Waveguide: Difference between revisions
Operation of waveguides cannot be described in terms of geometric optics. "Zigzag" propagation would result in modal dispersion. |
QuantumPhil (talk | contribs) m →Propagation modes and cutoff frequencies: Added a few more details on computation of propagation modes. |
||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
===Propagation modes and cutoff frequencies=== |
===Propagation modes and cutoff frequencies=== |
||
{{disputed-section|date=January 2010}} |
{{disputed-section|date=January 2010}} |
||
A [[propagation mode]] in a waveguide is one solution of the wave equations, or, in other words, the form of the wave.<ref name="balanis" /> Due to the constraints of the [[boundary conditions]], there are only limited frequencies and forms for the wave function which can propagate in the waveguide. The lowest frequency in which a certain mode can propagate is the [[cutoff frequency]] of that mode. The mode with the lowest cutoff frequency is the |
A [[propagation mode]] in a waveguide is one solution of the wave equations, or, in other words, the form of the wave.<ref name="balanis" /> Due to the constraints of the [[boundary conditions]], there are only limited frequencies and forms for the wave function which can propagate in the waveguide. The lowest frequency in which a certain mode can propagate is the [[cutoff frequency]] of that mode. The mode with the lowest cutoff frequency is the fundamental mode of the waveguide, and its cutoff frequency is the waveguide cutoff frequency.<ref>A. Y. Modi and C. A. Balanis, "PEC-PMC Baffle Inside Circular Cross Section Waveguide for Reduction of Cut-Off Frequency," in IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, vol. 26, no. 3, pp. 171-173, March 2016. |
||
doi: 10.1109/LMWC.2016.2524529</ref> |
doi: 10.1109/LMWC.2016.2524529</ref> |
||
Propagation modes are computed by solving the [[Helmholtz equation]] alongside a set of boundary conditions depending on the geometrical shape and materials bounding the region. The usual assumption for infinitely long uniform waveguides allows to assume a propagating form for the wave, i.e. stating that every field component has a known dependency on the propagation direction (i.e. <math>z</math>). More specifically, the common approach is to first replace all unknown time-varying unknown fields <math>u(x,y,z,t)</math> with their complex [[Phasor|phasors]] representation <math>U(x,y,z)</math>, sufficient to fully describe any infinitely long single-tone signal, and rewrite the Helmholtz equation and boundary conditions accordingly. Then, every unknown field is forced to have a form like <math>U(x,y,z)=\hat{U}(x,y)e^{-\gamma z}</math>, where the <math>\gamma</math> term represents the propagation constant (still unknown) along the direction along which the waveguide extends to infinity. The Helmholtz equation can be rewritten to accommodate such form and the resulting equality needs to be solved for <math>\gamma</math> and <math>\hat{U}(x,y)</math>, yielding in the end an eigenvalue equation for <math>\gamma</math> and a corresponding eigenfunction <math>\hat{U}(x,y)_\gamma</math>for each solution of the former. |
|||
===Impedance matching=== |
===Impedance matching=== |
||
Revision as of 08:01, 5 January 2017

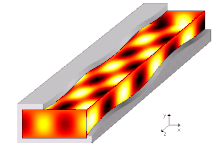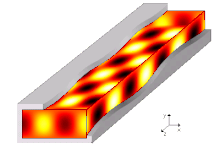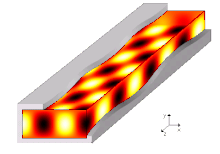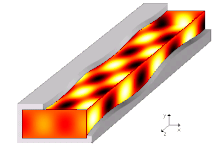
A waveguide is a structure that guides waves, such as electromagnetic waves or sound waves. They enable a signal to propagate with minimal loss of energy by restricting expansion to one dimension or two. This is a similar effect to waves of water constrained within a canal, or why guns have barrels that restrict hot gas expansion to maximize energy transfer to their bullets. Without the physical constraint of a waveguide, signals will typically be radiated and decreased according to the inverse square law as they expand into three dimensional space.
There are different types of waveguides for each type of wave. The original and most common[1] meaning is a hollow conductive metal pipe used to carry high frequency radio waves, particularly microwaves.
The geometry of a waveguide reflects its function. Slab waveguides confine energy to travel only in one dimension, fiber or channel waveguides for two dimensions. The frequency of the transmitted wave also dictates the shape of a waveguide: an optical fiber guiding high-frequency light will not guide microwaves of a much lower frequency. As a rule of thumb, the width of a waveguide needs to be of the same order of magnitude as the wavelength of the guided wave.
