2013–14 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season
| 2013–14 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season | |
|---|---|
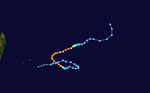
 Season summary map | |
| Seasonal boundaries | |
| First system formed | July 8, 2013 |
| Last system dissipated | Season currently active |
| Strongest storm | |
| Name | Bruce |
| • Maximum winds | 230 km/h (145 mph) (10-minute sustained) |
| • Lowest pressure | 912 hPa (mbar) |
| Seasonal statistics | |
| Total disturbances | 15 |
| Total depressions | 12 |
| Total storms | 9 |
| Tropical cyclones | 5 |
| Intense tropical cyclones | 5 |
| Total fatalities | 3 total |
| Total damage | At least $89.2 million (2014 USD) |
| Related articles | |
The 2013–14 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season is an ongoing event in the annual cycle of tropical cyclone formation set to end on June 30, 2014. The season officially began on July 1, 2013,[1] though the first tropical system designated by Météo-France was a short-lived tropical disturbance that developed on July 8. However, the first named storm was Cyclone Amara in December. Thus far, the strongest cyclone of the season is Cyclone Bruce, which originated from the Australian region and later intensified to a peak intensity with maximum sustained winds of 230 km/h (145 mph), making it the first system in the South-West Indian Ocean to reach Very Intense Tropical Cyclone status since Edzani in 2010.
Within this basin, tropical and subtropical disturbances are officially monitored by the Regional Specialised Meteorological Centre on Réunion island, while the Mauritius and Madagascar weather services assign names to significant tropical and subtropical disturbances.[1]
Seasonal summary

Storms
Tropical Disturbance
| Tropical disturbance (MFR) | |
| Duration | July 8 – July 9 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 45 km/h (30 mph) (10-min); 1001 hPa (mbar) |
On July 6, RSMC La Reunion started to monitor a weak low that had formed within the Australian region, and was moving westwards towards the basin.[2] The low struggled to maintain convection near its center, but it continued to produce near gale force winds. On July 8, La Reunion upgraded the low to a tropical disturbance after the low level circulation became better defined. The system was very asymmetric with winds of 10 to 25 knots within the center, and up to gale force in the southwestern quadrant.[3] On July 9, the storm weakened to a remnant low. On July 10, the remnant low of the tropical disturbance dissipated.
Tropical Depression 01
| Tropical depression (MFR) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | October 25 – October 28 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 55 km/h (35 mph) (10-min); 1000 hPa (mbar) |
The predecessor to the season's first designated tropical depression began as an area of persistent convection well removed from any landmasses. The JTWC began issuing products on the storm complex on October 21, noting recent consolidation patterns and its association with an ill-defined low-level circulation center.[4] Over subsequent hours, the system developed a central region of convection with incipient rainbands.[5] Despite these signs of potential tropical cyclogenesis in the very near future, the storm remained unclassified for several days as it tracked generally towards the west. At 1200 UTC on October 25, however, Météo-France classified the system as a tropical disturbance.[6] Though upper-level atmospheric conditions were rather conducive for continued strengthening, factors including decreasing convergence and marginally sustainable sea surface temperatures were expected to inhibit tropical development, and as such initial forecasts only anticipated minimal and gradual strengthening.[7]
At 0600 UTC on October 26, Météo-France upgraded the system to tropical depression status.[8] Forecasts upon the system's upgrade to tropical depression intensity expected more significant intensification, with the depression expected to peak as a moderate tropical storm.[8] However, the depression peaked in strength later that day with winds of 55 km/h (35 mph) and a minimum pressure of 1000 mbar (hPa; 29.53 inHg).[9] This intensity was sustained for several hours before the storm began to slowly weaken early on October 27.[10] During its weakening phase, the depression became elongated and its circulation center became exposed from the rest of the convection,[11] and at 1200 UTC that day Météo-France reclassified the storm as a tropical disturbance.[12] In an area no longer sufficient to support strengthening, the disturbance gradually diffused,[13] and six hours later Météo-France issued their last advisory on the system.[14]
Intense Tropical Cyclone Amara
| Intense tropical cyclone (MFR) | |
| Category 4 tropical cyclone (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | December 14 – December 23 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 205 km/h (125 mph) (10-min); 933 hPa (mbar) |
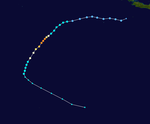
