Ulnar nerve
| Ulnar nerve | |
|---|---|
| File:Brachial plexus.JPG Click image to enlarge - ulnar nerve is visible in lower left | |
| File:Gray816.png Nerves of the left upper extremity. (Ulnar labeled at center left.) | |
| Details | |
| From | Medial cord |
| Innervates | flexor carpi ulnaris flexor digitorum profundis lumbrical muscles opponens digiti minimi flexor digiti minimi abductor digiti minimi interossei adductor pollicis |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nervus ulnaris |
| MeSH | D014459 |
| TA98 | A14.2.03.040 |
| TA2 | 6449 |
| FMA | 37319 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
In human anatomy, the ulnar nerve is a nerve which runs from the shoulder to the hand, at one part running near the ulna bone. It is the only exposed nerve in the human body (it is unprotected for a few centimeters at the elbow).
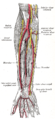
Course ARM • medial cord of the brachial plexus, runs distally ant to triceps medial to the brachial artery. • Around middle of the arm pierces the medial intermuscular septum and descends between it and the medial head of the triceps muscle. • passes between the medial epicondyle of and the olecronon to enter the forearm. • No branches in the arm. Forearm • enters the forearm by passing between the two heads of the flexor carpi ulnaris mm (FCU). • descend deep to this muscle on the FDP where it accompanies the ulnar artery near the middle of the forearm. • passes on the medial side of the ulnar artery and the lateral side of the tendon of the FCU. • distal forearm it is relatively superficial covered only by fascia and skin. • Supplies FCU and FDP (ulnar half) Wrist • pierces the deep fascia and passes superficial to the flexor retinaculum with the ulnar artery, lateral to the pisiform and between it and the hook of the hamate. The ulnar artery is on its lateral side. • This passage covered by a slip of the flexor retincaculum is called the canal of Guyton • just proximal to the wrist gives off a palmer cutaneous branch which passes superficial to the flexor retinaculum and the plamer aponeurosis and supplies the skin of the medial side of the palm. • also gives off a dorsal cutanous branch which supplies the medial half of the dorsum of the hand and 5th digit and medial half of the 4th digit. • distal border of the flexor retinaculum the ulnar nerve ends by dividing into the superficial and deep branch. • Superficial branch supplies cutaneous fibres to the anterior surface of the medical one and a half digits • deep branch supplies motor fibers to the hypothenar muscles, the medial 2 lumbricals, the adductor pollicis and the interossei and the wrist, intercarpal, CMC and IP joints.
Branches and innervation
Muscular
The ulnar nerve and its branches innervate the following muscles in the forearm and hand:
- In the forearm, via the muscular branches of ulnar nerve:
- Flexor carpi ulnaris
- Flexor digitorum profundus (medial half)
- In the hand, via the deep branch of ulnar nerve:
- In the hand, via the superficial branch of ulnar nerve:
Cutaneous
The ulnar nerve also provides sensory innervation to the part of the hand corresponding to the fourth and fifth digits:
- Palmar branch of ulnar nerve - anterior
- Dorsal branch of ulnar nerve - posterior
Ulnar nerve entrapment
The Ulnar nerve can be trapped or pinched in various ways as it proceeds down the arm from the Brachial plexus to the ring and middle fingers. One common cause is cubital tunnel syndrome, where the tunnel runs the inner outside side of the elbow. Pinching of the nerve often causes tingling symptoms in the little and ring fingers. In some cases moderate to severe pain is experienced from pinching this nerve. Often such pins and needles sensations can be caused by sleeping wrong on your arm, but sometimes the problems last for days. In severe cases, surgery is performed.
See also
Additional images
-
Brachial plexus
-
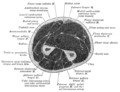
Cross-section through the middle of upper arm.
-
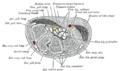
Cross-section through the middle of the forearm.
-
Transverse section across distal ends of radius and ulna.
-
Transverse section across the wrist and digits.
-
The palmar aponeurosis.
-
The axillary artery and its branches.
-
The brachial artery.
-
Ulnar and radial arteries. Deep view.
-
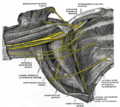
The right brachial plexus (infraclavicular portion) in the axillary fossa; viewed from below and in front.
-
Cutaneous nerves of right upper extremity. Anterior view.
-
Diagram of segmental distribution of the cutaneous nerves of the right upper extremity. Anterior view.
-
Cutaneous nerves of right upper extremity. Posterior view.
-
Diagram of segmental distribution of the cutaneous nerves of the right upper extremity. Posterior view.
-
Superficial palmar nerves.
-
Deep palmar nerves.
-
Front of right upper extremity, showing surface markings for bones, arteries, and nerves.
-
Back of right upper extremity, showing surface markings for bones and nerves.
External links
- Template:EMedicineDictionary
- Anatomy figure: 05:03-15 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "The major subdivisions and terminal nerves of the brachial plexus."
- Anatomy figure: 07:04-04 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Anterior view of the nerves, vessels, and superficial tendons that cross the left wrist."
- Anatomy figure: 08:03-07 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Transverse section through the carpal tunnel and distal row of the carpal bones."
- Ulnar nerve at the Duke University Health System's Orthopedics program
- Template:MUNAnatomy
- Hand kinesiology at the University of Kansas Medical Center
- Atlas image: hand_plexus at the University of Michigan Health System - "Axilla, dissection, anterior view"
- Overview at neuro.wustl.edu