results in a robust, extensible term-concept network for tagging and information retrieval, containing over 2,000,000 concepts with mappings to over 3,000,000 unique terms. |
Information retrieval, concept search, Wikipedia, text mining. | |
| Stacey Kuznetsov | Motivations of contributors to Wikipedia | SIGCAS Comput. Soc., Vol. 36, No. 2. (June 2006) | 2006 | [259] |
This paper aims to explain why people are motivated to contribute to the Wikipedia project. A comprehensive analysis of the motivations of Wikipedians is conducted using the iterative methodology developed by Batya Friedman and Peter Kahn in Value Sensitive Design and Information Systems and co-developed by Nissenbaum and Friedman in Bias in Computer Systems. The Value Sensitive Design (VSD) approach consists of three stages: Empirical Investigation, Conceptual Investigation, and Technical Investigation. During the empirical phase, motivations of the contributors to Wikipedia are identified through analysis of data from two published surveys and a pilot survey conducted at New York University. The underlying values behind these motivations are then defined in the conceptual phase of the study. Finally, a technical investigation is conducted in order to determine how features of the Wiki technology support and facilitate these values. |
Wikipedia, motivations, value sensitive design | |
| Pierpaolo Dondio, Stephen Barrett, Stefan Weber, Jean Seigneur | Extracting Trust from Domain Analysis: A Case Study on the Wikipedia Project | Autonomic and Trusted Computing (2006), pp. 362-373. | 2006 | [260] |
The problem of identifying trustworthy information on the World Wide Web is becoming increasingly acute as new tools such as wikis and blogs simplify and democratize publications. Wikipedia is the most extraordinary example of this phenomenon and, although a few mechanisms have been put in place to improve contributions quality, trust in Wikipedia content quality has been seriously questioned. We thought that a deeper understanding of what in general defines high-standard and expertise in domains related to Wikipedia – i.e. content quality in a collaborative environment – mapped onto Wikipedia elements would lead to a complete set of mechanisms to sustain trust in Wikipedia context. Our evaluation, conducted on about 8,000 articles representing 65% of the overall Wikipedia editing activity, shows that the new trust evidence that we extracted from Wikipedia allows us to transparently and automatically compute trust values to isolate articles of great or low quality. |
analysis, domain, trust, wikipedia | |
| Lorenzen, Michael | Vandals, Administrators, and Sockpuppets, Oh My! An Ethnographic Study of Wikipedia’s Handling of Problem Behavior. | MLA Forum 5, no. 2, | 2006 | [261] |
Wikipedia is a 21st Century phenomena which is forcing many to reconsider what is and what is not valid and authoritative online. Wikipedia is an online encyclopedia that anyone can edit. This creates many opportunities to expand knowledge but it also opens the project up to vandalism and abuse. Many writers have commented on this and determined that Wikipedia has a good defense against problematic behavior even if these same writers are unsure of the legitimacy of Wikipedia as a whole. Other writers have noted the need for identified authors for legitimacy to be attainable. This ethnographic study looks at a public system that Wikipedia uses to identify and correct problem behaviors from contributors. It concludes that Wikipedia does have a good system in place that can protect the integrity of articles in many instances. However, this study was limited in scope and was unable to determine if the system in place for abuse reporting is truly able to vouch for the status of Wikipedia as an authoritative resource. |
||
| Capocci A, Servedio VDP, Colaiori F, Buriol LS, Donato D, Leonardi S, Caldarelli G | Preferential attachment in the growth of social networks: The internet encyclopedia Wikipedia | Phys. Rev. E 74 (3): 036116 | 2006 | [262] |
We present an analysis of the statistical properties and growth of the free on-line encyclopedia Wikipedia. By describing topics by vertices and hyperlinks between them as edges, we can represent this encyclopedia as a directed graph. The topological properties of this graph are in close analogy with those of the World Wide Web, despite the very different growth mechanism. In particular, we measure a scale-invariant distribution of the in and out degree and we are able to reproduce these features by means of a simple statistical model. As a major consequence, Wikipedia growth can be described by local rules such as the preferential attachment mechanism, though users, who are responsible of its evolution, can act globally on the network. |
Computer-supported collaborative work; Organizational Impacts; Information Systems; Systems and Software; Web-based services | |
| Chesney, Thomas | An empirical examination of Wikipedia's credibility | First Monday. 11 (11) November 2006. | 2006 | [263] |
Wikipedia is a free, online encyclopaedia; anyone can add content or edit existing content. The idea behind Wikipedia is that members of the general public can add their own personal knowledge, anonymously if they wish. Wikipedia then evolves over time into a comprehensive knowledge base on all things. Its popularity has never been questioned, although some have speculated about its authority. By its own admission, Wikipedia contains errors. A number of people have tested Wikipedia’s accuracy using destructive methods, i.e. deliberately inserting errors. This has been criticised by Wikipedia. This short study examines Wikipedia’s credibility by asking 258 research staff with a response rate of 21 percent, to read an article and assess its credibility, the credibility of its author and the credibility of Wikipedia as a whole. Staff were either given an article in their own expert domain or a random article. No difference was found between the two group in terms of their perceived credibility of Wikipedia or of the articles’ authors, but a difference was found in the credibility of the articles — the experts found Wikipedia’s articles to be more credible than the non–experts. This suggests that the accuracy of Wikipedia is high. However, the results should not be seen as support for Wikipedia as a totally reliable resource as, according to the experts, 13 percent of the articles contain mistakes. |
||
| Nikolaos Th. Korfiatis, Marios Poulos, George Bokos | Evaluating authoritative sources using social networks: an insight from Wikipedia | Online Information Review, Volume 30 Number 3 2006 pp. 252-262 | 2006 | [264] |
The purpose of this paper is to present an approach to evaluating contributions in collaborative authoring environments and in particular wikis using social network measures. A social network model for wikipedia has been constructed and metrics of importance such as centrality have been defined. Data have been gathered from articles belonging to the same topic using a web crawler in order to evaluate the outcome of the social network measures in the articles. This work tries to develop a network approach to the evaluation of wiki contributions and approaches the problem of quality of wikipedia content from a social network point of view. We believe that the approach presented here could be used to improve the authoritativeness of content found in Wikipedia and similar sources. |
Encyclopaedias; Social networks | |
| Stephan Bloehdorn and Sebastian Blohm | A Self Organizing Map for Relation Extraction from Wikipedia using Structured Data Representations | International Workshop on Intelligent Information Access, 2006. | 2006 | [265] | video? [266] |
In this work, we will report on the use of selforganizing maps (SOMs) in a clustering and relation extraction task. Specifically, we use the approach of self-organizing maps for structured data (SOMSDs) (i) for clustering music related articles from the free online encyclopedia Wikipedia and (ii) for extracting relations between the created clusters. We hereby rely on the bag-of-words similarity between individual articles on the one hand but additionally exploit the link structure between the articles on the other. |
information-retrieval text-mining wikipedia |
| Rosenzweig, Roy | Can History Be Open Source? Wikipedia and the Future of the Past | Journal of American History 93 (1): 117-146 | 2006 | [267] |
History is a deeply individualistic craft. The singly authored work is the standard for the profession; only about 6 percent of the more than 32,000 scholarly works indexed since 2000 in this journal’s comprehensive bibliographic guide, “Recent Scholarship,” have more than one author. Works with several authors—common in the sciences—are even harder to find. Fewer than 500 (less than 2 percent) have three or more authors. Historical scholarship is also characterized by possessive individualism. Good professional practice (and avoiding charges of plagiarism) requires us to attribute ideas and words to specific historians—we are taught to speak of “Richard Hofstadter’s status anxiety interpretation of Progressivism.”2 And if we use more than a limited number of words from Hofstadter, we need to send a check to his estate. To mingle Hofstadter’s prose with your own and publish it would violate both copyright and professional norms. A historical work without owners and with multiple, anonymous authors is thus almost unimaginable in our professional culture. Yet, quite remarkably, that describes the online encyclopedia known as Wikipedia, which contains 3 million articles (1 million of them in English). History is probably the category encompassing the largest number of articles. Wikipedia is entirely free. And that freedom includes not just the ability of anyone to read it (a freedom denied by the scholarly journals in, say, jstor, which requires an expensive institutional subscription) but also—more remarkably—their freedom to use it. You can take Wikipedia’s entry on Franklin D. Roosevelt and put it on your own Web site, you can hand out copies to your students, and you can publish it in a book—all with only one restriction: You may not impose any more restrictions on subsequent readers and users than have been imposed on you. And it has no authors in any conventional sense. Tens of thousands of people—who have not gotten even the glory of affixing their names to it—have written it collaboratively. The Roosevelt entry, for example, emerged over four years as five hundred authors made about one thousand edits. This extraordinary freedom and cooperation make Wikipedia the most important application of the principles of the free and open-source software movement to the world of cultural, rather than software, production |
