Intraglomerular mesangial cell
| Intraglomerular mesangial cell | |
|---|---|
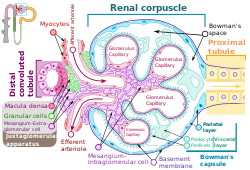 Renal corpuscle showing the intraglomerular mesangial cells | |
| Anatomical terminology |
Intraglomerular mesangial cells are located among the glomerular capillaries within a renal corpuscle of a kidney.
Characteristics
Mesangial cells are macrophages[1] and resemble pericytes.[2] They typically cover 30% of glomerular capillaries. They are both vimentin and desmin positive.
Function
There are five known functions of intraglomerular mesangial cells: structural support of glomerular capillaries, regulation of the glomerular filtration rate, mesangial matrix formation, phagocytosis, and monitoring of capillary lumen glucose concentration.
Intraglomerular mesangial cells have contractile activity. The initiation of contraction of mesangial cells is similar to that of smooth muscle. Contraction of mesangial cells is coupled with contraction of the basement membrane of the endothelium of glomerular capillaries. This causes a decrease in surface area of the basement membrane and thus a decreased glomerular filtration rate.
Intraglomerular mesangial cells synthesize and secrete the extracellular matrix. It contains fibronectin, type IV collagen, perlecan, and laminin.
Intraglomerular mesangial cells phagocytize glomerular basal lamina components and immunoglobulins. They are an unusual example of phagocytic cells derived from smooth muscle and not monocytes. Intraglomerular mesangial cells aid neutrophils in removing other mesangial cells undergoing apoptosis, and other debris.
Intraglomerular mesangial cells monitor capillary lumen glucose concentration via processes sent into the capillary lumen.
See also
References
External links
- Histology image: 16006loa – Histology Learning System at Boston University