Some naturally occurring structures can also act as waveguides. The SOFAR channel layer in the ocean can guide the sound of whale song across enormous distances.[2]
Principle of operation

Waves propagate in all directions in open space as spherical waves. The power of the wave falls with the distance R from the source as the square of the distance (inverse square law). A waveguide confines the wave to propagate in one dimension, so that, under ideal conditions, the wave loses no power while propagating. Due to total reflection at the walls, waves are confined to the interior of a waveguide.
History
The first structure for guiding waves was proposed by J. J. Thomson in 1893, and was first experimentally tested by Oliver Lodge in 1894. The first mathematical analysis of electromagnetic waves in a metal cylinder was performed by Lord Rayleigh in 1897.[3] For sound waves, Lord Rayleigh published a full mathematical analysis of propagation modes in his seminal work, “The Theory of Sound”.[4]
The study of dielectric waveguides (such as optical fibers, see below) began as early as the 1920s, by several people, most famous of which are Rayleigh, Sommerfeld and Debye.[5] Optical fiber began to receive special attention in the 1960s due to its importance to the communications industry.
The development of radio communication initially occurred at the lower frequencies because these could be more easily propagated over large distances. The long wavelengths made these frequencies unsuitable for use in hollow metal waveguides because of the impractically large diameter tubes required. Consequently, research into hollow metal waveguides stalled and the work of Lord Rayleigh was forgotten for a time and had to be rediscovered by others. Practical investigations resumed in the 1930s by George C. Southworth at Bell Labs and Wilmer L. Barrow at MIT. Southworth at first took the theory from papers on waves in dielectric rods because the work of Lord Rayleigh was unknown to him. This misled him somewhat; some of his experiments failed because he was not aware of the phenomenon of waveguide cutoff frequency found in Lord Rayleigh's work. Serious theoretical work was taken up by John R. Carson and Sallie P. Mead. This work led to the discovery that for the TE01 mode in circular waveguide losses go down with frequency and at one time this was a serious contender for the format for long distance telecommunications.[6]
The importance of radar in World War II gave a great impetus to waveguide research, at least on the Allied side. The magnetron developed in 1940 by John Randall and Harry Boot at the University of Birmingham in the United Kingdom provided a good power source and made microwave radars feasible. The most important centre of research was at the Radiation Laboratory (Rad Lab) at MIT but many others took part in the US, and in the UK such as the Telecommunications Research Establishment. The head of the Fundamental Development Group at Rad Lab was Edward Mills Purcell. His researchers included Julian Schwinger, Nathan Marcuvitz, Carol Gray Montgomery, and Robert H. Dicke. Much of the Rad Lab work concentrated on finding lumped element models of waveguide structures so that components in waveguide could be analysed with standard circuit theory. Hans Bethe was also briefly at Rad Lab, but while there he produced his small aperture theory which proved important for waveguide cavity filters, first developed at Rad Lab. The German side, on the other hand, largely ignored the potential of waveguides in radar until very late in the war. So much so that when radar parts from a downed British plane were sent to Siemens & Halske for analysis, even though they were recognised as microwave components, their purpose could not be identified.
At that time, microwave techniques were badly neglected in Germany. It was generally believed that it was of no use for electronic warfare, and those who wanted to do research work in this field were not allowed to do so.
— H. Mayer, wartime vice-president of Siemens & Halske
German academics were even allowed to continue publicly publishing their research in this field because it was not felt to be important.[7]
Immediately after World War II waveguide was the technology of choice in the microwave field. However, it has some problems; it is bulky, expensive to produce, and the cutoff frequency effect makes it difficult to produce wideband devices. Corrugated-waveguide devices (for instance the corrugated-waveguide filter) can address the bandwidth problem, but a better solution is to use a technology working in TEM mode (that is, non-waveguide) such as coaxial conductors since TEM does not have a cutoff frequency. A shielded rectangular conductor can also be used and this which certain manufacturing advantages over coax and can be seen as the forerunner of the planar technologies (stripline and microstrip). However, planar technologies really started to take off when printed circuits were introduced. These methods are significantly cheaper than waveguide and have largely taken its place in most bands. However, waveguide is still favoured in the higher microwave bands from around Ku band upwards.[8]
Uses

The uses of waveguides for transmitting signals were known even before the term was coined. The phenomenon of sound waves guided through a taut wire have been known for a long time, as well as sound through a hollow pipe such as a cave or medical stethoscope. Other uses of waveguides are in transmitting power between the components of a system such as radio, radar or optical devices. Waveguides are the fundamental principle of guided wave testing (GWT), one of the many methods of non-destructive evaluation.