Wikipedia, autorship, collaboration | |
| Kolbitsch J, Maurer H | The Transformation of the Web: How Emerging Communities Shape the Information We Consume | Journal of Universal Computer Science 12 (2): 187-213. | 2006 | [268] |
To date, one of the main aims of the World Wide Web has been to provide users with information. In addition to private homepages, large professional information providers, including news services, companies, and other organisations have set up web-sites. With the development and advance of recent technologies such as wikis, blogs, podcasting and file sharing this model is challenged and community-driven services are gaining influence rapidly. These new paradigms obliterate the clear distinction between information providers and consumers. The lines between producers and consumers are blurred even more by services such as Wikipedia, where every reader can become an author, instantly. This paper presents an overview of a broad selection of current technologies and services: blogs, wikis including Wikipedia and Wikinews, social networks such as Friendster and Orkut as well as related social services like del.icio.us, file sharing tools such as Flickr, and podcasting. These services enable user participation on the Web and manage to recruit a large number of users as authors of new content. It is argued that the transformations the Web is subject to are not driven by new technologies but by a fundamental mind shift that encourages individuals to take part in developing new structures and content. The evolving services and technologies encourage ordinary users to make their knowledge explicit and help a collective intelligence to develop. |
blogs; collaborative work; community building; emergence; file sharing; information systems; podcasting; self-organisation; social networks; web-based applications; wikis | |
| Kolbitsch J, Maurer H | Community Building around Encyclopaedic Knowledge | Journal of Computing and Information Technology 14 | 2006 | [269] | Despite not mentioning Wikipedia in title or abstract, the paper discusses it as one of the main examples. | This paper gives a brief overview of current technologies in systems handling encyclopaedic knowledge. Since most of the electronic encyclopaedias currently available are rather static and inflexible, greatly enhanced functionality is introduced that enables users to work more effectively and collaboratively. Users have the ability, for instance, to add annotations to every kind of object and can have private and shared workspaces. The techniques described employ user profiles in order to adapt to different users and involve statistical analysis to improve search results. Moreover, a tracking and navigation mechanism based on trails is presented. The second part of the paper details community building around encyclopaedic knowledge with the aim to involve “plain” users and experts in environments with largely editorial content. The foundations for building a user community are specified along with significant facets such as retaining the high quality of content, rating mechanisms and social aspects. A system that implements large portions of the community-related concepts in a heterogeneous environment of several largely independent data sources is proposed. Apart from online and DVD-based encyclopaedias, potential application areas are e-Learning, corporate documentation and knowledge management systems. |
Digital Libraries, Electronic Encyclopaedias, Knowledge Brokering Systems, Active Documents, Annotations, Knowledge Management, Tracking, Adaptation, Community Building |
| Wagner, Christian | Breaking the Knowledge Acquisition Bottleneck through Conversational Knowledge Management | Information Resources Management Journal Vol. 19, Issue 1 | 2006 | [270] |
Much of today’s organizational knowledge still exists outside of formal information repositories and often only in people’s heads. While organizations are eager to capture this knowledge, existing acquisition methods are not up to the task. Neither traditional artificial intelligence-based approaches nor more recent, less-structured knowledge management techniques have overcome the knowledge acquisition challenges. This article investigates knowledge acquisition bottlenecks and proposes the use of collaborative, conversational knowledge management to remove them. The article demonstrates the opportunity for more effective knowledge acquisition through the application of the principles of Bazaar style, open-source development. The article introduces wikis as software that enables this type of knowledge acquisition. It empirically analyzes the Wikipedia to produce evidence for the feasibility and effectiveness of the proposed approach. |
knowledge acquisition; knowledge artifacts; knowledge management; open source development; wiki | |
| Quiggin, John | Blogs, wikis and creative innovation | International Journal of Cultural Studies Vol. 9, No. 4, 481-496 | 2006 | [271] |
In this article, recent developments in the creation of web content, such as blogs and wikis, are surveyed with a focus on their role in technological and social innovation. The innovations associated with blogs and wikis are important in themselves, and the process of creative collaboration they represent is becoming central to technological progress in general. The internet and the world wide web, which have driven much of the economic growth of the past decade, were produced in this way. Standard assumptions about the competitive nature of innovation are undersupported in the new environment. If governments want to encourage the maximum amount of innovation in social production, they need to de-emphasize competition and emphasize creativity and cooperation.. |
blogs, cooperation, creative commons, innovation, wikis | |
| Altmann U | Representation of Medical Informatics in the Wikipedia and its Perspectives | Stud Health Technol Inform 116: 755-760 | 2005 | [272] |
A wiki is a technique for collaborative development of documents on the web. The Wikipedia is a comprehensive free online encyclopaedia based on this technique which has gained increasing popularity and quality. This paper's work explored the representation of Medical Informatics in the Wikipedia by a search of specific and less specific terms used in Medical Informatics and shows the potential uses of wikis and the Wikipedia for the specialty. Test entries into the Wikipedia showed that the practical use of the so-called WikiMedia software is convenient. Yet Medical Informatics is not represented sufficiently since a number of important topics is missing. The Medical Informatics communities should consider a more systematic use of these techniques for disseminating knowledge about the specialty for the public as well as for internal and educational purposes. |
Wiki, Wikipedia, Encyclopaedia, Medical Informatics | |
| Barton M D | The future of rational-critical debate in online public spheres | Computers and Composition 22 (2): 177-190 | 2005 | [273] | Despite not mentioning Wikipedia in title or abstract, the paper discusses it as one of the main examples. |
This paper discusses the role of blogs, wikis, and online discussion boards in enabling rationalcritical debate. I will use the work of Jurgen Habermas to explain why wikis, blogs, and online bulletin boards are all potentially valuable tools for the creation and maintenance of a critical public sphere. Habermas’ story ends on a sad note; the public writing environments he argues were so essential to the formation of a critical public sphere failed as commercialism and mass media diminished the role of the community and private persons. Unfortunately, the Internet will likely suffer a similar fate if we do not take action to preserve its inherently democratic and decentralized architecture. Here, I describe the integral role that blogs, wikis, and discussion boards play in fostering public discussion and ways they can be incorporated into college composition courses. |
Habermas; Wikis; Blogs; Forums; Public spheres |
| McKiernan, Gerry | WikimediaWorlds Part I: Wikipedia | Library Hi Tech News. 22 (8) November 2005 | 2005 | [274] |
This article of part 1 of a two part series on wikis. Part 1 focuses on wikipedia. The article is prepared by a library professional and provides a summary of the main features. A wiki is a piece of server software that allows users to freely create and edit web page content using any web browser. Wiki supports hyperlinks and has a simple text syntax for creating new pages and crosslinks between internal pages on the fly. This article is a useful summary of a development of interest to library and information management professionals. |
Communication technologies; Computer applications; Computer software | |
| Ruiz-Casado Maria, Enrique Alfonseca, Pablo Castells | Automatic Assignment of Wikipedia Encyclopedic Entries to WordNet Synsets | Advances in Web Intelligence (2005), pp. 380-386. | 2005 | [275] |
We describe an approach taken for automatically associating entries from an on-line encyclopedia with concepts in an ontology or a lexical semantic network. It has been tested with the Simple English Wikipedia and WordNet, although it can be used with other resources. The accuracy in disambiguating the sense of the encyclopedia entries reaches 91.11% (83.89% for polysemous words). It will be applied to enriching ontologies with encyclopedic knowledge. |
information-retrieval, ontology, semantic, wiki, wordnet | |
| Miller, Nora | Wikipedia and the Disappearing "Author" | ETC.: A Review of General Semantics, Vol. 62, 2005 | 2005 | [276] | no open content |
