Arctic Circle
This article needs additional citations for verification. (December 2006) |

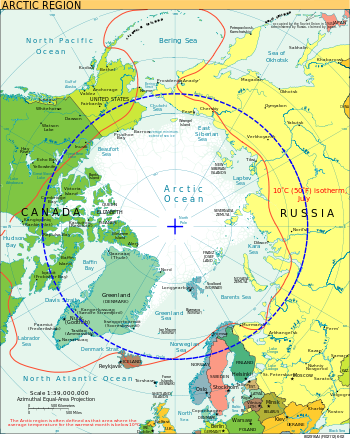
The Arctic Circle is one of the five major circles of latitude that mark maps of the Earth. In 2024, it is the parallel of latitude that runs approximately 66° 33′ 39″ (or 66.56083°) north of the Equator. The region north of this circle is known as the Arctic, and the zone just to the south is called the Northern Temperate Zone. The equivalent Polar circle in the Southern Hemisphere is called the Antarctic Circle.
The Arctic Circle marks the southern extremity of the polar day (24-hour sunlit day, often referred to as the "midnight sun") and polar night (24-hour sunless night). North of the Arctic Circle, the sun is above the horizon for 24 continuous hours at least once per year and below the horizon for 24 continuous hours at least once per year. On the Arctic Circle those events occur, in principle, exactly once per year, at the June and December solstices, respectively.
In fact, because of atmospheric refraction and because the sun appears as a disk and not a point, part of the midnight sun may be seen on the night of the summer solstice up to about 50′ (90 kilometres (56 mi)*) south of the Arctic Circle; similarly, on the day of the winter solstice, part of the sun may be seen up to about 50′ north of the Arctic Circle. That is true at sea level; those limits increase with elevation above sea level although in mountainous regions, there is often no direct view of the horizon.
The position of the Arctic Circle is not fixed, but directly depends on the Earth's axial tilt, which fluctuates within a margin of 2° over a 40,000 year period,[1] notably due to tidal forces resulting from the orbit of the Moon. The Arctic Circle is currently drifting northwards at a speed of about 15 m (49 ft) per year, see Circle of latitude for more information.
Geography
Relatively few people live north of the Arctic Circle due to the Arctic climate. The three largest communities above the Arctic Circle are situated in Russia; Murmansk (population 325,100), Norilsk (135,000), and Vorkuta (85,000). Tromsø (in Norway) has about 62,000 inhabitants, whereas Rovaniemi (in Finland), which lies slightly south of the line, has slightly fewer than 58,000. Arctic Village, Alaska was recorded as having 152 residents in the 2000 United States Census.
The Arctic Circle passes through the Arctic Ocean, the Scandinavian Peninsula, North Asia, Northern America and Greenland. The land on the Arctic Circle is divided among eight countries: Norway, Sweden, Finland, Russia, the United States (i.e. Alaska), Canada, Denmark (i.e. Greenland) and passes just north of Iceland.
Starting at the Prime Meridian and heading eastwards, the Arctic Circle passes through:
See also
- Antarctic Circle
- Arctic haze
- Scott Polar Research Institute
- Territorial claims in the Arctic
- Tropic of Cancer
- Tropic of Capricorn
References
External links
- Terra Incognita: Exploration of the Canadian Arctic—Historical essay about early expeditions to the Canadian Arctic, illustrated with maps, photographs and drawings