Specific examples:
- Optical fibers transmit light and signals for long distances and with a high signal rate.
- In a microwave oven a waveguide transfers power from the magnetron, where waves are formed, to the cooking chamber.
- In a radar, a waveguide transfers radio frequency energy to and from the antenna, where the impedance needs to be matched for efficient power transmission (see below).
- A waveguide called a stripline can be created on a printed circuit board, and is used to transmit microwave signals on the board. This type of waveguide is very cheap to manufacture and has small dimensions which fit inside printed circuit boards.
- Waveguides are used in scientific instruments to measure optical, acoustic and elastic properties of materials and objects. The waveguide can be put in contact with the specimen (as in a medical ultrasonography), in which case the waveguide ensures that the power of the testing wave is conserved, or the specimen may be put inside the waveguide (as in a dielectric constant measurement[9]), so that smaller objects can be tested and the accuracy is better.
Propagation modes and cutoff frequencies
This section's factual accuracy is disputed. (January 2010) |
A propagation mode in a waveguide is one solution of the wave equations, or, in other words, the form of the wave.[5] Due to the constraints of the boundary conditions, there are only limited frequencies and forms for the wave function which can propagate in the waveguide. The lowest frequency in which a certain mode can propagate is the cutoff frequency of that mode. The mode with the lowest cutoff frequency is the fundamental mode of the waveguide, and its cutoff frequency is the waveguide cutoff frequency.[10]
Propagation modes are computed by solving the Helmholtz equation alongside a set of boundary conditions depending on the geometrical shape and materials bounding the region. The usual assumption for infinitely long uniform waveguides allows to assume a propagating form for the wave, i.e. stating that every field component has a known dependency on the propagation direction (i.e. ). More specifically, the common approach is to first replace all unknown time-varying unknown fields with their complex phasors representation , sufficient to fully describe any infinitely long single-tone signal, and rewrite the Helmholtz equation and boundary conditions accordingly. Then, every unknown field is forced to have a form like , where the term represents the propagation constant (still unknown) along the direction along which the waveguide extends to infinity. The Helmholtz equation can be rewritten to accommodate such form and the resulting equality needs to be solved for and , yielding in the end an eigenvalue equation for and a corresponding eigenfunction for each solution of the former.
Impedance matching
This section's factual accuracy is disputed. (January 2010) |
In circuit theory, the impedance is a generalization of electrical resistivity in the case of alternating current, and is measured in ohms ().[5] A waveguide in circuit theory is described by a transmission line having a length and self-impedance. In other words, the impedance is the resistance of the circuit component (in this case a waveguide) to the propagation of the wave. This description of the waveguide was originally intended for alternating current, but is also suitable for electromagnetic and sound waves, once the wave and material properties (such as pressure, density, dielectric constant) are properly converted into electrical terms (current and impedance for example).
Impedance matching is important when components of an electric circuit are connected (waveguide to antenna for example): The impedance ratio determines how much of the wave is transmitted forward and how much is reflected. In connecting a waveguide to an antenna a complete transmission is usually required, so their impedances are matched.
The reflection coefficient can be calculated using: , where is the reflection coefficient (0 denotes full transmission, 1 full reflection, and 0.5 is a reflection of half the incoming voltage), and are the impedance of the first component (from which the wave enters) and the second component, respectively.
An impedance mismatch creates a reflected wave, which added to the incoming waves creates a standing wave. An impedance mismatch can be also quantified with the standing wave ratio (SWR or VSWR for voltage), which is connected to the impedance ratio and reflection coefficient by: , where are the minimum and maximum values of the voltage absolute value, and the VSWR is the voltage standing wave ratio, which value of 1 denotes full transmission, without reflection and thus no standing wave, while very large values mean high reflection and standing wave pattern.
Electromagnetic waveguides
Waveguides can be constructed to carry waves over a wide portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, but are especially useful in the microwave and optical frequency ranges. Depending on the frequency, they can be constructed from either conductive or dielectric materials. Waveguides are used for transferring both power and communication signals.

Optical waveguides
Waveguides used at optical frequencies are typically dielectric waveguides, structures in which a dielectric material with high permittivity, and thus high index of refraction, is surrounded by a material with lower permittivity. The structure guides optical waves by total internal reflection. An example of an optical waveguide is optical fiber.