(summary) In this article, Nora Miller examines wikis in the light of authorship theories. She examines authoring a text has meant over the course of history. Miller explains that wikis (and other forms of digital spaces) are redefining the notion of textual ownership through means of collaboration. She mentions copyright laws and the resultant belief that there exists "self-evident" rights for authors to control and own their texts. As Miller shows with her own contributions to an entry in Wikipedia, wikis disrupt these notions of authorial rights. Much of the discussion about wikis and theory is limited to collaboration; I was happy to find one discussing wikis through the lens of authorship theory. |
Wikis, Wikipedia, collaboration |
| Holloway, Todd, Miran Bozicevic, Katy Börner | Analyzing and Visualizing the Semantic Coverage of Wikipedia and Its Authors | arXiv.org cs. IR/0512085 / Submitted to Complexity, Special issue on Understanding Complex Systems. | 2005 | [277] |
This paper presents a novel analysis and visualization of English Wikipedia data. Our specific interest is the analysis of basic statistics, the identification of the semantic structure and age of the categories in this free online encyclopedia, and the content coverage of its highly productive authors. The paper starts with an introduction of Wikipedia and a review of related work. We then introduce a suite of measures and approaches to analyze and map the semantic structure of Wikipedia. The results show that co-occurrences of categories within individual articles have a power-law distribution, and when mapped reveal the nicely clustered semantic structure of Wikipedia. The results also reveal the content coverage of the article's authors, although the roles these authors play are as varied as the authors themselves. We conclude with a discussion of major results and planned future work. |
digital libraries, information storage, information retrieval | |
| Ebersbach, Anja & Glaser, Markus | Towards Emancipatory Use of a Medium: The Wiki. | International Journal of Information Ethics, 11 | 2004 | [278] | Despite not mentioning Wikipedia in title or abstract, the paper discusses it as one of the main examples. |
With the rapid growth of the Internet in the 1990ies due to the WWW, many people’s hopes were raised that the spirit of egality, the emancipatory power of the medium then, would be brought to the masses. With the increasing commercialization, the net became and is becoming more and more a one-way medium for advertising. Against this development, a new form of web pages has emerged and is becoming increasingly popular: the Wiki. Its distinctive feature is that any web page can be edited by anyone. Participants attribute the success to this openness and to the resulting collective production of content. In his 1970 article “Constituents of a theory of the media”, Enzensberger developed a list of seven criteria that qualify, in his opinion, the use of a medium as emancipatory. These are used to investigate the question: Can wikis be thought of as a new form of emancipatory use of the medium? |
9, Natural language, User Interfaces, Hypertext, Hypermedia, Theory and models; Computer-supported cooperative work; Asynchronous interaction; Web-based interaction |
| Wagner, Christian | Wiki: A Technology for Conversational Knowledge Management and Group Collaboration. | Communications of the Association of Information Systems Vol 13 March 2004 | 2004 | [279] | Despite not mentioning Wikipedia in title or abstract, the paper discusses it as one of the main examples. |
Wikis (from wikiwiki, meaning “fast” in Hawaiian) are a promising new technology that supports “conversational” knowledge creation and sharing. A Wiki is a collaboratively created and iteratively improved set of web pages, together with the software that manages the web pages. Because of their unique way of creating and managing knowledge, Wikis combine the best elements of earlier conversational knowledge management technologies, while avoiding many of their disadvantages. This article introduces Wiki technology, the behavioral and organizational implications of Wiki use, and Wiki applicability as groupware and help system software. The article concludes that organizations willing to embrace the “Wiki way” with collaborative, conversational knowledge management systems, may enjoy better than linear knowledge growth while being able to satisfy ad-hoc, distributed knowledge needs. |
16, wiki, knowledge management, conversational knowledgemanagement, weblog, groupware, group decision support system |
| Ciffolilli, Andrea | Phantom authority, self–selective recruitment and retention of members in virtual communities: The case of Wikipedia. | First Monday. 8 (12) December 2003 | 2003 | [280] |
Virtual communities constitute a building block of the information society. These organizations appear capable to guarantee unique outcomes in voluntary association since they cancel physical distance and ease the process of searching for like–minded individuals. In particular, open source communities, devoted to the collective production of public goods, show efficiency properties far superior to the traditional institutional solutions to the public goods issue (e.g. property rights enforcement and secrecy). This paper employs team and club good theory as well as transaction cost economics to analyse the Wikipedia online community, which is devoted to the creation of a free encyclopaedia. An interpretative framework explains the outstanding success of Wikipedia thanks to a novel solution to the problem of graffiti attacks — the submission of undesirable pieces of information. Indeed, Wiki technology reduces the transaction cost of erasing graffiti and therefore prevents attackers from posting unwanted contributions. The issue of the sporadic intervention of the highest authority in the system is examined, and the relatively more frequent local interaction between users is emphasized. The constellation of different motivations that participants may have is discussed, and the barriers–free recruitment process analysed. A few suggestions, meant to encourage long term sustainability of knowledge assemblages, such as Wikipedia, are provided. Open issues and possible directions for future research are also discussed. |
||
| Cedergren, Magnus (2003). | Open content and value creation. | First Monday. 8 (8) August 2003. | 2003 | [281] | Despite not mentioning Wikipedia in title or abstract, the paper discusses it as one of the main examples. |
The borderline between production and consumption of media content is not so clear as it used to be. For example on the Internet, many people put a lot of effort into producing personal homepages in the absence of personal compensation. They publish everything from holiday pictures to complete Web directories. Illegal exchange of media material is another important trend that has a negative impact on the media industry. In this paper, I consider open content as an important development track in the media landscape of tomorrow. I define open content as content possible for others to improve and redistribute and/or content that is produced without any consideration of immediate financial reward — often collectively within a virtual community. The open content phenomenon can to some extent be compared to the phenomenon of open source. Production within a virtual community is one possible source of open content. Another possible source is content in the public domain. This could be sound, pictures, movies or texts that have no copyright, in legal terms. Which are the driving forces for the cooperation between players that work with open content? This knowledge could be essential in order to understand the dynamics of business development, technical design and legal aspects in this field. In this paper I focus on these driving forces and the relationships between these players. I have studied three major open content projects. In my analysis, I have used Gordijn’s (2002) value modeling method "e3value", modified for open content value creation and value chains. Open content value chains look much the same as commercial value chains, but there are also some major differences. In a commercial value chain, the consumers’ needs trigger the entire chain of value creation. My studies indicate that an open content value chain is often triggered by what the creators and producers wish to make available as open content. Motivations in non-monetary forms play a crucial role in the creation of open content value chains and value. My study of these aspects is based on Feller and Fitzgerald’s (2002) three perspectives on motivations underlying participation in the creation of open source software. |
|
| Benkler, Yochai | Coase's penguin, or, Linux and The Nature of the Firm | The Yale Law Jounal. v.112, n.3, pp.369-446. | 2002 | [282] | Despite not mentioning Wikipedia in title or abstract, the paper discusses it as one of the main examples. |
Commons based peer production (e.g., free software) has emerged in the pervasively networked digital information economy as a third method of production which for some projects, has productivity gains, in the form of information and allocation gains, over market and firm-based production. |
property rights, peer production |
| Stalder, Felix and Hirsh, Jesse | Open Source Intelligence | First Monday. 7 (6) Jun 2002 | 2002 | [283] |
The Open Source movement has established over the last decade a new collaborative approach, uniquely adapted to the Internet, to developing high-quality informational products. Initially, its exclusive application was the development of software (GNU/Linux and Apache are among the most prominent projects), but increasingly we can observe this collaborative approach being applied to areas beyond the coding of software. One such area is the collaborative gathering and analysis of information, a practice we term "Open Source Intelligence". In this article, we use three case studies - the nettime mailing list, the Wikipedia project and the NoLogo Web site - to show some the breadth of contexts and analyze the variety of socio-technical approaches that make up this emerging phenomenon. |
Reviews
- Remy, Melanie (2002). Wikipedia: The Free Encyclopedia. Online Information Review 26(6):434. Emerald
- Levack, Kinley (2003). If Two Heads Are Better than One, Try 7,000 with Wikipedia. Econtent Magazine 26(4):12–13, April 2003.