Amara developed from a disturbance within the monsoon trough on December 14.[15][16] The following day, the system attained tropical depression status.[17] Despite its ill-defined organization,[18] the depression was able to continue strengthening, reaching moderate tropical storm status on December 16 as it tracked southwest.[19] Situated in a favorable atmospheric environment, a period of rapid intensification ensued after Amara reached tropical cyclone status on December 18.[20][21] After fluctuating in strength,[22][23] the cyclone peaked with maximum sustained winds of 205 km/h (125 mph) and a minimum barometric pressure of 933 mbar (hPa; 27.55 inHg) on December 21, making it an intense tropical cyclone based on the intensity scale utilized by Météo-France.[24] Shortly after, wind shear strengthened as Amara tracked southeast, resulting in a weakening phase.[25] The shearing effects caused the cyclone to rapidly decay,[26] and by December 23, Amara was determined to have degenerated into a remnant low.[27]
Amara was initially expected to track directly over the island of Rodrigues, prompting widespread precautionary measures and resulting in the issuance of a Class 4 warning – denoting a warning of highest urgency – by the Mauritius Meteorological Services.[28][29] Though the tropical cyclone eventually passed to the east of the island, Amara was close enough to Rodrigues to severely effect the island.[28] Strong winds, peaking at a measured 152 km/h (94 mph) in Pointe Canon,[29] resulted in widespread infrastructural damage, including the tearing of metal sheeting and uprooting of trees.[28][30] Widespread power outage cut power to 12,000 homes and shut off communications to and from the island.[30][31] Heavy rains produced by Amara also triggered flooding in some locations and caused soil erosion.[32][33]
Very Intense Tropical Cyclone Bruce
| Very intense tropical cyclone (MFR) | |
| Category 5 tropical cyclone (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | December 19 (Entered basin) – December 24 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 230 km/h (145 mph) (10-min); 912 hPa (mbar) |
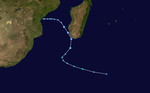
On December 16, a complex of disturbed weather near Indonesia was designated as a tropical low by the Australian Bureau of Meteorology.[34] In an area of only moderate inhibiting atmospheric conditions, the low was able to steadily intensify, reaching tropical cyclone status on December 18 as it tracked southwestward.[35] At 0000 UTC on December 20, Bruce moved into the area of responsibility of Météo-France after crossing 90°E with maximum sustained winds of 155 km/h (100 mph).[36] Upon passage into the southwest Indian Ocean Bruce already had a well-defined eye and further strengthening was anticipated.[36][37] Six hours later the storm was upgraded to intense tropical cyclone status.[38] At 1800 UTC that day, Météo-France upgraded the system to very intense tropical cyclone status, the highest rating possible on their tropical cyclone intensity scale.[39] Over the next day, Bruce transiently weakened to intense tropical cyclone status,[40] but later regained the maximum classification at 0000 UTC on December 22. Consequently, Bruce reached its peak intensity with winds of 230 km/h (145 mph) and a minimum pressure of 912 mbar (hPa; 26.93 inHg).[41]
Following peak intensity, Bruce began to steadily weaken as the storm's deep region of convection began to diminish.[42] At 1200 UTC on December 22, the storm was downgraded back to intense tropical cyclone status for a final time as it was becoming increasingly asymmetric.[43][44] During the same timeframe Bruce began to curve around the western periphery of a nearby subtropical ridge, redirecting the cyclone's path towards the south.[44] On December 23, the cyclone's eye finally succumbed to cooling sea surface temperatures and Bruce was downgraded to a low-end tropical cyclone by Météo-France.[45][46] By the end of the day, Bruce was downgraded further to severe tropical storm intensity as the bulk of convection began to shear away from the low-level circulation center.[47][48] Accelerating southeastwards, Bruce transitioned into an extratropical cyclone on December 24, ceasing Météo-France's monitoring operations.[49] Its remnants exited the basin on December 25.[citation needed]
Intense Tropical Cyclone Bejisa
| Intense tropical cyclone (MFR) | |
| Category 3 tropical cyclone (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | December 28 – January 6 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 165 km/h (105 mph) (10-min); 953 hPa (mbar) |
In late December 2013, computer forecast models began to predict the development and cyclogenesis of a disturbance within the monsoon trough north of Madagascar.[50] At 1800 UTC on December 27, the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) noted a discrete area of disturbed weather approximately 1,350 km (840 mi) north-northwest of Réunion that corresponded with model forecasts and had the potential to develop.[51] Accompanied by a low-level circulation center, the monitored storm complex developed rainbands about its southern periphery the following day.[52] At 1200 UTC on December 28, Météo-France deemed the system sufficiently organized to be considered a tropical disturbance, the fourth system to be given such a classification by the agency that season.[53] Upon its designation, the disturbance was analyzed to have an unusually high barometric pressure, based on nearby weather station observations.[54] Météo-France projected for the system to peak as a tropical cyclone before slightly weakening before impacting the Mascarene Islands.[55]
