Many-to-many (data model)
This article needs additional citations for verification. (January 2013) |
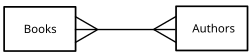
In systems analysis, a many-to-many relationship is a type of cardinality that refers to the relationship between two entities[1] A and B in which A may contain a parent instance for which there are many children in B and vice versa.
For example, think of A as Authors, and B as Books. An Author can write several Books, and a Book can be written by several Authors.
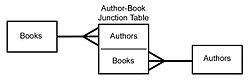
In a relational database management system, such relationships are usually implemented by means of an associative table (also known as join table, junction table or cross-reference table), say, AB with two one-to-many relationships A -> AB and B -> AB. In this case the logical primary key for AB is formed from the two foreign keys (i.e. copies of the primary keys of A and B).
In web application frameworks such as CakePHP and Ruby on Rails, a many-to-many relationship between entity types represented by logical model database tables is sometimes referred to as a HasAndBelongsToMany (HABTM) relationship.[2]
See also
References
- ^ Also see entity–relationship model.
- ^ 3.7.6.5 hasAndBelongsToMany (HABTM) Archived 2012-08-15 at the Wayback Machine. Cakephp.org