- Crawford, Walt; Wikipedia and Worth. Cites & Insights, Oct 2004[284].
- Crawford, Walt; Wikipedia and Worth [Revisited]. Cites & Insights, Feb 2005[285].
- Denning, Peter; Jim Horning; David Parnas; and Lauren Weinstein (2005). Wikipedia risks. Communications of the ACM 48(12):152, December 2005. doi:10.1145/1101779.1101804
- Giles, Jim (2005). Internet encyclopaedias go head to head. Nature 438, 900-901 (15 Dec 2005) [286]
- Levack, Kinley. If Two Heads Are Better than One, Try 7,000 with Wikipedia. EContent. April 2003. [287]
- Lipczynska, Sonya (2005). Power to the people: the case for Wikipedia. Reference Reviews 19(2):6–7.Emerald Ingenta (abstract)
- Lawler, Cormac. A ‘resource review’ of Wikipedia. Counselling and Psychotherapy Research. 1473-3145 (Print) 1746-1405 (Online). Volume 6, Number 3/September 2006
- Clauson, Kevin A; Hyla H Polen, Maged N Kamel Boulos & Joan H Dzenowagis (2008). Scope, Completeness, and Accuracy of Drug Information in Wikipedia. The Annals of Pharmacotherapy. Vol. 42, No. 12, pp. 1814-1821
Books and book chapters
Editorials
- Nature editors (2005). Wiki's wild world. Nature 438, 890-890 (15 Dec 2005) [288]
Valuable articles in non-peer reviewed magazines
- Reagle, Joseph, (2009), Wikipedia: The Happy Accident, Interactions, Volume 16, Issue 3, pp. 42-45.
- Hardy, Mat, (2007), Wiki Goes to War, Australian Quarterly, Vol. 79, Issue 4, p. 17-22
- Ann M. Lally, Carolyn E. Dunford, Using Wikipedia to Extend Digital Collections, D-Lib Magazine, May/June 2007
- Meijssen, Gerard (2005): Wikipedia: Localization in a Free Content Community. In: LISA (Localization Industry Standards Association), June 2005 [289]
- Sanger, Larry (2005): The Early History of Nupedia and Wikipedia: A Memoir. In: DiBona; Cooper & Stone (Eds.): Open Sources 2.0. O'Reilly. Online: part 1, part 2
- Möller, Erik (2003). Tanz der Gehirne. Telepolis, May 9-30. Four parts: "Das Wiki-Prinzip", "Alle gegen Brockhaus", "Diderots Traumtagebuch", "Diesen Artikel bearbeiten". Summary and table of contents: http://www.heise.de/newsticker/data/fr-30.05.03-000/
- Sonya Lipczynska (2005). "The role of Wikipedia in higher education" (PDF). Sconul Focus. 35.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - Lanier, Jaron, (2006), DIGITAL MAOISM: The Hazards of the New Online Collectivism, Edge 183 — May 30, 2006 [290]
- Lakhani, Karim R. and Andrew P. McAfee, Case Study: Wikipedia, Harvard Business School, 30 January 2007
- Tom McArthur (2006). "Citing, quoting, and critiquing the Wikipedia". English Today. 22 (03): 2.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) Note: This is not a peer-reviewed article. This is a call for others to write such an article. - Giddings, Janet M. SBL Forum Ethical Issues in Pedagogy: Wikipedia
- Simmons, John (Editor), The Wikipedia Muhammad Cartoons Debate: A W A R O F I D E A S, Iraq Museum International
Theses
| Author | Title | Thesis type | Institution | Year | Notes | Abstract
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amir Hossein Jadidinejad | Mining Structured Information from Unstructured Texts using Wikipedia-based Semantic Analysis | Master's thesis | IAU | 2009 | Persian | |
| Benjamin Grassineau | La dynamique des réseaux coopératifs : l'exemple des logiciels libres et du projet d'encyclopédie libre et ouverte Wikipédia | Thèse de doctorat | Université Paris Dauphine | 2009 | Français |
Les pratiques organisationnelles et sociales non-marchandes et non-hiérarchiques liées aux nouvelles technologies de l’information et de la communication suscitent aujourd’hui de nombreuses réactions et controverses. Certains acteurs et chercheurs en contestent l’existence, d’autres affirment qu’il s’agit d’un phénomène minoritaire ou non durable, d’autres enfin, les cantonnent à la sphère virtuelle. S’inscrivant dans ces débats, ce travail analyse les différentes approches théoriques qui les sous-tendent, et les confronte à une observation empirique du réseau coopératif des logiciels libres et du projet d’encyclopédie libre et ouverte Wikipédia, en les replaçant dans le contexte idéologique propre à l’activité informatique. En développant un cadre conceptuel adéquat pour l’étude de ces entités sociales qui s’appuie sur l’interactionnisme symbolique et la sociologie critique d’Ivan Illich, cette réflexion dévoile la spécificité organisationnelle, économique et sociale de ces nouvelles pratiques, et expose ce qui a favorisé leur développement et leur croissance au cours de ces trois dernières décennies. L’accent est tout particulièrement mis sur l’intégration des facteurs culturels et sur la compréhension des mécanismes qui favorisent l’essor et l’expansion de ces nouvelles pratiques dans d’autres activités. Au final, cette réflexion rejoint un des questionnements fondamentaux de la société contemporaine, à savoir, celui posé par le développement de l’économie non-marchande et non-hiérarchique et par la déprofessionnalisation des activités immatérielles. |
| Felipe Ortega | Wikipedia: A Quantitative Analysis | PhD thesis | Universidad Rey Juan Carlos | 2009 | notes | Presently, the Wikipedia project lodges the largest collaborative community ever known in the history of mankind. Due to the large number of contributors, along with the amazing popularity level of Wikipedia in the Web, it has soon become a topic of interest for researchers of many academic disciplines. However, in spite of the increasing significance of Wikipedia in scholar publications over the past years, we oftenly find studies concentrating either on very specific aspects of the project, or else, on a specific language version. As a result, there is a need of broadening the scope of previous research works to present a more complete picture of the Wikipedia project, its community of contributors and the evolution of this project over time. This doctoral thesis offers a quantitative analysis of the top ten language editions of Wikipedia, from different perspectives. The main goal has been to trace the evolution in time of key descriptive and organizational parameters of Wikipedia and its community of authors. The analysis is focused on logged authors (those editors who created a personal account to participate in the project). The comparative study encompasses general evolution parameters, a detailed analysis of the inner social structure and stratification of the Wikipedia community of logged authors, a study of the inequality level of contributions (among authors and articles), a demographic study of the Wikipedia community and some basic metrics to analyze the quality of Wikipedia articles and the trustworthiness level of individual authors. This work concludes with the study of the influence of the main findings presented in this thesis for the future sustainability of Wikipedia in the following years. The analysis of the inequality level of contributions over time, and the evolution of additional key features identified in this thesis, reveals an untenable trend towards progressive increase of the effort spent by the most active authors, as time passes by. This trend may eventually cause that these authors will reach their upper limit in the number of revisions they can perform each month, thus starting a decreasing trend in the number of monthly revisions, and an overall recession of the content creation and reviewing process in Wikipedia. As far as we know, this is the first research work implementing a comparative analysis, from an quantitative point of view, of the top ten language editions of Wikipedia, presenting complementary results from different research perspectives. Therefore, we expect that this contribution will help the scientific community to enhance their understanding of the rich, complex and fascinating working mechanisms and behavioral patterns of the Wikipedia project and its community of authors. Likewise, we hope that WikiXRay will facilitate the hard task of developing empirical analyses on any language version of the encyclopaedia, boosting in this way the number of comparative studies like this one in many other scientific disciplines. |