Tracking southward, the disturbance steadily organized following December 28. As a result of wind shear, the system's low-level circulation center remained partially exposed, though the shearing conditions were expected to lessen [56] At 0000 UTC on December 29, the disturbance was upgraded to a tropical depression.[57] At 1800 UTC that day, the depression intensified to moderate tropical storm intensity, thus receiving the name Bejisa by the Mauritius Meteorological Services.[58][59] This coincided with the improving satellite appearance of the storm's central dense overcast.[59] Intensification subsequently quickened, and at 0600 UTC the next day Bejisa was considered to be a severe tropical storm.[60] Concurrently a strengthening ridge in the mid-levels of the troposphere began to steer the storm towards the south-southeast.[61] Following the development of a small pinhole eye, Bejisa was upgraded to tropical cyclone status at 1200 UTC on December 30,[62] followed by intense tropical cyclone status six hours thereafter.[63] This intensification phase was short-lived, as an eyewall replacement cycle resulted in a slight deterioration and fluctuation of the storm's organization and structure.[64]
Tropical Depression 05
| Tropical depression (MFR) | |
| Duration | January 8 – January 11 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 65 km/h (40 mph) (10-min); 992 hPa (mbar) |
The initial development of the season's fifth tropical depression was quickly paced. The JTWC first began monitoring the system in its advisories at 1800 UTC on January 7, while the area of disturbed weather was within the Mozambique Channel. By that time, a well-defined low-level circulation center had already developed, and computer models indicated that tropical cyclogenesis was a likely probability due to the storm's expected track within a favorable atmospheric environment.[65] At 1200 UTC on January 8, Météo-France classified the system as a zone of disturbed weather,[66] though at the time the storm's convective activity was intermittent.[67] Shortly after designation the system developed, albeit shallow, convective banding.[65] At 0600 UTC the following day, the zone of disturbed weather was upgraded to tropical depression status while just off the west coast of Madagascar.[68]
Forecasts early in the depression's history indicated that heavy rainfall was likely in areas of southwestern Madagascar,[69] though these rains would come during an extended period of abnormally dry weather.[70] As a result, the Madagascar National Bureau for Risk and Disaster Management issued a red alert, signifying imminent heavy rain, for five Malagasy districts and a yellow alert, signifying a threat of heavy rain, in seven districts. In Morondava, 205 people were evacuated to safe havens where authorities provided food.[69]
Intense Tropical Cyclone Colin
| Intense tropical cyclone (MFR) | |
| Category 4 tropical cyclone (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | January 9 (Entered basin) – January 16 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 185 km/h (115 mph) (10-min); 930 hPa (mbar) |
A tropical low in the Australian region basin formed on January 6, 450 km (280 mi) east-northeast of Christmas Island.[71] Over the next days the system moved rapidly westwards and entered the Southwest Indian Ocean during the morning of January 9.[72] Despite being under significant wind shear, the system managed to organize a low level eye which was detectable in microwave imagery.[73] As a result, the storm was upgraded to Moderate Tropical Storm strength and named Colin the next day.[74] On January 11 shear let up, allowing Colin favorable conditions for strengthening. Tracking southwest, Colin rapidly intensified much faster than initial predictions expected into an Intense Tropical Cyclone during the succeeding 24 hours. Six hours later on January 12 Colin had reached its peak intensity of 185 km/h (115 mph).[75] Just like cyclones Amara and Bruce, Colin had underwent rapid deepening. But by January 13, Colin's eyewall had become severely eroded and the system was downgraded to a severe tropical storm. As it tracked further into cooler waters, the storm weakened to Tropical Storm strength early on January 14 and made a turn to the southeast. Environmental conditions continued to become unfavorable and the storm transitioned into an extratropical cyclone on January 16.[76]
Moderate Tropical Storm Deliwe
| Moderate tropical storm (MFR) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | January 16 – January 18 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 85 km/h (50 mph) (10-min); 992 hPa (mbar) |
An area of convection accompanied by a broad circulation was first noted within a region of moderate wind shear by the Joint Typhoon Warning Center on January 15. It was located for the most part over land, and it drifted out into the Mozambique Channel during the same day. On January 16, the small system tracked south-southwest and was designated by MFR as Tropical Disturbance 7. Shortly thereafter, JTWC declared it as Tropical Cyclone 09S. At 1800z, Météo-France noted that the system was maintaining a tight curved band pattern and the Madagascar Meteorological Service named the storm Deliwe.[77] Throughout the next 24 hours, Deliwe managed to persist as a moderate tropical storm while it moved away from the Madagascar coast, but increasing shear associated with an upper-level trough weakened the storm back to a tropical depression. Deliwe turned west and convection sheared away to the south, exposing the low-level circulation center, but the storm maintained a small region of gale force winds for a brief period after Réunion issued their last advisory on the system.[78] The remnants of Deliwe turned back to the north, dissipating as they approached Mozambique.