Other types of optical waveguide are also used, including photonic-crystal fiber, which guides waves by any of several distinct mechanisms. Guides in the form of a hollow tube with a highly reflective inner surface have also been used as light pipes for illumination applications. The inner surfaces may be polished metal, or may be covered with a multilayer film that guides light by Bragg reflection (this is a special case of a photonic-crystal fiber). One can also use small prisms around the pipe which reflect light via total internal reflection [2]—such confinement is necessarily imperfect, however, since total internal reflection can never truly guide light within a lower-index core (in the prism case, some light leaks out at the prism corners).
Acoustic waveguides
An acoustic waveguide is a physical structure for guiding sound waves. A duct for sound propagation also behaves like a transmission line. The duct contains some medium, such as air, that supports sound propagation. Acoustic waveguides have no cutoff frequency, which is in sharp contrast to electromagnetic waveguides.
Mathematical waveguides
Waveguides are interesting objects of study from a strictly mathematical perspective. A waveguide (or tube) is defined as type of boundary condition on the wave equation such that the wave function must be equal to zero on the boundary and that the allowed region is finite in all dimensions but one (an infinitely long cylinder is an example.) A large number of interesting results can be proven from these general conditions. It turns out that any tube with a bulge (where the width of the tube increases) admits at least one bound state. This can be shown using the variational principles. An interesting result by Jeffrey Goldstone and Robert Jaffe [11] is that any tube of constant width with a twist, admits a bound state.
Sound synthesis
Sound synthesis uses digital delay lines as computational elements to simulate wave propagation in tubes of wind instruments and the vibrating strings of string instruments.
See also
References
- ^ Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, “The IEEE standard dictionary of electrical and electronics terms”; 6th ed. New York, N.Y., Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, c1997. IEEE Std 100-1996. ISBN 1-55937-833-6 [ed. Standards Coordinating Committee 10, Terms and Definitions; Jane Radatz, (chair)]
- ^ ORIENTATION BY MEANS OF LONG RANGE ACOUSTIC SIGNALING IN BALEEN WHALES, R. Payne, D. Webb, in Annals NY Acad. Sci., 188:110-41 (1971)
- ^ N. W. McLachlan, Theory and Applications of Mathieu Functions, p. 8 (1947) (reprinted by Dover: New York, 1964).
- ^ The Theory of Sound, by J. W. S. Rayleigh, (1894)
- ^ a b c Advanced Engineering Electromagnetics, by C. A. Balanis, John Wiley & Sons (1989).
- ^ Oliner, pp. 544-548
- ^
- Oliner, pp. 548-554
- Levy & Cohn, pp. 1055, 1057
- ^
- Oliner, pp. 556-557
- Han & Hwang, pp. 21-7, 21-50
- ^ J. R. Baker-Jarvis, "Transmission / reflection and short-circuit line permittivity measurements", NIST tech. note 1341, July 1990
- ^ A. Y. Modi and C. A. Balanis, "PEC-PMC Baffle Inside Circular Cross Section Waveguide for Reduction of Cut-Off Frequency," in IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, vol. 26, no. 3, pp. 171-173, March 2016. doi: 10.1109/LMWC.2016.2524529
- ^ *[1] Bound States in Twisting Tubes, J Goldstone, R.L. Jaffe, MIT Department of Physics
- Han, C C; Hwang, Y, "Satellite antennas", in, Lo, Y T; Lee, SW, Antenna Handbook: Volume III Applications, chapter 21, Springer, 1993 ISBN 0442015941.
- Levy, R; Cohn, S B, "A History of microwave filter research, design, and development", IEEE Transactions: Microwave Theory and Techniques, pages 1055–1067, volume 32, issue 9, 1984.
- Oliner, Arthur A, "The evolution of electromagnetic waveguides: from hollow metallic guides to microwave integrated circuits", chapter 16 in, Sarkar et al., History of Wireless, Wiley, 2006 ISBN 0471783013.
External links
- Waveguide A very basic explanation on what is a waveguide
- Waveguide basics Multiple pages giving detailed tutorial
- Electromagnetic Waves and Antennas: Waveguides Sophocles J. Orfanidis, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Rutgers University
- [3] Bound States in Twisting Tubes, J Goldstone, R.L. Jaffe, MIT Department of Physics














