Reflexology: Difference between revisions
m remove overly broad Category:Pseudoscience its already in subcat Category:Quackery |
→External links: NPOV |
||
| Line 122: | Line 122: | ||
[[Category:Manipulative therapy]] |
[[Category:Manipulative therapy]] |
||
[[Category:Quackery]] |
|||
[[de:Reflexzone]] |
[[de:Reflexzone]] |
||
Revision as of 01:18, 13 January 2006
Reflexology, or zone therapy, is the practice of stimulating points on the feet, hands, or ears (termed reflex zones), in the hopes that it will have a beneficial effect on some other parts of the body, or will improve general health. The most common form is foot reflexology, in which the reflexologist applies pressure to points on a person's foot. The foot is believed by practitioners and participants to be divided into a number of reflex zones corresponding to all parts of the body.
According to Bill Flocco, Director of the American Academy of Reflexology in California, "Reflexology is a powerful natural health science that studies the relationship of the reflex areas in the feet, hands and the ears to the rest of the body so that these areas can be worked on with the fingers and thumbs in a manner that will lead to improved health and the maintenance of good health."
In reflexology, it is believed that there is a "vital energy" that is circulating between organs of the human body, that penetrates into every living cell. Whenever this energy is blocked, the zone of blockage will be affected, and the reflex zones can reflect the blockage of energy in different organs. Therefore, if someone has a problem in a particular organ, a reflexologist will press on the corresponding reflex zone(s), and the person will experience pain. This pain is claimed to originate from the deposition of crystals in the reflex zone and, with massage, these crystalline structures can be broken down and the pain relieved. Simultaneously, the pressure applied to the reflex zones by the reflexologist is claimed to pass through the nerves to dissipate energy blocks.
History
Ancient Indian, Chinese, and Egyptians were the first to practice reflexology. The earliest evidence of reflexology study was found in a 4000 year old Egyptian tomb.

In 1913, Dr. William Fitzgerald noted that specific parts of the body could have an anesthetic effect on another area. Developing this theory, he divided the body into ten equal vertical zones, ending in the fingers and toes. He concluded that pressure on one part of the zone could affect everything else within that zone. In the 1930s, Eunice Ingham, a therapist, further developed and refined the zone therapy into what is now known as reflexology.
Practice
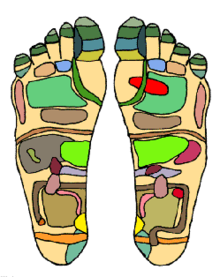
Reflexologists apply pressure on "reflex zones" found on the feet, hands and the ears, which are said to correspond to the different parts of the body. Application is done through thumb, finger and hand technique. Reflex areas, like hand and foot, composed of 7200 nerve endings are stimulated by pressure applied. An improved instruction to every gland, single part and organ of the body could be achieved by such a health science. The body is then believed to pursue a biologically correct, strengthened and reinforced state.
The image on the right shows the reflex zones found on the sole of the feet. Actually, one may find the reflex zones organized in a way such that it represents the whole body system.
Reflexology treatment
First of all, there should be a preliminary talk with the practitioner before treatment. The reflexologist then begins to work on the client's feet, or hands if necessary, noting problem areas. There may be discomfort in some places, but it is fleeting, and also an indication of congestion or imbalance in a corresponding part of the body. For the most of the part, the sensation is pleasant and soothing. Reflexology can help relax the client and is believed to stimulate the body's own healing mechanisms. Usually a treatment session lasts for about one hour. For some cases, a treatment can last nearly two hours. A course of treatment varies in length depending on the need of the client body. The reflexologist will discuss this with the patient at the first session.
Reported reactions
Case studies, not statistical conclusions, demonstrate that people treated by experts in reflexology, report a lot of reactions, including the following:
During treatment
- A sense of well-being
- A sense of relaxation
- Client may sigh, breathe deeply or yawn
- Fall asleep
- Client may feel like laughing or crying
- Experience a tingling sensation in the feet or through the body
- Pin stick type feelings in the feet over congested areas
- Temperature change either hot or cold
- Nausea
- A sense of unease due to emotional problems
- A sense of comfort
- A sense of lethargy, nausea or tearfulness
After treatment
- Cold-like symptoms such as a running nose as catarrh and sinus congestion are cleared.