Deliwe produced heavy rains in the Melaky region of Madagascar and caused significant flooding, resulting in at least two fatalities. Additionally, one person went missing after being swept away by the swollen Mahajamba River in Mitsinjo. In Mahajanga, rising waters left 463 people homeless. Strong wind gusts caused some damage, most notably the roof of a school in Soalala, Boeny, was blown off.[79]
Zone of Disturbed Weather 08
| Zone of disturbed weather (MFR) | |
| Duration | January 18 – January 18 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 35 km/h (25 mph) (10-min); 1004 hPa (mbar) |
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (January 2014) |
Tropical Disturbance 09
| Tropical disturbance (MFR) | |
| Duration | January 28 – January 29 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 45 km/h (30 mph) (10-min); 1003 hPa (mbar) |
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (January 2014) |
Severe Tropical Storm Edilson
| Severe tropical storm (MFR) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | February 4 – February 8 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 100 km/h (65 mph) (10-min); 980 hPa (mbar) |
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (February 2014) |
After one week since the last disturbance dissipated, another disturbance formed on February 3. Late on February 4, the MFR and JTWC upgraded it to Moderate Tropical Storm Edilson. The next day, the storm affected the Mauritius Islands with heavy rainfall.[80]
Severe Tropical Storm Fobane
| Severe tropical storm (MFR) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | February 6 – February 14 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 110 km/h (70 mph) (10-min); 975 hPa (mbar) |
As Severe Tropical Storm Edilson reached peak intensity, a tropical depression formed to its northeast. The depression was designated 11R by Météo-France, and it rapidly intensified into Severe Tropical Storm Fobane by February 8. Throughout February 9, Fobane rapidly accelerated to the south and curved to the east. The storm interacted with an upper level trough and low oceanic heat content, altering its structure. At 12z on February 10, Météo-France declared that Fobane had transitioned into a hybrid but warm-core cyclone, meriting the classification of subtropical depression. Convection rapidly formed coinciding with a 10 millibar drop on February 11[81] and Fobane reached peak intensity during the next day while subtropical. In the following days, Fobane turned south and then west, slowing down as a new ridge of high pressure built up to its west. The storm continued into cooler waters and became extratropical on February 14.
Severe Tropical Storm Guito
| Severe tropical storm (MFR) | |
| Category 1 tropical cyclone (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | February 18 – February 22 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 110 km/h (70 mph) (10-min); 977 hPa (mbar) |
An area of convection over eastern Mozambique moved into the Mozambique Channel and was designated a Tropical Disturbance on February 18.[82] Later that day, the JTWC gave the designation of 15S. It steadily intensified into Severe Tropical Storm Guito on February 18. The next day, Guito intensified into a Category 1 tropical cyclone and a ragged eye formed.[83]
Subtropical Depression 13
| Subtropical depression (MFR) | |
| Duration | February 27 – February 28 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 65 km/h (40 mph) (10-min); 996 hPa (mbar) |
During February 27, RSMC La Réunion reported that a subtropical depression had formed 725 km (450 mi) southeast of Durban, South Africa.[84]
Intense Tropical Cyclone Hellen
| Intense tropical cyclone (MFR) | |
| Category 4 tropical cyclone (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | March 27 – Currently active |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 215 km/h (130 mph) (10-min); 935 hPa (mbar) |
After one month after the last storm formed, a zone of disturbed weather rapidly intensified into Tropical Disturbance 14 late on March 27. Due to favorable conditions and entering warm waters, it rapidly became Severe Tropical Storm Hellen early on March 30. Explosive intensification occurred, making Hellen an intense tropical cyclone the same day.
Storm names
Within the South-west Indian Ocean Tropical Depressions and Subtropical Depressions that are judged to have 10-minute sustained windspeeds of 65 km/h, (40 mph) by the Regional Specialized Meteorological Center on La Réunion Island, France (RSMC La Réunion) are usually assigned a name. However it is the Sub-Regional Tropical Cyclone Advisory Centers in Mauritius and Madagascar who name the systems. The Sub-Regional Tropical Cyclone Advisory Center in Mauritius names the storm should it intensify into a moderate tropical storm between 55°E and 90°E, if the storm should intensify into a moderate tropical storm between 30°E and 55°E then the Sub-Regional Tropical Cyclone Advisory Center in Madagascar assigns the appropriate name to the storm. Tropical cyclones that move into this region from the Australian Region will not receive a new name. New name lists are used every year, whilst a name is normally only used once so thus no names are retired.[85] The next name to be used this season is Ivanoe.
|
|
During December, Severe Tropical Cyclone Bruce entered the Southwestern Indian Ocean basin from the Australian area of responsibility.
Seasonal effects
This table lists all of the tropical cyclones and subtropical cyclones that were monitored during the 2013–2014 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season. Information on their intensity, duration, name, areas affected, primarily comes from RSMC La Réunion. Death and damage reports come from either press reports or the relevant national disaster management agency while the damage totals are given in 2013 USD.
