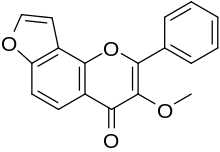
Karanjin
Appearance
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3-Methoxy-2-phenylfuro[2,3-h]chromen-4-one
| |
| Other names
3-Methoxy furano - 2, 3, 7, 8-flavone
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.565 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C18H12O4 | |
| Molar mass | 292.290 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Karanjin is a furanoflavonol, a type of flavonoid. It is obtained from the seeds of the karanja tree (Millettia pinnata or Pongamia glabra Vent.), a tree growing wild in south India. Karanjin is an acaricide and insecticide.[citation needed] Karanjin is reported to have nitrification inhibitory properties.[1]
References
- ^ Majumdar, Deepanjan; Pandya, Bhavesh; Arora, Anu; Dhara, Soni (2004). "Potential use of karanjin (3-methoxy furano-2′,3′,7,8-flavone) as a nitrification inhibitor in different soil types". Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science. 50 (4–5): 455. doi:10.1080/03650340410001689406.