- A cough as mucus is cleared from the lungs and respiratory passages
- More frequent urination
- More frequent bowel movements
- Flatulence
- Headaches
- Increased sweating
- Skin rash
- Yawning and tiredness
- Energizable
Alleged long-term effects
Reduced stress and induced relaxation
Many people try reflexology as their first foray into the world of massage, finding the treatment more relaxing than a general body massage. During the treatment, clients are only required to relax and expose their feet to the reflexologist. Treatment components also include soft music, essence oil and soft lighting, which combine to create a drowsy effect. Clients often fall asleep and describe the experience as the most relaxing hours of their day. After the treatment, they describe themselves as having a "refresh walk".
Approximately 75% of all illnesses are said to be related to stress. Stress can lead to headaches, neck and shoulder stiffness, as well as contracting the common cold and the more serious influenza. "Prevention is better than the cure", it is said, and so it is not surprising to see the growing popularity of reflexology as a means of relieving stress.
Feeling of increased energy
It is claimed that reflexology opens pathways to renew ourselves and boost our energy level, immediately after treatment and for several days afterwards. It could keep us free from the feeling of lacking motivation, tiredness, and inability to concentrate.
Alleged benefits
Reflexology advocates say that reflexology not only relieves symptoms, but also acts on improvements of our body as a whole. Some conditions are very much benefited from reflexology therapy. Examples are:
- Acute and chronic conditions
- Stress related conditions
- Sleep disorders
- Sports injuries
- Preventative therapy
Current status
Reflexology is a widespread practice in Asia, where foot reflexology (also known as foot massage) is quite popular. Although many people are skeptical about the concepts underlying this practice, its use is spreading, perhaps because it is being taken simply as a relaxing massage therapy. It is not the practice that reflexologists use foot reflexology only, they prefer to use a combination of foot, hand and ear reflexology to obtain a much better result.
Sales of foot reflexology equipment, such as rollers, are increasing rapidly. In addition, many new instruments using the same principle are being marketed, such as whole body vacuum cans. A kind of socks printing the footmap of the reflex zone was developed based on reflexology. People can easily locate the wanted zones by wearing the socks and apply pressure on them. Though not by professional hand, the "reflexology socks" gained very much popularity in Asia region like Taiwan and China. Inexpensive how-to books enabling people to perform the exercises by themselves are also available for self-help practice. Reflexologists advise caution in applying the techniques to oneself, and recommend people to consult an expert before using them if they are pregnant or have a chronic disease.
Other applications
Reflexology used on children
Advocates claim reflexology is just as effective when used on children as any adult. Some advocates go further and claim it is more effective. Advocates have also suggested that reflexology can also help child to create an awareness of self.
Skeptics' views
Reflexology is not a part of modern medical science. Skeptics point out that there are no reliable scientific studies proving its effectiveness as a medical treatment, or that there is any form of link between specific areas of the feet and the various organs of the body. Furthermore, the 'crystalline structures' rationale is unsustained by our current understanding of physiology. On the other hand research shows the relaxing and pleasurable nature of massage has many medical benefits.
Most scientists, health professionals, skeptics and others consider reflexology to be a pseudoscience, noting that there is no scientific evidence that healing can be achieved by it or that the claimed "energies" and their supposed pathways through the body even exist.
Robert Todd Carroll from the Skeptics Dictionary speculates: "One reason foot massage may be so pleasurable and is associated with significant improvement in mood is that the area of the brain that connects to the foot is adjacent to the area that connects to the genitals. There may be some neuronal overlapping."
See also
External links
- Reflexology FAQ
- Reflexology resource
- Skeptics Dictionary: Definition of Reflexology
- Reflexology: A Close Look by Stephen Barrett, M.D. – an article on Quackwatch, a guide to quackery and health fraud
- Scientific Research into Reflexology by William T. Jarvis, Ph.D.
- www.reflexology.org
- Reflexology Organisations in Different Countries
- Consumer Products on Relexology in Hong Kong
- Interactive Reflexology Chart for the Feet
- Reflexologist in the UK