| Liam Wyatt | The Academic Lineage of Wikipedia: Connections and Disconnections in the Theory and Practice of History | Honours Thesis | University of New South Wales | 2008 | English, written in the field of History. Awarded 1st class, the history prize and the university medal. Not publicly available due to potential for publication. Please ask for a copy. | The theory and practice of Wikipedia has a common heritage with professional history. In spite of the project being very new, the number and variety of its authors and the ambivalence of academia towards it, Wikipedians have created an encyclopedia that upholds high standards of scholarship and encyclopedism. Simultaneously it provides universal easy access to knowledge. The policies and practices enacted by Wikipedia to achieve these standards are rarely unique. Facing the same challenges that encyclopedists, lexicographers, translators, librarians and archivists have before, it does not achieve a uniformly high standard but it is a new chapter in a very old book. This thesis divides the relevant fields of historiography into three parts. The first discusses how the idea of “free” is related to history production and disseminationthe concept of the “author” over time to argue that it has never been static nor is Wikipedia unique. Rather, it is a new form. Specifically discussed are ideas of readership; of mass authorship; the authority of knowledge; cultures of reading and the universalist ideal. The third part deconstructs “truth” to show that Wikipedia is not undermining the importance of this complex idea. Elements examined are the value of professionalism as opposed to amateurism; the fixity of knowledge; and concepts of verifiability, neutrality and objectivity. by looking at methods by which it is curtailed—through copyright; censorship; destruction; price and language. Wikipedia is the latest in a long line of defenders of the ideal of free knowledge. The second part looks at Having demonstrated the relationship of Wikipedia’s theory and practice to the discipline of history, the final chapter uses Wikipedia’s articles to highlight practical means by which historians might engage with the project as a historical source and still maintain professional standards. Discussion pages, several associated paratexts and the statistics demonstrating article popularity are considered. Finally, there is a discussion about how historians can be directly involved in the Wikipedia project—by editing it. |
| Dennis Hoppe | Automatic Edit-War Detection in Wikipedia | Bachelor Thesis | Bauhaus-University Weimar | 2008 | German; Winner of the second prize of a thesis competition in Middle Germany, sponsored by the Society for the Promotion of Open Source Systems, GAOS e.V. | Gegenwärtig schreiben bei der freien Online-Enzyklopädie Wikipedia über 300.000 registrierte Benutzer mit. Besucher eines Artikels sind in der Lage, direkt ohne vorherige Authentifizierung Inhalte zu bearbeiten. Vor allem bei populären Artikeln, die von vielen Benutzern bearbeitet und betrachtet werden, kommt es immer wieder zu Meinungsverschiedenheiten zwischen einzelnen Benutzern. Sie streiten sich dabei überwiegend um den Inhalt des Artikels. Wikipedia bietet Benutzern Diskussionsseiten zu jedem Artikel an, auf denen Benutzer ihre Beweggründe hinsichtlich der von ihnen vorgenommen Änderungen am Artikel vortragen sollen. Diese werden allerdings dazu selten verwendet, denn die Mechanismen, die es Benutzern einerseits erlauben, mit Leichtigkeit Artikel zu verändern, führen andererseits dazu, dass sie bei Meinungsverschiedenheiten auf zeitraubende Diskussionen verzichten. Stattdessen nehmen sie die Änderungen im Artikel einfach zurück. Ein andauerndes Wechselspiel zwischen Wiederherstellen und Zurücknehmen der Inhalte mündet in einem sogenannten Bearbeitungskonflikt. Diese stören andere Autoren und verhindern die Weiterentwicklung des Artikels. Die englische Wikipedia umfasst derzeit mehr als zwei Millionen Artikel. Minütlich kommen bis zu einhundert neue Änderungen hinzu, von denen im Durchschnitt jede 30. Bearbeitung Teil eines Bearbeitungskonflikts ist. Die Wikipedia-Gemeinschaft ist daher bestrebt, zwischen Benutzern, die an Bearbeitungskonflikten beteiligt sind, zu vermitteln. Gegenwärtig sind Bearbeitungskonflikte jedoch ausschließlich manuell durch Beobachter erkennbar, so dass bei über zwei Millionen Artikeln und mehreren tausend Änderungen täglich viele Meinungsverschiedenheiten unentdeckt bleiben. In der vorliegenden Arbeit wird erstmalig ein Verfahren zur automatischen Erkennung von Bearbeitungskonflikte namens Edward vorgestellt. Auf dieseWeise werden Meinungsverschiedenheiten bereits im Entstehen erkennbar und sind zu schlichten. Eine aufwendige Beobachtung von Artikeln durch unparteiische Dritte ist verzichtbar. Zur Evaluierung des Verfahrens wurde ein Referenzkorpus per Hand angelegt, in dem 51 Bearbeitungskonflikte dokumentiert sind. Von diesen werden 49 Bearbeitungskonflikte erkannt. Beteiligte Versionen eines Artikels an Bearbeitungskonflikten werden mit einer Precision von 0,95 und einem Recall von 0,90 automatisch erfasst. |
| Daniel Kinzler | Automatischer Aufbau eines multilingualen Thesaurus durch Extraktion semantischer und lexikalischer Relationen aus der Wikipedia | Diploma thesis | Universtität Leipzig | 2008 | German; More info: http://brightbyte.de/page/WikiWord | Gegenwärtig schreiben bei der freien Online-Enzyklopädie Wikipedia über 300.000 registrierte Benutzer mit. Besucher eines Artikels sind in der Lage, direkt ohne vorherige Authentifizierung Inhalte zu bearbeiten. Vor allem bei populären Artikeln, die von vielen Benutzern bearbeitet und betrachtet werden, kommt es immer wieder zu Meinungsverschiedenheiten zwischen einzelnen Benutzern. Sie streiten sich dabei überwiegend um den Inhalt des Artikels. Wikipedia bietet Benutzern Diskussionsseiten zu jedem Artikel an, auf denen Benutzer ihre Beweggründe hinsichtlich der von ihnen vorgenommen Änderungen am Artikel vortragen sollen. Diese werden allerdings dazu selten verwendet, denn die Mechanismen, die es Benutzern einerseits erlauben, mit Leichtigkeit Artikel zu verändern, führen andererseits dazu, dass sie bei Meinungsverschiedenheiten auf zeitraubende Diskussionen verzichten. Stattdessen nehmen sie die Änderungen im Artikel einfach zurück. Ein andauerndes Wechselspiel zwischen Wiederherstellen und Zurücknehmen der Inhalte