| Name | Dates | Peak intensity | Areas affected | Damage (USD) |
Deaths | Refs | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Category | Wind speed | Pressure | ||||||
| Tropical disturbance | July 8 – 9 | Tropical Disturbance | 45 km/h (30 mph) | 1001 hPa (29.56 inHg) | None | None | None | |
| 01 | October 25 – 28 | Tropical Depression | 55 km/h (35 mph) | 1000 hPa (29.53 inHg) | Diego Garcia | None | None | |
| Amara (Official) | December 14 – 23 | Intense Tropical Cyclone | 195 km/h (120 mph) | 933 hPa (27.55 inHg) | Rodrigues | None | None | |
| Bruce | December 19 – 24[nb 1] | Very Intense Tropical Cyclone | 230 km/h (145 mph) | 912 hPa (26.93 inHg) | None | None | None | |
| Bejisa | December 28 – January 6 | Intense Tropical Cyclone | 165 km/h (105 mph) | 953 hPa (28.14 inHg) | Seychelles, Madagascar, Réunion, Mauritius | >$89.2 million | 1 | |
| 05 | January 8 – 11 | Tropical Depression | 65 km/h (40 mph) | 992 hPa (29.29 inHg) | Mozambique, Madagascar | None | None | |
| Colin | January 9 – 16 | Intense Tropical Cyclone | 185 km/h (115 mph) | 930 hPa (27.46 inHg) | None | None | None | |
| Deliwe | January 16 – 18 | Moderate Tropical Storm | 85 km/h (50 mph) | 992 hPa (29.29 inHg) | Madagascar, Mozambique | Unknown | 2 | |
| 08 | January 18 | Zone of Disturbed Weather | 35 km/h (25 mph) | 1004 hPa (29.65 inHg) | Madagascar | None | None | |
| 09 | January 28 – 29 | Tropical Disturbance | 45 km/h (30 mph) | 1003 hPa (29.62 inHg) | Mozambique | None | None | |
| Edilson | February 4 – 8 | Severe Tropical Storm | 100 km/h (65 mph) | 980 hPa (28.94 inHg) | Mauritius, Réunion | None | None | |
| Fobane | February 6 – 14 | Severe Tropical Storm | 110 km/h (70 mph) | 975 hPa (28.79 inHg) | None | None | None | |
| Guito | February 18 – 22 | Severe Tropical Storm | 110 km/h (70 mph) | 977 hPa (28.85 inHg) | Mozambique, Madagascar | None | None | |
| 13 | February 27 – 28 | Subtropical Depression | 65 km/h (40 mph) | 996 hPa (29.41 inHg) | None | None | None | |
| Hellen | March 27 – Currently active | Intense Tropical Cyclone | 195 km/h (120 mph) | 948 hPa (27.99 inHg) | Mozambique, Madagascar | None | None | |
| Season aggregates | ||||||||
| 15 systems | July 8 – Currently active | 230 km/h (145 mph) | 912 hPa (26.93 inHg) | >$89.2 million | 3 | |||
See also
- List of Southern Hemisphere cyclone seasons
- Atlantic hurricane seasons: 2013, 2014
- Pacific hurricane seasons: 2013, 2014
- Pacific typhoon seasons: 2013, 2014
- North Indian Ocean cyclone seasons: 2013, 2014
- 2013–14 Australian region cyclone season
- 2013–14 South Pacific cyclone season
Notes
- ^ Bruce formed in the Australian cyclone region on December 16, but entered the South-West Indian Ocean on December 19. It entered Australian region on December 25, when it is tropical low.
References
- ^ a b The RA I Tropical Cyclone Committee (2012). "Tropical Cyclone Operational Plan: 2012". World Meteorological Organisation. p. 11. Archived from the original (PDF) on December 5, 2012. Retrieved December 5, 2012.
- ^ "ITCZ Bulletin". Météo France. 6 July 2013. Retrieved 8 July 2013.
- ^ "ITCZ Bulletin". Météo France. 8 July 2013. Retrieved 8 July 2013.
- ^ Joint Typhoon Warning Center (October 21, 2013). "Significant Tropical Weather Advisory For The Indian Ocean – October 21, 1130 UTC". Pearl Harbor, Hawaii: United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on October 23, 2013. Retrieved 26 December 2013.
- ^ Joint Typhoon Warning Center (October 21, 2013). "Significant Tropical Weather Advisory For The Indian Ocean – October 21, 1800 UTC". Pearl Harbor, Hawaii: United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on October 23, 2013. Retrieved 26 December 2013.
- ^ Météo-France (October 25, 2013). "Tropical Disturbance 1 Warning Number 001/1". United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on October 27, 2013. Retrieved 21 December 2013.
- ^ Météo-France (October 25, 2013). "Tropical Disturbance 1 Forecast Warning Number 001/1". United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on October 27, 2013. Retrieved 21 December 2013.
- ^ a b Météo-France (October 26, 2013). "Tropical Depression 1 Warning Number 003/1". United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on October 27, 2013. Retrieved 21 December 2013.
- ^ Météo-France (October 26, 2013). "Tropical Depression 1 Warning Number 005/1". United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on October 27, 2013. Retrieved 21 December 2013.
- ^ Météo-France (October 27, 2013). "Tropical Depression 1 Warning Number 007/1". United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on October 27, 2013. Retrieved 21 December 2013.
