Ginkgo-toothed beaked whale: Difference between revisions
misspelled ginkgo |
|||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
==Conservation== |
==Conservation== |
||
The only observations of this species while alive have come from hunters off the coasts of Japan and [[Taiwan]], who occasionally take an individual. They are also affected by drift gillnets. The ginkgo-toothed beaked whale is covered by the Memorandum of Understanding for the Conservation of Cetaceans and Their Habitats in the Pacific Islands Region ([ |
The only observations of this species while alive have come from hunters off the coasts of Japan and [[Taiwan]], who occasionally take an individual. They are also affected by drift gillnets. The ginkgo-toothed beaked whale is covered by the Memorandum of Understanding for the Conservation of Cetaceans and Their Habitats in the Pacific Islands Region ([[Pacific Islands Cetaceans Memorandum of Understanding|Pacific Cetaceans MOU]]) |
||
==Specimens== |
==Specimens== |
||
Revision as of 16:26, 20 September 2012
| Ginkgo-toothed beaked whale | |
|---|---|

| |
| Size comparison against an average human | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Missing taxonomy template (fix): | Mesoplodon ginkgodens |
| Binomial name | |
| Mesoplodon ginkgodens Nishiwaki and Kamiya, 1958
| |
| |
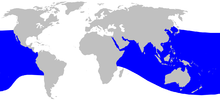
| Ginkgo-toothed Beaked Whale range | |
The ginkgo-toothed beaked whale (Mesoplodon ginkgodens) is a poorly known species of whale even for a beaked whale, and was named for the unusual shape of its dual teeth. It is a fairly typical-looking species, but is notable for the males not having any scarring.
Physical appearance
Ginkgo-toothed beaked whales are more robust than most mesoplodonts, but otherwise look fairly typical. Halfway through the jaw, there is a sharp curve up where the ginkgo leaf-shaped tooth is. Unlike other species such as Blainville's beaked whale and Andrews' beaked whale, the teeth do not arch over the rostrum. The beak itself is of a moderate length. The coloration is overall dark gray on males with light patches on the front half of the beak and around the head, and small white spots on the bottom of the tail, but the location may be variable. Females are a lighter gray and have countershading. Both genders reach 4.9 meters (16 feet) in length. They are around 2.4 meters long (8 feet) when born. The largest sizes for male and female are 4.8 meters and 4.9 meters, respectively. The size of these whales at birth are about two meters.
Population and distribution
This beaked whale has had less than 20 strandings off the coasts of Japan, California, the Galapagos Islands, New South Wales, New Zealand, Sri Lanka, the Maldives, and the Strait of Malacca. Its range is essentially tropical and temperate waters in the Indian and Pacific Ocean. There is no way to estimate the population.
Behavior
The males probably do not engage in combat, and the species probably feeds on squid and fish. No other information is known.
Conservation
The only observations of this species while alive have come from hunters off the coasts of Japan and Taiwan, who occasionally take an individual. They are also affected by drift gillnets. The ginkgo-toothed beaked whale is covered by the Memorandum of Understanding for the Conservation of Cetaceans and Their Habitats in the Pacific Islands Region (Pacific Cetaceans MOU)
Specimens
- MNZ MM002618/1, collected Pakawau, Golden Bay, New Zealand, 2004.
References
- Template:IUCN2008 Database entry includes a brief justification of why this species is of data deficient.
- Encyclopedia of Marine Mammals. Edited by William F. Perrin, Bernd Wursig, and J.G.M Thewissen. Academic Press, 2002. ISBN 0-12-551340-2
- Sea Mammals of the World. Written by Randall R. Reeves, Brent S. Steward, Phillip J. Clapham, and James A. Owell. A & C Black, London, 2002. ISBN 0-7136-6334-0