mündet in einem sogenannten Bearbeitungskonflikt. Diese stören andere Autoren und verhindern die Weiterentwicklung des Artikels. Die englische Wikipedia umfasst derzeit mehr als zwei Millionen Artikel. Minütlich kommen bis zu einhundert neue Änderungen hinzu, von denen im Durchschnitt jede 30. Bearbeitung Teil eines Bearbeitungskonflikts ist. Die Wikipedia-Gemeinschaft ist daher bestrebt, zwischen Benutzern, die an Bearbeitungskonflikten beteiligt sind, zu vermitteln. Gegenwärtig sind Bearbeitungskonflikte jedoch ausschließlich manuell durch Beobachter erkennbar, so dass bei über zwei Millionen Artikeln und mehreren tausend Änderungen täglich viele Meinungsverschiedenheiten unentdeckt bleiben. In der vorliegenden Arbeit wird erstmalig ein Verfahren zur automatischen Erkennung von Bearbeitungskonflikte namens Edward vorgestellt. Auf dieseWeise werden Meinungsverschiedenheiten bereits im Entstehen erkennbar und sind zu schlichten. Eine aufwendige Beobachtung von Artikeln durch unparteiische Dritte ist verzichtbar. Zur Evaluierung des Verfahrens wurde ein Referenzkorpus per Hand angelegt, in dem 51 Bearbeitungskonflikte dokumentiert sind. Von diesen werden 49 Bearbeitungskonflikte erkannt. Beteiligte Versionen eines Artikels an Bearbeitungskonflikten werden mit einer Precision von 0,95 und einem Recall von 0,90 automatisch erfasst. |
| Robert Gerling | Automatic Vandalism Detection in Wikipedia | Diploma Thesis | Bauhaus-University Weimar | 2008 | German | Die freie Online-Enzyklop?adie Wikipedia baut auf dem Wiki-Prinzip auf. Es erlaubt jedem Besucher Wikipedias einen Artikel des Lexikons nicht nur zu lesen, sondern auch zu editieren. Diese kollaborative Zusammenarbeit f?uhrt dazu, dass die Enzyklop?adie best?andig weiterentwickelt wird, indem z. B. neue Fakten eingebracht, Rechtschreibund Grammatikfehler korrigiert, weiterf?uhrende Links erg?anzt oder strukturelle Verbesserungen vorgenommen werden. Diese Besonderheit des Wiki-Prinzips wird von manchen Personen missbraucht. Sie ver?andern Artikel mit destruktiven Absichten und untergraben damit die konstruktive Arbeit der Gemeinschaft. Dieses Ph?anomen wird in Wikipedia als Vandalismus bezeichnet. Ziel dieser Arbeit ist es, Verfahren des maschinellen Lernens f?ur die automatische Erkennung von Vandalismus in Wikipedia einzusetzen und diesen Ansatz zu evaluieren. Die Motivation f?ur diese Untersuchung liefern die Erfolge, die maschinelle Lernverfahren bei der ?ahnlichen Problematik der SPAM-Mail Identi�kation erzielen konnten. Um Vandalismus automatisch erkennen zu k?onnen, ist es notwendig, sich intensiv mit dessen Charakteristik zu besch?aftigen. Dazu wurden 301 Vandalismusf?alle manuell untersucht und dokumentiert. Es zeigten sich vielf?altige Auspr?agungen von Vandalismus, welche sich anhand der vorgenommenen Ver?anderung am Artikel (Einf?ugen, Ersetzen, L?oschen) und am ver?anderten Inhalt (Text, Link, Medien, Formatierung) unterscheiden lassen. Dar?uber hinaus lie�en sich charakteristische Eigenschaften von Vandalismus feststellen, die erstmalig zu 16 Features modelliert wurden, welche beim maschinellen Lernen eingesetzt werden k?onnen. Die 301 Vandalismusf?alle, sowie weitere 639 Beispiele von konstruktiven Ver?anderungen an Artikeln, wurden zum ersten Wikipedia-Vandalismus- Korpus (kurz WEBIS-VC07-11) zusammengefasst. Auf diesem Korpus wurde das Lernverfahren trainiert und getestet. Im Zuge der Evaluierung wurde das Lernverfahren mit zwei etablierten autonomen Anti- Vandalismus-Bots verglichen. Die Bots erkennen Vandalismus aufgrund von vorde�nierten Regeln. Die Vandalismuserkennung durch das Lernverfahren erzielte eine Precision von 83 % bei einen Recall von 77 % und ?ubertra damit den Recall der beiden Bots, von 16 % bzw. 43 %, deutlich. Dabei lag die Verarbeitungsgeschwindigkeit auf dem Niveau der Bots. |
| Joel Nothman | Learning Named Entity Recognition from Wikipedia | Honours thesis | University of Sydney | 2008 | We present a method to produce free, enormous corpora to train taggers for Named Entity Recognition (NER), the task of identifying and classifying names in text, often solved by statistical learning systems. Our approach utilises the text of Wikipedia, a free online encyclopedia, transforming links between Wikipedia articles into entity annotations. Having derived a baseline corpus, we found that altering Wikipedia’s links and identifying classes of capitalised non-entity terms would enable the corpus to conform more closely to gold-standard annotations, increasing performance by up to 32% F score. The evaluation of our method is novel since the training corpus is not usually a variable in NER experimentation. We therefore develop a number of methods for analysing and comparing training corpora. Gold-standard training corpora for NER perform poorly (F score up to 32% lower) when evaluated on test data from a different gold-standard corpus. Our Wikipedia-derived data can outperform manually-annotated corpora on this cross-corpus evaluation task by up to 7% on held-out test data. These experimental results show that Wikipedia is viable as a source of automatically-annotated training corpora, which have wide domain coverage applicable to a broad range of NLP applications. | |
| Joseph Reagle | In good faith: Wikipedia collaboration and the pursuit of the universal encyclopedia | PhD thesis | New York University | 2008 | ||
| Joachim Schroer | Wikipedia: Auslösende und aufrechterhaltende Faktoren der freiwilligen Mitarbeit an einem Web-2.0-Project | PhD thesis | University of Würzburg | 2008 | German | |
| Mark W. Bell | The transformation of the encyclopedia : a textual analysis and comparison of the Encyclopædia Britannica and Wikipedia | Master's thesis | Ball State University | 2007 | ||
| Razvan Bunescu | Learning for Information Extraction: From Named Entity Recognition and Disambiguation To Relation Extraction | PhD thesis | Ohio University | 2007 | Information Extraction, the task of locating textual mentions of specific types of entities and their relationships, aims at representing the information contained in text documents in a structured format that is more amenable to applications in data mining, question answering, or the semantic web. The goal of our research is to design information extraction models that obtain improved performance by exploiting types of evidence that have not been explored in previous approaches. Since designing an extraction system through introspection by a domain expert is a laborious and time consuming process, the focus of this thesis will be on methods that automatically induce an extraction model by training on a dataset of manually labeled examples. Named Entity Recognition is an information extraction task that is concerned with finding textual mentions of entities that belong to a predefined set of categories. We approach this task as a phrase classification problem, in which candidate phrases from the same document are collectively classified. Global correlations between candidate entities are captured in a model built using the expressive framework of Relational Markov Networks. Additionally, we propose a novel tractable approach to phrase classification for named entity recognition based on a special Junction Tree