- ^ Joint Typhoon Warning Center (October 27, 2013). "Tropical Cyclone 01S (One) Warning NR 002". Pearl Harbor, Hawaii: United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on October 28, 2013. Retrieved 26 December 2013.
- ^ Météo-France (October 27, 2013). "Tropical Disturbance 1 Warning Number 008/1". United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on October 28, 2013. Retrieved 21 December 2013.
- ^ Joint Typhoon Warning Center (October 28, 2013). "Tropical Cyclone 01S (One) Warning NR 003". Pearl Harbor, Hawaii: United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on October 28, 2013. Retrieved 26 December 2013.
- ^ Météo-France (October 27, 2013). "Tropical Disturbance 1 Warning Number 009/1". United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on October 28, 2013. Retrieved 21 December 2013.
- ^ "Bulletin For Cyclonic Activity And Significant Tropical Weather In The Southwest Indian Ocean – December 13, 1200 UTC". Météo-France. December 13, 2013. Archived from the original (PDF) on December 14, 2013. Retrieved 21 December 2013.
- ^ Météo-France (December 14, 2013). "Tropical Disturbance 2 Warning Number 001/2". United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on December 15, 2013. Retrieved 21 December 2013.
- ^ Météo-France (December 15, 2013). "Tropical Depression 2 Warning Number 003/2". United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on December 15, 2013. Retrieved 21 December 2013.
- ^ Joint Typhoon Warning Center (December 15, 2013). "Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert – December 15, 1500 UTC". Honolulu, Hawaii: United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on December 17, 2013. Retrieved 21 December 2013.
- ^ Météo-France (December 16, 2013). "Moderate Tropical Storm 2 (Amara) Warning Number 009/2". United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on December 17, 2013. Retrieved 21 December 2013.
- ^ Joint Typhoon Warning Center (December 18, 2013). "Tropical Cyclone 03S (Amara) Warning NR 004". Honolulu, Hawaii: United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on December 19, 2013. Retrieved 23 December 2013.
- ^ Météo-France (December 18, 2013). "Tropical Cyclone 2 (Amara) Warning Number 016/2". United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on December 19, 2013. Retrieved 23 December 2013.
- ^ Joint Typhoon Warning Center (December 18, 2013). "Tropical Cyclone 03S (Amara) Warning NR 006". Honolulu, Hawaii: United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on December 20, 2013. Retrieved 23 December 2013.
- ^ Météo-France (December 19, 2013). "Tropical Cyclone 2 (Amara) Warning Number 019/2". United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on December 20, 2013. Retrieved 23 December 2013.
- ^ Météo-France (December 21, 2013). "Intense Tropical Cyclone 2 (Amara) Warning Number 027/2". United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on December 21, 2013. Retrieved 23 December 2013.
- ^ Joint Typhoon Warning Center (December 21, 2013). "Tropical Cyclone 03S (Amara) Warning NR 011". Honolulu, Hawaii: United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on December 22, 2013. Retrieved 23 December 2013.
- ^ Joint Typhoon Warning Center (December 22, 2013). "Tropical Cyclone 03S (Amara) Warning NR 012". Honolulu, Hawaii: United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on December 23, 2013. Retrieved 23 December 2013.
- ^ Météo-France (December 22, 2013). "Tropical Depression 2 (Ex-Amara) Warning Number 036/2". United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on December 24, 2013. Retrieved 24 December 2013.
- ^ a b c "Amara continue de se rapprocher de Rodrigues" (in French). Imaz Press Réunion. December 20, 2013. Retrieved 23 December 2013. Cite error: The named reference "AmaraRaproacher" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ a b "Rodrigues en alerte maximale" (in French). Clicanoo.re. December 21, 2013. Retrieved 23 December 2013.
- ^ a b Hoair, Gilbert (December 21, 2013). "Rodrigues sous le cyclone tropical intense Amara" (in French). France Télévisions. Retrieved 23 December 2013.
- ^ United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs: (December 23, 2013). Southern Africa: Weekly Report (17 to 23 December 2013) (Report). ReliefWeb. Retrieved 23 December 2013.
{{cite report}}: CS1 maint: extra punctuation (link) - ^ Catastrophes Naturelles. "Rodrigues touchée par le cyclone Amara" (in French). National Commission for Computing and Liberties. Retrieved 23 December 2013.
- ^ "Rodrigues : Le passage du cyclone Amara provoque "des dégâts considérables"" (in French). Zinfos974. December 21, 2013. Retrieved 23 December 2013.
- ^ Bureau of Meteorology (December 16, 2013). "Tropical Cyclone Technical Bulletin for Tropical Low 03U – December 16, 0600 UTC". Perth, Australia: United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on December 16, 2013. Retrieved 26 December 2013.
- ^ Bureau of Meteorology (December 18, 2013). "Tropical Cyclone Technical Bulletin for Tropical Cyclone Bruce 03U – December 18, 0000 UTC". Perth, Australia: United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on December 18, 2013. Retrieved 26 December 2013.
