Espiritú Santo Fault System
| Espíritu Santo Fault | |
|---|---|
| Falla de Espíritu Santo | |
| Etymology | Espíritu Santo River |
| Coordinates | 07°07′20″N 75°01′38″W / 7.12222°N 75.02722°W |
| Country | |
| Region | Andean |
| State | Antioquia |
| Characteristics | |
| Range | Central Ranges, Andes |
| Part of | Andean oblique faults |
| Length | 124.4 km (77.3 mi) |
| Strike | 033.9 ± 5 |
| Dip | Northwest |
| Dip angle | High to vertical |
| Displacement | 0.2–1 mm (0.0079–0.0394 in)/yr |
| Tectonics | |
| Plate | North Andean |
| Status | Active |
| Earthquakes | ~500 years ago |
| Type | Oblique strike-slip fault |
| Movement | Normal dextral |
| Rock units | Puquí Complex, Valdivia Group |
| Age | Quaternary |
| Orogeny | Andean |
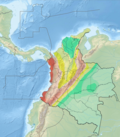
The Espíritu Santo Fault (Template:Lang-es) is a dextral oblique strike-slip fault in the department of Antioquia in northwestern Colombia. The fault has a total length of 124.4 kilometres (77.3 mi) and runs along an average northeast to southwest strike of 033.9 ± 5 in the Central Ranges of the Colombian Andes. Estimated activity took place around 500 years ago.
Etymology
The fault is named after the Espíritu Santo River, Antioquia.[1]
Description
The Espíritu Santo Fault is one of the more prominent Cenozoic faults in the northern Central Ranges of the Colombian Andes. The fault extends from the Sabanalarga Fault near the town of Liborina in the southwest, as far northeast as the town of Cáceres in the Bajo Cauca area. There, it disappears under young sediment of the Cauca and Nechí River valleys. It has a reverse sense in the northern part and normal sense in the southern part. The Espíritu Santo Fault places Precambrian metamorphic rocks to the south against Paleozoic metamorphic rocks to the north. The fault displaces rocks of the Puquí Complex, Valdivia Group, and mafic and ultramafic rocks and sediments of the Bajo Cauca.[1] The Santa Rita Fault terminates against the Espíritu Santo Fault.[2]
The fault forms well developed fault lines and valleys. The fault trace is marked by young morphologic features such as ground ruptures, saddles, shutter ridges, closed depressions, aligned and captured drainages and linear scarps on recent sediment. There is clear offset of 50-100 thousand year old terraces and Quaternary deposits around El Doce. In addition, the fault has displaced a Tertiary erosion surface. The last activity of the fault has been estimated at around 500 years ago.[3]
The fault displays dextral (right-lateral) movement in ramps, displacing older deformational structures and forming an intense cataclasis. Rotated foliations are observed in a northeasterly direction, overprinting older foliations of a north-northwest trend.[4]