representation. Classifying entity mentions into a predefined set of categories achieves only a partial disambiguation of the names. This is further refined in the task of Named Entity Disambiguation, where names need to be linked to their actual denotations. In our research, we use Wikipedia as a repository of named entities and propose a ranking approach to disambiguation that exploits learned correlations between words from the name context and categories from the Wikipedia taxonomy. Relation Extraction refers to finding relevant relationships between entities mentioned in text documents. Our approaches to this information extraction task differ in the type and the amount of supervision required. We first propose two relation extraction methods that are trained on documents in which sentences are manually annotated for the required relationships. In the first method, the extraction patterns correspond to sequences of words and word classes anchored at two entity names occurring in the same sentence. These are used as implicit features in a generalized subsequence kernel, with weights computed through training of Support Vector Machines. In the second approach, the implicit extraction features are focused on the shortest path between the two entities in the word-word dependency graph of the sentence. Finally, in a significant departure from previous learning approaches to relation extraction, we propose reducing the amount of required supervision to only a handful of pairs of entities known to exhibit or not exhibit the desired relationship. Each pair is associated with a bag of sentences extracted automatically from a very large corpus. We extend the subsequence kernel to handle this weaker form of supervision, and describe a method for weighting features in order to focus on those correlated with the target relation rather than with the individual entities. The resulting Multiple Instance Learning approach offers a competitive alternative to previous relation extraction methods, at a significantly reduced cost in human supervision. | |
| Sylvain Firer-Blaess | Wikipédia: le Refus du Pouvoir | Master's thesis | Institut d'études politiques de Lyon | 2007 | French | |
| Seah Ru Hong | Knowledge contribution in Wikipedia | Honors | National University of Singapore | 2007 | ||
| Benjamin Keith Johnson | Wikipedia as Collective Action: Personal incentives and enabling structures | Master's thesis | Michigan State University | 2007 | Wikipedia is an online encyclopedia created by volunteers, and is an example of how developments in software platforms and the low cost of sharing and coordinating on the Internet are leading to a new paradigm of creative collaboration on a massive scale. This thesis addresses the questions of why individuals choose to give away their time and effort and how the challenges associated with collective action are addressed by Wikipedia’s technologies, organization, and community. Interviews with editors of the encyclopedia were used to identify what personal gains and other motivations compel contributors, what challenges to collaboration exist, and what technological and social structures aid their ability to create a freely available repository of human knowledge. | |
| Julian Madej | Wolność i Wiedza: Aksjonormatywny Wymiar Wikipedii (Freedom and Knowledge: The Axiomatic Dimension of Wikipedia) | Master's thesis | Warsaw Univeristy | 2007 | Internet traktowany jest coraz częściej jako przedmiot badań społecznych, a rozmaite zjawiska zachodzące w cyberprzestrzeni otwierają przed naukami społecznymi nowe, szerokie horyzonty. Dzięki rozrostowi Internetu, a takŜe jego rozwojowi jakościowemu, nie brakuje interesujących tematów badawczych dla socjologów tej dziedziny. Wiele tego typu fenomenów ma jednak charakter ulotny, efemeryczny i nienamacalny, co moŜe stwarzać badaczom określone problemy. Ze względu na moje zainteresowanie tematyką internetową byłem zdecydowany na napisanie pracy magisterskiej właśnie z szeroko pojętej socjologii Internetu, chciałem jednakŜe zająć się zjawiskiem po pierwsze względnie trwałym, a po drugie interesującym socjologicznie. Wikipedia zafascynowała mnie praktycznie w momencie, kiedy po raz pierwszy wszedłem na jej strony i zorientowałem się w sposobie jej funkcjonowania. Jak to? To kaŜdy moŜe edytować? I to wszystko za darmo? Zacząłem spędzać sporo czasu na przeglądaniu artykułów w Wikipedii i poznawaniu jej mechanizmów. Zadziwienie nie minęło – wciąŜ zastanawiałem się, jak taki projekt mógł powstać, zadziałać i utrzymać ład oraz wysoki poziom mimo rosnącej popularności i liczby haseł. W moim subiektywnym odczuciu natrafiłem na najbardziej interesujący socjologicznie fenomen internetowy – opierający się na dobrowolnym działaniu i zakładający pewien cel, ale realizowany zupełnie oddolnie. Całkowita niekomercyjność tej encyklopedii takŜe jest cechą zastanawiającą i rzadko spotykaną w dzisiejszym świecie. Tym jednak, co w największym stopniu odróŜnia Wikipedię od innych sławnych zjawisk internetowych i co w duŜej mierze przesądziło o wyborze tematu niniejszej pracy, jest powaŜny charakter tego przedsięwzięcia. Większość społecznych inicjatyw w Internecie, często podobnych w sposobie działania do Wikipedii, ma charakter i cel rozrywkowy. Wikipedia stanowi wyjątek – tu celem i efektem jest wiedza, a nie zabawa. Funkcjonowanie i popularność tej internetowej encyklopedii jest więc tym bardziej zadziwiające. Postanowiłem więc sprawdzić i zbadać, jak to działa, dlaczego działa i czy działa dobrze. Chciałbym w tym miejscu szczególne podziękowania złoŜyć trzem osobom – Wikipedystom, którzy poświęcili mi najwięcej czasu i najbardziej przyczynili się do powstania tej pracy. Dziękuję Polimerkowi za wprowadzenie mnie w świat Wikipedii, Wulfstanowi za inspirującą intelektualnie rozmowę oraz Przykucie za objaśnienie mi wielu tajników Wikipedii i socjologiczną nić porozumienia. Ponadto, chciałbym serdecznie podziękować wszystkim Wikipedystom, którzy wzięli udział w mojej ankiecie i wypełnili ją. Wśród nich znaleźli się m.in. Adoomer, Aegis Maelstrom, Anniolek, Beno, Berasategui, BrokenglaSS, Dodek, Ency, Holek, Joymaster, Kenraiz, kirq, kocio, Lajsikonik, legologo, Leinad, Lilia, Ludmiła Pilecka, lzur, mfx, michalwadas, Miczek, Mo Cuishle, Nemo5576, Nux, odder, P, Paterm, Patrol110, PawełS, Pimke, Pmgpmg, Pwjb, radomil, Sacud, Vuvar1, WarX, Witek1988, wladek, wpedzich, Yarl i Zureks. Wielkie podziękowania naleŜą się takŜe promotorowi niniejszej pracy, Profesorowi Krzysztofowi Kicińskiemu, który czuwał nad moimi postępami, poddawał bardzo ciekawe pomysły i wątki do wykorzystania, a jednocześnie zaufał w moje umiejętności oraz wizję tej pracy, za co jestem Mu niezmiernie wdzięczny. Wreszcie, równie gorąco chciałbym podziękować mojej Rodzinie i Przyjaciołom za dyskusje, podpowiedzi i wszelkiego rodzaju wsparcie. Mam nadzieję, Ŝe lektura mojej pracy będzie interesująca zarówno dla osób, które o Wikipedii nie wiedzą prawie nic, jak i dla tych, którzy znają się na rzeczy całkiem nieźle lub wręcz są aktywnymi Wikipedystami. JeŜeli któryś z Czytelników pragnąłby podzielić się ze mną swoimi uwagami na temat niniejszej pracy bądź ogólnie Wikipedii, jestem do dyspozycji pod adresem elektronicznym julian@hot.pl – z chęcią przeczytam wszelkie opinie i odpowiem na ewentualne pytania. | |