- ^ a b Météo-France (December 20, 2013). "Tropical Cyclone 3 (Bruce) Warning Number 001/3". Unisys. Archived from the original (TXT) on December 21, 2013. Retrieved 26 December 2013.
- ^ Joint Typhoon Warning Center (December 20, 2013). "Tropical Cyclone 04S (Bruce) Warning NR 006". Honolulu, Hawaii: United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on December 20, 2013. Retrieved 26 December 2013.
- ^ Météo-France (December 20, 2013). "Intense Tropical Cyclone 3 (Bruce) Warning Number 002/3". Unisys. Archived from the original (TXT) on December 21, 2013. Retrieved 26 December 2013.
- ^ Météo-France (December 20, 2013). "Very Intense Tropical Cyclone 3 (Bruce) Warning Number 004/3". United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on December 21, 2013. Retrieved 26 December 2013.
- ^ Météo-France (December 21, 2013). "Intense Tropical Cyclone 3 (Bruce) Warning Number 007/3". United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on December 22, 2013. Retrieved 26 December 2013.
- ^ Météo-France (December 22, 2013). "Very Intense Tropical Cyclone 3 (Bruce) Warning Number 009/3". Unisys. Archived from the original (TXT) on December 22, 2013. Retrieved 26 December 2013.
- ^ Joint Typhoon Warning Center (December 22, 2013). "Tropical Cyclone 04S (Bruce) Warning NR 011". Honolulu, Hawaii: United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on December 23, 2013. Retrieved 26 December 2013.
- ^ Météo-France (December 22, 2013). "Intense Tropical Cyclone 3 (Bruce) Warning Number 011/3". United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on December 22, 2013. Retrieved 26 December 2013.
- ^ a b Joint Typhoon Warning Center (December 23, 2013). "Tropical Cyclone 04S (Bruce) Warning NR 012". Honolulu, Hawaii: United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on December 23, 2013. Retrieved 26 December 2013.
- ^ Météo-France (December 23, 2013). "Tropical Cyclone 3 (Bruce) Warning Number 015/3". United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on December 24, 2013. Retrieved 26 December 2013.
- ^ Joint Typhoon Warning Center (December 23, 2013). "Tropical Cyclone 04S (Bruce) Warning NR 013". Honolulu, Hawaii: United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on December 24, 2013. Retrieved 26 December 2013.
- ^ Météo-France (December 23, 2013). "Severe Tropical Cyclone 3 (Bruce) Warning Number 016/3". United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on December 24, 2013. Retrieved 26 December 2013.
- ^ Joint Typhoon Warning Center (December 23, 2013). "Tropical Cyclone 04S (Bruce) Warning NR 014". Honolulu, Hawaii: United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on December 24, 2013. Retrieved 26 December 2013.
- ^ Météo-France (December 24, 2013). "Post-Tropical Depression 3 (Ex-Bruce) Warning Number 017/3". United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on December 24, 2013. Retrieved 26 December 2013.
- ^ "Bulletin For Cyclonic Activity And Significant Tropical Weather In The Southwest Indian Ocean – December 27, 1200 UTC". Météo-France. December 27, 2013. Archived from the original (PDF) on December 30, 2013. Retrieved 30 December 2013.
- ^ Joint Typhoon Warning Center (December 27, 2013). "Significant Tropical Weather Advisory For The Indian Ocean – December 27, 1830 UTC". Pearl Harbor, Hawaii: United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on December 29, 2013. Retrieved 30 December 2013.
- ^ Joint Typhoon Warning Center (December 28, 2013). "Significant Tropical Weather Advisory For The Indian Ocean– December 28, 1000 UTC". Pearl Harbor, Hawaii: United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on December 29, 2013. Retrieved 30 December 2013.
- ^ Météo-France (December 28, 2013). "Tropical Disturbance 4 Warning Number 001/4". United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on December 29, 2013. Retrieved 30 December 2013.
- ^ "Bulletin For Cyclonic Activity And Significant Tropical Weather In The Southwest Indian Ocean – December 28, 1200 UTC". Météo-France. December 28, 2013. Archived from the original (PDF) on December 30, 2013. Retrieved 30 December 2013.
- ^ Météo-France (December 28, 2013). "Tropical Disturbance 1 Forecast Warning Number 001/4". United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on December 29, 2013. Retrieved 30 December 2013.
- ^ Joint Typhoon Warning Center (December 29, 2013). "Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert –December 29, 0300 UTC". Honolulu, Hawaii: United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on December 29, 2013. Retrieved 30 December 2013.
- ^ Météo-France (December 29, 2013). "Tropical Depression 4 Warning Number 003/4". United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on December 29, 2013. Retrieved 30 December 2013.
- ^ Météo-France (December 29, 2013). "Moderate Tropical Storm 4 (Bejisa) Warning Number 007/4". United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on December 30, 2013. Retrieved 30 December 2013.