| Maik Anderka | Methoden zur sprachübergreifenden Plagiaterkennung | Master's thesis | University of Paderborn | 2007 | German | |
| Evgeniy Gabrilovich | Feature Generation for Textual Information Using World Knowledge | PhD thesis | Technion – Israel Institute of Technology | 2006 | Imagine an automatic news filtering system that tracks company news. Given the news item "FDA approves ciprofloxacin for victims of anthrax inhalation", how can the system know that the drug mentioned is an antibiotic produced by Bayer? Or consider an information professional searching for data on RFID technology | |
| Chun-yu Huang | A Study of Phenomena of Knowledge Sharing in Wikipedia | Master's thesis | National Central University, Taiwan | 2006 | Chinese | Wikipedia is an encyclopedia on the Internet. It provides a lot of knowledge for the user. The first Wikipedia appeared in 2001 and was only in English. After six year of development, there are now various versions in more than 250 languages. Contents in Wikipedia were contributed and edited not by authorities, but by users of Wikipedia. As long as one wants, one can contribute to the contents of Wikipedia. Many users spent their time and energy to devote themselves to Wikipedia. Wikipedia gives no monetary reward to its contributor, but there are more and more users sharing their knowledge to Wikipedia. Does this reveal a massive pro-social phenomenon? This study thus attempts to look into factors that effect knowledge sharing of these sharing individuals. A web based questionnaire was designed, and known Wikipedia users were invited as informants. 156 valid samples were tallied out of a total of 181 returns. Empirical results reveal that reputation and altruism have positive effects on attitude of knowledge sharing, while expected reward has significant but negative effect on attitude of knowledge sharing. External control and community identification have moderating effect on the relationship between attitude of knowledge sharing and behavior of knowledge sharing. However, we failed to find evidence that support the effect of attitude of knowledge sharing on behavior of knowledge sharing. This is an issue that calls for more studies. |
| Natalia Kozlova | Automatic Ontology Extraction for Document Classification | Master's thesis | Saarland University | 2006 | The amount of information in the world is enormous. Millions of documents in electronic libraries, thousands of them on each personal computer waiting for the expert to organize this information, to be assigned to appropriate categories. Automatic classification can help. However, synonymy, polysemy and word usage patterns problems usually arise. Modern knowledge representation mechanisms such as ontologies can be used as a solution to these issues. Ontology-driven classification is a powerful technique which combines the advantages of modern classification methods with semantic specificity of the ontologies. One of the key issues here is the cost and difficulty of the ontology building process, especially if we do not want to stick to any specific field. Creating a generally applicable but simple ontology is a challenging task. Even manually compiled thesauri such as WordNet can be overcrowded and noisy. We propose a flexible framework for efficient ontology extraction in document classification purposes. In this work we developed a set of ontology extraction rules. Our framework was tested on the manually created corpus of Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. We present a software tool, developed with regard to the claimed principles. Its architecture is open for embedding new features in. The ontology-driven document classification experiments were performed on the Reuters collection. We study the behavior of different classifiers on different ontologies, varying our experimental setup. Experiments show that the performance of our system is better, in comparison to other approaches. In this work we observe and state the potential of automatic ontology extraction techniques and highlight directions for the further investigation. |
Lectures
- Jansson, Kurt (2002): "Wikipedia. Die Freie Enzyklopädie." Lecture at the 19th Chaos Communications Congress (19C3), December 27, Berlin. Online description: http://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Benutzer:Kurt_Jansson/Vortrag_auf_dem_19C3
- Möller, Erik (2003): "Belanglose Käfer. Eine Reise in die Welt der Wikis." July 1, Merz-Akademie, Stuttgart, Germany.
- Philippe Aigrain (2003): The Individual and the Collective in Open Information Communities at 16th BLED Electronic Commerce Conference, 9-11 June 2003. http://opensource.mit.edu/papers/aigrain3.pdf
Survey and poll results
- Reminder: this is for academic or semi-academic surveys and polls of Wikipedia aimed at increasing our understanding of Wikipedia. For Wikipedia's own surveys used for determining consensus, policy making and dispute resolution, see Wikipedia:Requests for comment and Wikipedia:Straw polls.
- See also: Category:Wikipedia surveys and polls, Wikipedia:Centralized discussion, MediaWiki talk:Sitenotice, meta:Category:Surveys, meta:Category:Polls and meta:CentralNotice.
To do: parse and analyze this
- Usability studies: [291]- ongoing from Jan'2009
- 2009 Wikimedia survey of scholarly community on Wikipedia (data set)
- Wikimania 2009 satisfaction survey
- Wikipedia:Survey 2008 - the first real "census" of Wikipedians, see story in Signpost
- 2008 Poll by Jimbo on Facebook about ads on Wikipedia
- 2007 Hebrew Wikipedia satisfaction survey
- Wikipedia Signpost 2007 readers survey
- 2007 Wikimedia brand survey
- 2006 survey on conflict and conflict resolution
- 2006 survey on the reasons behind the success of Wikipedia
- 2006 survey on Motivation of Contributors to Wikipedia
- 2005 A small scale study of Wikipedia
- 2005 German Wikipedia survey
- 2004 French Wikipedia survey
- 2004 Developer payment poll
- 2003 English Wikipedia Quality Survey
Data sets
Unpublished
- Assini, Pasqualino (2006). Wikipedia chapter in draft PhD thesis on Principles and Patterns of Social Knowledge Applications
- Endrizzi, Laure (2006). L'édition de référence libre et collaborative : le cas de Wikipédia. http://www.inrp.fr/vst/Dossiers/Wikipedia/sommaire.htm
- Garcia, J. M., Steinmueller W. E. (June 2003): Applying the Open Source Development Model to Knowledge Work. SPRU - Science and Technology Policy Research, INK Open Source Working Paper No. 2. http://siepr.stanford.edu/programs/OpenSoftware_David/oswp2.pdf
- Hong, Seah Ru, Knowledge Contribution in Wikipedia, National University of Singapore, Thesis, http://www-appn.comp.nus.edu.sg/~seahruho/ruhongwiki.pdf
- Reagle, Joseph M. Jr. Wikipedia's heritage: vision, pragmatics, and happenstance. http://reagle.org/joseph/2005/historical/digital-works.html
- Stvilia, B., Twidale, M., Gasser, L., Smith, L. (2005). "Information quality discussions in Wikipedia"
- Voss, Jakob (2006). "Collaborative thesaurus tagging the Wikipedia way" [292].
- Wattenberg, Martin, Viégas, Fernanda B. (2003). history flow. preliminary report http://researchweb.watson.ibm.com/history/ Published at CHI 04, available through the ACM Digital Library.