- ^ a b Météo-France (December 29, 2013). "Moderate Tropical Storm 4 (Bejisa) Forecast Warning Number 006/4". United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on December 30, 2013. Retrieved 30 December 2013.
- ^ Météo-France (December 30, 2013). "Severe Tropical Storm 4 (Bejisa) Warning Number 008/4". United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on December 30, 2013. Retrieved 30 December 2013.
- ^ Météo-France (December 30, 2013). "Severe Tropical Storm 4 (Bejisa) Forecast Warning Number 008/4". United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on December 30, 2013. Retrieved 30 December 2013.
- ^ Météo-France (December 30, 2013). "Tropical Cyclone 4 (Bejisa) Warning Number 009/4". Unsys. Archived from the original (TXT) on December 31, 2013. Retrieved 31 December 2013.
- ^ Météo-France (December 30, 2013). "Intense Tropical Cyclone 4 (Bejisa) Warning Number 010/4". Unsys. Archived from the original (TXT) on December 31, 2013. Retrieved 31 December 2013.
- ^ Météo-France (December 31, 2013). "Intense Tropical Cyclone 4 (Bejisa) Forecast Warning Number 013/4". United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on December 31, 2013. Retrieved 31 December 2013.
- ^ a b Joint Typhoon Warning Center (January 7, 2014). "Significant Tropical Weather Advisory For The Indian Ocean – January 7, 1800 UTC". Pearl Harbor, Hawaii: United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on January 8, 2014. Retrieved 9 January 2014. Cite error: The named reference "05-JTWC-STWA-071800" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ Météo-France (January 8, 2014). "Zone of Disturbed Weather 5 Warning Number 001/5" (in French). United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on January 9, 2014. Retrieved 9 January 2014.
- ^ Météo-France (January 8, 2014). "Zone of Disturbed Weather 5 Forecast Warning Number 001/5". United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on January 9, 2014. Retrieved 9 January 2014.
- ^ Météo-France (January 9, 2014). "Tropical Depression 5 Warning Number 002/5" (in French). United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original (TXT) on January 9, 2014. Retrieved 9 January 2014.
- ^ a b United Nations Office for the Coordination of Human Affairs (January 8, 2014). Tropical Depression Path (as of 8th January 2014) (PDF) (Report). ReliefWeb. Retrieved 10 January 2014.
- ^ United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Climate Prediction Center (January 8, 2014). Africa Hazards Outlook January 9 – January 15, 2014 (Report). ReliefWeb. Retrieved 10 January 2014.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Outlook for the Western Region, Issued at 1:35 pm WST on Monday 6 January 2014". TCWC Perth. 6 January 2014. Retrieved 7 January 2014.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Outlook for the Western Region, Issued at 2:00 pm WST on Thursday 9 January 2014". TCWC Perth. 9 January 2014. Retrieved 9 January 2014.
- ^ "Moderate Tropical Storm 6 (Colin) - Warning #3". RSMC La Réunion. 10 January 2014. Retrieved 19 February 2014.
- ^ "Cyclone Warning 003 for Moderate Tropical Storm Colin". RSMC La Réunion. 10 January 2014. Retrieved 10 January 2014.
- ^ "Intense Tropical Cyclone 6 (Colin) - Warning #12". RSMC La Réunion. 12 January 2014. Retrieved 19 February 2014.
- ^ "NASA Sees Tropical Cyclone Colin's Final Bow". NASA. Retrieved January 15, 2014.
- ^ "Moderate Tropical Storm 7 (Deliwe) - Warning #2". RSMC La Réunion. 16 January 2014. Retrieved 19 February 2014.
- ^ "Remnant Low 7 (Deliwe) - Warning #7". RSMC La Réunion. 18 January 2014. Retrieved 19 February 2014.
- ^ Template:Fr icon "Le cyclone Deliwe dévaste l'Ouest de Madagascar". L'Express de Madagascar. January 18, 2014. Retrieved January 19, 2014.
- ^ "NASA Spots Very Heavy Rainfall Rates in Tropical Cyclone Edilson". NASA. Retrieved February 7, 2014.
- ^ "NASA's TRMM Satellite Eyes Rainfall in Tropical Cyclone Fobane". Rob Gutro, & NASA. Retrieved February 10, 2014.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Forecast Warning 01". RSMC La Réunion. Archived from the original on February 18, 2014. Retrieved February 18, 2014.
- ^ "NASA satellite sees a ragged eye develop in Tropical Cyclone Guito". Retrieved February 19, 2014.
- ^ "Forecast Warning 001 for Subtropical Depression 13". RSMC La Réunion. 27 February 2014. Retrieved 27 February 2014.
- ^ Regional Association I Tropical Cyclone Committee (2010). "Tropical Cyclone Operational Plan for the South-West Indian Ocean" (PDF). World Meteorological Organization. Retrieved 2013-07-04.